nurs 116 - lec 5
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
glucocorticoid side effects
none or minimal
acute tx only (high dose, IV/IM, short term)
local route (ex injection into joint)
risk of systemic effects
long term tx
systemic route (PO, IV, IM)
cushing syndrome
how to stop glucocorticoid tx?
negative feedback - NO ABRUPT STOPPAGE
wean until 0 bc if it suddenly stops, the body will think it had enough and will stop producing it
cushing syndrome ss
red cheeks
fat pads
abd stretch marks
bruise easy (lose platelets, WBC)
muscle wasting
why is cushing syndrome so dangerous?
by the time you realize it, it’s already too late
what is liver steatosis
fat build up in liver
acute inflammation time frame
-occurs within 15 min (allergy)
-leaves in less than 10 days
chronic inflammation time frame
acute inflammation (15 min) → more than 10 days
chronic inflammation steps
1) clotting occurs with cells (WBC, collagen, fibroblasts)
2) granulation restores vascular supply → epithelial cells fill in granulation tissue
3) restored epithelium thickens and forms scar tissue
why is chronic inflammation bad?
-tissue destruction bc of repetitive inflammatory cascade → effects fx
-secretion of regenerative mediators (ex. tissue growth factors) leads to neoplasms (cancer)
-scar tissue formation
less vascular (less perfusion)
less flexible (tears easier)
less strong (80% of former strength)
what is the most common allergy in yeg?
allergic rhinitis, 40% of pop
allergic rhinitis ss, bw and tx
ss: rhinitis (nasal discharge and swelling), conjunctivitis (eyes), sneezing, snoring, itching, headache from nasal-sinus infection
bw: high eosinophils
tx: 1) antihistamines pre/during exposer; 2) intranasal corticosteroids (insufflation) for nasal mucosa inflammation
allergic rhinitis drugs “flat mom butt”
fluticasone
mometasone
budenoside
atopic dermatitis characteristics (3)
allergic disease, autoimmune profile
high IgE in plasma
lichenification: scar formation
risk of super infection: bacterial + viral
what is the cause of eczema (skin mutation)?
filaggrin gene mutation in skin → more water escapes → allergens get in easier
can you grow out of atopic dermatitis?
yes
do you use soap when treating dermatitis?
no, will dry out skin
atopic dermatitis tx
topical glucocorticoids
antihistamines
antibiotics/virals for infections
risk factors of psariosis
family hx + triggers
psoriasis skin changes
hyperkeratosis (thickening of skin)
thinned stratum granulosum
vasodilation
dilated dermal papillae
psoriasis ss and tx
ss: dry scaly skin patches, non pruritic (itchy = no histamine)
tx: glucocorticoids (local→ systemic as needed), moisturizing cream
eczema vs psoriasis
eczema: intense itching, oozing & crusting, appears on flexural skin surfaces
psoriasis: itching less severe, scaling, appears on extensor skin surfaces
what is arthritis
joint inflammation
what is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
chronic systemic rheumatic (inflammatory) disease
autoimmune
risk factors of RA
family hx, gender
steps for RA
1) WBC and pro-inflammatory mediators
2) dysfunction of synovial cavity (pannus)
3) destruction of surrounding tissue (bone, cartilage)
4) thickening and deformity of affected tissue → autoimmune
pannus joint
-no cartilage
-bone erosion
-swollen synovial membrane
RA ss, bw and tx
ss: synovial join inflammation, anorexia
bw: high c-reactive protein
tx: NSAIDs, glucocorticoids (PO)
RA biologic drugs: response modifying agent
stops cytokines
end in “mab”
parenteral
RA biologic drugs: DMARDS (disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs)
enhance anti-inflammatory mediators (ex. adenosine)
methotrexate
parenteral
what is osteoarthritis (OA)
degenerative disorder of articular cartilage
wear and tear arthritis (fewer joints affected)
OA risk factors
mechanical stress, obesity, age, gender
how does estrogen effect bones to prevent OA?
it protect bones so menopause increases risk
OA steps
cartilage changes
less proteoglycans
less collagen
inflammatory mediator release (cytokines, prostaglandins) → more inflammation
cartilage tissue destruction → bone-bone articulating surface
bone spurs
bone overgrowth caused by bone-bone contact which stim more growth (+ feedback)
OA tx drug classes
NSAIDS, glucocorticoids (local)
OA local glucocorticoid treatment
cortisone joint injection using ultrasound
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
group of chronic inflammatory conditions in GI tract
canada has the highest incidence in the world
crohn’s vs. ulcerative IBD
crohn’s: gums → bums, patchy inflammation
ulcerative colitis: inner lining of bowel/lg int, continuous
IBD ss, dx
ss: tummy pain, weight loss, fever, tiredness
dx: flare-ups affect skin, eyes, liver, joint/use x-rays and stool samples
T or F: there is a cure for IBD
F
what is a fistula
abnormal connection b/w 2 organs which makes the area less flexible → pain
IBD trigger
endogenous GI host flora (antigen) → inflammation
IBD tx drug classes
-DMARDS → biologics
-glucocorticoids
sulfasalazine tx, drug class, drugs, admin + subjugates
IBD
DMARD: biologic
azulfidine, salazopyrun
PO: activate metabolites → 5-ASA, sulfapyridine
5-ASA drugs (“mat”) + fx
mesalamine, asacol, teva
treat IBD, esp ulcerative colitis
local NSAID effect
PO, rectal (long-sustaining tablet)
sulfapyridine tx, s/e?
treat IBD
systemic ADME + anti-inflammatory = side effects
what is asthma
chronic inflammatory airway disorder (not autoimmune)
how many canadians have asthma
10%
risk fx for asthma
family hx, triggers
asthma inflammation pathway
inflammation, degranulation
WBC signaling, esp T + interleukins
th2 helper cells→ signal B to make IgE→ cross link→ degranulation
bronchial inflammation, bronchoc, mucous prod (makes it hard for inhaled med to reach target)
what does an epithelial injury in the bronchi cause?
chronic hypersensitivity of bronchial airways
asthma attack ss
hard to breathe
tachycardia
anxiety, panic
fatigue
systemic effects of asthma
fast inhale, slow exhale → traps air in alveoli
hyperinflated lungs with minimal gas exchange
ventilation-perfusion mismatch (lots of blood, little O2)
low O2, high CO2
hypoxemia, hypercarbia, high pulmonary pressure → increased RVEDP → low CO
asthma management tx
-stabilize inflammation, reduce # of attacks
-maintenance drugs (controllers)
-meds should be as local as possible
-daily
what type of drugs do you need for asthma attack tx
rescue drugs (relievers)
asthma tx MUST HAVES
rx for maintenance and rescue drugs
know when to call 911
asthma inhaled anti-inflammatory drug classes
glucocorticoids, mast cell stabilizers, leukotrine modifiers (PO)
using glucocorticoids for asthma
1st line maintenance tx
prophylaxis against attacks
inhaled every day (nebulizers in clinical settings)
prophylaxis
preventative tx
asthma: glucocorticoid drug names (bad bitch flute)
budenoside
beclomethasone
fluticasone
asthma tx: mast cell stabilizers fx
inhibits histamine
asthma: mast cell stabilizer drug + characteristics
cromolyn
inhaler
slow onset
dose 3-4/day
not common
synergy with glucocorticoids
what do leukotriene mods do?
block leuko receptors
modify inflammatory response pre-exposure
asthma tx: leuko mod drug + characteristics
montelukast (singulair)
PO
systemic effect
slow onset
prophylaxis
synergy tx
short exposure to decrease side effects for long term use
asthma tx: biologics-monoclonal antibodies drug + characteristics
xolair (omalizumab)
SC
longterm tx plan
high affinity for IgE
binds free IgE/decreases mast-cell bound IgE (no degranulation)
rescue asthma tx drug classes
beta 2 adrenergic agonists, anticholinergics
beta 2 adrenergic agonist properties
rescue asthma tx
potent
stimulate SNS B2 receptors
fast
beta 2 adrenergic agonist drug names '“betas are for sale”
formoterol (oxeze)
salbutamol (ventolin)
anticholinergic drug class properties
less potent
antagonist PNS (bronchod) to allow SNS to take effect
slow onset
synergy w beta 2 adrenergic agonist
anticholinergics drug name
atrovent (iptraprotrium)
asthma attack ER admin tx
oscar’s banana split makes a great apple
O2
beta 2 adrenergy agonists/nebulizer is best
ventolin
sympathomimetics, IV
epinephrine → vasoc for perfusion
magnesium sulfate, IV
vaso/bronchod
anticholinergic, nebulizer
synergy
atrovent
glucocorticoid, IV
dexamethasone
antihistamine, IV
benadryl
asthma tx: magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) - class, admin
drug class: electrolyte, enzymatic activator, calcium channel blocker
IV
titrate to effect for severe bronchoc
rescue med
what does inhibition of ca channel do? (asthma)
inhibit in smooth musc → no depol → bronchod → stabilize mast & t-cells → decreased pro/inflammatory mediators
side effect of mgso4 asthma tx
hypotension
what does mgso4 cause to be released?
enhanced release of NO → vasod, pulm vasod → improved gas exchange
how do you treat a local allergy like contact dermatitis?
antihistamine, topical (ex. benadryl cream)
how to treat known allergen with systemic exposure present?
antihistamine, non-drowsy (ex reactin - 1tb)
how to treat eye symptom exposure
antihistamine, topical to eye (ex. patanol, eye drops)
what do you do if allergen exposure anticipated in high doses?
prophylaxis w leuko mods → singulair, 1tb x 2 days pre-exposure
what is anaphylaxis
systemic inflammation & severe vasod
anaphyalxis ss
airway: SOB
skin: hives
brain: anxiety
heart: hypotension
stomach: nausea
asthma attack vs. anaphylaxis
asthma: airway/breathing; no hives, swelling, vomiting or diarrhea
tx focused on airway/breathing
ana: systemic vasod & bronchoc; breathing issues most prominent
tx focused on perfusion, airway/breathing
what do you do when you are unsure if a person is having an asthma attack or is in anaphylaxis?
administer epinephrine then albuterol
air trapping
bc of bronchoc + edema mucous, gas exchange can’t be completed
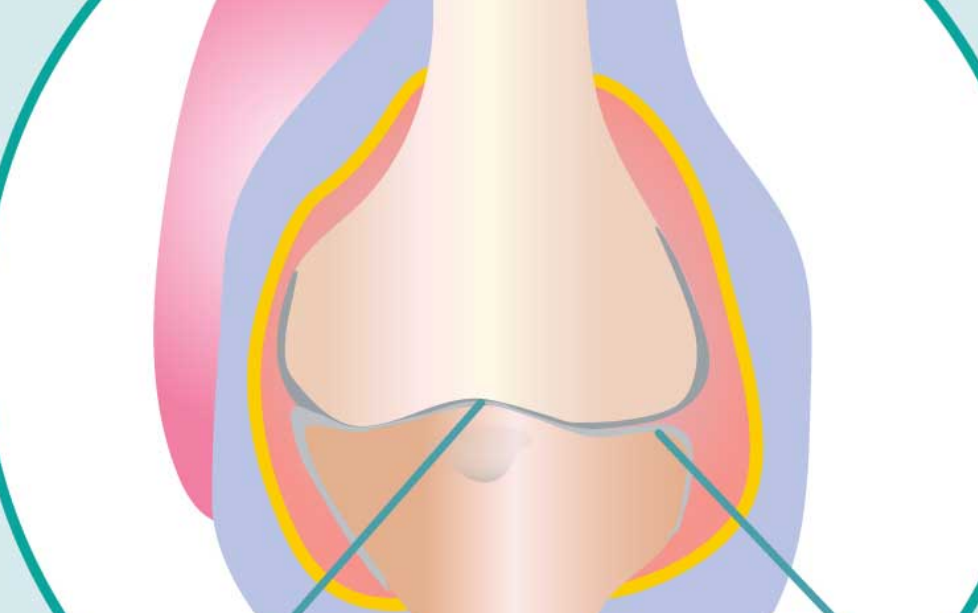
dx?
OA/wear and tear
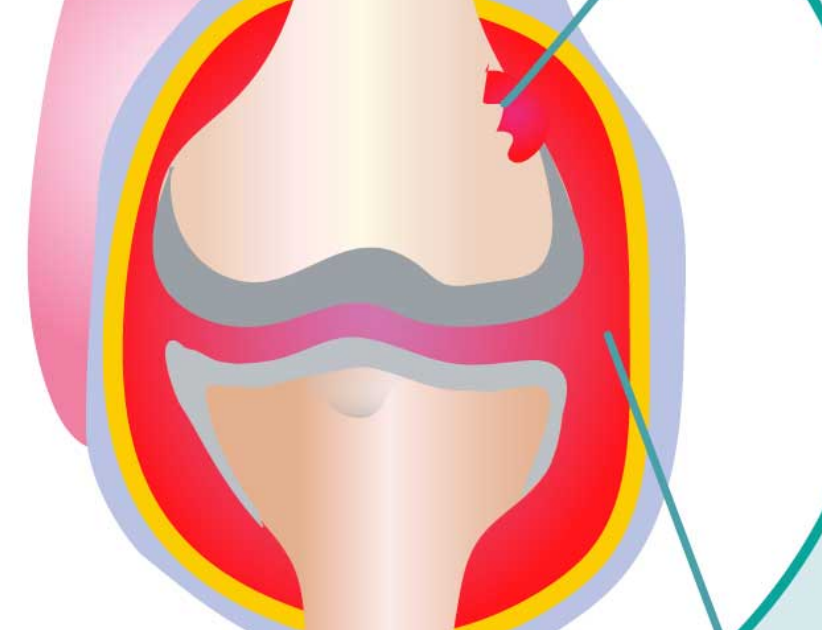
dx?
RA → MUST HAVE SWOLLEN SYNOVIAL MEMB