digestive system
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
substances are not considered IN the body until…
they cross a cell membrane
why is the mouth to anus considered an “open tube” ?
continuous with exterior
what are the 4 main functions of the GI tract ?
motility, secretion, digestion and absorption (into blood or lymph)
what is the automatic wave-like movement of the muscles that line your gastrointestinal tract called ?
peristalsis
role of mouth
mastication
initial stages of carb digestion
role of stomach
protein digestion, churns food with acid & enzymes
role of small intestine
main site of digestion and absorption (proteins, carbs, fats, nucleic acids)
role of large intestine
final digestion and absorption
water absorption
waste concentration
what are the 4 layers of the GI wall ?
muscosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
serosa
serosa
outer-layer of GI wall
lubricates and prevents friction between organs
muscularis externa
smooth muscle for peristalsis
contains myenteric plexus - nerve network between 2 layers
mucosa
secretes digestive juices and blood-borne hormones
highly folded
submucosa
connective tissue for elasticity
submucosal plexus
muscle tone
amount of tension (or resistance to movement) in muscles
role of the myenteric plexus nerve
peristaltic movement of the bowels
in what layer of the GI tract is the myenteric plexus nerve found ?
muscularis externa
role of submucosa plexus
sensory and secretory, controls endocrine and exocrine secretion
why do different parts of the GI need to communicate ?
sufficient secretion when food present and avoid overabundance in absence
enteric nervous system
operates independently of CNS to control digestive system
swallowing and saliva production is stimulated by…
chemoreceptors and mechanoreceptors - respond to food presence
afferent impulses to salivary centre in brainstem
PNS stimulates saliva secretion
saliva contains what enzymes ? what is their role ?
salivary amylase and bicarbonate
moistens food, antibacterial effects
the stomach secretes…
intrinsic factors
mucus
pepsinogen
acid
pepsinogen is activated by
Hcl
intrinsic factor
vitamin B12 absorption in ileum
why does peristalsis start and end ?
pacemaker region
antrum and pyloric sphincter
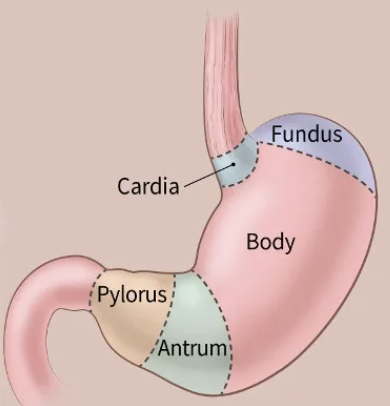
contraction of pyloric sphincter causes…
gastric mixing
gastrin
hormone secreted by stomach in 3 phases
in response to GRP (gastric-releasing-peptide)
what are the 3 phases of gastric secretion ?
cephalic, gastric, intestinal
function of intestinal phase of gastric secretion
triggers chyme release in duodenum
inhibits further gastric secretions
carb state leaving stomach
partial disaccharides (amylase)
protein state leaving stomach
small peptides (pepsin and HCl)
fat state leaving stomach
triglycerides (not digested yet)
why are bile salts and enzymes inactivated once reaching duodenum ?
acidic environment (neutralised by bicarb)
size and capacity of gall bladder
9cm long, 50ml
the gall bladder releases bile into the
duodenum
the liver produces approx. how much bile per day ?
1000ml
bile contains
water, bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, phospholipids
role of secretin
stimulates bile generation
gall bladder contraction
bile secretion into duodenum
CCK release is stimulated by
fats and proteins in duodenum
role of CKK (cholecystokinin)
stimulates bile & pancreatic enzyme release
regulates gastric emptying
role of hydrochloric acid (HCl)
does not digest any nutrients
antimicrobial activity - kills microorganisms ingested with food
aids breakdown of connective tissue and muscle fibres
denatures proteins
activates pepsinogen - forms pepsin
pepsin functions optimally in what pH
acidic
where is intrinsic factor synthesised ?
stomach
intrinsic factor is required for
absorption of VitB12 at terminal ileum - required for RBC synthesis
a deficiency in intrinsic factor can lead to
pernicious anaemia - not enough RBCs due to deficiency in vitamin B12
weakness and fatigue
pernicious anaemia is treated with
intramuscular injections
why does the stomach absorb alcohol and drugs but not nutrients ?
alcohol and aspirin - lipid soluble, diffuses across plasma mem and enters blood
the stomach produces…
HCl, peptidase and mucosa
what is meant by the pancreas has a “dual function”
endo and exocrine
the release of pancreatic juice is stimulated by
secretin and CCK
2 components of pancreatic juice
bicarbonate - neutralises stomach acid (allows pancreatic enzymes to work)
pancreatic enzymes - amylase, lipase, proteolytic
why are proteolytic enzymes secreted as inactive precursors ?
prevent digestion of cells and tissues that produce them
where does protein digestion begin ?
stomach
amino acids in the small intestine are broken down by
peptidases on microvilli
carbohydrates are digested by what enzyme ?
amylase
lactose is composed of what monosaccharides ?
Glucose + Galactose
sucrose is composed of what monosaccharides ?
Glucose + Fructose
maltose is composed of what monosaccharides ?
Glucose + Glucose
role of bile salts
breakdown fat droplets into lipid emulsions so lipase can access triglycerides beneath surface
prevent re-aggregation of fat droplets that have been broken down by mechanical digestion
pancreatic lipase
breaks down TGs into FFAs and monoglycerides