cell transport/permeability *FINISH
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
diffusion
The movement of particles (like molecules or ions) from an area of high concentration to low concentration until evenly spread out.
Simple diffusion
Direct movement of small, nonpolar molecules (like oxygen, carbon dioxide) through the cell membrane without help.
Readily dissolve in lipids
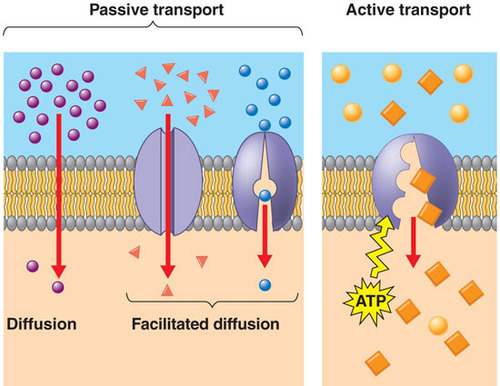
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of larger or charged molecules (like glucose or ions) across the membrane through transport proteins.
Still passive (high → low, no energy).
Uses: Channel proteins or carrier proteins
passive transport
Movement of substances across a cell membrane without using energy (ATP).
How: Relies on natural concentration gradients (high → low).
Types include:
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
active transport
Movement of substances across a membrane against the concentration gradient (low → high).
Energy use: Requires ATP (cellular energy).
Example: Sodium-potassium pump in nerve cells.
Osmosis
A special type of diffusion—the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from high water concentration (low solute) → low water concentration (high solute).
HIGH water (low solute) to LOW water (high solute)