Ch 15 - NMR Spectroscopy
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
B Spin state
opposing B0, higher energy spin state
a spin
aligned with B0, lower energy spin state
Shielded atom
feels the B0 less thus requires less energy to spin
high electron density around the nucleus =
more shielding
What does it mean for an atom to be in resonance in NMR?
the atom flipped from an a spin state → b spin state.
absorbed energy
Homotopic Protons
if the molecule has an axis of rotational symmetry that allows one proton to be rotated onto the other without changing the molecule
chemically equivalent
Enantiotopic Protons
if the molecule has a plane of reflection that makes one proton the mirror image of the other
chemically equivalent
Diastereotopic protons
do not have any kind of symmetry → not chemically equivalent
2+ chiral centers = diastereomers
Finding signals Shortcut #1
the 2 protons on a CH2 group will be equivalent if there are no chiral centers in the molecule
Finding signals Shortcut #2
The 2 protons on a CH2 group will not be equivalent if there is a chiral center in the molecule
Finding signals Shortcut #3
the 3 protons on a methyl group will always be equivalent to each other
Finding Signals Shortcut #4
multiple protons are equivalent if they can be interchanged through rotational or reflectional symmetry
NMR spectra characteristics
Number of signals
signal location (chemical shift)
signal intensity
signal shape (splitting pattern)
Downfield
left side of NMR spectra. low field strength
unshielded protons
Upfield
right side of NMR spectra. high filed strength
shielded protons
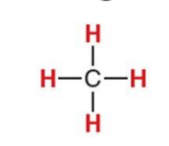
What NMR signal does this compound give?
1.0ppm
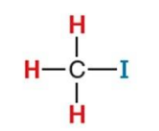
What NMR signal does this compound give?
2.2 ppm
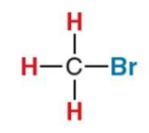
What NMR signal does this compound give?
2.7ppm
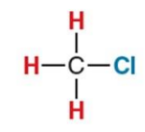
What NMR signal does this compound give?
3.1ppm
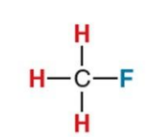
What NMR signal does this compound give?
4.3 ppm
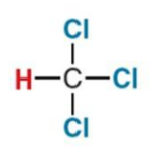
What NMR signal does this compound give?
7.3
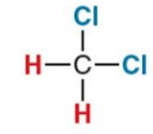
What NMR signal does this compound give?
5.3 ppm
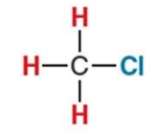
What NMR signal does this compound give?
3.1ppm
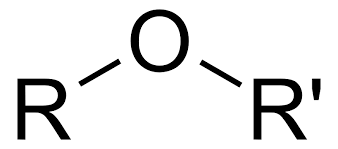
The Oxygen of an alcohol or ether has how much effect on Alpha protons?
+2.5ppm
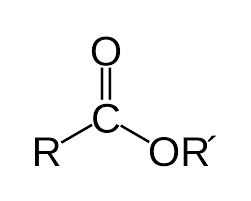
The Oxygen of an ester has how much effect on Alpha protons?
+3ppm
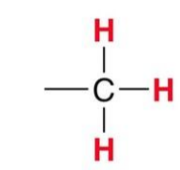
A standard Methyl group gives what signal?
~0.9ppm
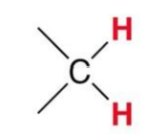
A standard Methylene group gives what signal?
~1.2ppm
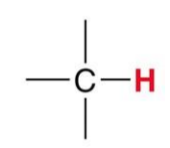
A standard Methine group gives what signal?
~1.7ppm
The effect on beta protons is _______ the effect on alpha protons.
1/5
Diamagnetic ansiotropy
different regions of localized space have different magnetic strengths
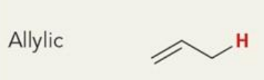
what is the chemical shift
~2ppm
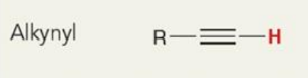
what is the chemical shift
~2.5 ppm
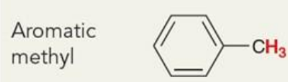
what is the chemical shift
~2.5ppm

what is the chemical shift
~2- 4ppm

what is the chemical shift
~2 - 5ppm

what is the chemical shift
~4.5-6.5ppm
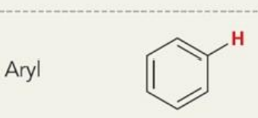
what is the chemical shift
6.5-8ppm

what is the chemical shift
~10ppm
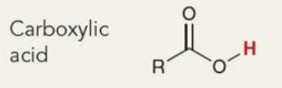
What is the chemical shift
~12ppm