Sleep-Wake Disorders- Krysiak
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Which two main phases make up a normal sleep cycle?
Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
During which NREM stages does deep (delta) sleep occur?
idk how imp
Stages 3 and 4 of NREM sleep
How many NREM/REM cycles does an adult typically experience each night and how long is one cycle?
idk how imp
Four to six cycles, each lasting 70–120 minutes
What age-related change in sleep is common in the elderly?
idk how imp
Lighter, more fragmented sleep with reduced slow-wave (delta) sleep
Which neurotransmitters are sleep promoting?
GABA, adenosine
Which neurotransmitters are wake promoting?
DA, NE, Ach, Histamine
The DSM-5 classifies sleep-wake disorders into 10 categories.
What are they?
idk how imp, just RECOGNIZE
insomnia
hypersomnolence
narcolepsy
breathing-related sleep disorders
circadian rhythm sleep disorders
non-REM sleep arousal disorder
nightmare disorder
REM sleep behavior disorder
restless leg syndrome (RLS)
substance/ medication induced sleep disorder
List the DSM-5 criteria regarding frequency and duration for diagnosing chronic insomnia.
Sleep difficulty at least three nights per week for at least three months
What’s the main difference between primary and comorbid/ secondary insomnia?
Primary insomnia is endogenous—> secondary/comorbid insomnia is a symptom of another medical disorder
What classes of meds commonly cause insomnia?
anticonvulsants
central adrenergic blockers
diuretics
SSRIs
steroids
stimulants
What are the 3 categories of insomnia?
transient—> acute stressor, resolves quickly
short-term—> associated with stress, treated like transient
chronic—> requires careful assessment, nonpharm approaches
Is insomnia normally treated with or without pharm therapy?
WITHOUT—> 70-80% of insomnia can be treated with non-pharm and have a positive response
List non-pharm options for insomnia:
stimulus control therapy
sleep restriction
relaxation therapy
cognitive therapy
paradoxical intention
biofeedback
education on sleep hygiene
What are some recommendations for good “sleep hygiene”?
exercise routinely
create a comfy environment
d/c or reduce alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine
avoid drinking large amounts of liquids in the evening
do something relaxing before bed
List the drugs that are benzodiazepine receptor agonists (BZDRAs):
temazepam
estazolam
quazepam
flurazepam
triazolam
Which BZDRA is preferred in the elderly for insomnia?
Temazepam
Answer the following about BZDRAs:
MOA
C- ___ medication
warnings
duration of therapy
MOA: bind to GABAA in the brain—> hyperpolarize neuron
C-IV medication
warnings:
avoid in pregnancy, sleep apnea, substance abuse history, and hepatic disease
SHORT TERM USE ONLY (ex: 7-10 days)
Why should BZDRAs be used cautiously in elderly patients?
half-lives are prolonged in older patients—> risk of drug accumulation
Why should BZDRAs NOT be abruptly discontinued?
rebound insomnia
List the non-benzodiazepine receptor agonists (NBRAs):
Eszopiclone
Zaleplon
Zolpidem
Zolpmist—> oral spray
Edluar, Intermezzo—> SL tablet
What is the max dose of zolpidem (Ambien) in females and the elderly?
5 mg
Which is preferred first line for insomnia?
a. benzos
b. NBRAs
b. (bc less likelihood of withdrawal, tolerance, and rebound insomnia)
What are 2 important drug interactions with Zaleplon (Sonata)?
Cimetidine and Rifampin
Should NBRAs be taken with or without food before bed?
WITHOUT—> food decreases absorption
List the melatonin receptor agonists:
Ramelteon
Tasimelteon
tip: all have “mel” in the middle= melatonin receptor agonists
What is the indication for each melatonin receptor agonists?
Ramelteon—> sleep-onset insomnia
Tasimelteon—> ONLY for non 24 hours sleep-wake disorder
Which melatonin receptor agonist is NOT a controlled substance and is a good option for pts. with a history of substance abuse?
Ramelteon
Difference between Ramelteon and melatonin?
taking melatonin—> simply increases the levels of that hormone in your body
taking ramelteon—> influences receptor in your brain that responds to melatonin, allows for enhanced effects on sleep induction
List the Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonists (DORAs):
Suvorexant
Lemborexant
Daridorexant
tip: all have “orex” in the middle of the name—> orexin receptor antagonists
How do dual orexin receptor antagonists (DORAs) promote sleep?
They block orexin A and B receptors, turning off wake signaling—> DO NOT INDUCE SLEEPINESS
Answer the following about DORAs:
C-___ medication
ADRs
which has the shortest t 1/2?
C/I
C-IV medication
ADRs:
Next-day somnolence, narcolepsy associated events, suicidal thoughts, worsening depression
Daridorexant has the shortest t ½
C/I in NARCOLEPSY!!!!
Which OTC antihistamine is often used for insomnia and why is long-term use discouraged?
Diphenhydramine—> tolerance develops quickly and anticholinergic side effects occur
What low-dose antidepressant (≤6 mg) is FDA-approved for sleep maintenance insomnia?
Doxepin
What is another insomnia agent that is popular for its use in patients prone to substance abuse.
trazodone
List 2 herbals used for insomnia?
valerian root and melatonin (still not recommended in guidelines)
Patients with short-term or chronic insomnia should be evaluated after ______ of therapy.
a. one month
b. two months
c. one week
d. two weeks
c.
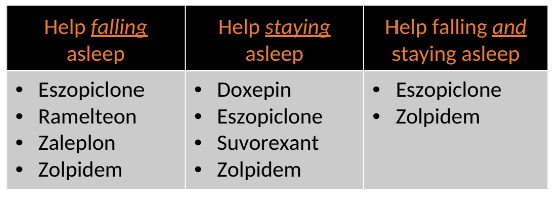
What insomnia agents should you use in each of the following scenarios:
help falling asleep
help staying asleep
help falling and staying asleep
Describe the classic narcolepsy tetrad.
Excessive daytime somnolence (EDS)
irresistible urge to sleep
cataplexy
sudden bilateral loss of muscle tone
hallucinations
sleep paralysis
Patients with narcolepsy should take ≥__ scheduled daytime naps.
2
First-line pharmacologic agents for narcoleptic EDS:
Modafinil or armodafinil
What are the warnings with modafinil and armodafinil?
idk how imp
CNS effects
derm effects (SJS, DRESS)
use caution in CV disease, hepatic impairment, and tourette’s
What is the 2nd line tx for narcoleptic EDS therapy?
amphetamines
Answer the following about amphetamines:
names
C-___ medication
names
dextroamphetamine- FDA approved
methyphenidate- FDA approved
dextro+amphetamine
lisdexamfetamine
C-II medications
What boxed warnings accompany sodium oxybate?
CNS depression, abuse/misuse potential (GHB)—> REMS PROGRAM
When is Sodium oxybate C/I?
use with sedative-hypnotics or alcohol
How is sodium oxybate dosed each night?
Two divided doses: first at bedtime in bed, second 2.5–4 hours later.
What is restless leg syndrome (RLS)? Difference between primary and secondary RLS?
paresthesias that are usually felt deep in calf muscle—> can also appear in thighs and arms with the urge to keep limbs in motion
primary—> idiopathic
secondary—> iron deficiency, CKD, and pregnancy
What is the diagnostic criteria for RLS?
idk how imp

WHAT CLASS IS 1st LINE TX FOR RLS? List the FDA approved drugs.
Dopamine agonists—> ropinirole, pramipexole, rotigotine
Warnings with ropinirole and pramipexole?
idk how imp
may exacerbate dyskinesias
may cause orthostatic hypotension
Which dopamine agonist is available as a transdermal patch for RLS?
Rotigotine
What antiepileptic pro-drug is also FDA-approved for RLS symptoms?
Gabapentin enacarbil
What are some non-FDA approved therapies for RLS?
idk how imp
levodopa/carbidopa
opioids
sedative-hypnotics