Sac State Paramedic 22-1 missed mod questions
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
Electrical Pathway Through the Heart and the different HR
SA Node(60-100)--AV node(40-60) conducts impulses to bundle of his(20-40)---bundle of his carries impulses to R & L branches----impulses travel to Purkinjie fibers
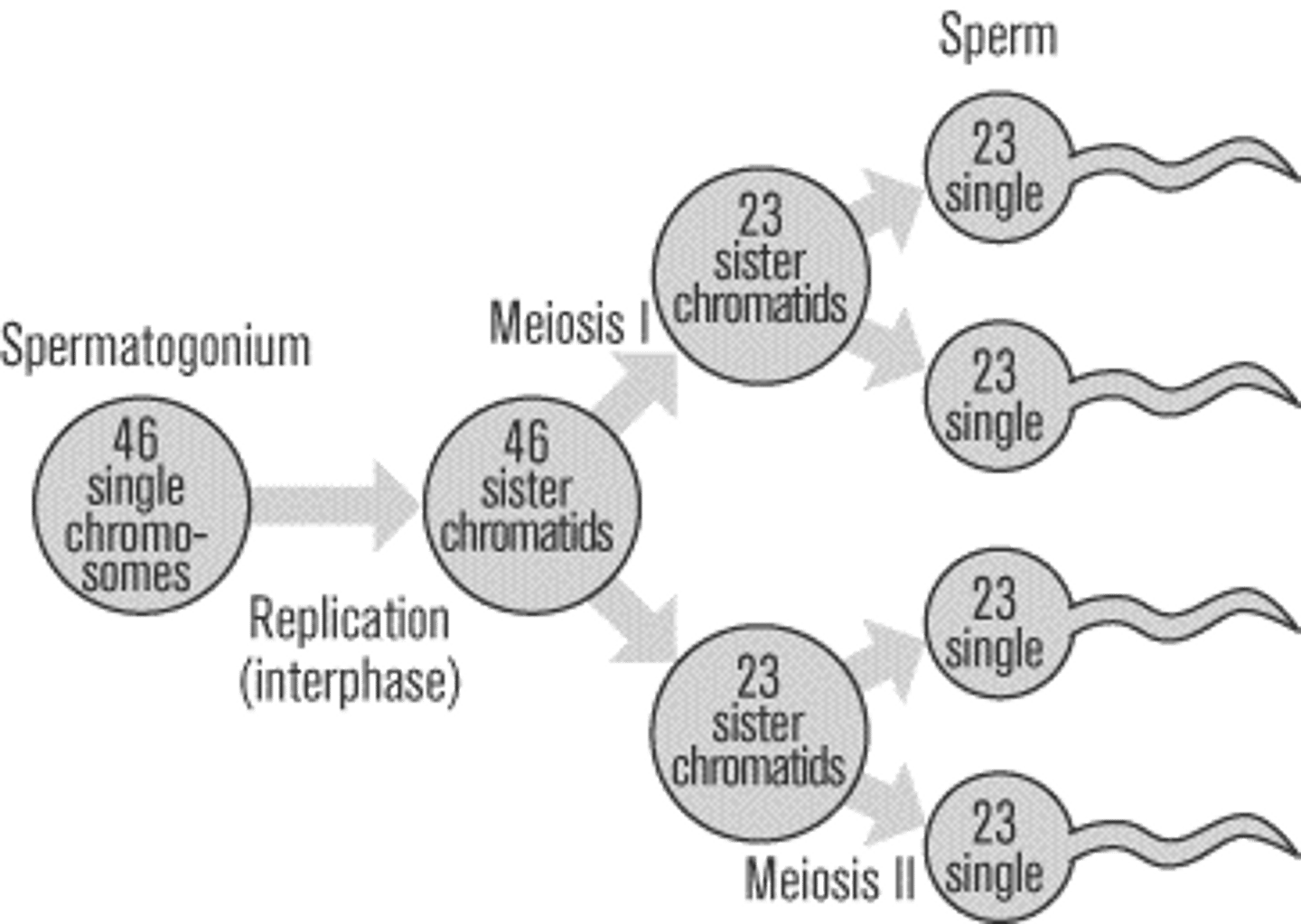
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm
dopamine response
may cause renal vasoconstriction. Increases cardiac output, increases blood flow, and improved renal blood flow
layers of central nervous system
3 protective layers around the brain and spinal chord.
Dura Mater: Outer Most
Arachnoid
Pia Mater: Inner Most
Pancreas Functions
exocrine secretes hormones into small intestine; endocrine secretes hormones into bloodstream; Insulin stimulates muscles to remove glucose from the blood when glucose levels are high (like after a meal); Islets of Langerhans secrete glucagon that respond to low levels of blood glucose
Olifactory Nerve #/Function
1 Smell
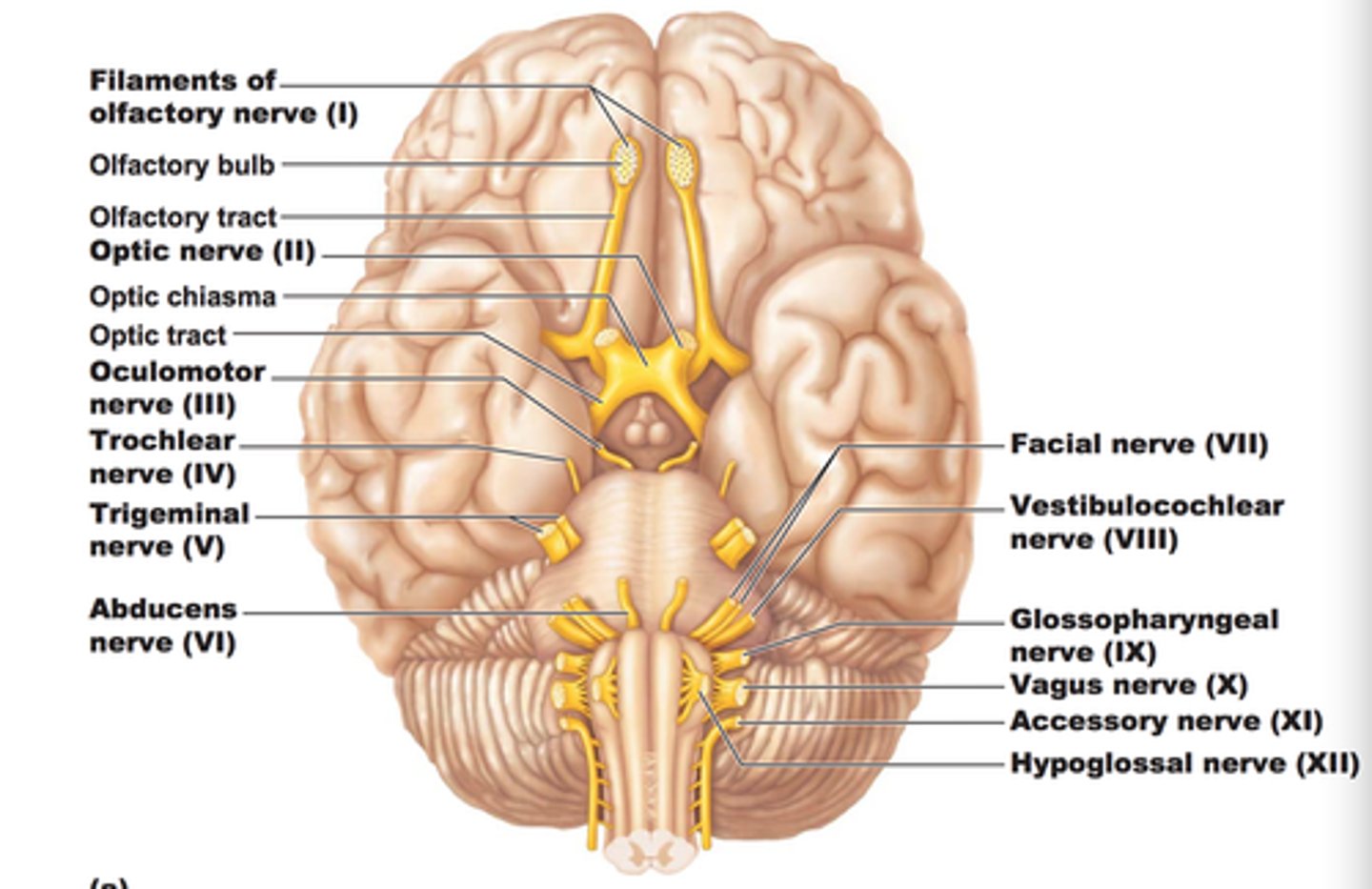
Optic Nerve
2 Vision/sight
Occulomotor Nerve
3 Eye Movement
Upper eye lid/pupilary muscle
Trochlear Nerve
4 eye movement
Trigeminal Nerve
5 Facial sensation
Abducens Nerve
6. eye movement
Facial Nerve
7 Facial expression
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
8, hearing and balance
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
9 Taste
Vagus Nerve
10 swallowing/speech
Acessory Nerve
11 Tilt head/ Shrug Shoulders
Hypoglossal Nerve
12 Tongue Movement
Pulmonary Blood Flow
Pulmonary Artery: deoxygenated blood away from the heart
Pulmonary Vein: Oxygenated blood to the heart
Systemic Circulation
Artery: Oxygenated blood away from the heart (only difference is Pulmonary artery)
Vein: Deoxygenated blood to the heart
Process of Digestion
1.Ingestion
2.Mechanical Process
3.Digestion
4.Secretion (acid, water, enzyme release)
5.Absorption
6.Excretion
White Blood Cell types
Stored in Lymph + Blood
- Move through Capillary Wall into Tissue
- Elevated during Immune/inflammatory response
Neutrophils
- Finds and Destroys Bacteria(Unibomber)
- First responders to inflammation
- Backstage pass to all tissue/cells/organs
- produced in Bone Marrow
Eosinophils
- Memory Cells in the immune system
- Kill + Record
Basophils
Allergy +Inflammatory Response
- Release Histamine and Heparin
(Found in Blood Stream, create Mast Cells)
Monocytes
- Healers, ingest broken down tissue
- produced in Bone Marrow
Inner workings of the Kidney (Nephrons)
Glomerulus: Blood vessel inside Bowmans Capsule
Bowmans capsule: Collects fluid from the Glomerulus
Proximal Convoluted Tubule: Absorbs: salt, water, glucose, amino acids, potassium, urea, phosphate, and citrate
Loop of Henle: reabsorption of water and sodium chloride (Urine formation)
Distal Convoluted Tubule: regulate pH of blood by regulating H+ ion
Spleen
Largest Lymphatic organ. Breaks down old RBC/ Filters
Helps produce Lymphocytes
How much ATP is created after Glycolysis
2 Net ATP (2 spent, 4 produced)
2 Pyruvates
2NADH
How much ATP is created after Krebs
2 more ATP
How much ATP is created after Electron Transport Chain
34 from ETC with a total of 38 after everything
Mast Cells
Release Histamine and Heparin
- Histamine triggers Allergic response
- Heparin prevents clotting
Where does fertilization occur?
fallopian tubes
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system pathway Diagram
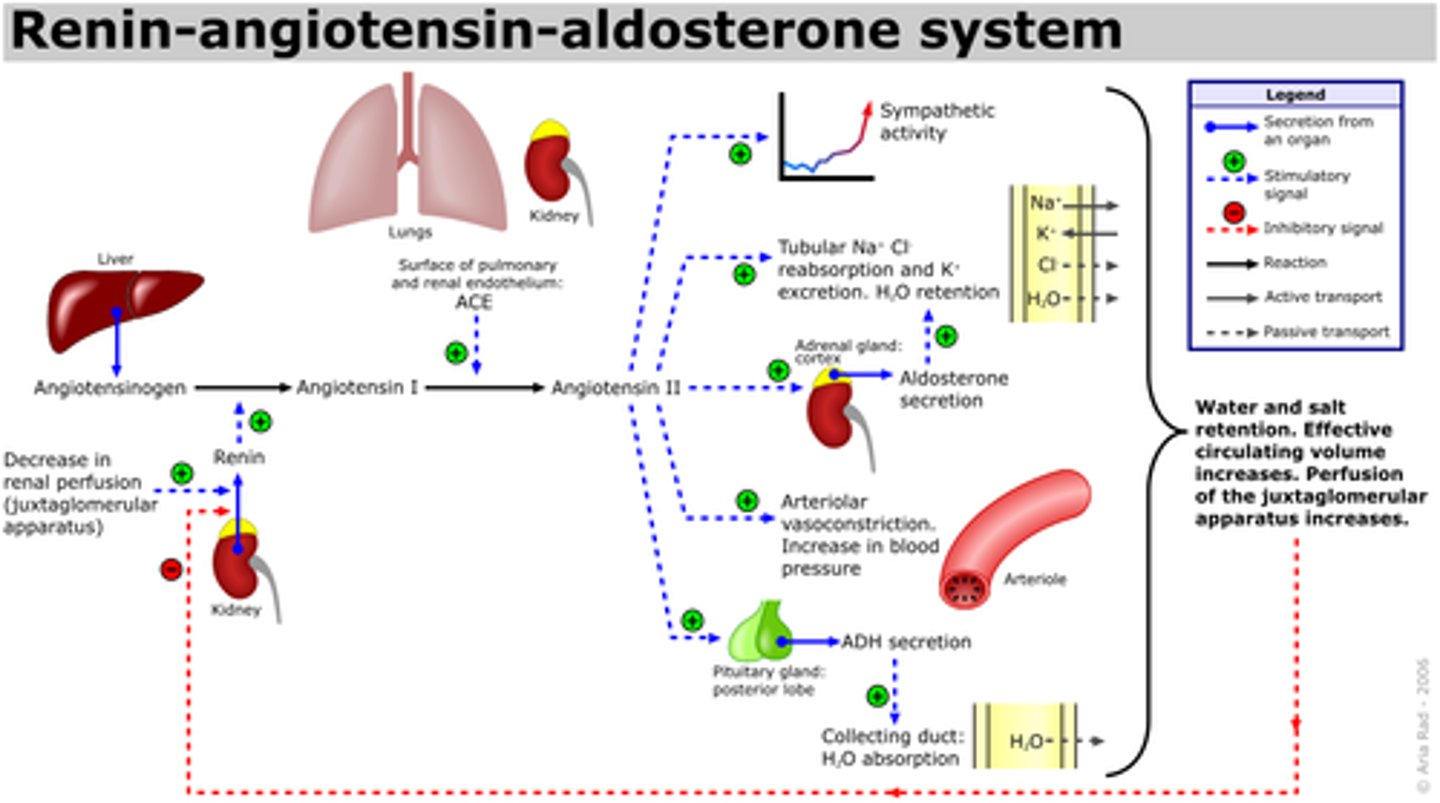
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
a hormone cascade pathway that helps regulate blood pressure and blood volume
Neuron Action potential Threshold
-55
4 Steps of Action Potential
1. Depolarization- Sodium Channels open and sodium leaves making room for potassium on outside
2.Action potential- "Message sent" Sodium ion chanells close
3. Repolarization- sodium Ions pushed out (K inside. NA Outside)
4.Hyperpolarization- NA closed off, K being pulled inside the cell
Hypoxic Drive
Backup system for body where the body switches to breathing being controlled by amount of O2
Upper and Lower airway separation
The airways are separated at the Larynx
Upper Airway and Lower Airway
Upper:
Nasopharynx, pharynx, laryngopharynx. larynx
Lower:
Bronchiole, Bronchiole Branches, Alveoli
How to increase pressure in vascular system
Increase volume via fluid
Beta 1 Receptors
Beta-1 = Heart (Beta 1, One Heart)
Increased Heart Rate
(Positive chronotropic Effect)
Increase Force of Contraction
(Positive inotropic effect)
Increased conduction velocity
(Positive dromotropic effect)
Beta 2 Receptors
Beta-2 (Beta-2, Two lungs)
Bronchodilation and Vasodilation in muscle/liver
Alpha 1 Receptors
Vasoconstriction of peripheral vasculature
Alpha 2 Receptors
Decrease in Sympathetic Nervous System (Brain)
Alpha Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist
- Prevent endogenous catecholamines from reaching alpha receptors
(lowers BP and decreases systemic vascular resistance)
-Prescribed for patients with hypertension, enlarged prostate, glaucoma
Needle Cric. Contraindication
Any other Airway
VAD's
Ventricular Assist Device
A-Fib can lead to
Stoke, PE, and MI
Aortic disection
Injury of the inner most layer of the Aorta, causing blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall
First thing to do on scene
BSI/ Scene Safe
Stable vs Unstable V-Tac
Unstable v-tac can result in ALOC or a Loss of Consciousness
Functions of the skin
Thermo Regulation, protection, water retention, sensation, secretion, absorption
Treatment for Aortic Disection
Manage PT stress and administer Analgesiscs to bring PT Heart rate and Blood pressure down to prevent further damage
How does septic Shock Cause Hypotension
Sepsis causes Vasodilation and third spacing throughout the body resulting in hypotension
Intervention for a patient with shallow ineffective respirations?
BVM
Treatment for acute limb Ischemia
−If limb ischemia affects a lower extremity, sit the patient up, with feet lower than chest.
−Keep the ambulance warm to avoid vasoconstriction of the skin.
•Do not apply heat or cold to affected limb.
What limb leads have what polar charge
L Arm (+/-)
R Arm (-/-)
L Leg (+/+)
Electrons
Negatively charged particles
Protons
Positively charged particles
Neurons
Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information.
Stable Angina
−Follows a predictable, recurrent pattern
1) Pain occurs after a predictable amount of exertion, with a predictable location, intensity, and duration.
(2) Patients often take some form of NTG.
(3) ST-segment depression or inverted T waves show on ECG.
(4) ECG changes resolve when the heart's oxygen demand is met.
Unstable Angina
−More serious, higher level of obstruction
−Changes in frequency, severity, and duration
−May begin during sleep or at rest
−Warning of impending MI
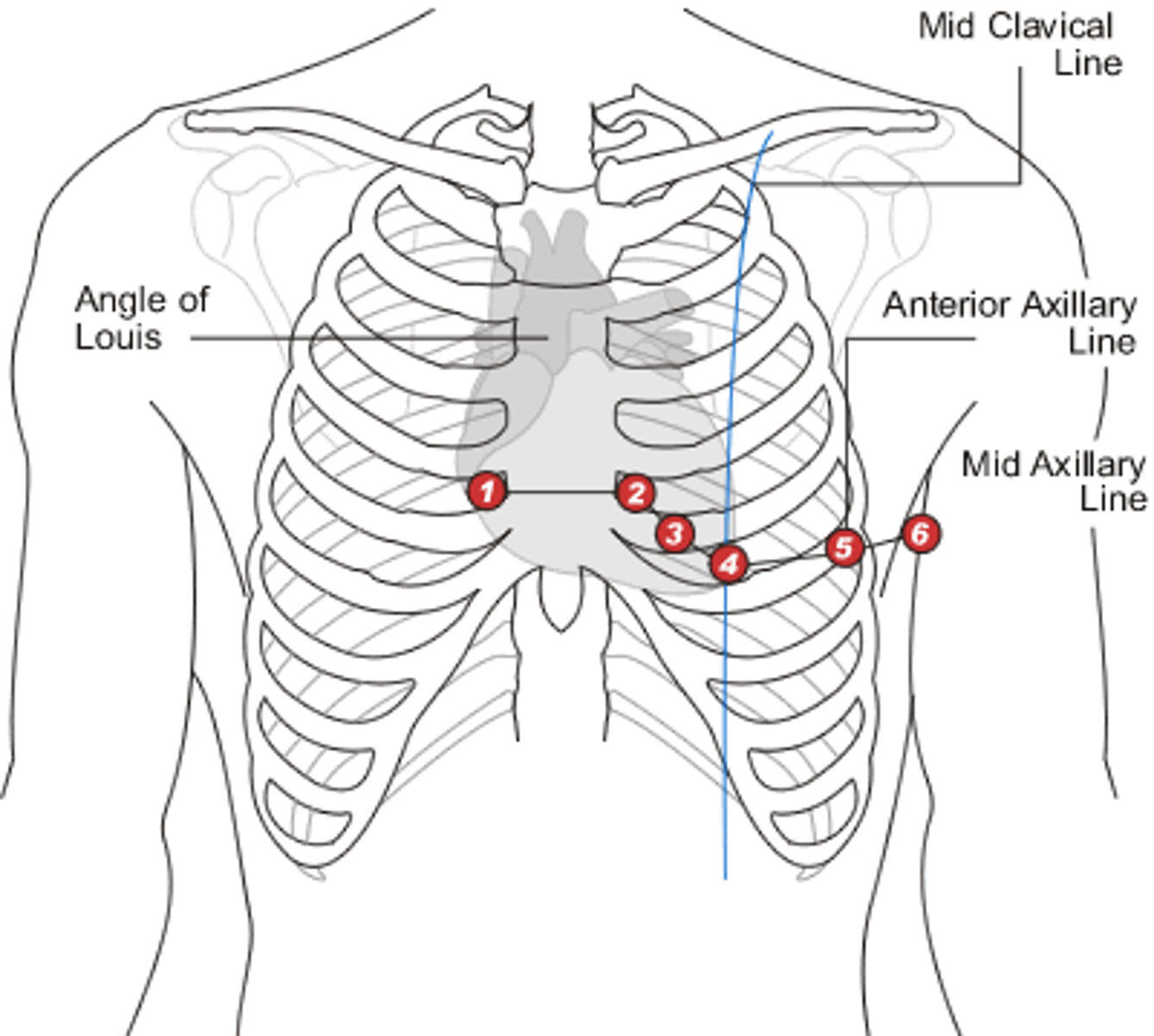
Where are 12 lead electrodes placed
Distributive Shock Types
neurogenic, anaphylactic, septic
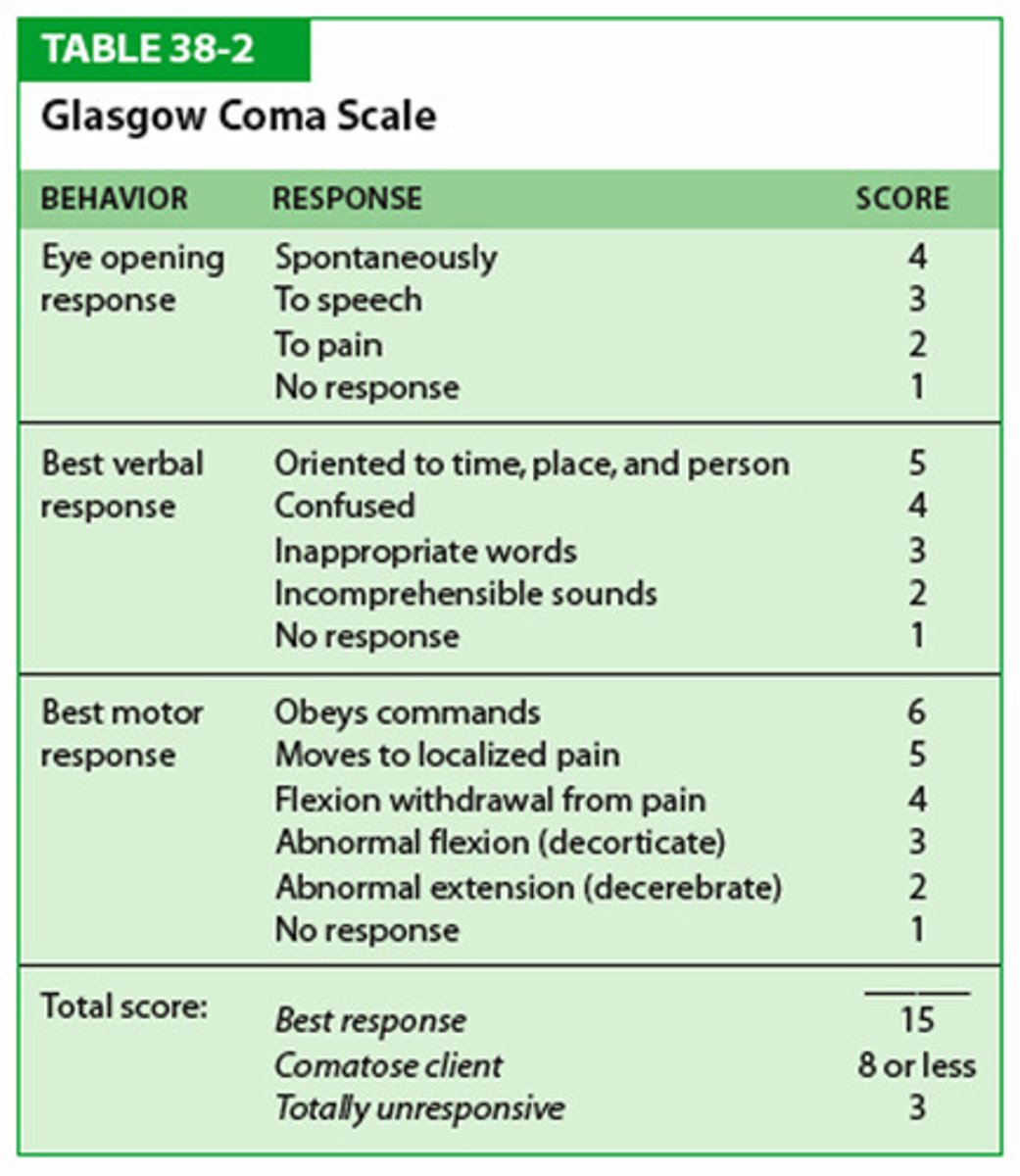
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
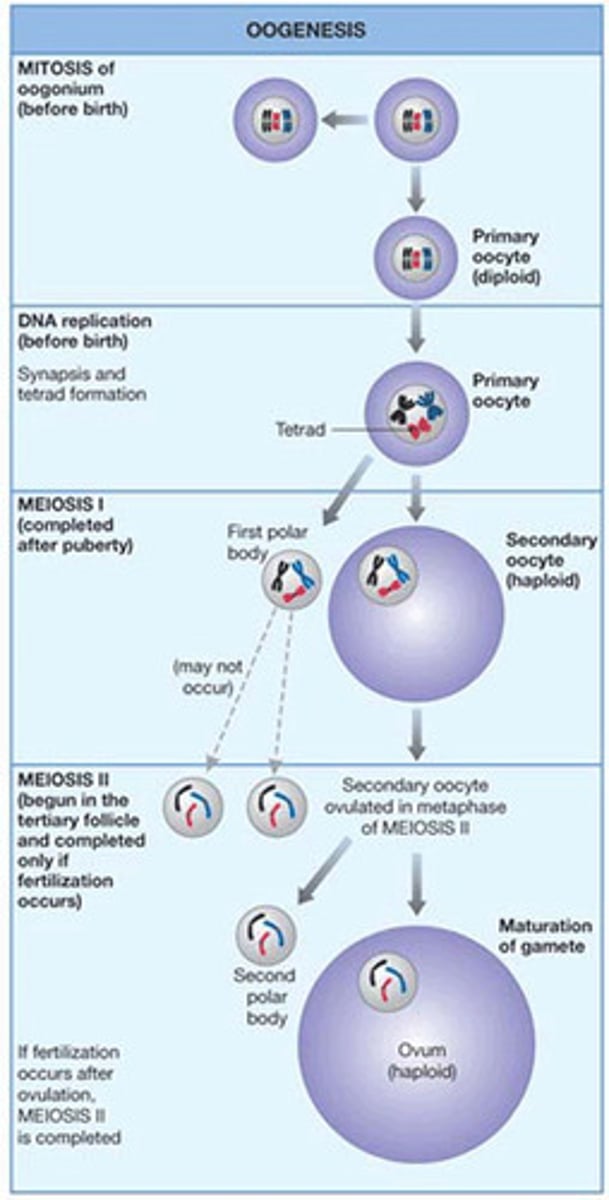
Oogenesis
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
Hypoventilation leads to
Respiratory Acidosis
H's and T's
5 H's
H ypoxia
H ypovolemia
H ydrogen Ion (acidosis)
H ypo / Hyper kalemia
H ypothermia
H ypogylcemia
5 T's
T ension pneumothorax
T amponade
T oxins
T hrombosis (pulmonary)
T hrombosis (coronary)
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
The bodys response to a drop in Blood Pressure
peripheral Vasoconstriction, shunting blood to the core and increasing heartrate
CPAP contraindications
respiratory arrest, pneumothorax or chest trauma, tracheostomy, GI bleeding or vomiting, unable to follow verbal commands, Low Blood Pressure
organo phosphate poisoning
SLUDGEM
Treatment: Atropine 2-4mg
Beta Blockers and Calcium Channel Blocker OD Treatment
Atropine
1mg with a max of 3mg
Beta Blockers OD S/S
Irregular/slow HR
lightheadedness
Low BP
Signs of shock
Cushings Triad (ICP)
HTN (Widened pulse pressure)
Bradycardia
Irregular respirations
Becks Triad
Muffled heart sounds
JVD
Narrowing pulse pressure (Hypotension)
Upper GI Bleed S/S
Bright red bloody emesis
Dark tarry/coffee ground stools
(Not a disease it is a symptom)
Tx: Fluid, zofran if needed, O2, etc
Lower GI Bleed
Coffee ground emesis
Bright red hematochezia
Tx: Fluid, zofran if needed, O2, etc
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome (HHS)
Type 2 diabetes
From hyperglycemia and no ketones being metabolized
ALOC
Lethargic
Dehydration
Partial paralysis/muscle weakness
If sugar does not raise high enough overtime from dextrose we should...
Repeat dose as needed
What does EMS need to worry about with toxic/hazmat environments?
There could be multiple patients
If a patient is hypotensive and tachycardic we should...
Give fluid boluses at minimum
In regards to ABC's
Do not advance to the next step until airway is secured
Pt is getting adequate oxygenation (if it is from themselves or a BVM etc)
Pt bleeding is controlled
(For trauma we go in order of C.A.B. if needed)
s/s of hemorroids
Itching or irritation around the anus
pain or discomfort
Swelling of the anus
Hematochezia
S/S of gastroenteritis
Inflammation of the stomach and intestines
nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, diarrhea
be cautious, could go into hypovolemic or septic shock
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
5 F's (Fat, Fair, Fertile, 40-50, Female)
Severe RUQ pain
appendicitis
inflammation of the appendix
3 phases
-Early: Gradual onset of pain
-Ripe: Extreme pain (RLQ could be referred to McBurneys point)
-Rupture: Burst of appendix, no pain, stool released in abdomen could cause peritonitis and sepsis
Diverticulitis
inflammation/weak area of the diverticula
Low fiber diet
LLQ pain
pacreatitis
sudden severe LUQ epigastric pain -steady boring through to the back
usually with a history of chronic alcohol abuse
may have abdominal tenderness and or distention
Grey Turners sign and or Cullen Sign
ulcerative colitis
a chronic condition of unknown cause in which repeated episodes of inflammation in the rectum and large intestine cause ulcers and irritation
AGES 15-25 and 55-65
Be cautious the ones above could be abdominal scenarios in the final skills
TCA Overdose S/S and Treatment
(Could be a scenario after Mod 3...)
Red as a beat, Dry as a bone, mad as a hatter, blind as a bat, hot as a hare, Widening QRS, Dilated pupils
Tx: Sodium bicarb
Examples: Amyltriptaline/nortryptaline
Describe status epilepticus
Seizures that last 4-5 minutes or multiple seizures with little to breaks in between
prehospital treatment for a stroke
Vitals
Oxygen
Monitor
IV
Transport
Prehospital care for a pt with increase ICP?
Recognize
Vitals
Oxygen
Monitor
Iv
Transport
-Remember to elevate the pt 30* and hyperventilate to vasoconstrict for the brain (no more than 5 minutes)
Phases of Renal Problems
Acute Kidney Injury
Chronic Kidney Disease
Renal Failure/End Stage Renal Disease