Lecture 17: Synaptic Transmission, Nueral Intergration and CNS
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
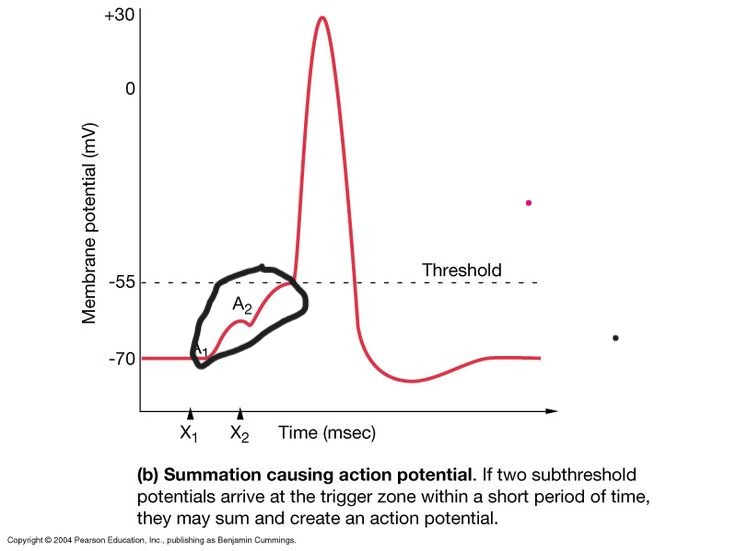
What is temporal Summation?
Same stimulus coming from the presynaptic neuron
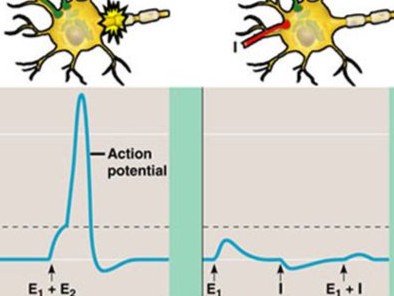
What is Spatial Summation?
Different stimuli with multiple presynaptic neuron
What is a neuromuscular junction?
between neuron & muscle
What is a neuroglandular junction?
between neuron & gland
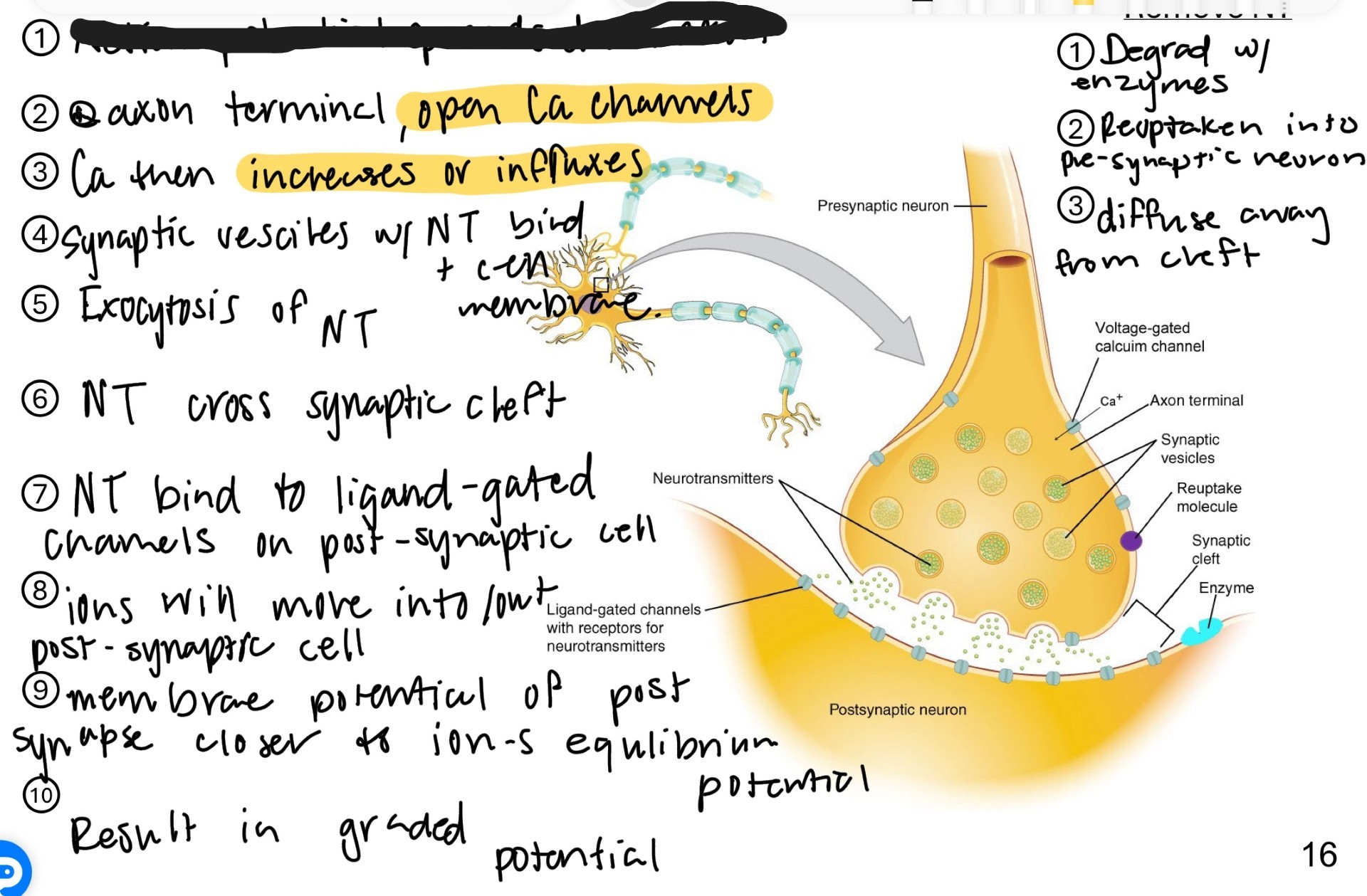
What is the first step of Chemical Synapse and NT release?
Action potential spreads down the axon
Second step of chemical synapse & NT release
@ axon terminal, open Ca Channels
third step of chemical synapse & NT release
Ca then influxes
fourth step of chemical synapse & NT release
Synaptic vesicles w/ NT bind + cell membrane
fifth step of chemical synapse & NT release
Exocytosis of NT
sixth step of chemical synapse & NT release
NT cross the synaptic cleft
seventh step of chemical synapse & NT release
NT bind to ligand-gated channels on post-synaptic cleft
eighth step of chemical synapse & NT release
ions move into/out post-synaptic cell
nineth step of chemical synapse & NT release
membrane potential of post synapse closer to ions equilibrium potential
tenth step of chemical synapse & NT release
Result in graded potential
How many steps are there to remove a NT?
three
First step to remove NT
Degrade with enzymes
second step to remove NT
Reuptake into pre-synaptic neuron
third step to remove NT
diffuse away from cleft
How many steps are in the mechanism of fast response to a NT?
4
first step in the mechanism of fast response to a NT
NT binds to receptor
second step in the mechanism of fast response to a NT
channel opens
third step in the mechanism of fast response to a NT
ions move
fourth step in the mechanism of fast response to a NT
membrane potential of the cell moves closer to the equilibrium
How many steps are there in a slow response: direct coupling to a NT
7
first step of slow response: direct coupling to a NT
NT binds to receptor
second step of slow response: direct coupling to a NT
Activate G-protein
third step of slow response: direct coupling to a NT
GDP falls off Alpha subunit
fourth step of slow response: direct coupling to a NT
GTP attaches to subunit
fifth step of slow response: direct coupling to a NT
Alpha GTP slides over
sixth step of slow response: direct coupling to a NT
Open/ close channel
seventh step of slow response: direct coupling to a NT
membrane potential of post-synaptic change
What are the names of the two slow responses to a NT?
Secondary messenger and Direct coupling
How many steps are in the slow response: Secondary messenger to a NT
4
First step of Slow response: Secondary messenger in response to a NT
NT binds to a receptor
second step of Slow response: Secondary messenger in response to a NT
Activate G-Protein mechanism
third step of Slow response: Secondary messenger in response to a NT
Activate amplifier enzyme
fourth step of Slow response: Secondary messenger in response to a NT
open/ close channel then changes membrane potential of cell
How many types of graded potentials are there?
4
Where are postsynaptic potentials located?
neurons
where are End-plate potentials locate ?
Skeletal muscle
where are slow-wave potentials located?
smooth muscle
Where are pacemaker’s potentials located?
Cardiac Muscles
In fast EPSP’s what does it open?
Na/K channels
In slow EPSP’s what does it close?
K channels
In EPSP’s are the Na/ K depolarizing or hyperpolarizing?
depolarizing
In IPSP’s what are the two things the fast channel open?
K & Cl- channels
Is the IPSP fast open channels hyperpolarizing or depolarizing?
Hyperpolarizing
What exception do the open Cl- channels do in IPSPs? Depol or stable at rest
stable at rest
How many steps are in fast response EPSP
5
first step of fast response EPSP mechanism
NT binds to receptor
second step of fast response EPSP mechanism
channel
third step of fast response EPSP mechanism
Na influx & K efflux through same channel
fourth step of fast response EPSP mechanism
Na ions will bring their positive into cell
fifth step of fast response EPSP mechanism
depolarization of post-synaptic cell
first step of slow response EPSP mechanism
NT binds to a receptor
second step of slow response EPSP mechanism
activate 2nd messenger
third step of slow response EPSP mechanism
cell response closes K channels
fourth step of slow response EPSP mechanism
Allows more K to stay inside cell, having outside membrane a more positive
fifth step of slow response EPSP mechanism
Cell depolarization
First step of Fast IPSP: K channels mechanism
NT binds to receptor
second step of Fast IPSP: K channels mechanism
open K channels
third step of Fast IPSP: K channels mechanism
Increases K efflux
fourth step of Fast IPSP: K channels mechanism
Membrane potential hyperpolarizes
What are the 2 initial conditions of the Fast IPSP: Cl- channels
Cl- pumps with primary active transport create Cl- gradient
Acetyl Coa + Choline =
Acetylcholine
first step of acetylcholine synapse
make acetylcholine
second step of acetylcholine synapse
Ca influx of voltage gated Ca+ channels
third step of acetylcholine synapse
exocytosis of Ach
fourth step of acetylcholine synapse
Ach in cleft will bind to cholinergic receptor on post-synaptic cell
Nictinic slow or fast?
fast
Muscarinic slow or fast?
slow
How do you degrade away Ach?
turn Ach → acetate & choline
Does acetate once broken down diffuse away or reuptaken by presynaptic neuron?
diffuse away
Does choline once broken down diffuse away or reuptaken by presynaptic neuron?
reuptaken by presynaptic neuron
Where is Monoamine oxidase found?
synaptic cleft
What is the function of Monoamine oxidase?
Breaksdown biogenic amines