Heredity, Reproduction and Growth
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

23 Terms
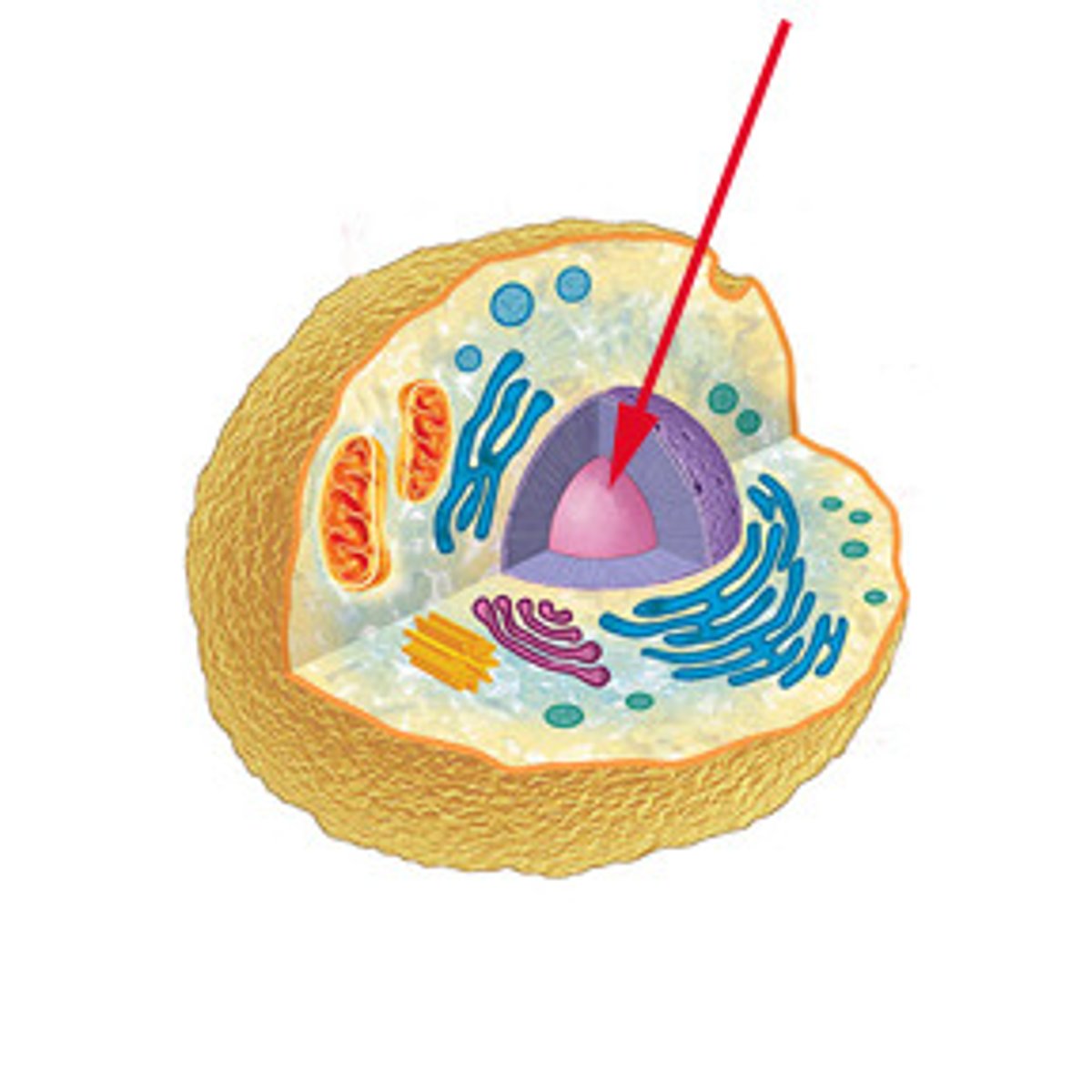
Nucleus
The control center of the cell that contains DNA and RNA and uses this genetic code to regulate all cell activities and functions an is essential for cell growth and reproduction.
Allele
Different forms of a gene

gene variation
Differences among individuals in the design of their gene or other DNA segments.
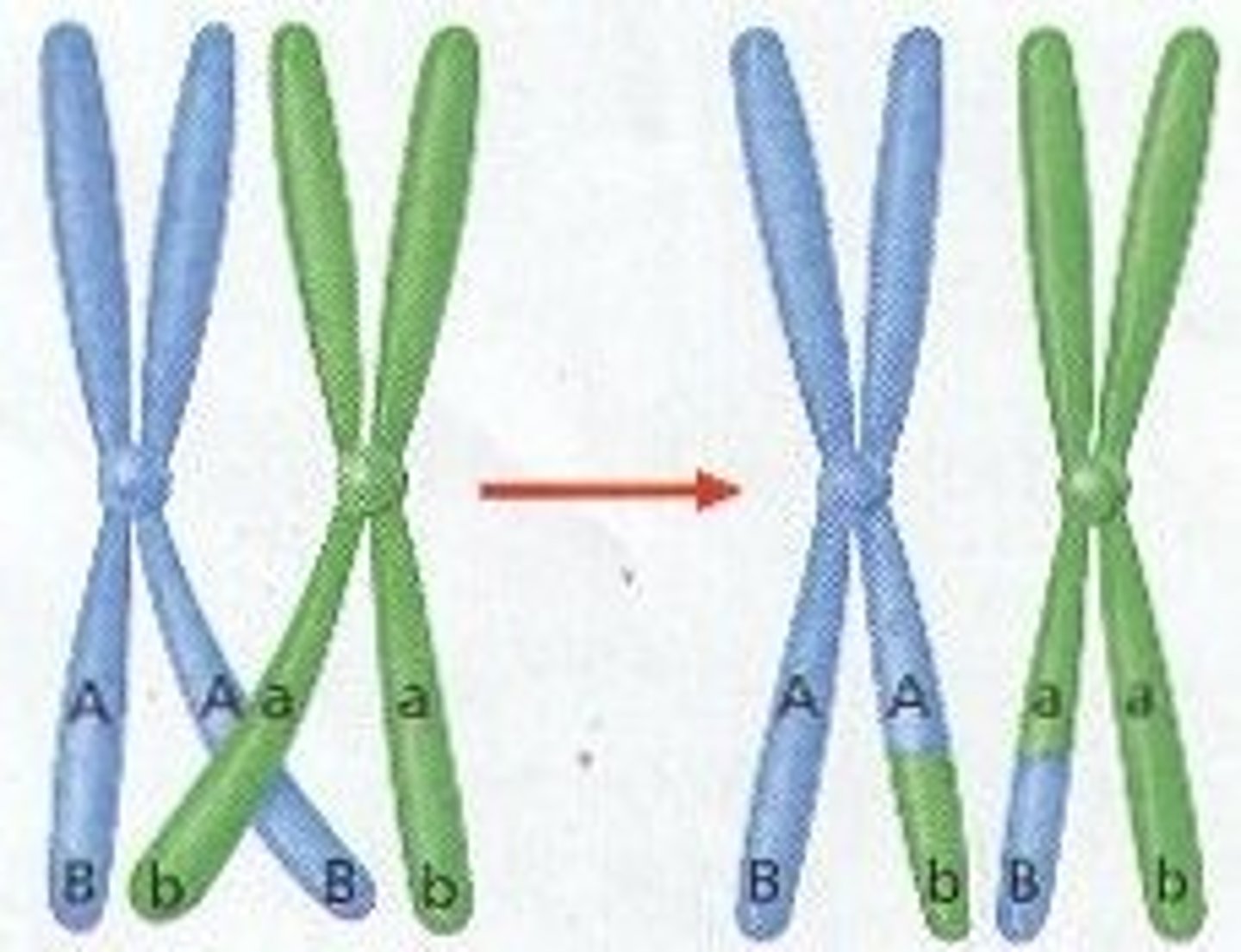
Mutation
a random error or change in DNA that leads to a change, that can be positive or negative

offspring
Product of reproduction, a new organism produced by one or more individuals

Genotype
Alleles/Genes of an organism that determine specific traits.
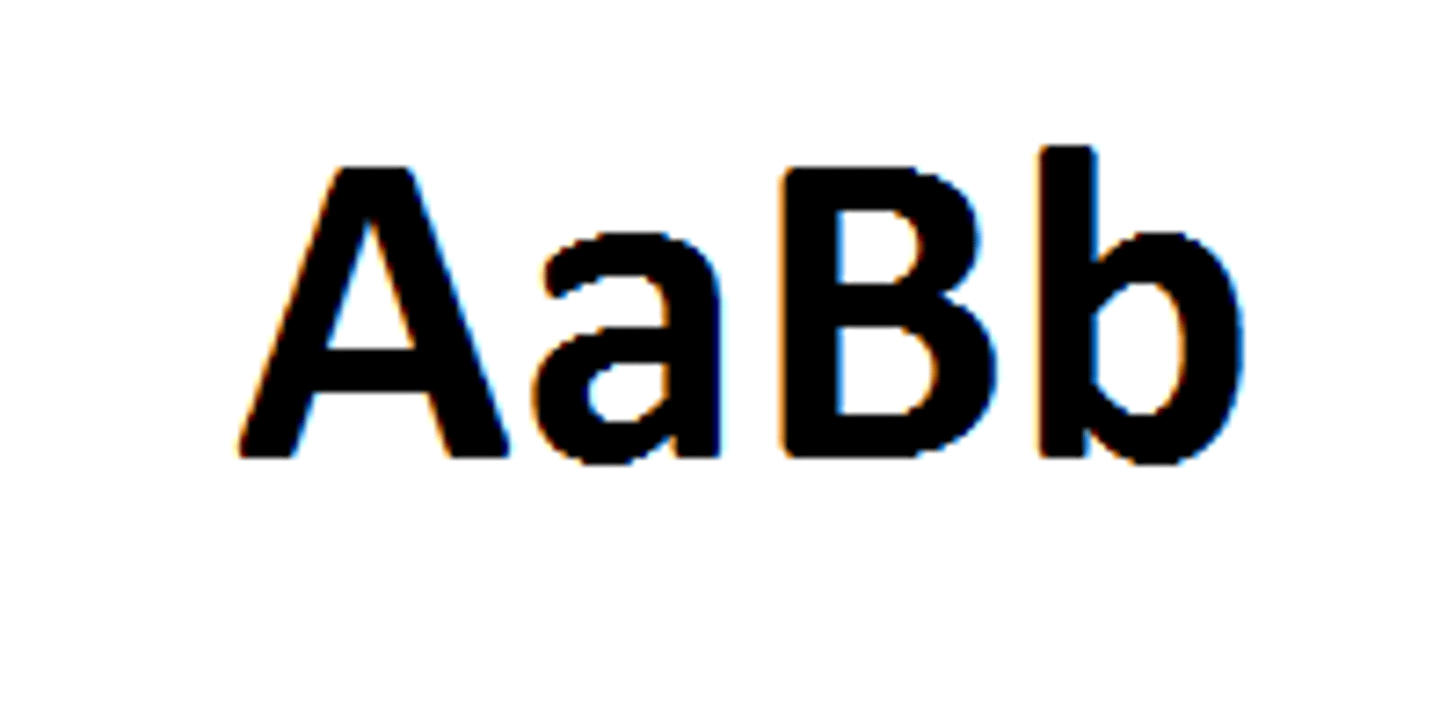
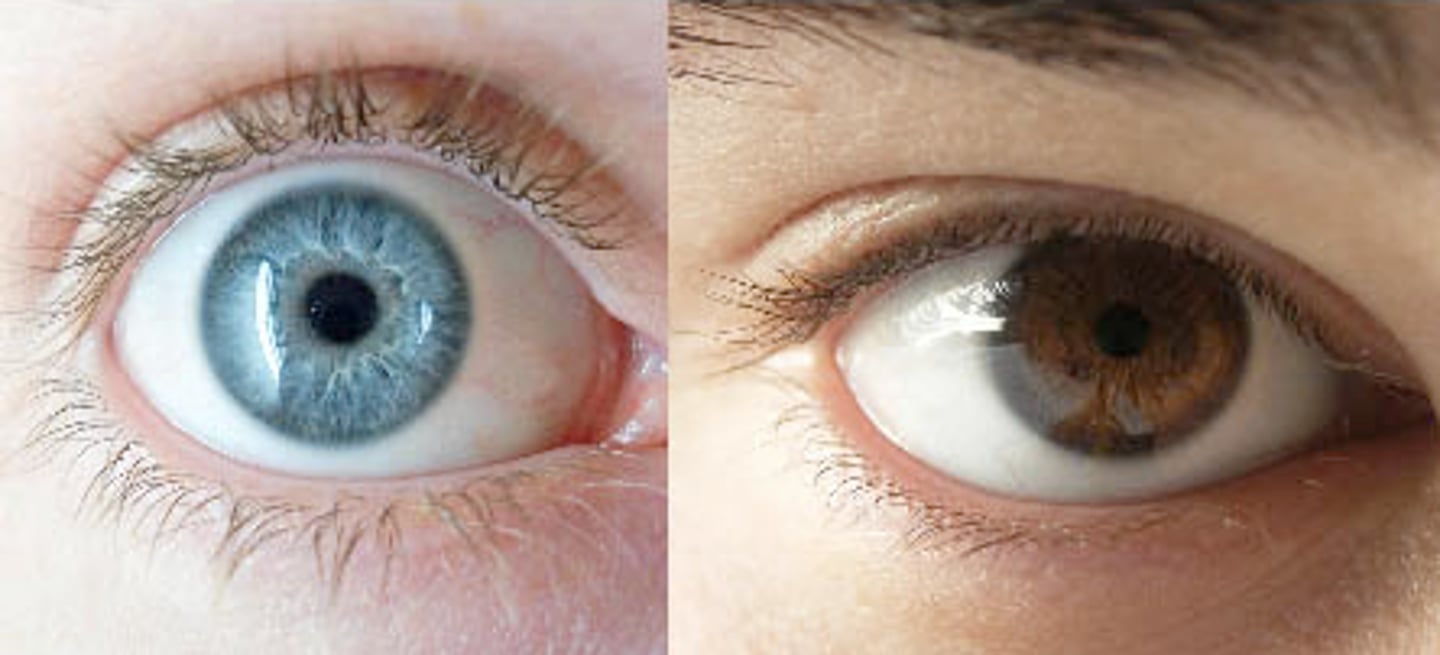
Phenotype
The observable and developmental traits of an organism that result from their specific genes
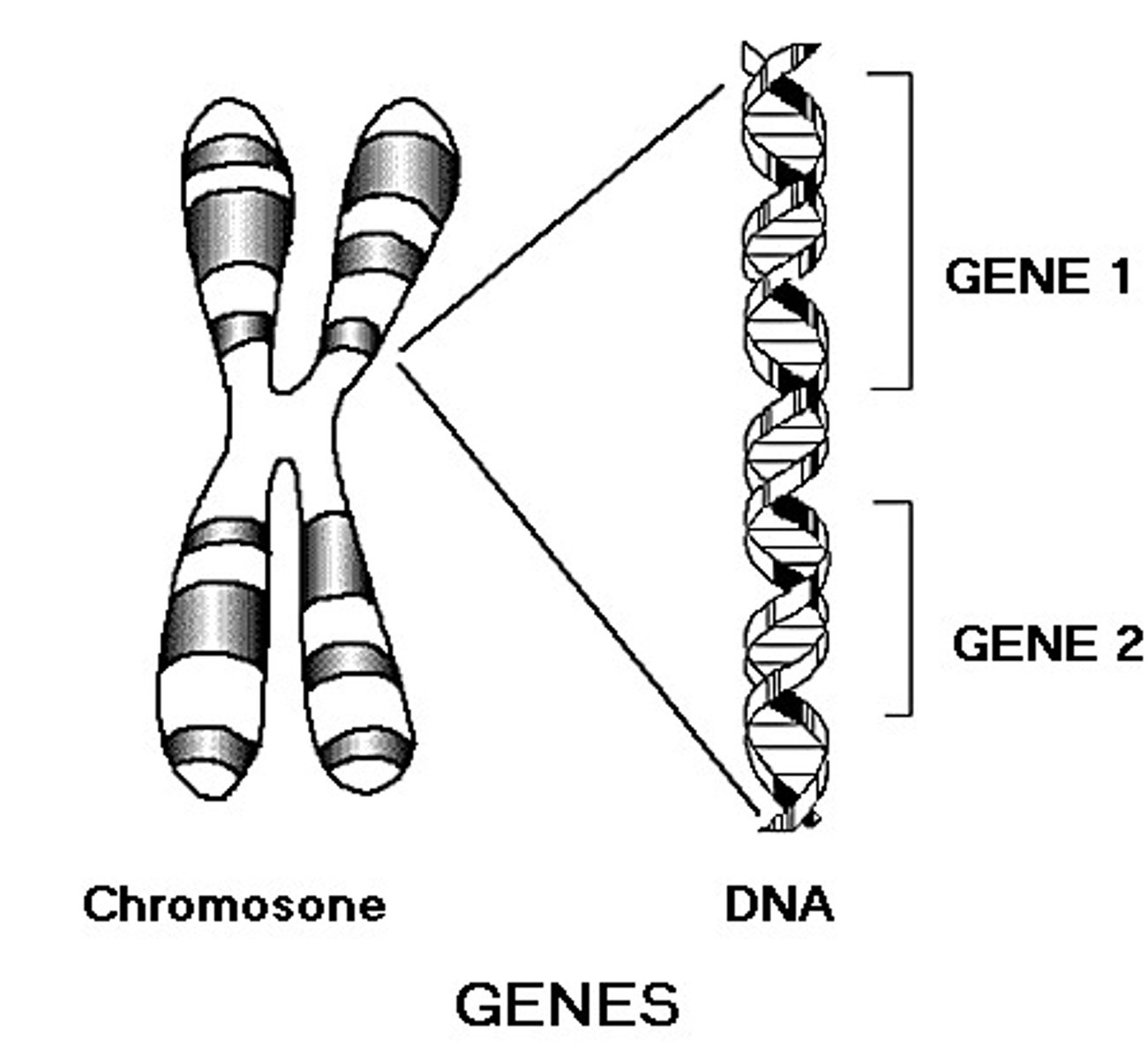
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genetic information necessary for the development, functioning, and reproduction of organisms. Found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
asexual reproduction
a type of reproduction where offspring are genetically identical to the parent, requiring only one parent and resulting in rapid population growth
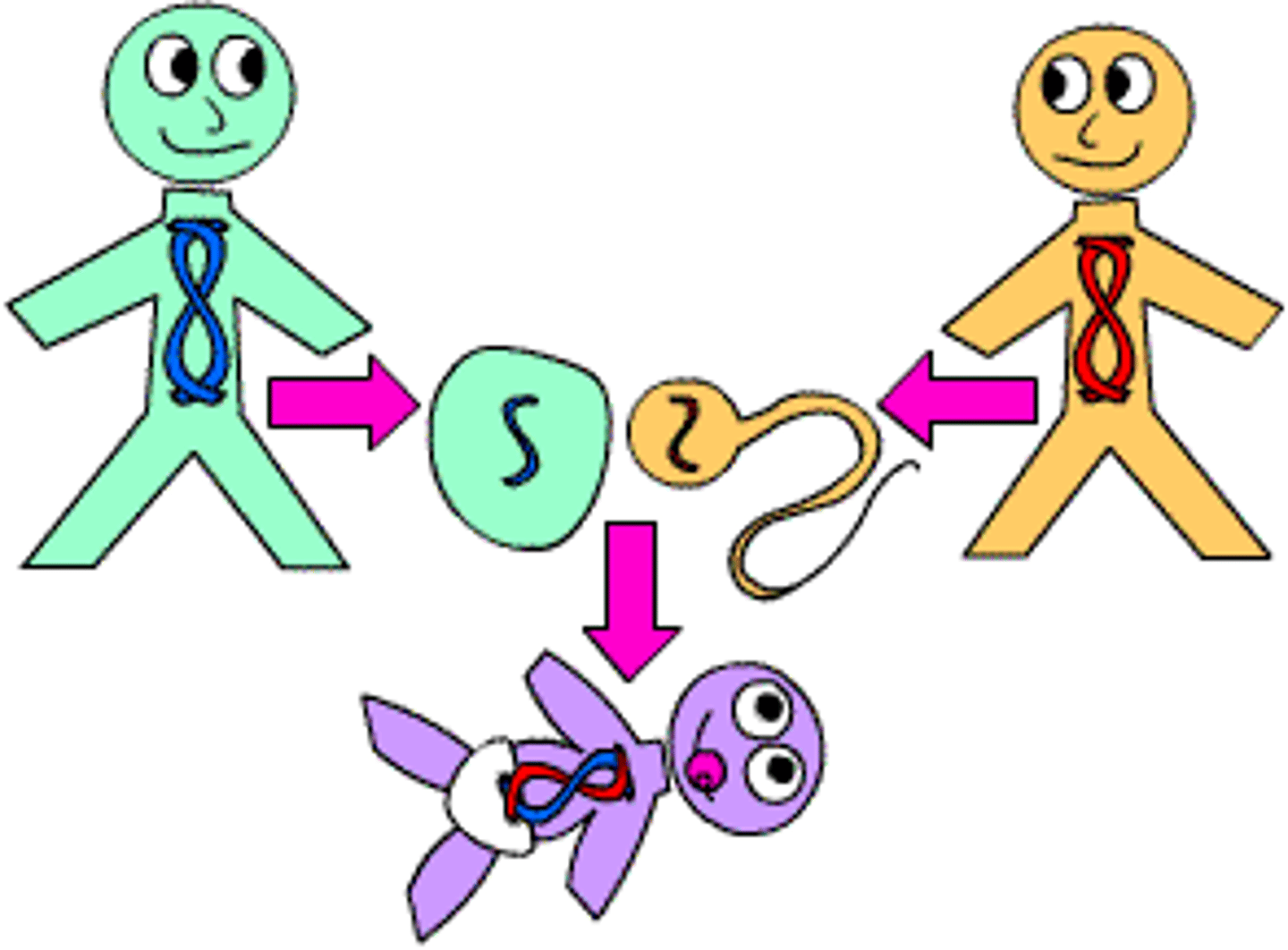
sexual reproduction
Process by which male and female gametes of the same species combine to make a new organism. Offspring receive a combination of the genetic information from both parents.
Homozygous pair
When two alleles in a pair are the same (both dominant or recessive).
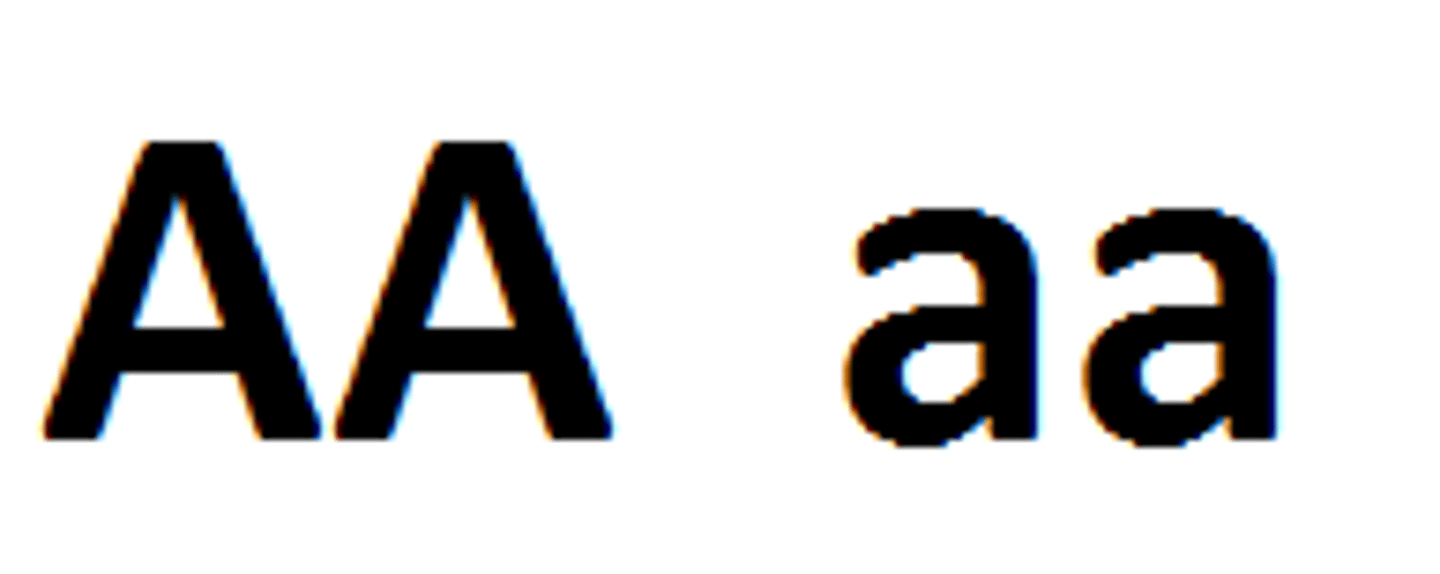
heterozygous pair
When two alleles in a pair are different (one is dominant, and one is recessive).
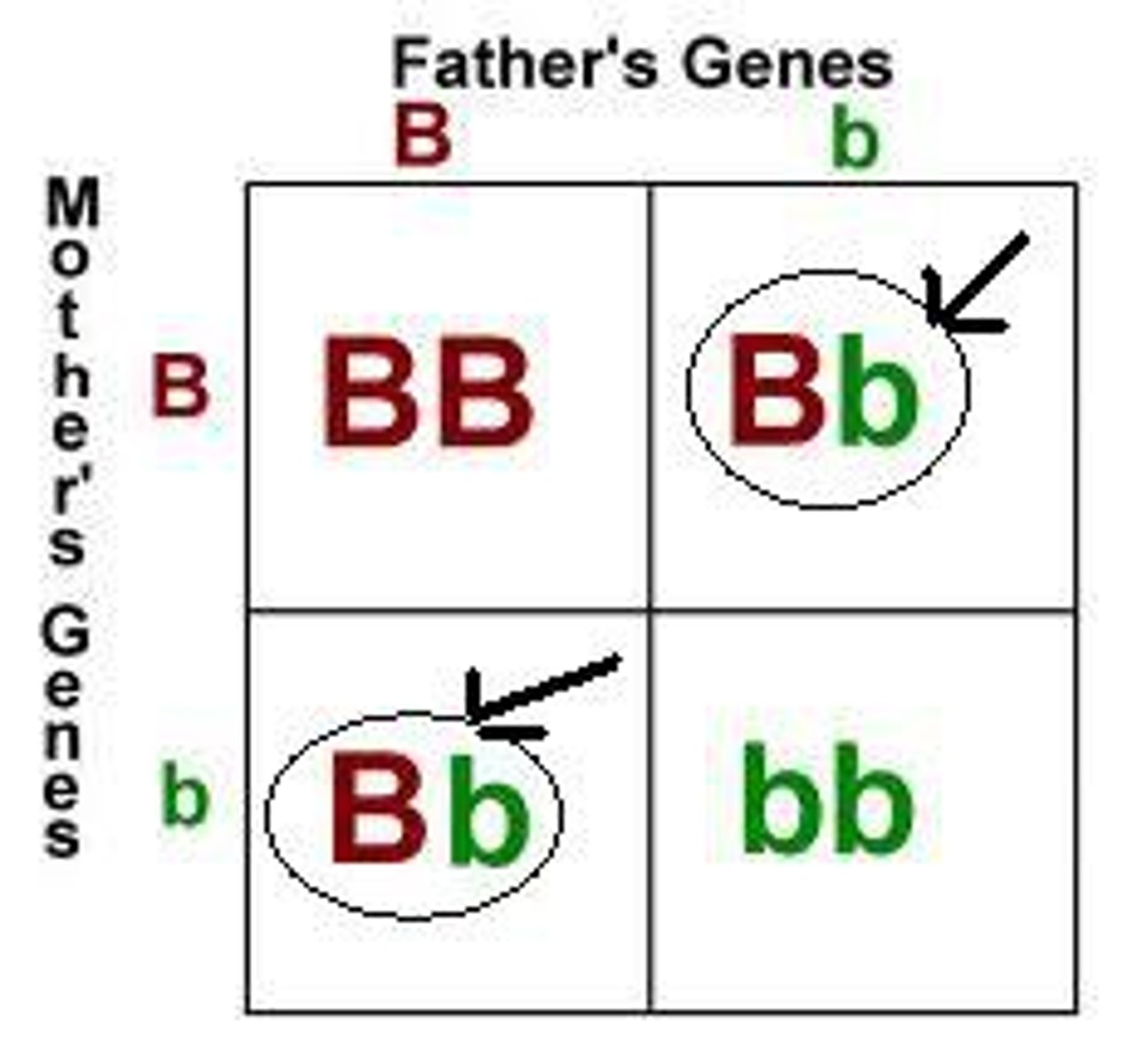
Trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
dominant trait
a genetic factor that overpowers another genetic factor
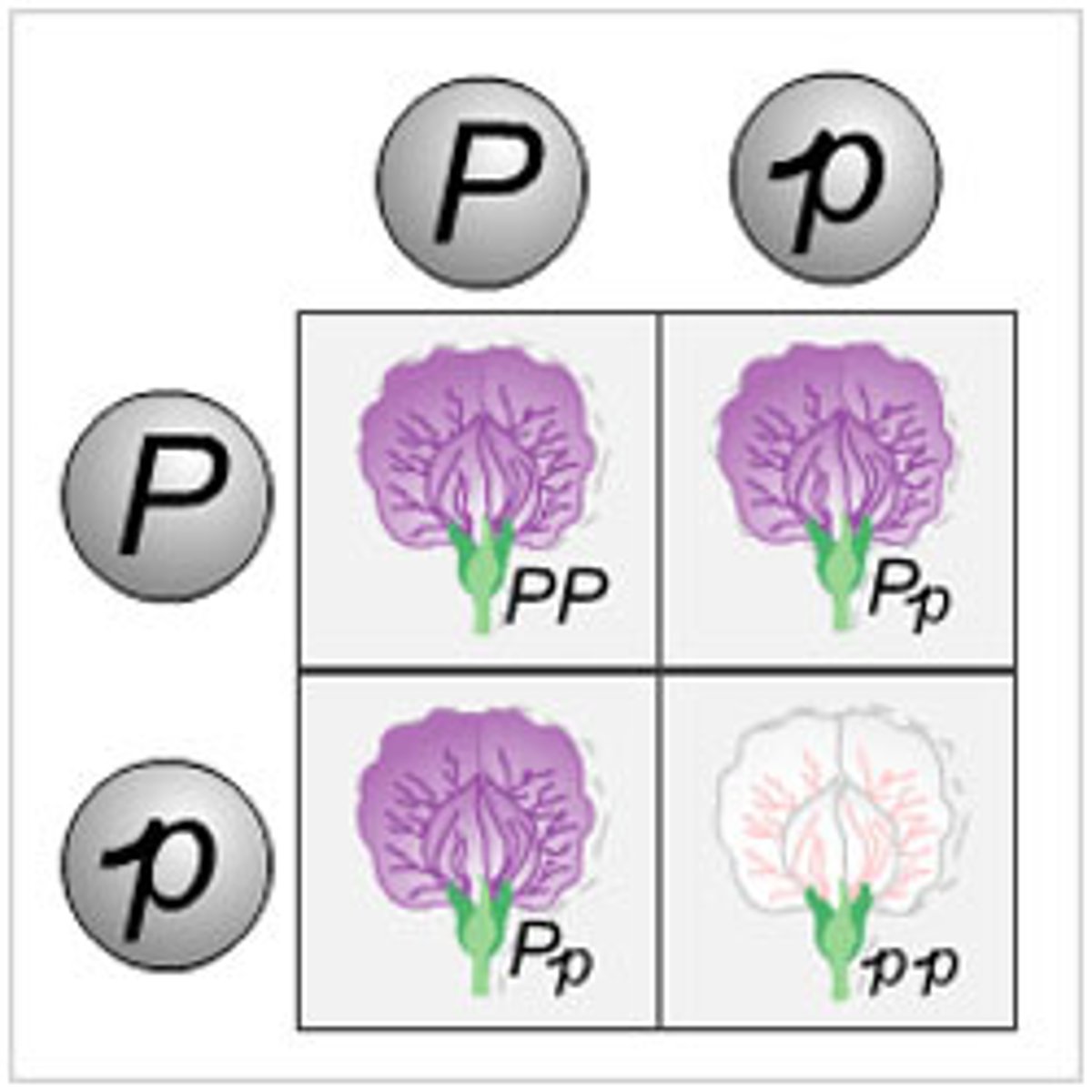
recessive trait
a genetic factor that is overpowered by the presence of a dominant factor. Only expressed if two traits are the same
limiting factor
An environmental factor that prevents a population from increasing

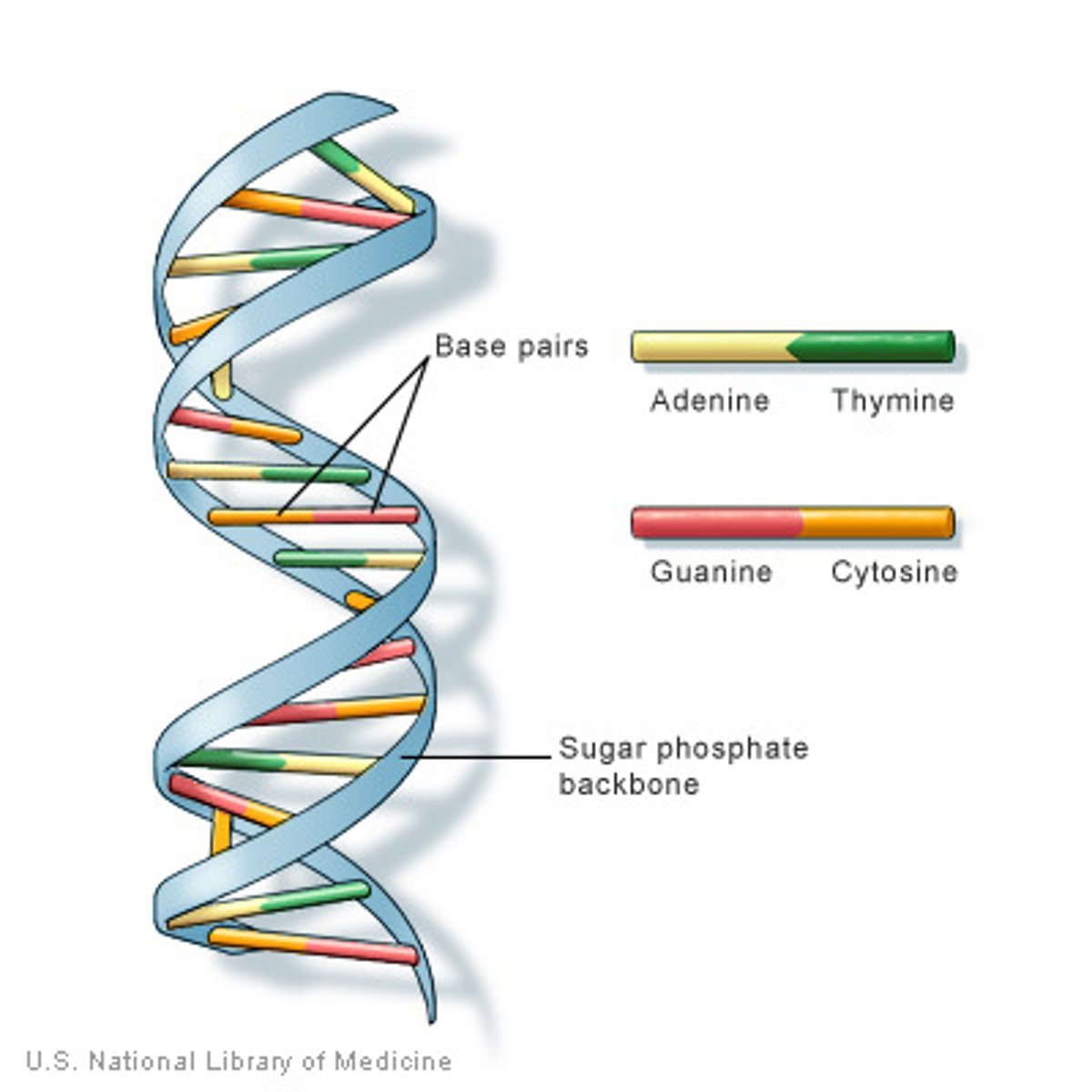
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the 46 chromosomes.
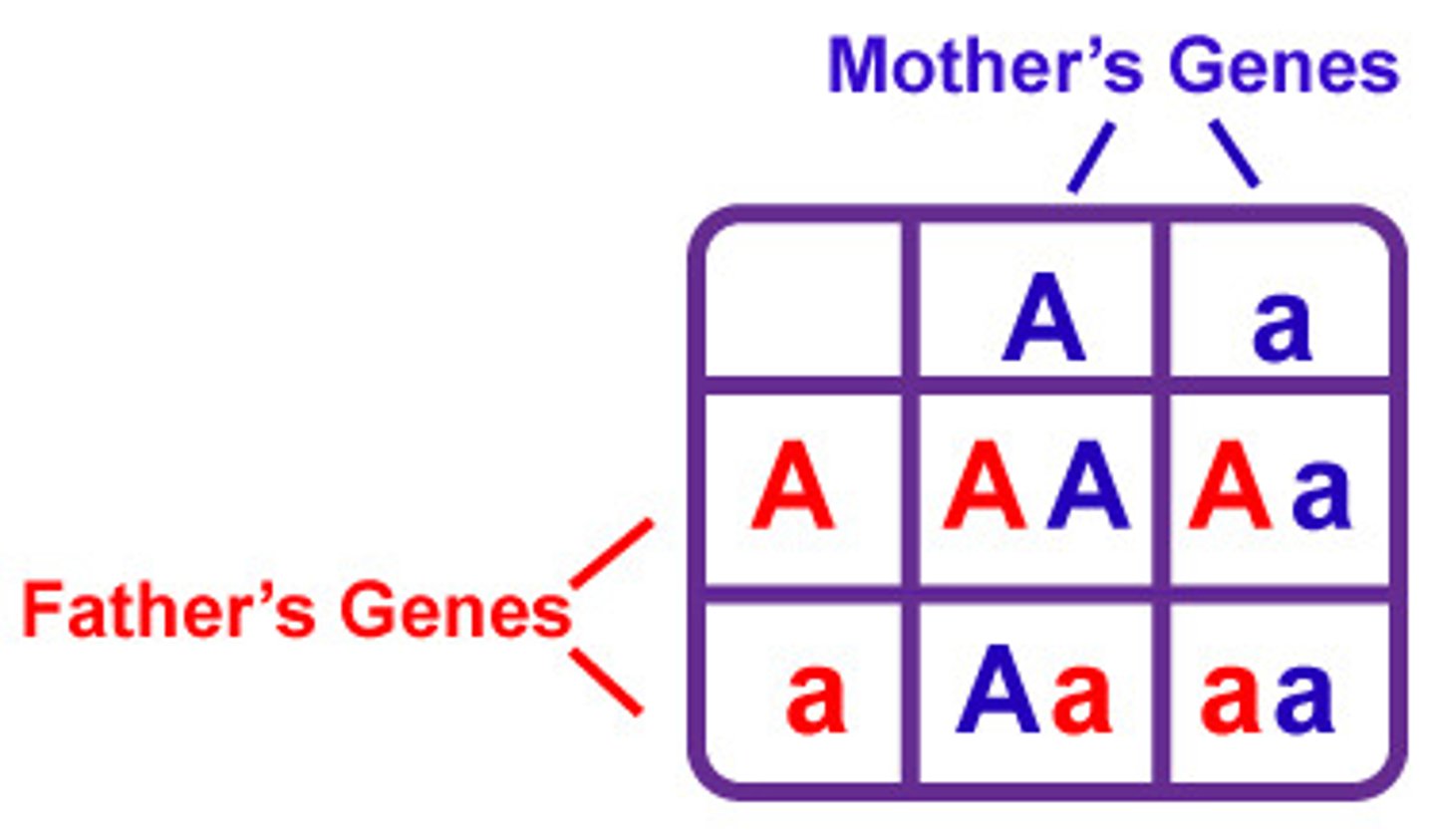
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles/traits that can result from sexual reproduction
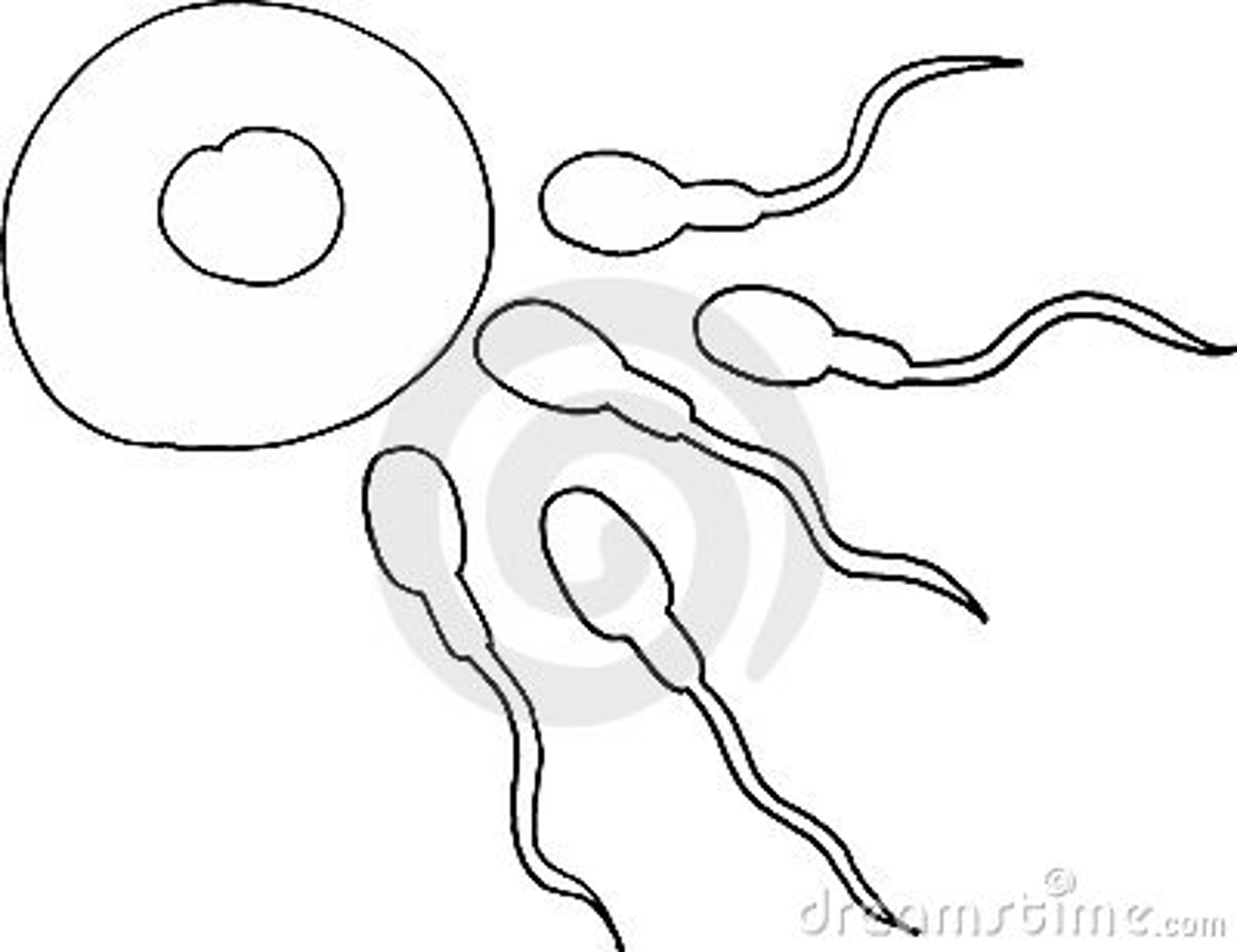
Gametes
reproductive cells (ex: sperm and egg )
Gene
A segment/section of DNA on a chromosome that codes or provides genetic instructions responsible for a specific trait.
Chromatin
Tightly coiled DNA around protein structures called Histones, forming chromosomes during cell division.
Incomplete Dominance
Traits where one allele is not completely dominant and does not mask the recessive alleles in the phenotype. This results in a blending of both alleles in the offspring’s phenotype. An example is the flower color in snapdragons, where red and white flowers produce pink offspring.
carrier
An individual who has one copy of a recessive allele for a trait, but does not exhibit the trait themselves. Carriers can pass the recessive allele to their offspring.