APUSH Period 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Lord Baltimore
1694- He was the founder of Maryland, a colony which offered religious freedom, and a refuge for the persecuted Roman Catholics.

Act of Toleration
a 1649 Maryland law that provided religious freedom for all Christians

Roger Williams
A dissenter who clashed with the Massachusetts Puritans over separation of church and state and was banished in 1636, after which he founded the colony of Rhode Island to the south

Anne Hutchinson
She preached the idea that God communicated directly to individuals instead of through the church elders. She was forced to leave Massachusetts in 1637.

antinomianism
The idea that faith alone, not deeds, is necessary for salvation. Idea ran against Puritan clergy.

Halfway Covenant
Applied to those members of the Puritan colonies who were the children of church members, but who hadn't achieved grace themselves. Allowed them to participate in some church affairs.

Quakers
Members of the Religious Society of Friends who believed in the equality of men and women, opposition to slavery, welcoming of Native Americans, nonviolence, and resistance to military service.

William Penn
A Quaker that founded Pennsylvania to establish a place where his people and others could live in peace and be free from persecution.

rice plantations
This food production required a large land area and many slaves; popular in Carolina
tobacco
Popular in the earliest settlements in Virginia, but soil butchery and over production led to decline in a few decades and some turned to rice and indigo as most profitable crops.

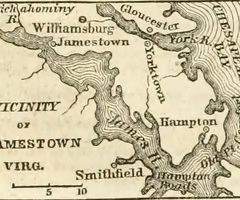
Jamestown
In 1607, the first permanent English colony in America was founded at this location. The Virginia Company, was a a joint-stock company chartered by England's King James I.

Captain John Smith
Because of his forceful leadership, Jamestown barely survived its first five years.

John Rolfe
He helped Jamestown develop a new variety of tobacco which became popular in Europe and became a profitable crop.

Pocahontas
Powhatan's daughter, she was the American Indian wife of John Rolfe in early settlement days in Jamestown.

Puritans
A religious group who wanted to purify the Church of England. They came to America for religious freedom and settled Massachusetts Bay.

Separatists
English Protestants who would not accept allegiance in any form to the Church of England. Included the Pilgrims and Quakers

Mayflower
Name of the boat that the Pilgrims sailed to Plymouth. Arrived in 1620.

Plymouth Colony
This colony was started by the Pilgrims. In the first winter nearly half of them perished. They were helped by friendly American Indians and celebrated the first Thanksgiving in 1621.
John Winthrop
Puritan governor of Massachusetts Bay Colony. Speaker of "City upon a hill"

Great Migration
This movement started because of a civil war in England. Nearly 15,000 settlers came to the Massachusetts Bay Colony for religious freedom.
James Oglethorpe
Founder of Georgia's first settlement, Savannah, in 1733. He acted as governor of Georgia and had strict laws which included a ban on rum and slavery.

Metacom
Aka King Philip, Native American ruler, who in 1675 led attack on colonial villages throughout Massachusetts

King Philip's War
From 1675 to 1676, the American Indian chief Metacom (King Philip), waged a vicious war against the English settlers in southern New England.

Mayflower Compact
1620 - The first agreement for self-government in America. It was signed by the 41 men on the Mayflower and set up a government for the Plymouth colony.

Virginia House of Burgesses
The first representative assembly in the new world. Created in 1619 due to distance between Great Britain and the colonies.

Sir William Berkeley
Royal Governor of Virginia who favored large plantation owners and did not support or protect smaller farms from Indian raids. He put down Bacon's Rebellion in 1676.

Bacon's Rebellion
In 1676, Nathaniel Bacon led a group of army volunteers that raided Native American villages, fought the governor's forces, and set fire to Jamestown. The rebellion lost momentum when Bacon died of dysentery. The rebellion was caused by the Governor's unfair favoritism of large plantation owners and refusal to protect small farms from Native American raids.

Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
In 1639, the Hartford settlers drew up the first written constitution in America. It established a representative government made up of a legislature elected by the people and a governor chosen by the legislature.

New England Confederation
In 1643, Plymouth, Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, and New Haven colonies formed a military alliance to deal with the threat from the Native Americans. It lasted until 1684.

Chesapeake Colonies
In 1632, the area once known as the Virginia colony, has divided into the Virginia and Maryland colony. Maryland became the first proprietary colony.
Virginia Company
England's King James I chartered the joint-stock company that founded the first permanent English colony in America at Jamestown in 1607.
mercantilism
An economic policy in which the colonies were to provide raw materials to the parent country of growth and profit of the parent country.

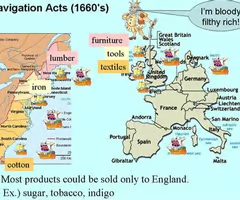
Navigation Acts
Between 1650 and 1673 England passed a series of acts which establish rules for colonial trade.
Trade to and from the colonies could be carried only by English or colonial-built ships, which could be operated only by English or colonial crews.
All goods imported in the colonies, except some perishables, had to pass through the ports in England.
Specified goods from the colonies could be exported only to England.
Sir Edmund Andros
In 1686, King James II combined New York, New Jersey, and additional New England colonies into a single unit called the Dominion of New England. He was sent England to govern the dominion. he was very unpopular by levying new taxes, limiting town meetings, and revoking land titles.

indentured servants
Young people from England under contract with a master who paid for their passage. Worked for a specified period for room and board, then they were free.

headright system
A method for attracting immigrants, Virginia offered 50 acres of land to each immigrant who paid for passage to America and to any plantation owner who paid for an immigrants passage.

triangular trade
Merchants traded colonist rum for African slaves, African slaves for West Indies sugar cane, and sugar cane was brought back to the colonies to make rum.
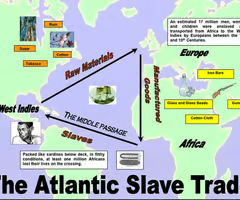
Middle Passage
Voyage from West Africa to the West Indies. It was miserable for the slaves transported and many died.
Benjamin Franklin
He was the most popular and successful American writer of the 18th century. Influential enlightenment philosopher, inventor, and diplomat.

Poor Richard's Almanack
Written by Benjamin Franklin, this book written in 1732 and annually revised, contained aphorisms and advice.

Phillis Wheatley
American poet (born in Africa) who was the first recognized Black writer in America (1753-1784)

established church
a church supported by the government

Great Awakening
A religious movement that swept through the colonies in the 1730s and 1740s It was characterized by fervent expressions of religious feeling among masses of people.

Jonathan Edwards
Preacher during the First Great Awakening; "Sinners in the hands of angry god"; argued that God was rightfully angry with human sinfulness. Those who repented could be saved by God's grace, but those who did not would suffer eternal damnation.

George Whitfield
Christian preacher whose tour of the English colonies attracted big crowds and sparked the First Great Awakening. Leader of the "New Lights"

colonial families
Couples married young and had many children in New World colonies. Most families lived on farms. Men worked, owned land, and dominated politics. Women did housework, educated the children, and worked with her husband.

Germans
This group of immigrants settled chiefly on the rich farmlands west of Philadelphia. By 1775, they comprised 6 percent of the colonial population.

Scotch-Irish
Ethnic group that had already relocated once before immigrating to America and settling largely on the Western frontier of the middle and southern colonies

Africans
The largest single group of non-English immigrants did not come to America by choice. By 1775, their population (slave and free) comprised 20 percent of the colonial population. About 90 percent were in the southern colonies.

John Peter Zenger
Journalist who questioned the policies of the governor of New York in the 1700's. He was jailed; he sued, and this court case was the basis for our freedom of speech and press. He was found not guilty.

Enlightenment
In the 18th century, some colonists were attracted to this European movement in literature and philosophy. They believed that human reason could be used to solve most of humanity's problems. They reasoned that while the state is supreme, it is bound to follow natural law based on the rights of individual. The movement influenced early American politicians.
town meetings
The dominant form of local government in the New England colonies, in which the people of the town would regularly come together to vote directly on public issues.

limited democracy
In the mid 18th century, colonial democracy was limited to mostly white men that owned land. Those barred from voting included white women, poor white men, all slaves, and most free blacks.

Elect
In Calvinist doctrine, those who have been chosen by God for salvation.
Primogeniture Laws
English laws that only led eldest sons inherit land, leading younger sons to search for money via things like joint-stock companies.

joint-stock company
A business, often backed by a government charter, that sold shares to individuals to raise money for its trading enterprises and to spread the risks (and profits) among many investors.

Anglo-Powhatan Wars
1614-1644; Series of wars between English Virginia Company settlers and local Indian tribes; "Irish tactics" used; Settled by Marriage of Pocahontas and John Rolfe; Led to the banishment of Chesapeake Indians and English encroachment of land.

Walter Raleigh
Received a charter from Queen Elizabeth I to explore the American coastline. His ships landed on Roanoke, which became a "lost colony."

Elizabeth 1
Queen of England from 1558 to 1603; a skillful politician and diplomat, she reasserted Protestant supremacy in England. Sought to build a new world empire.

Starving time
1609-1610
A period of hunger and death endured by the Jamestown colonists that nearly wiped out the entire settlement.
