Smoking Cessations
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PEBC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
smoking
releases dopamine = “feel good” effect —> addiction and physical dependence
increases risk of:
cancer
Heart attack
diabetes
stroke
nicotine
beneficial effects:
improves anxiety, depression, schizophrenia
decreases appetite
improves ADHD, Tourette’s, pain
triggers alertness and memory
harmful effects:
addictive
teratogenic —> affects blood flow to baby and development
increases BP (5-10 mmHg)
Increases HR (10-20 bpm)
5 A’s
systematic approach to treat tobacco use and dependence
Ask = What is your patients smoking status?
do you use any tobacco products?
Advise = highlight the importance of smoking cessation in a manner that is personally relevant
ex. smoking status can affect your asthma
Assess = is your patient willing to quit? is your patient ready for change?
are you thinking about quitting smoking?
Assist = create a quit plan with patient, recommend appropriate pharmacological therapy and offer educational resources
set realistic quit date
anticipate barriers
enlist social support
Arrange = book follow up with patient
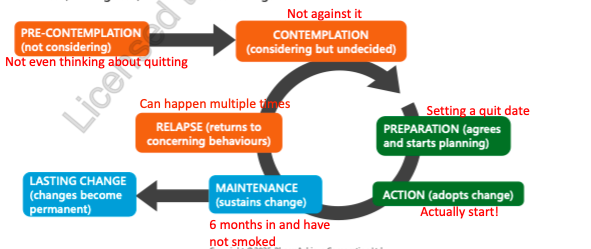
cycle of change
before recommending any behavioural changes, clinicians should assess patients’ readiness, willingness and barriers to change
pre-contemplation = not considering
contemplation = considering but undecided
not against it —> “im thinking of quitting”
preparation = Agrees and starts planning
setting a quit date
ACTION = adopts change
actually start
Maintenance = sustains change
6 months in and have not smoked
a) lasting change = changes become permanent
b) relapse = returns to concerning behaviours (can happen multiple times)
assist
create a quit plan with patient, recommend appropriate pharmacological therapy and offer educational resources
set realistic quit date
Anticipate barriers:
identify situations that trigger smoking habits
Educate patients regarding withdrawal symptoms: irritability, lack of focus, hunger, headaches, flu-like symptoms —> effects peak 2-3 days after quitting and decrease over weeks-months
Enlist social support
5 D’s to reduce cravings:
Delay
Distract
Deep breathing
Drink water
Discuss
treatment
1st line:
NRT = patches, gum, lozenges, inhaler, spray
Varenicline
Bupropion
2nd line:
Cytisine = NHP
Nortriptyline
others (limited benefit)
Clonidine
SSRI
electronic cigarettes
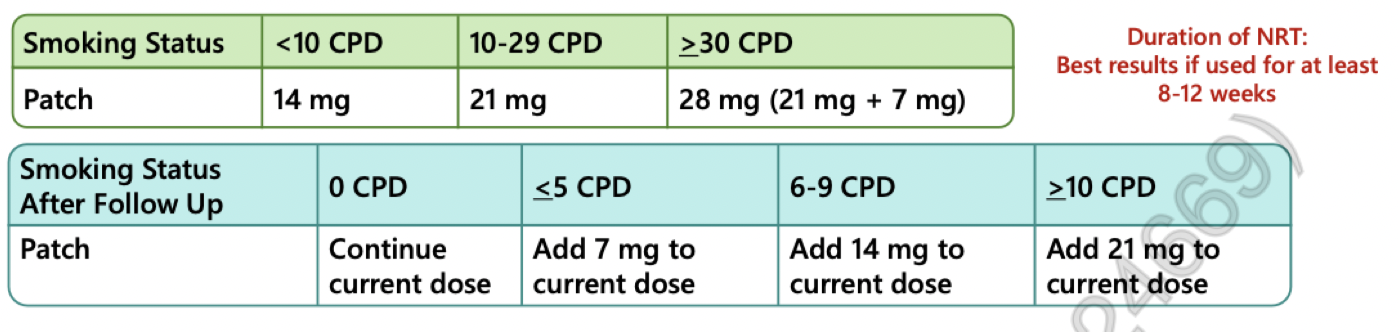
selecting NRT patch
when initiating a patch:
select an additional short acting NRT for breakthrough cravings (nicotine gum - 1 piece ever hr prn)
when patient is ready to reduce NRT:
reduce patch by 7 mg q1-2 weeks until off patch → then reduce short acting NRT until not needed
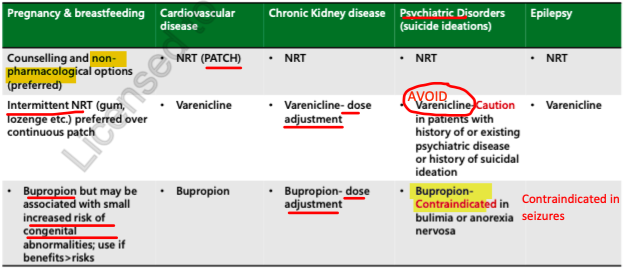
Relative contraindications:
pregnancy and breastfeeding
smoking while using this medication (nicotine toxicity)
age <18 y
NRT patch
provides consistent nicotine delivery
strengths = 7, 14, 21mg
s/e:
skin reactions = erythema, pruritus, edema, blisters, rash, burning sensation
insomnia and vivid dreams = can remove at night
headache, dizziness, paresthesia
palpitations, chest pain, blood pressure changes, tachycardia
abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth, nausea and vomiting
Administration:
1 patch/day (24 hr) or 16 hr application (remove at bedtime)
apply to dry hairless area of upper arm, chest or hip
rotate application sites
Time to peak = 2-6 hrs
remove patch before prolonged, strenuous exercise —> re-apply after exercise
NRT gum
rapid relief of cravings
buccal absorption
strengths = 2, 4mg
s/e:
jaw soreness
hiccups
nausea
heartburn
headache
administration:
flexible dosing
bite and park technique = place 1 piece of gum in the mouth. Bite down once or twice then park it between the teeth and gums for about 1 min. Repeat when the desire to smoke arises or once the tingling sensation stops (up to once per min for up to 30 min) then discard piece
acidic foods and fluids impair buccal absorption —> AVOID for 15 mins before use
time to peak = 20-30 mins
max dose = 20 pieces/day
NRT lozenge
rapid relief of cravings
buccal absorption
strengths = 1, 2, 4 mg
s/e:
Hiccups
Nausea
Headache
Administration:
flexible dosing
suck until strong taste and park
acidic foods and fluids impair buccal absorption = avoid for 15 mins before use
GI upset if swallowed
time to peak = 20-60 mins
max = 15-25/d (depends on strength)
NRT inhaler
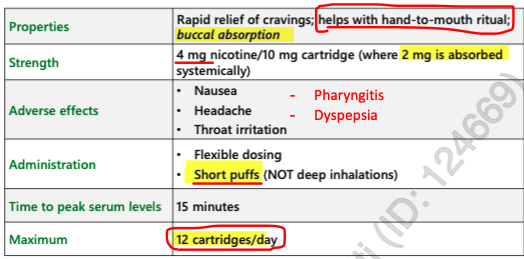
NRT spray

varenicline (champix)
strength = 0.5, 1mg
s/e:
vivid/ abnormal dreams
nausea, vomiting
insomnia
constipation and flatulence
HA
Administration:
start 1-2 weeks prior to quit date (quit smoking 1–2 wk after starting)
0.5 mg x 3 days, then 0.5 mg BID x 4 days, then 1 mg BID x 3 months
renal impairment (max dose) = 0.5 mg BID
cardiovascular risk - inconclusive evidence
CAUTION - pts w Hx of or experiencing psychiatric disease, Hx of suicidal ideation
DO NOT give to ppl with psyc diseases and Hx of Suicide
lack of data in pregnancy —> AVOID
bupropion (zyban)
strength = 150 mg
s/e:
dry mouth
insomnia
weight loss
CONTRAINDICATED IN ANOREXIA/ BULLIMIA
agitation
SEIZURES!!!!!!!!
CONTRAINDICATED IN SEIZURE DISORDERS!!
administration:
start 1-2 weeks prior to quit date
150 mg daily x 3 days, then BID x 3 months
8 hr interval for BID dosing
CrCl <60 = 150mg/d
C/I:
bullimia, Anorexia
Seizures
taking MAO INHIBITORS!! Within 14 days
precautions:
May use in pregnancy if benefits > risks = no good studies on this
substance use disorder or withdrawal
hepatic or renal failure
taking anti-depressants, antipsychotics, corticosteroids, stimulants, theophylline, quinolone antibiotics
Strong CYP2D6 inhibitor = increase concentrations of Atomoxtine, Duloxetine, Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, metoclopramide and tamsulosin
decreases efficacy of tamoxifen and codeine by decreasing their metabolites
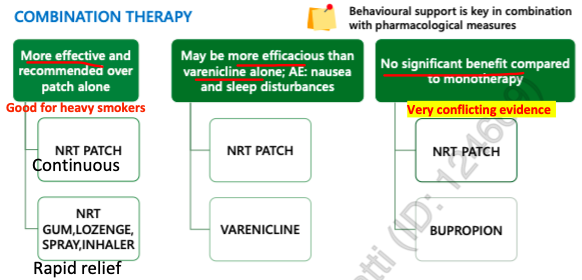
combination therapy
cytisine
plant based alkaloid = acts as partial agonist on nicotinic receptor
NHP = less strict regulatory requirements regarding efficacy and safety
evidence: similar in efficacy and may be more effective than NRT BUT POOR QUALITY data
s/e:
sleep disturbances
dyspepsia
nausea
complex dosing
nortriptyline
2nd line
not officially indicated for smoking cessation but some evidence of efficacy
TCA
use for ~12 weeks
s/e:
sedation
dry mouth
blurred vision
dizziness
tremor
urinary retention
orthostatic hypotension
special populations
interactions
cigarette smoking (tobacco smoke) induces CYP1A2
results in increased drug metabolism, decreased serum concentration and decreased efficacy
drug affected:
clozapine
fluvoxamine
caffeine
olanzapine
propranolol
theophylline
warfarin —> monitor
patients drinking > 4 cups coffee/day should HALF their daily intake when they quit smoking (otherwise they will have a lot of caffeine in their body)
ecigarettes
not recommended
unregulated
limited studies available
use is uncertain
may reinforce smoking behaviours