Genetics and Evolution
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Genetic Code of an Organism
Genetic code of an organism is stored in its deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Organisms will always display a dominant trait, but sometimes carry a gene for a recessive trait
If an organism has a gene for a dominant trait, and a gene for a recessive trait, it shows the one that’s dominant
e.g. eye color, brown eyes in dominant blue eyes is recessive
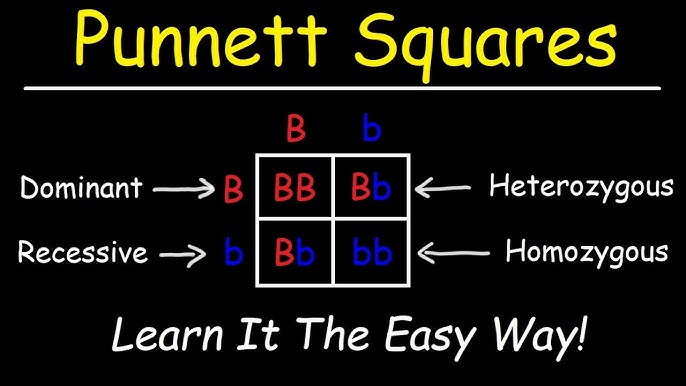
Punnett Square Question on Exam
What’s the probability that two parents, both of whom have brown eyes, but who are carriers of a recessive gene for blue eyes, what’s the probability that they’ll have a blue-eyed child?
B → Brown
b→ Blue
Use a Punnett square
BB: The child has brown eyes
Bb: The child still has brown eyes
bb: The child has blue eyes
You don’t know if person has 2 dominant genes or a dominant and a recessive gene.
Gregor Mendel
Scientist and Monk
Pioneer in Dominant and Recessive Gene Study
Crossbred pea plants, wrinkly and smooth peas
1st time he bred them
all the resulting peas were smooth because they were all carrying a recessive gene for being wrinkly, but smooth trait dominated
2nd time he bred them
a quarter of the offspring were wrinkly. This is how we discovered idea of
Successive Generations: the passing of traits over time
However, a recessive trait can be passed down through generations without showing up until two carriers (who each have one copy of the recessive gene) have a child who inherits both recessive copies. This can happen even if the parents show the dominant trait.
Successive Trait
the passing of traits over time
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
Asserts that organisms have changed overtime to adapt to the unique and varied demands of their changing environments
organisms have diff traits that may be slightly diff than their parents and we call this variants
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution: VARIANTS
Organisms have diff traits that may be slightly diff than their parents
Variation on the parents
e.g. Giraffe w/ longer neck than parents that’s a random variation. That occurred because the way the DNA got combined when they reproduced
Advantageous or Disadvantageous
Depends on the Environment in which an organism exists Giraffe Explain
That trait is not necessarily advantageous or disadvantageous; it depends on the environment in which the giraffe exists
e.g.
If there are high trees where there’s fruit other giraffes can’t reach because they have shorter necks, he enjoys that food exclusively, he’ll
feed,
be healthy,
reproduce,
and pass on the trait eventually propagate.
However, if trees are short, extra neck length may slow giraffes down, more susceptible to predators
Overall Idea of Organisms Adapting
The traits that they’re advantageous get propagated, and organisms, who have disadvantageous traits end up dying off overtime,
That’s how we get evolution of different types of organisms
Supporting Evidence for Evolution 2 Ways
Fossil Records
Comparative Anatomy
Supporting Evidence for Evolution Fossil Records
Look at fossil records of diff organisms over time
and
see how minor variations have occurred, and one organism led to the next.
Supporting Evidence for Evolution Comparative Anatomy
Look certain type of animals, whales, they have little feet buried under their blubber.
Useless to them, but vestigial remain from when they were a land based animal
DNA sequences (between hippos and whales) see they’re very similar even though they look like different creatures
Adaptation vs. Accomodation
Pair of terms we gotta know how to differentiate
Accommodations (Non-Genetic Changes)
Non-genetic changes, allow individual organisms to respond to TEMPORARY CHANGES in the environment
e.g.
When cold out, the blood vessels in your body contract, conserving heat.
When it gets warmer, they’ll expand again increasing blood flow.
Not a genetic change.
Ability to contract blood vessels- evolutionary
Action itself- that’s accomodation
Adaptations (Genetic Change)
CHANGES AT THE GENETIC LEVEL ALLOWING A POPULATION TO RESPOND TO LONG TERM CHANGE in the environment
e.g.
effects population, not just me as an individual
e.g. trees getting taller and taller, giraffes in that region evolve a longer neck to be able to reach fruit on those trees
This has to occur over generations
Also, the dilation of the human eye changes temporarily as a temporary change in the environment's amount of light