3.6 organisms respond to changes in their environment
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
define stimulus
a detectable change in the external or internal environment of an organism that leads to a response
advantages of reflex arc
greater chance of survival, raising offspring, and passing on alleles to the next generation
it doesn’t overload the brain as it’s a subconscious response
protects the body from harm
quick due to the short neuron pathway and absence of the decision-making process
reflex arc steps:
stimulus > receptor > coordinator > effector > response
taxes (taxi definition)
a simple response whose direction is determined by the direction of the stimulus
positive and negative taxis
positive taxis: movement towards the stimulus
negative taxis: movement away from the stimulus
kinesis definition
a form of response where the organism doesn’t move towards or away from the stimulus - instead it changes the speed of its movement and the rate at which it changes direction
tropisms definition
the growth of the part of the plant in response to a directional stimulus
shoots: positive phototropism, negative gravitropism
roots: negative phototropism, positive gravitropism
what controls tropisms (plant cell growth)
IAA (indole-3-acetic acid)
positive phototropism in flowering plants:
cells in the tip produce IAA, which move down and evenly distribute through the plant
light causes movement of IAA from light to shaded side
a greater conc of IAA builds up on the shaded side of the shoot
the cells on the shaded side elongate faster, causing the shoot tip to bend towards the light
gravitropism in flowering plants
cells in the tip of the root produce IAA which moves along the root
gravity causes movement of IAA to the lower side of the root
IAA stops elongation of root cells and as there is greater concentration of IAA on the lower side the upper side elongates quicker causing the root to bend downwards by the force of gravity
the spinal chord
consists of a column of nervous tissue along the back, inside the column for protection
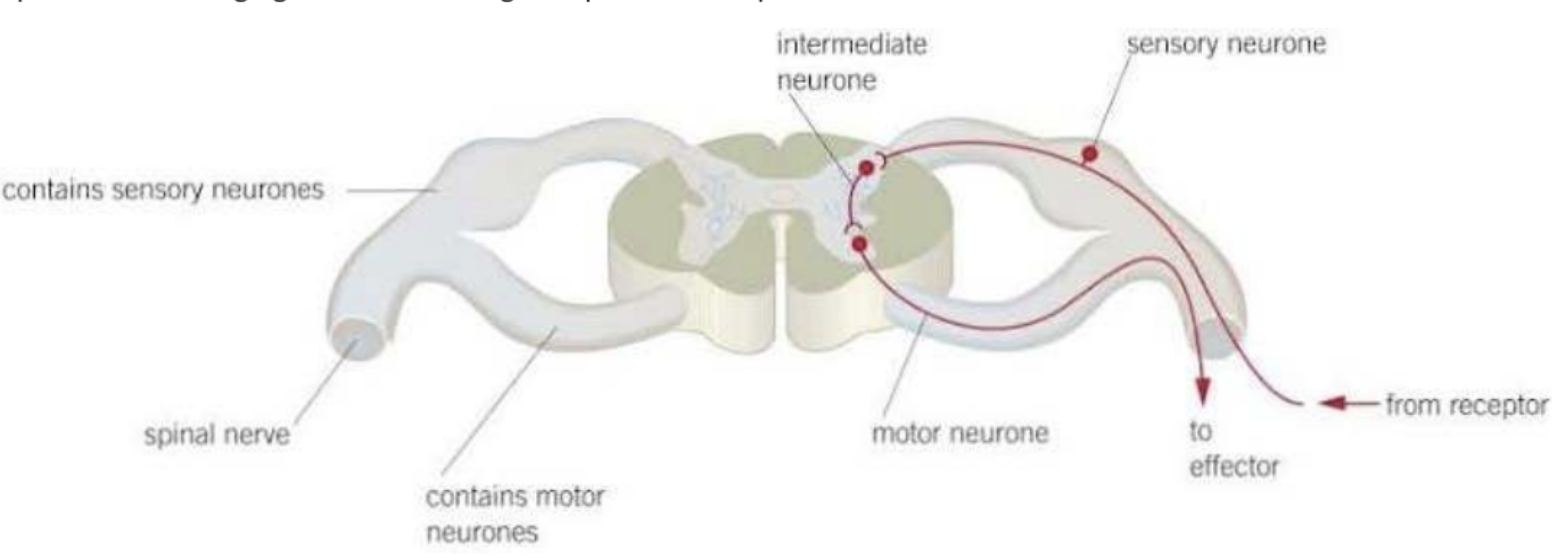
the three neurons
sensory, relay, motor neurons.
the 7 steps of the reflex arc:
stimulus
receptor
sensory neuron
coordinator (relay neuron)
motor neuron
effector
response
what is the pacinian capsule
a sensory receptor that responds to changes in mechanical pressure
features of a pacinian capsule
specific to a single type of stimulus
produces a generator potential, that converts energy from the stimulus into nerve impulses
receptors convert one form of energy into another (producing generator potential)
where are pacinian capsules located
fingers, soles of feet, external genetalia, ligaments, joints, tendons
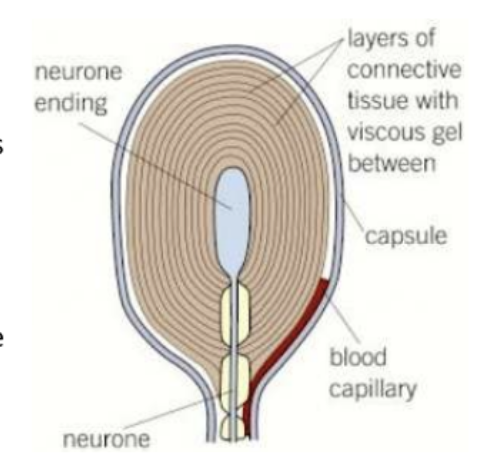
structure of pacinian capsule
plasma membranes have channel proteins
the sensory neurone ending has stretched-mediated sodium channels in the membrane
when these channels are deformed (by pressure) they become permeable to sodium ions
function of the pacinian capsule
resting state: the stretching mediated sodium channels are too narrow
when pressure is applied the channels deform causing the membrane to stretch which widens the sodium channels allowing sodium ions to diffuse into the neutron
the influx of sodium ions depolarises the neuron
this creates an action potential
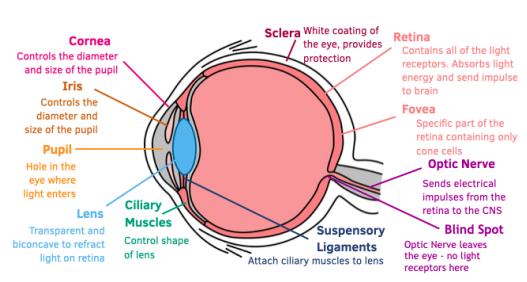
structure of the eye
features of ROD CELLS (6)
rod-shaped
greater number compared to cone cells
more at the periphery of the retina, absent at the fovea
poor visual acuity (clarity)
sensitivity to low-intensity light
one type only
features of CONE CELLS (6)
cone-shaped
fewer number compared to rod cells
fewer at periphery of the retina, concentrated at the fovea
structure of receptors in the eye
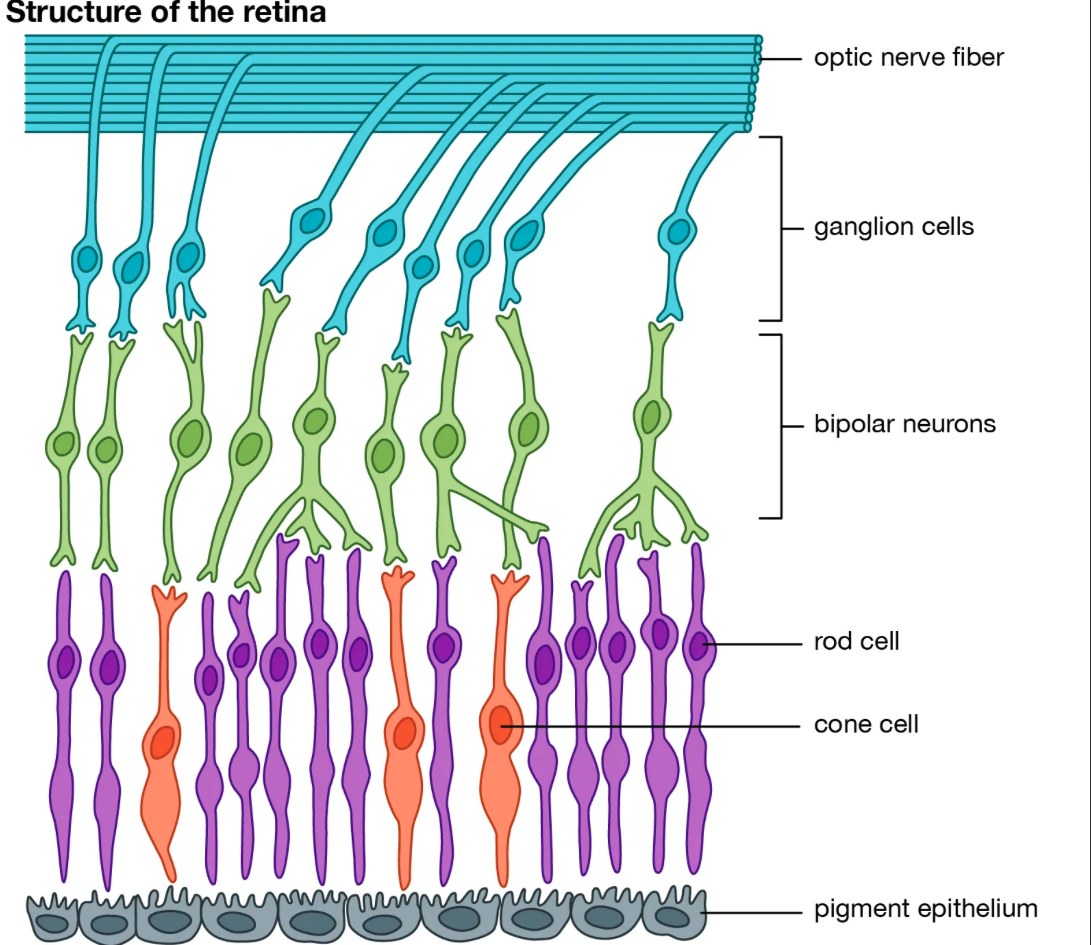
where are light receptors found
on the retina
how do rods and cones act as transducers
by converting light energy into an impulse
functions of ROD cells
breaks down rhodopsin to generate an action potential
many rods connect to a single neuron (only sending one impulse) = brain can’t distinguish between separate sources of light that stimulated the impulse = poor visual acuity
functions of CONE cells
breaks down iodopsin to generate an actions potential
each type of cone cells contains an specific type of iodopsin that’s sensitive to different light wavelengths
each cone cell connected to its own neuron = high visual acuity
where are the most cone cells found and why
the fovea
lens focuses the light onto the fovea, which receives the most amount of light, so this is where the most amount of cone cells are found
what is the cardiac muscle called tissue of the heart called
myogenic tissue
what two systems control the organ systems
the nervous and hormonal system
hormonal system
communication by hormone chemicals
transmission by the blood system
transmission is relatively slow
hormones travel to all parts of the body, but only to the target cells response
response is widespread
response is slow
response is long-lasting
effects may be permanent and irreversible
nervous system
communication is by nerve impulses
tranmission is by neurones
transmission is very rapid
nerve impulses travel to specific parts of the body
response is localised
repsonse is rapid
respsone is short-lived
effect is usually temporary and reversible elc
cell body
nucleus and large amount of RER associated with production of proteins and neutron
where is the pacemaker of the heart
in the wall of the right atrium there is a region of specialised fibres called the sinoatrial node
what does the sinoatrial node do
initiates a wave of electrical stimulation which causes the atria to contract at roughly the same time
why does the ventricle only contract when the atria have finished
due to the presence of tissue at the base of the atria which is unable to conduct the wave of excitation
path of the electrical wave
the electrical wave entually reaches the atrioventricular node between the two atria
this passes the wave of excitation to the ventricles, down the bundle of His to the apex of the heart
the bundle of His branches into Purkyne fibres which carry the wave upwards - this causes the ventricles to contract therefore emptying them
resting potential
difference in charge across the membrane when a neurone is not firing - (-70mv)
how is resting potential maintained
by keeping more pos ions outside the cell than inside
1) done by using a Na+/K+ pump, ATP pumps 3Na and 2K in - a neurone with a more pos charge outside than inside creating a negative resting potential
2) membrane also has more protein channels for K+ than Na+ and due to the concentration of K+ being higher inside, it diffuses out of the neurone, making the resting potential even lower
3) many neg charge molecules also present inside the cell, and the membrane is impermeable to them, so neurone is more negative inside
action potential
rapid change in potential difference across the membrane caused by changes in permeability of cell surface membrane to Na+ and K+
a synapse is a junction between
two neurones, a neurones and an effector