Enzymes: Kinetics, Specificity, and Applications in Biochemistry
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate the rate of biochemical reactions by factors of a million or more.
What is the role of enzymes in living systems?
Enzymes accelerate and control the rates of important biochemical reactions.
How is rate defined in the context of chemical reactions?
Rate is how much a quantity changes in a given period of time, similar to speed in driving.
What is the Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions?
It states that effective collisions between molecules form an activated complex or transition state.
What is the average rate of a reaction?
The average rate is the change in concentration of a reactant or product over time.
What are substrates in enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
Reactants in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are referred to as substrates.
What is catalytic power?
Catalytic power is the ratio of the enzyme-catalyzed rate of a reaction to the uncatalyzed rate.
What is enzyme specificity?
Specificity refers to the selectivity of enzymes for their substrates.
What are coenzymes and cofactors?
Helpers that are nonprotein components essential to enzyme activity.
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
Enzymes lower the activation energy (Ea) by adsorbing substrates onto an active site.
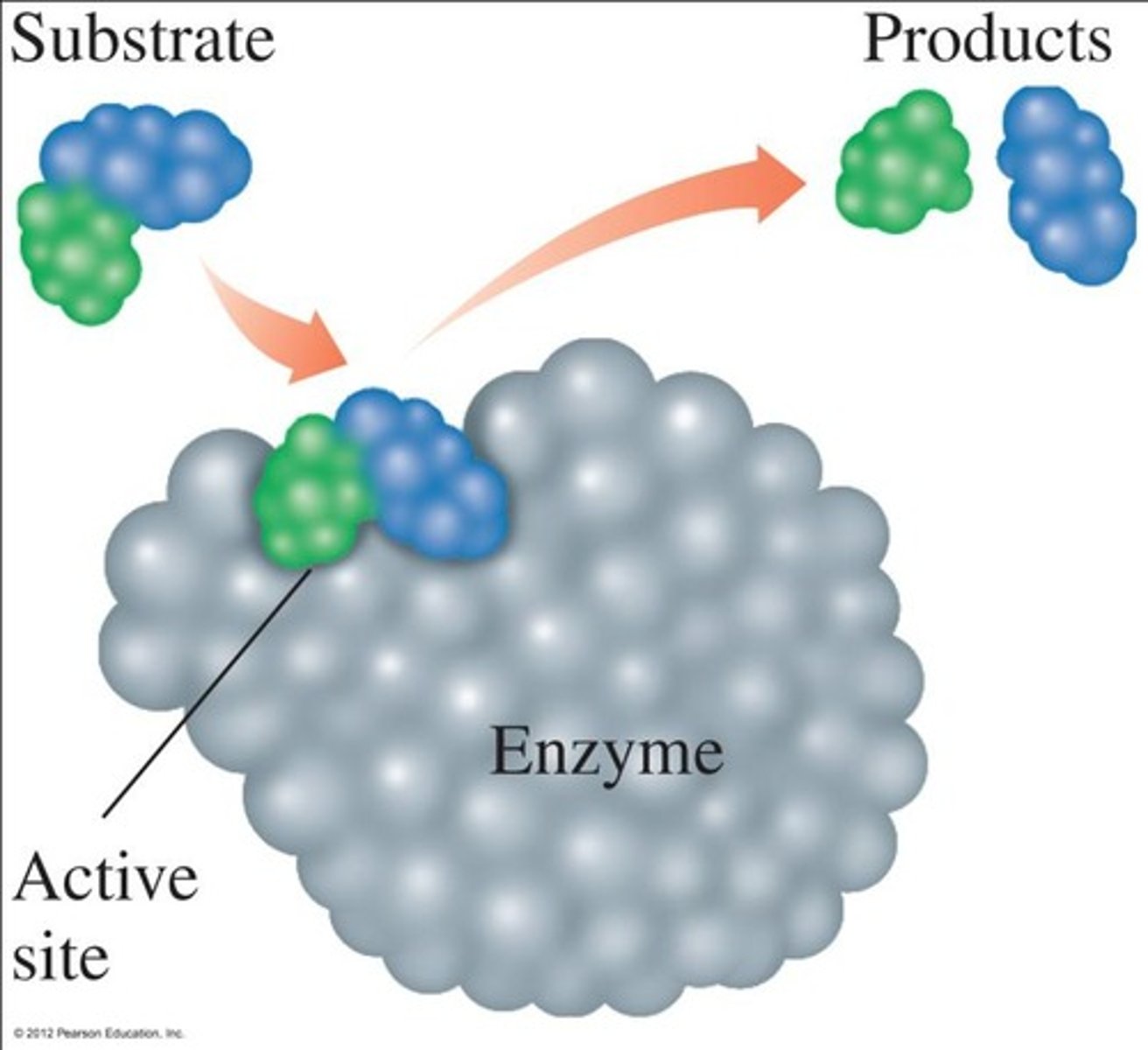
What occurs at the active site of an enzyme?
The substrate binds to the active site, forming an enzyme-substrate complex, leading to product release.
What is enzyme kinetics?
The study of the factors that affect the rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
What does the rate law express?
The relationship of the rate of reaction to the rate constant and the concentrations of reactants.
What is the difference between first-order and second-order reactions?
First-order reactions depend on one reactant's concentration, while second-order reactions depend on either one reactant squared or two reactants.
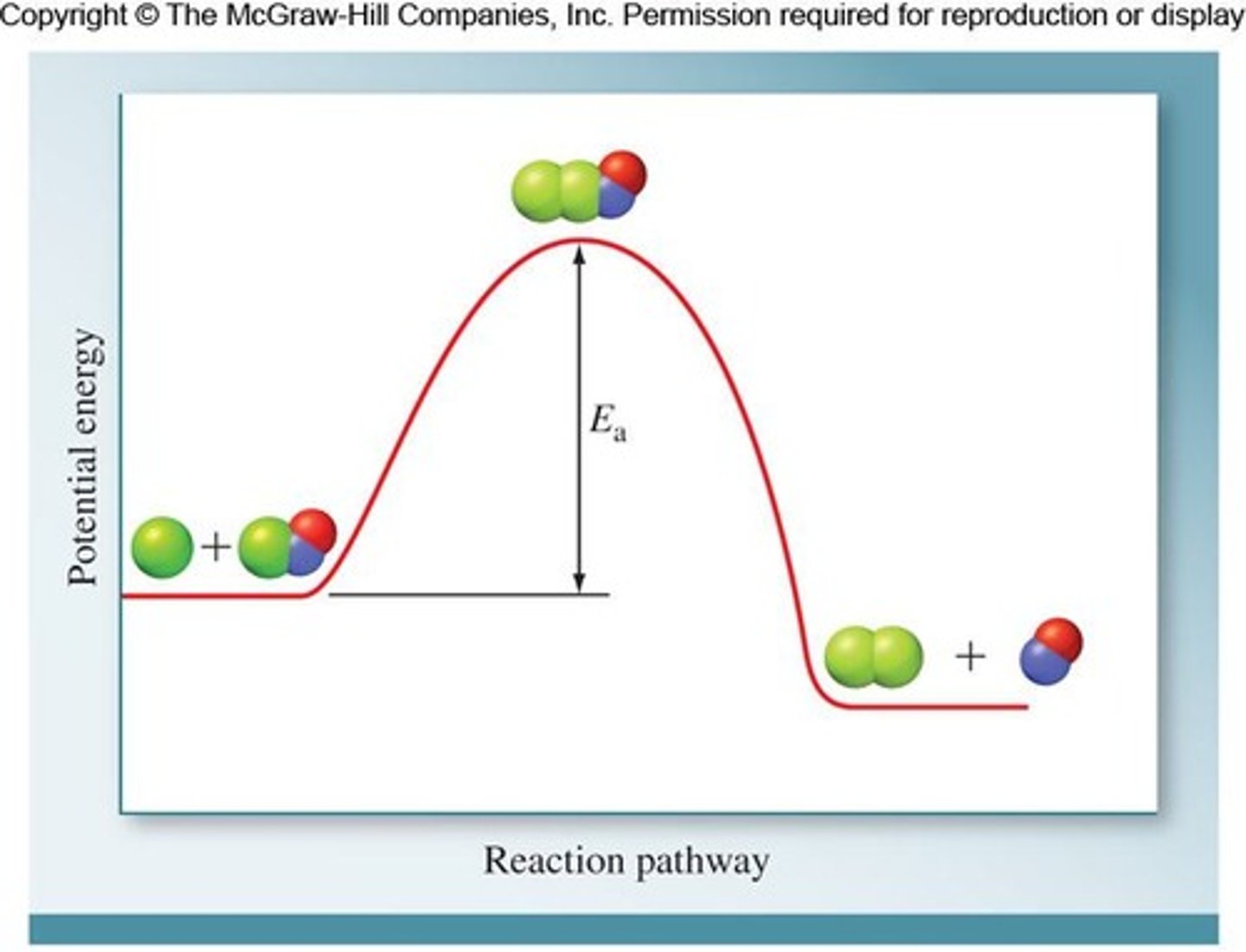
What is the transition state in a chemical reaction?
A molecular form that is neither substrate nor product, requiring activation energy to form.
What is the Michaelis-Menten Equation?
It describes the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions under saturation conditions.
What happens to reaction rate at low substrate concentrations?
The rate is proportional to substrate concentration and follows first-order kinetics.
What happens to reaction rate at high substrate concentrations?
The reaction approaches zero-order kinetics due to saturation of the enzyme.
What is the significance of the activation energy (Ea)?
Lowering Ea increases the reaction rate, facilitating the formation of the transition state.
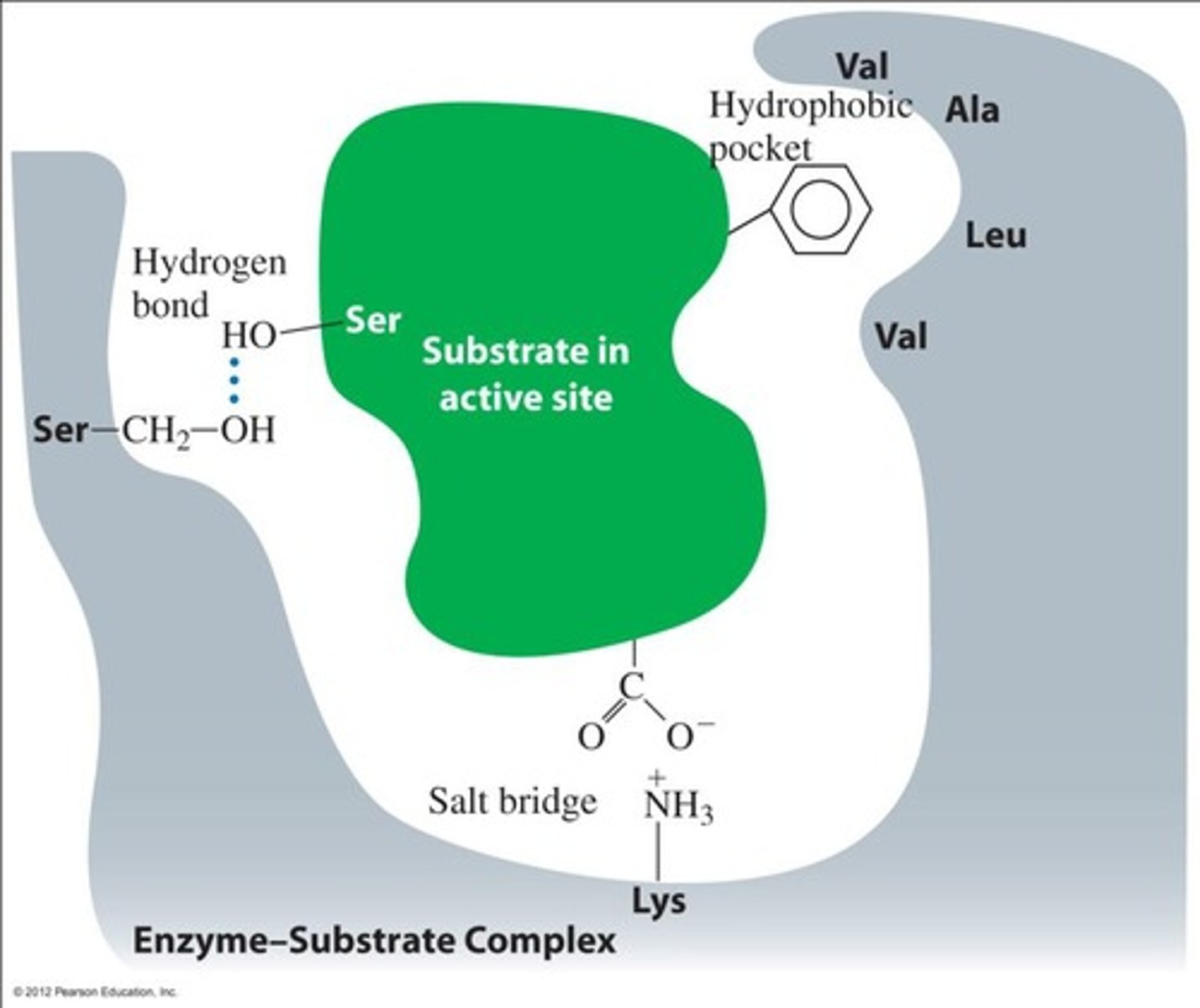
What is the role of amino acids in the active site of enzymes?
They bind the substrate and facilitate the reaction by forming the enzyme-substrate complex.
What is the purpose of studying enzyme kinetics?
To gain insights into enzyme mechanisms and metabolic pathways, allowing manipulation of metabolic events.
What is the saturation effect in enzyme kinetics?
At high substrate concentrations, the enzyme's reaction rate no longer increases with substrate concentration.
What is the relationship between reaction order and rate?
The reaction order is the exponent of the concentration of a reactant in the rate law equation.
What is the difference between zero-order and first-order reactions?
Zero-order reactions have a rate independent of reactant concentration, while first-order reactions depend on one reactant's concentration.
What does the term 'molecularity' refer to in a reaction?
The number of reactant particles involved in a reaction.
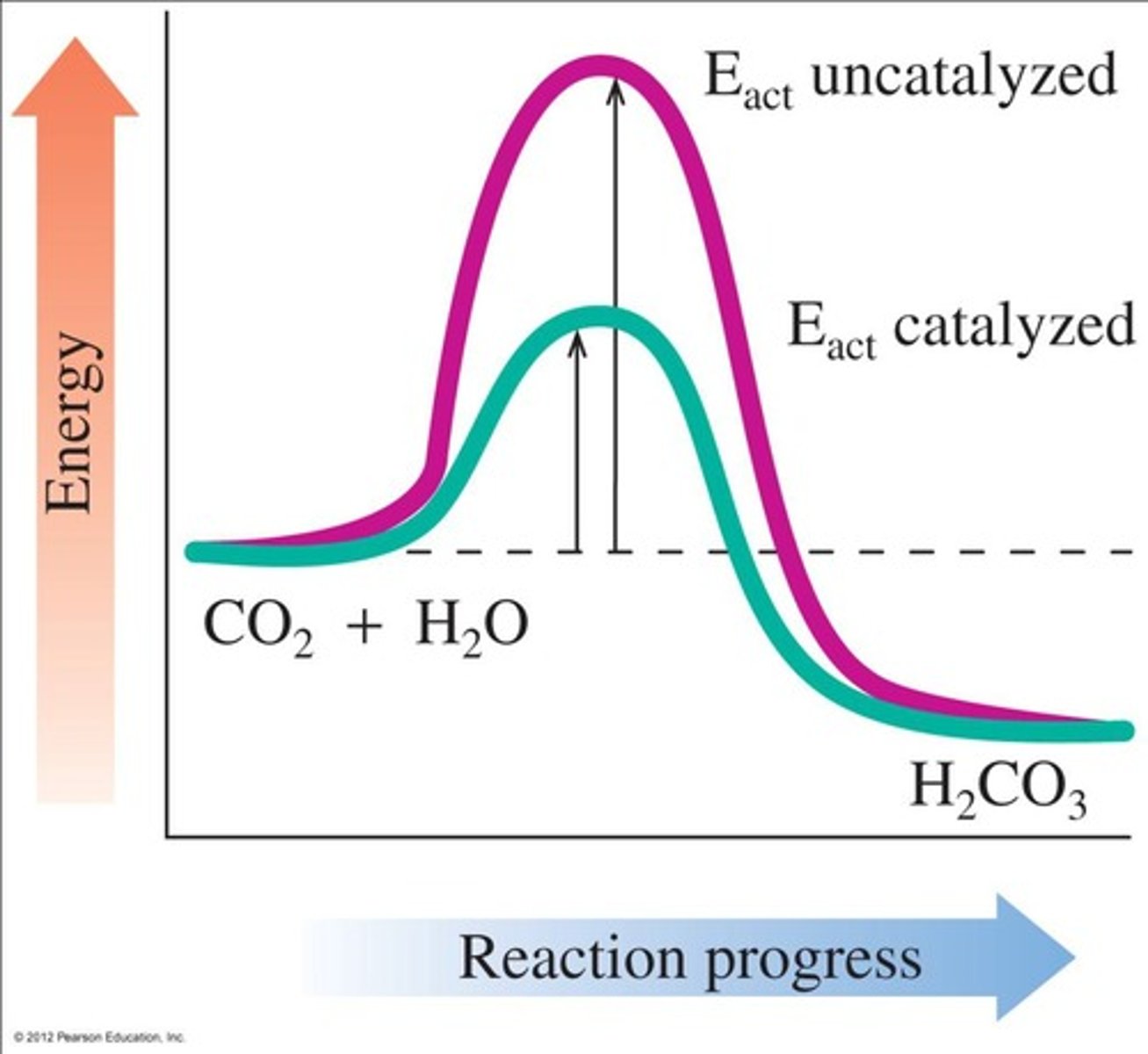
What is the significance of the energy diagram in enzyme kinetics?
It illustrates the difference in activation energy between uncatalyzed and catalyzed reactions.
What is the Michaelis-Menten model used for?
It describes enzyme kinetics, measuring velocity as a function of substrate concentration with a fixed amount of enzyme.
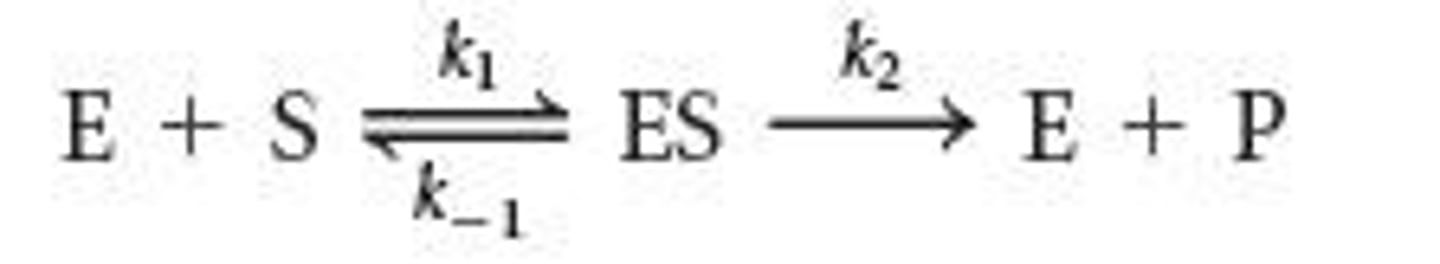
What does the Michaelis-Menten equation describe?
It describes the initial reaction velocity (V0) as a function of substrate concentration [S].
![<p>It describes the initial reaction velocity (V0) as a function of substrate concentration [S].</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e8329f20-2009-4d67-971f-455a9c6570e4.jpg)
What is the significance of Km in enzyme kinetics?
Km is the substrate concentration that yields ½ Vmax and indicates the enzyme's substrate binding affinity.
What is Vmax in the context of enzyme kinetics?
Vmax is the maximum velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
How is the initial velocity (V0) determined experimentally?
By measuring product formation as a function of time at different substrate concentrations.
What is the Lineweaver-Burk equation?
It is a double-reciprocal equation that yields a straight-line plot for analyzing enzyme kinetics.
What does a lower Km value indicate about an enzyme?
It indicates a higher binding affinity and higher enzyme efficiency.
What is the turnover number (kcat)?
It is the number of substrate molecules converted into product per second by an enzyme.
What is catalytic efficiency?
It is the ratio of kcat to Km, indicating how efficiently an enzyme converts a specific substrate into a product.
What are the main types of enzyme classes?
Oxidoreductases, Transferases, Hydrolases, Lyases, Isomerases, and Ligases.
What is the Lock and Key model of enzyme action?
It suggests that the enzyme's active site is complementary to the substrate's shape, allowing for a perfect fit.
What is the Induced Fit model?
It proposes that the active site of the enzyme changes shape to better fit the substrate upon binding.
What factors affect enzyme activity?
Temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors.
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity generally increases with temperature up to an optimum point, after which activity declines due to denaturation.
What happens to enzymes at low temperatures?
Enzymes show little activity at low temperatures, such as 4°C.
What is the role of the active site in an enzyme?
It is the region where substrate binding occurs and catalysis takes place, often involving weak interactions.
What is the significance of enzyme specificity?
It depends on the molecular architecture at the active site, determining which substrates can be processed.
What is the effect of inhibitors on enzyme activity?
Inhibitors decrease enzyme activity by interfering with substrate binding or catalysis.
How does the enzyme-substrate complex form?
The enzyme binds to the substrate, forming an enzyme-substrate (ES) complex before converting it to product.
What is the transition state in enzyme kinetics?
It is the state where the substrate is transformed into product, often involving tighter binding at the active site.
How does pH influence enzymatic activity?
Enzymes have ionizable side chains that affect their structure and active site, making them active only over a limited range of pH known as optimum pH.
What happens to the rate of reaction as substrate concentration increases?
The rate of reaction increases until the enzyme becomes saturated, reaching maximum activity.
What are inhibitors in the context of enzymes?
Inhibitors are molecules that cause a loss of catalytic activity in enzymes, which can be reversible or irreversible.
What are the four main types of enzyme inhibition?
1. Competitive Inhibition 2. Noncompetitive Inhibition 3. Uncompetitive Inhibition 4. Irreversible Inhibition.
What characterizes competitive inhibition?
compete with the substrate for the same active site on the enzyme, altering Km but not Vmax.
Provide an example of competitive inhibition.
Succinate dehydrogenase is inhibited by malonate, which competes with succinate.
What is noncompetitive inhibition?
In noncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to a different site than the substrate, decreasing Vmax without altering Km.
What is uncompetitive inhibition?
Uncompetitive inhibitors bind only to the enzyme-substrate complex, changing both intercepts in a Lineweaver-Burk plot while keeping the slope constant.
What is irreversible inhibition?
Irreversible inhibitors form covalent bonds with enzymes, permanently disabling their catalytic activity, such as penicillin with glycoprotein peptidase.
How are enzymes used in medical diagnostics?
Diagnostic enzymes indicate tissue damage; elevated levels of enzymes like CK, AST, and LDH can signal myocardial infarction.
What is the role of tPA in medical applications?
tPA is a therapeutic enzyme used as a blood clot buster in conditions like heart attacks.
What is the mechanism of Viagra as an enzyme inhibitor?
Sildenafil (Viagra) is a competitive inhibitor of phosphodiesterase, increasing cGMP levels and improving blood flow.
What is Methotrexate and its role as an enzyme inhibitor?
Methotrexate is a competitive inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase, blocking cell division in cancer treatment.
What is enzyme engineering?
Enzyme engineering involves modifying enzymes through techniques like in vitro mutagenesis to enhance their catalytic properties.
What is enzyme immobilization?
Enzyme immobilization is a technique used to improve enzyme stability and allow for enzyme recycling in industrial applications.
How do specific enzymes function in the detergent industry?
Enzymes like protease, amylase, lipase, cellulase, and mannanase target specific stains to enhance cleaning efficiency.
What is the role of anti-cholinesterase insecticides?
Anti-cholinesterase insecticides disable the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, causing insect incapacitation by preventing neurotransmitter regulation.
How is lactose-free milk produced using enzymes?
Lactose-free milk is produced by passing milk through a column with immobilized lactase, breaking down lactose into simpler sugars.
What is the significance of enzyme activity in myocardial infarction diagnosis?
Elevated enzyme levels like CK, AST, and LDH in the blood can indicate myocardial infarction severity.
What is the effect of competitive inhibitors on enzyme kinetics?
Competitive inhibitors increase Km while Vmax remains unchanged, as shown in Lineweaver-Burk plots.
What distinguishes noncompetitive inhibition from competitive inhibition?
Noncompetitive inhibition does not affect Km but decreases Vmax, unlike competitive inhibition which affects Km.
What is the impact of uncompetitive inhibitors on enzyme kinetics?
change both the Km and Vmax intercepts in a Lineweaver-Burk plot while maintaining the slope.
What is the role of enzymes in industrial applications?
Enzymes are engineered for various industrial processes, enhancing efficiency and specificity in applications like detergents and pharmaceuticals.