chesmisty
5.0(2)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:34 AM on 6/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
solid particles
* incompressible
* Fixed in position
* Vibrate in their places
* Strong attraction between particles
* Fixed volume
* Fixed shape
* Fixed in position
* Vibrate in their places
* Strong attraction between particles
* Fixed volume
* Fixed shape
2
New cards
liquid particles
* incompressible
* Vibrate
* move freely throughout the liquid but stay close together
* particles cane flow and take shape of container
* Strong attraction between particles (but not as strong as solid)
* Fixed volume
* Vibrate
* move freely throughout the liquid but stay close together
* particles cane flow and take shape of container
* Strong attraction between particles (but not as strong as solid)
* Fixed volume
3
New cards
gas particles
* Compressible
* **large spaces** between gas particles and they are not stuck together
* free to move in **straight lines** until they collide with another gas particle or the side of the container
* Weak attraction between particles
* Take volume of container
* Take shape of container
* **large spaces** between gas particles and they are not stuck together
* free to move in **straight lines** until they collide with another gas particle or the side of the container
* Weak attraction between particles
* Take volume of container
* Take shape of container
4
New cards
particle model- change of state
When a substance is heated
* Particles have more energy and move faster
* Solid particles can vibrate out of position ie melt
* Liquid particles move faster and separate ie evaporate
When a substance is cooled
* Particles have less energy and move slower
* Gas particles slow down and get closer together ie condense.
* Liquid particles slow down and form an ordered structure ie freeze/solidify
* Particles have more energy and move faster
* Solid particles can vibrate out of position ie melt
* Liquid particles move faster and separate ie evaporate
When a substance is cooled
* Particles have less energy and move slower
* Gas particles slow down and get closer together ie condense.
* Liquid particles slow down and form an ordered structure ie freeze/solidify
5
New cards
particle model- Expansion
* Substance is heated, makes particles move faster and take more space but not enough energy for change of state
* When the temperature increases, the particles vibrate faster, pushing each other apart.
* When the temperature increases, the particles vibrate faster, pushing each other apart.
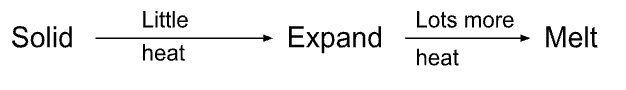
6
New cards
particle model- contraction
* Substance is cooled, makes particles slow down and takes less space but not enough for a change of state
* When the temperature decreases, particles vibrate more slowly, allowing them to be packed close together.
* When the temperature decreases, particles vibrate more slowly, allowing them to be packed close together.
7
New cards
particle model- dissolving
* When a substance dissolves, the solute particles are distributed evenly throughout the solvent particles
8
New cards
Solution
mixture of solute dissolved in solvent. Solutions may be transparent or coloured.
Solution = solute + solvent
Solution = solute + solvent
9
New cards
Solute
substance that is dissolved in the solvent to form a solution.
10
New cards
Solvent
substance in which the solute dissolves in to form a solution.
11
New cards
particle model- diffusion
* The movement of gases or liquids spreading out in another gas or liquid
* Given time, if two liquids are mixed together, their particles will **diffuse** and mix evenly without stirring. The same occurs when two gases are mixed.
* Increasing temperature speeds up diffusion
* Given time, if two liquids are mixed together, their particles will **diffuse** and mix evenly without stirring. The same occurs when two gases are mixed.
* Increasing temperature speeds up diffusion
12
New cards
atom
* smallest indivisible particle of matter
* Made up of protons, neutrons and electrons
* Made up of protons, neutrons and electrons
13
New cards
element
* pure substance made up of only one type of atom
14
New cards
molecule
* two or more atoms bonded together.
* These can be the same type of atom or different types
* These can be the same type of atom or different types
15
New cards
compound
* pure substance made up of two or more different elements (types of atoms)
* The elements in a compound are chemically bonded together.
\
* The elements in a compound are chemically bonded together.
\
16
New cards
Mixture
* combination of two or more pure substances
* can be separated
* can be separated
17
New cards
periodic table- periods
* rows across the periodic table
* there are 7 periods
* there are 7 periods
18
New cards
periodic table- groups
* columns down the periodic table
* There are 18 groups
* There are 18 groups
19
New cards
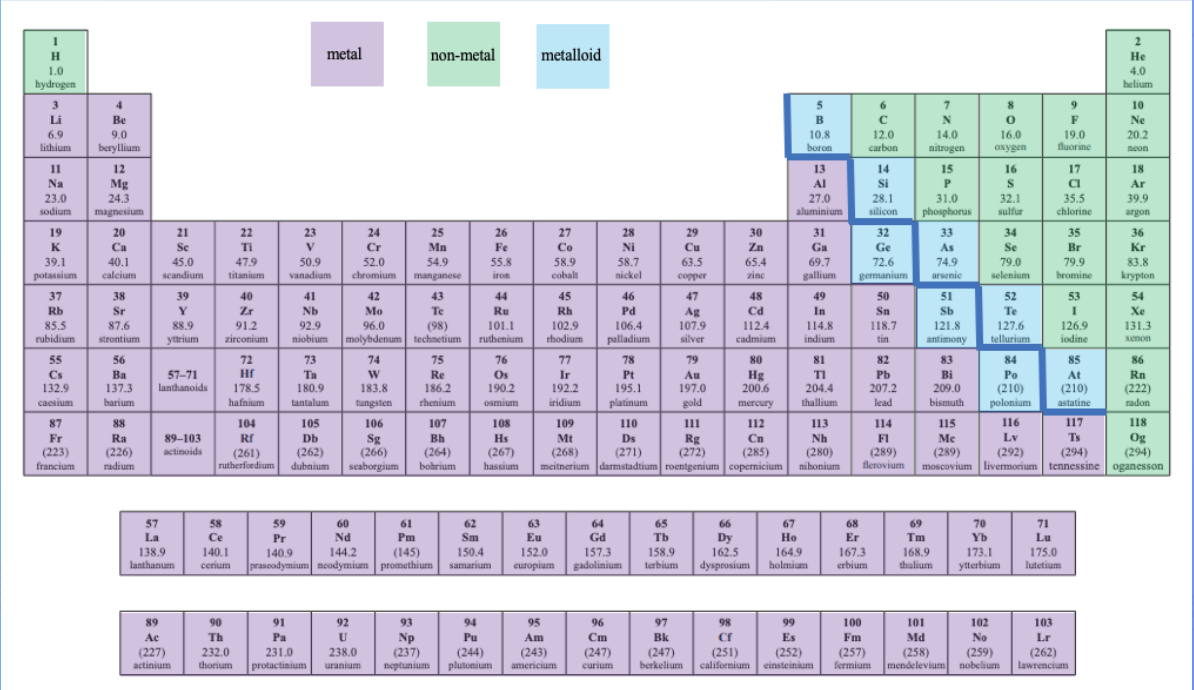
periodic table-metals, non-metals and metalloids
* **Metals- left side of the table**
* **Non-metals on the right side of the table**
* **Metalloids- in between them**
* **Non-metals on the right side of the table**
* **Metalloids- in between them**
20
New cards
Metals
* Shiny (lustrous)
* Hard
* High melting and boiling points
* Good conductors of heat and electricity
* Mainly solid at room temperature
* Malleable - shape them
* Ductile -make wires
* Hard
* High melting and boiling points
* Good conductors of heat and electricity
* Mainly solid at room temperature
* Malleable - shape them
* Ductile -make wires
21
New cards
Non-metals
* Dull
* Soft
* Brittle
* Low melting and boiling points
* Poor conductors of heat and electricity
* Solids, liquid and gases at room temperature
* Soft
* Brittle
* Low melting and boiling points
* Poor conductors of heat and electricity
* Solids, liquid and gases at room temperature
22
New cards
metalloids
Have properties of both metals and nonmetals
23
New cards
Monatomic elements
* elements containing only one type of single atom
* only six, which are all noble gases (helium, neon, krypton, xenon, argon, radon – oganesson ??)
* only six, which are all noble gases (helium, neon, krypton, xenon, argon, radon – oganesson ??)
24
New cards
Molecular elements
* clusters of two or more of the same atom bonded (joined) together
* examples- oxygen O2, Nitrogen N2, bromine Br2
* examples- oxygen O2, Nitrogen N2, bromine Br2
25
New cards
Crystal lattices
* grid-like structures that repeat the same arrangement of atoms
* There are two main types: metallic ( lead, copper) and non-metallic ( graphite, diamond)
* There are two main types: metallic ( lead, copper) and non-metallic ( graphite, diamond)
26
New cards
Physical changes
* does not produce new substances
* Identifying a physical change
* Changes in shape or form
* Expands (gets bigger)
* Contracts (gets smaller)
* Change in state (solid, liquid or gas)
* Mixing with another substance
* Identifying a physical change
* Changes in shape or form
* Expands (gets bigger)
* Contracts (gets smaller)
* Change in state (solid, liquid or gas)
* Mixing with another substance
27
New cards
**Chemical change**
* produce new substances
* Identifying a chemical change
* A ***colour*** change
* A ***gas*** is produced- smell, bubbles, smoke
* A ***precipitate*** (solid) forming
* ***Energy being released or absorbed. released -in the form of heat, light or both- exothermic. Absorbed- cause surroundings to cool- endothermic.***
* Identifying a chemical change
* A ***colour*** change
* A ***gas*** is produced- smell, bubbles, smoke
* A ***precipitate*** (solid) forming
* ***Energy being released or absorbed. released -in the form of heat, light or both- exothermic. Absorbed- cause surroundings to cool- endothermic.***
28
New cards
chemical reaction
* Show the “before” and “after” of a chemical change
* Start with reactants - reactants react to produce products
* **Reactants → products**
*Example:*
\
hydrogen gas + oxygen gas → water
Reactants: hydrogen gas + oxygen gas
Products: water
* Start with reactants - reactants react to produce products
* **Reactants → products**
*Example:*
\
hydrogen gas + oxygen gas → water
Reactants: hydrogen gas + oxygen gas
Products: water