Health Science Final Exam
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
5 Major Functions of the Integumentary system
Protection (keeping foreign invaders out)
Removal of waste
Vitamin D synthesis
Receives sensory information
Thermal regulation
Connective Tissue
Found
Skeletal system (bones, ligaments, cartilages, tendons)
In between layers of organs and other structures
Function
Connect and attach organs and other tissues.
Epithelial Tissue
Found
Skin
Outside / inner lining of most structures and organs
Function
Protects structures
Inner and outer lining of major organs
Allows diffusion
Muscle Tissue
Found
Heart
Attached to bones
Inside most major organs
Function
Movement
Posture
Joint stability
Heat production
Nervous Tissue
Found
Central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord)
Function
Transferring of information from organ to organ through nerves and electrical signals
Respiratory System
Responsible for gas exchange. It brings in oxygen from the air and removes carbon dioxide through the lungs.
Alveoli
small air sacs at the end of the air passageways in the lungs that have very thin walls to allow gas exchange and diffusion to occur within the capillaries
Trachea
long air passageway that brings air from the upper to lower respiratory track + filters out air
Surrounded by rings of cartilage
Larynx
contains the vocal cords + vibrates air to produce sound
Epiglottis
stops solid and liquids from entering the trachea
Diaphragm
very thin muscle under the lungs that changes air pressure in the lungs to make you inhale and exhale
4 Major Functions of the Circulatory System
Kills pathogens
Removes waste products
Thermoregulation
Delivers materials throughout the body
Veins vs. Arteries vs. Capillaries
Vein | Artery | Capillary | |
Function | Brings blood to the heart | Brings blood away from heart | Diffusion of materials |
Pressure | Low | High | N/A |
Lumen | Larger than an artery | Smaller than a vein | Extremely small |
Smooth muscle | Thin layer | Thicker layer | N/A |
V - veins
E - enter
A - arteries
L - leave
There are 3 layers of tissue in arteries and veins. What are the names of these three layers AND What type of tissue is each layer made of?
Name of Layer | Type of Tissue |
Tunica intima (inner layer, closest to lumen) | Epithelial tissue |
Tunica media (middle layer) | Smooth muscle tissue |
Tunica externa (outer later) | Connective tissue |
How to differentiate between a vein vs artery [for diagram]?
veins [blue] have valves because they have low blood pressure (will have a line through it or something like that)
3 major types of structures in the heart
Valves - stops backwards blood flow
Chambers - where blood is stored and then pumped to the next place
Vessel - carries blood into and out of the heart
What is the order of blood flow in the heart?
Vena Cava
Right atrium
Tricuspid valve
Right ventricle
Pulmonary valve
Pulmonary artery
Lungs
Pulmonary vein
Left atrium
Bicuspid valve
Left ventricle
Aortic valve
Aorta
Everywhere else in the body
Platelets
or thrombocytes; clot blood + stop excessive bleeding
<1%
Red blood cells
or erythrocytes; carry oxygen using hemoglobin
~45%
White blood cells
or leukocytes; killing pathogens + fighting infections
<1%
Plasma
liquid part of blood + carries all other major materials
~55%
Systolic
top number; pressure when the heart is contracting
Diastolic
bottom number; pressure when the heart is at rest
Skeletal System
Provides structure, support, and protection for the body’s organs. It also produces blood cells and stores minerals like calcium. Includes bones, cartilage, and joints.
What is the difference between a Tendon vs. Ligament vs. Cartilage?
Tendon | Ligament | Cartilage |
Muscle to bone | Bone to bone | Acts as a cushion and lubricant between bones; providing frictionless movement + shock absorption |
*they are all made of connective tissue
What are the 2 types of Bone Marrow
Red bone marrow - creates blood cells (red, white, and platelets)
White bone marrow - stores fat and minerals
Muscular System
Works with the skeletal system to enable movement. It also helps with posture and heat production. Includes skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
Smooth Muscle Tissue
involuntary
nonstriated
moves internal bodily fluids around the body + found throughout all the body such as in organs
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
involuntary
striated
pumps blood around the body
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
voluntary
straited
attached to all the bones + allows body movement
What is the strongest muscle?
masseter/jaw
What is the longest muscle?
sartorius
What is the largest muscle?
gluteus maximus
Immune System
Defends the body against infections and diseases. It includes white blood cells, lymph nodes, the spleen, and other components that identify and destroy harmful pathogens.
Reproductive System
Enables the production of offspring. In females, it includes the ovaries, uterus, and associated structures. In males, it includes the testes and associated structures.
Excretory System
Removes waste products from the body and helps maintain water and salt balance. Major parts include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Digestive System
Breaks down food into nutrients the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas.
Endocrine System
Produces hormones that regulate body processes such as metabolism, growth, and mood. Includes glands like the thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas.
Nervous System
Controls and coordinates body activities by transmitting signals between different parts of the body. It includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Label a Neuron
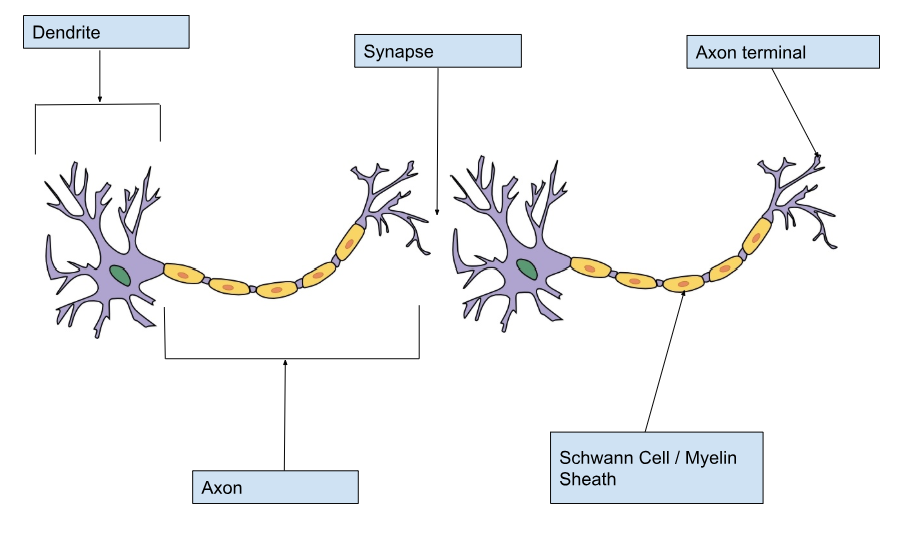
Nerve impulse direction
from the dendrite to the axon end
What is the difference nerve impulse in neurons vs in synapse?
Neuron - electrical impulse
Synapse - space in between two neurons + chemical neurotransmitter
What are the 3 major parts of brain and description?
Cerebrum - higher level thinking, emotion, logic
Cerebellum - motor skills, balance, muscle coordination
Brainstem - connects the nerve impulses from the spine to the brain + controls all involuntary actions of the body (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure)
What are the 4 lobes of cerebrum and description?
Frontal lobe - personality, critical thinking, problem solving
Parietal lobe - touch, taste, smell, spacial reasoning
Temporal lobe - auditory processing and hearing
Occipital lobe - visual processing and sight
Graphing information
X-axis (left side of table)
Y-axis (right side of table)
Malaria
a disease caused by a parasite. The parasite is spread to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes.
It effects the circulatory, immune, and respiratory systems.
Primarily affects the blood and other tissues, potentially leading to organ damage and even death.