BB 3: ABO Blood Group Review
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
what refers to the concept that individuals will form immune antibodies (naturally occurring) to ABO blood group antigens that they do not possess?
landsteiner’s law
the rule of thumb for determining an individual’s genotype is to always use the ____ genotype when trying to determine all possible genotypes.
heterozygous
which gene antigen is necessary for the expression of normal ABO antigens?
H
which gene antigen codes for the enzyme that adds the sugar, fructose, to the terminal sugar of a precursor substance?
H
the terminal sugar N-acetylglucosamine attaches to the ____ antigen.
A
the terminal sugar D-galactose attaches to the ____ antigen.
B
list the following ABO types from the greatest amount of H to the least amount of H:
A1
A1B
A2
A2B
B
O
O > A2 > B > A2B > A1 > A1B
what ABO gene antigen is associated with the following glucosyltransferase (enzyme): L-fucosyl transferase)?
H
what ABO gene antigen is associated with the following glucosyltransferase (enzyme): N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase?
A
what ABO gene antigen is associated with the following glucosyltransferase (enzyme): D-galactosyl transferase?
B
what ABO gene antigen is associated with the immunodominant sugar L-fucose?
H
what is the secretory gene?
FUT2
which gene is described below
inherited autosomal dominant
responsible for expression of H antigen on glycoprotein structures in body secretions
found in 80% of population
Se
what percent of the population are nonsecretors (sese)?
20%
“se” and “O” genes are examples of ____ genes, meaning nothing is expressed.
amorphic
which ABO linkage is founds for body fluids and secretions (aka Type 1)?
beta 1-3
which ABO linkage is founds for RBCs and some body fluids and secretions (aka Type 2)?
beta 1-4
RBC antigens or soluble substances: basic backbone are glycolipids?
RBC antigens
RBC antigens or soluble substances: basic backbone are glycoproteins?
soluble substances
RBC antigens or soluble substances: 1st sugar is GL?
RBC antigens
RBC antigens or soluble substances: 1st sugar is GALNAC?
soluble substances
RBC antigens or soluble substances: beta 1-4 linkage?
RBC antigens
RBC antigens or soluble substances: beta 1-3 linkage?
soluble substances
RBC antigens or soluble substances: FUT 1 by H gene for 2-L-fucosyltransferase?
RBC antigens
RBC antigens or soluble substances: FUT 2 by Se gene for 2-L-fucosyltransferase?
soluble substances
it is possible for a an AB and O parent to produce an AB child if the A and B antigens are inherited in the ____ position on the chromosome.
cis
ABO antibodies are naturally occurring and first appear after ____ months of age.
3-6
reverse typing on cord blood is not performed until 6 months or older. true or false?
true
group A and B antibodies are ____.
IgM
anti-A and anti-B (for group O) are primarily ____.
IgM
anti-A,B (for group O) is a single ____ antibody that cannot be separated into individual parts.
IgG
the ____ antibody in O individuals have the potential to cause HDFN in A (more commonly) or B babies because it is IgG and can cross the placenta.
anti-A,B
the H1 and H2 forms of the H antigen are ____ chains.
unbranched straight
the H3 and H4 forms of the H antigen are ____ chains.
complex branched
straight chain H1 is converted to ____ antigens.
Aa
straight chain H1 is converted to ____ antigens.
Ab
both A1 and A2 enzymes can convert the straight chain H antigens, but the ____ enzyme is less efficient.
A2
complex H3 is converted to ____ antigens.
Ac
complex H4 is converted to ____ antigens.
Ad
conversion of complex H antigens are done okay by the A1 enzymes but very poorly by ____.
A2
due to poor conversion, more unconverted H antigens are available on _____ RBCs.
A2
which A subgroup is described below
unexpected anti-A1
found in 1-8% of population
A2
which A subgroup is described below
demonstrates a mixed field pattern of agglutination by anti-A and anti-A,B reagents
A3
which A subgroup is described below
not agglutinated by anti-A reagent
agglutinated by anti-A,B reagent
anti-A1 commonly found
Ax
which A subgroup is described below
cells demonstrate only about 10% or less agglutinated in mixed field agglutination with antisera
Aend
which A subgroup is described below
not agglutinated or by anti-A or anti-A,B reagents
Am
which A subgroup is described below
unagglutinated by anti-A or anti-A,B reagents
Ay
which A subgroup is described below
unagglutinated by anti-A or anti-A,B reagents
adsorption and elution studies show the presence of A antigen
unexpected anti-A1 present
Ael
which B subgroup may demonstrate a mixed field agglutination?
B3
what refers to the absence of H, A, and B antigens on RBCs due to the mutation of the FUT-1 (H) gene producing a silenced gene incapable of coding for the H transferase?
bombay
____ patients will present with no agglutination with anti-A, anti-B, or H lectin.
bombay
the following describes a ____ patient:
phenotypes O but is incompatible with group O RBCs
potent anti-H in serum
presence of anti-A, anti-B, and anti-A,B
bombay
the following describes a ____ patient:
A, B, H nonsecretor (no substances in saliva; silent FUT-2 [Se] gene)
absence of H enzyme (a-2-L-fucosyltransferase) in serum and H antigen on RBC
presence of A or B enzymes in serum
bombay
a true bombay recipient always needs another bombay donor or autologous units. true or false?
true
what condition is described below
acquired, transient serological discrepancy
usually found in type A patients who have septicemia, GI disorders, carcinoma of the colon/rectum, or wound infections
acquired B
what condition is caused by enzymes produced by certain strains of E. coli or some strains of Proteus vulgaris?
acquired B
in _____, enzymes can cause deacetylation of N-acetyl-galactosamine which leads to D-galactosamine (similar to D-galactose)
acquired B
the following ABO discrepancies indicates problems with ____
weak reacting antigen (subgroups)
missing antigens (null, deleted/mosaic)
extra antigens
mixed field (mf) reactions/chimerism
RBCs
the following ABO discrepancies indicates problems with ____
weak reacting
missing antibodies
extra antibodies
serum
rouleux may cause false ____ reactions.
positive
the following are examples may result in extra ____ reactions in forward grouping:
acquired B
B(A) phenotype due to disease
rouleux
polyagglutination
wharton’s jelly
antigen
for patients with acquired B, in order to resolve the discrepancy in testing, the patient’s RBCs should be tested with anti-B reagent acidified to the pH of ____.
6.0
group A people with acquired B should received group A ____ (or group O).
washed RBCs
only ____ typing is performed on cord blood.
forward
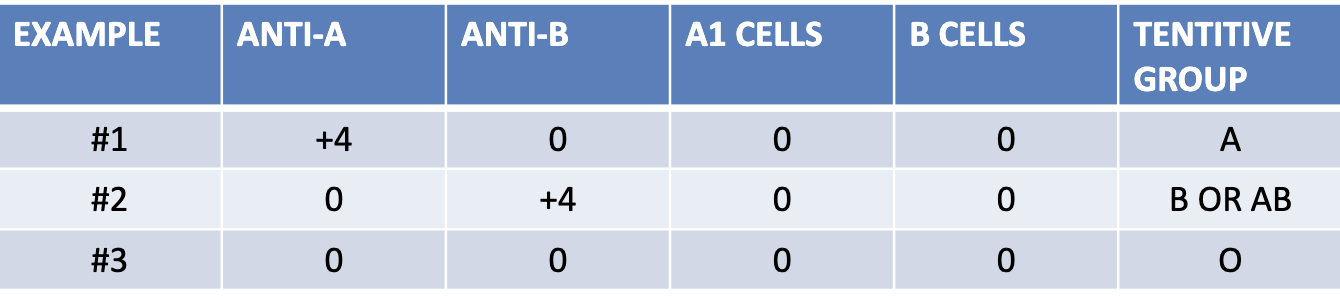
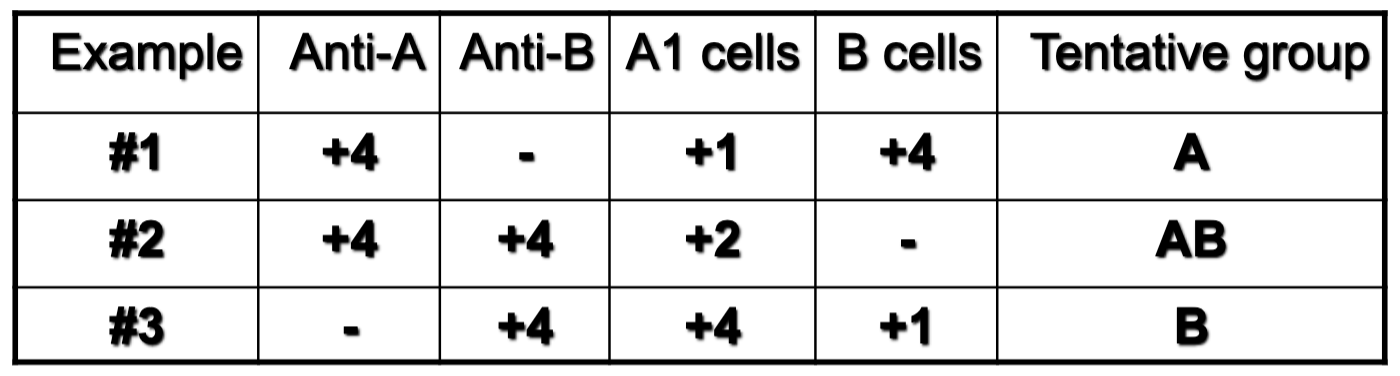
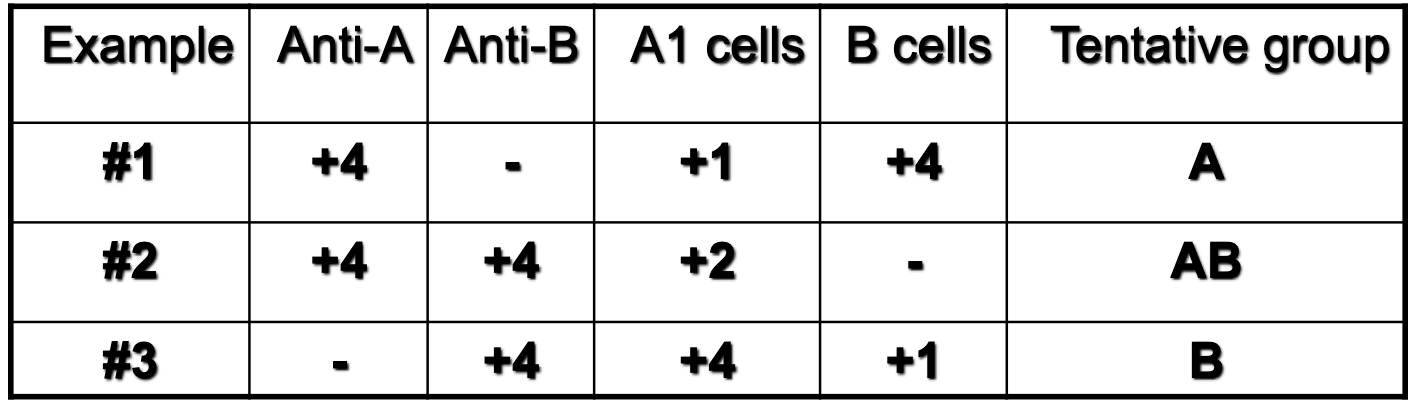
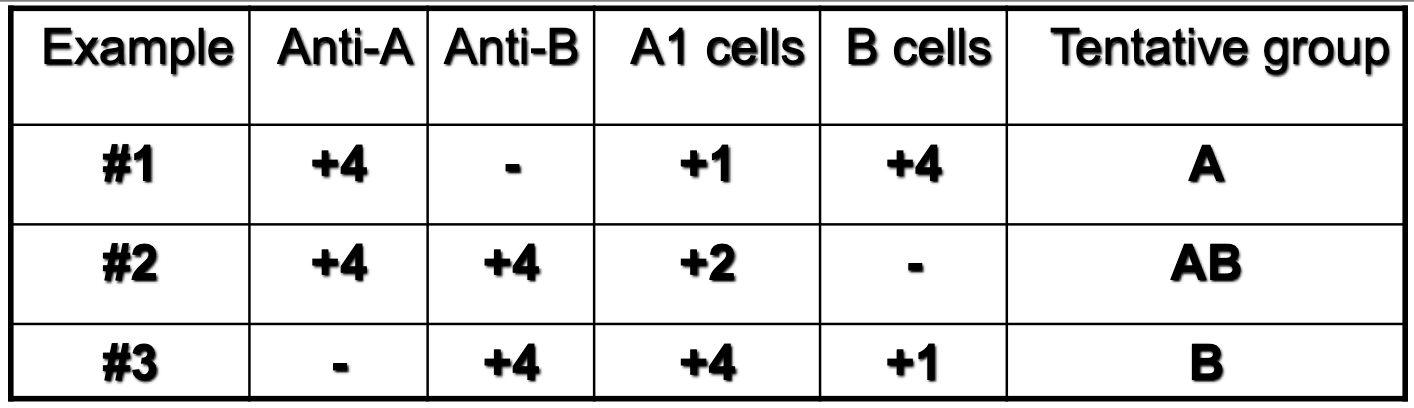
which example presents a newborn patient?
1
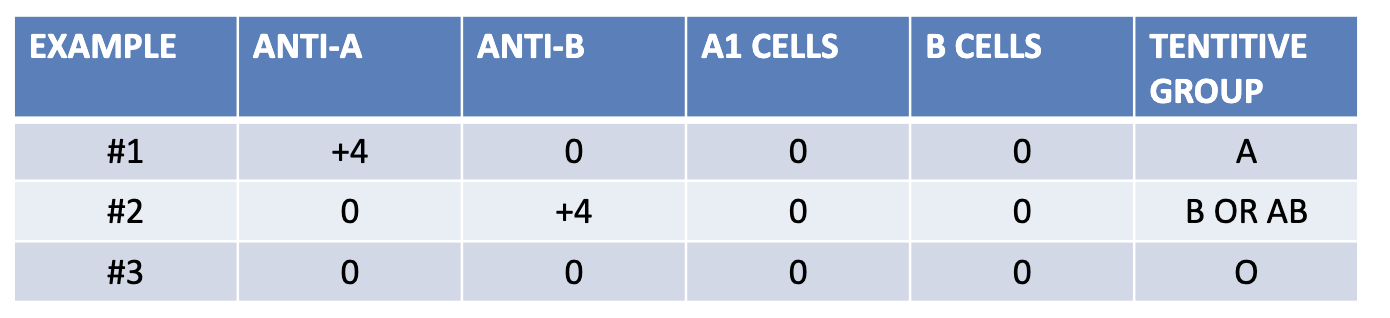
which example presents a geriatric patient?
2
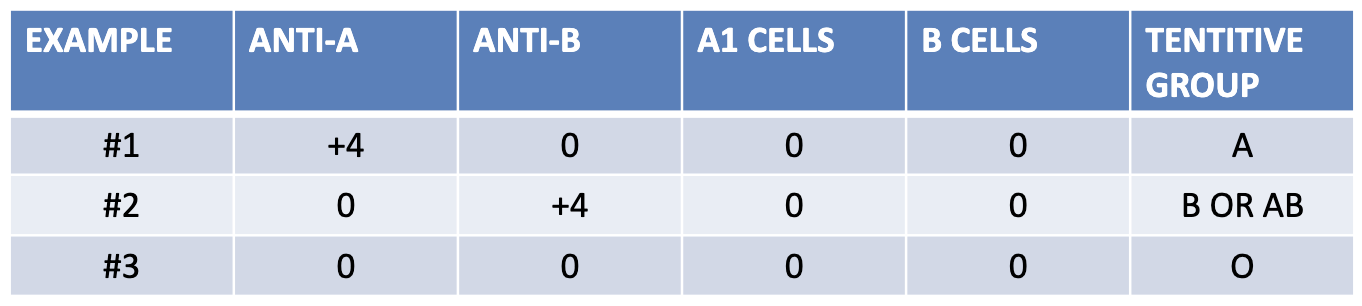
which example presents a patient with hypogammaglobuinemia?
3
the following are examples may result in extra ____ reactions in reverse grouping:
cold antibodies (allo- or auto-)
may include anti-I, H, M, N, P, Le
rouleux
anti-A1 in an A2 or A2B individual
recent transfusion of incompatible plasma products
IV Ig infusion
antibody
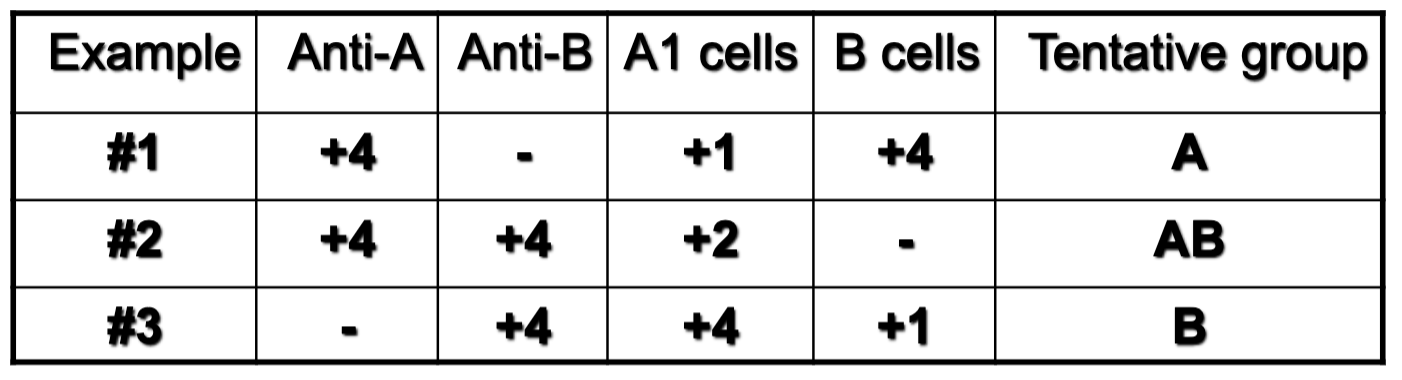
which example depicts anti-A1 in A2 or A2B patient?
1; 2
which example depicts irregular IgM allo antibodies?
3
which example depicts rouleux?
1; 3
which example depicts auto anti-I?
1; 3
____ can result in the following reactions
stronger at IS
weak at 37°C
no agglutination at AHG
rouleux
the following may cause ____ in a sample:
complement binding antibodies
bacterial contamination
physical causes
water (IV)
mechanical strain during blood collection
extreme temperature exposure (hot/cold)
hemolysis