Understanding Mood Disorders and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Therapeutic approach addressing thoughts and behaviors.
Challenging Situation
A scenario causing significant stress or anxiety.
Physiological Reactions
Bodily responses like increased heart rate or sweating.
Automatic Thoughts
Immediate, often negative thoughts in response to situations.
Cognitive Distortions
Irrational thought patterns leading to negative emotions.
Alternate Thoughts
Reframed perspectives to improve emotional responses.
Mood Disorders
Psychological conditions characterized by severe mood changes.
Depressive Episode
Low mood lasting at least two weeks with symptoms.
Mania
Elevated mood state often leading to impulsive behavior.
Major Depressive Episode
Severe depression with cognitive and physical symptoms.

Individual vs. Collective Societies
Cultural distinction affecting mental health perspectives.
Sociocultural Factors
Cultural influences impacting the prevalence of disorders.
DSM-5
Diagnostic manual for mental health disorders.
Bipolar Disorder
Mood disorder with alternating depressive and manic episodes.
Feelings of Worthlessness
Negative self-assessment common in depressive episodes.
Altered Sleeping Patterns
Changes in sleep duration or quality during mood disorders.
Significant Weight Changes
Noticeable gain or loss of weight linked to mood disorders.
Listlessness
Lack of energy or enthusiasm for activities.
Suicide Risk
Increased danger of self-harm in severe depression.
Therapist's Role
Guide clients to healthier thought patterns and interpretations.
Volunteer Orientation
Event for new volunteers to learn about responsibilities.
Cognitive Symptoms
Thought-related issues like indecisiveness during mood disorders.
Anhedonia
Inability to experience pleasure or enjoyment.
Average duration of depressive episode
Typically lasts 9 months untreated.
Behavioral activation
Level of engagement in activities and behaviors.
Manic episode
High mood state with exaggerated elation or joy.
Extreme pleasure in mania
Patients may feel continuous orgasm-like pleasure.
Sleep requirements in mania
Patients require very little sleep.
Grandiose plans
Beliefs of being able to achieve anything.
Flight of ideas
Rapid, incoherent speech due to many ideas.
Impulsive behavior in mania
Reckless actions like spending life savings.
Hypomanic episode
Less severe manic episode without major impairment.
Unipolar depression
Condition with only depressive episodes.
Bipolar mood disorder
Condition alternating between depression and mania.
Euthymia
Periods of normal mood between episodes.
Remission
Full recovery for at least two months.
Partial remission
Retaining some symptoms after episodes.
Depressive disorders
Characterized by sad, empty, or irritable mood.
Somatic symptoms
Bodily changes affecting functioning capacity.
Psychomotor retardation
Slowed movements due to depressive symptoms.
Psychomotor agitation
Increased, jerky movements due to symptoms.
Major Depressive Disorder
Defined by DSM-5 criteria for depressive episodes.

Duration and timing
Differentiates types of depressive disorders.
DSM-5 criteria for mania
Requires at least one week duration.
Average duration of manic episode
Typically lasts two to six months untreated.
Grief
Sadness from loss, often temporary.
Symptoms Overlap
Shared symptoms between grief and depression.
Clinician Discretion
Clinicians determine diagnosis based on symptoms.
Suicidal Ideas
Thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
Severe Impairment
Significant dysfunction in daily activities.
Single Episode
Diagnosis for one depression occurrence.
Recurrent Episode
Two or more depression episodes with breaks.
Persistent Depressive Disorder
Chronic depression lasting at least two years.
Comorbidity
Co-occurrence of multiple mental disorders.
Double Depression
Persistent depression with major depressive episodes.
Anxious Distress
Anxiety symptoms accompanying depressive disorder.
Mixed Features
Presence of manic symptoms without manic episode.
Melancholic Features
Distinct depression with inability to feel pleasure.
Psychotic Features
Hallucinations or delusions related to mood.
Catatonic Features
Motor symptoms like mutism or posturing.
Atypical Features
Positive reactions to events, weight gain, hypersomnia.
Seasonal Pattern
Depression episodes linked to specific seasons.
Peripartum Onset
Depression onset during or after pregnancy.
Seasonal Affective Disorder
Depression episodes tied to winter seasons.
SAD
Seasonal Affective Disorder linked to low daylight exposure.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
Severe distress before menstruation affecting functioning.
DSM-V
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition.
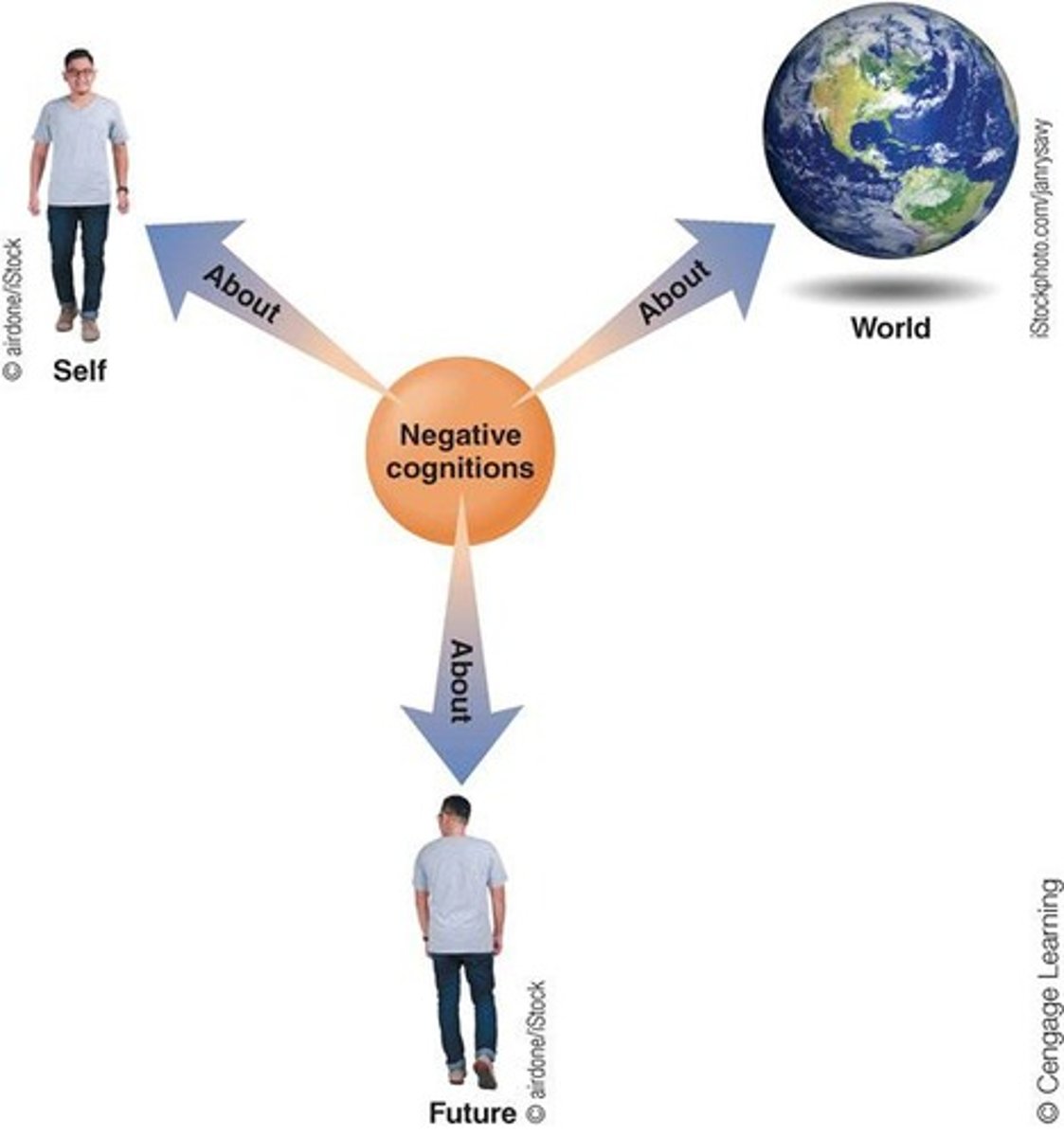
Cognitive Triad
Negative thoughts about self, world, and future.
Arbitrary Inference
Negative emphasis in interpreting situations.
Rumination
Repetitive focus on negative autobiographical content.

Brain Fog
Cognitive impairment affecting concentration and memory.
Negative Affect
Emotional state characterized by negative emotions.
Low Energy Levels
Fatigue impacting daily activities and engagement.
Isolation
Withdrawal from social interactions worsening depression.
Negative Cognitive Styles
Patterns of negative interpretation leading to depression.
Distress
Emotional suffering impacting daily functioning.
Impairment
Reduced ability to perform daily tasks.
Physiological Cycle
Monthly biological changes affecting mood in women.
Depressive Disorder
Mental health condition marked by persistent sadness.
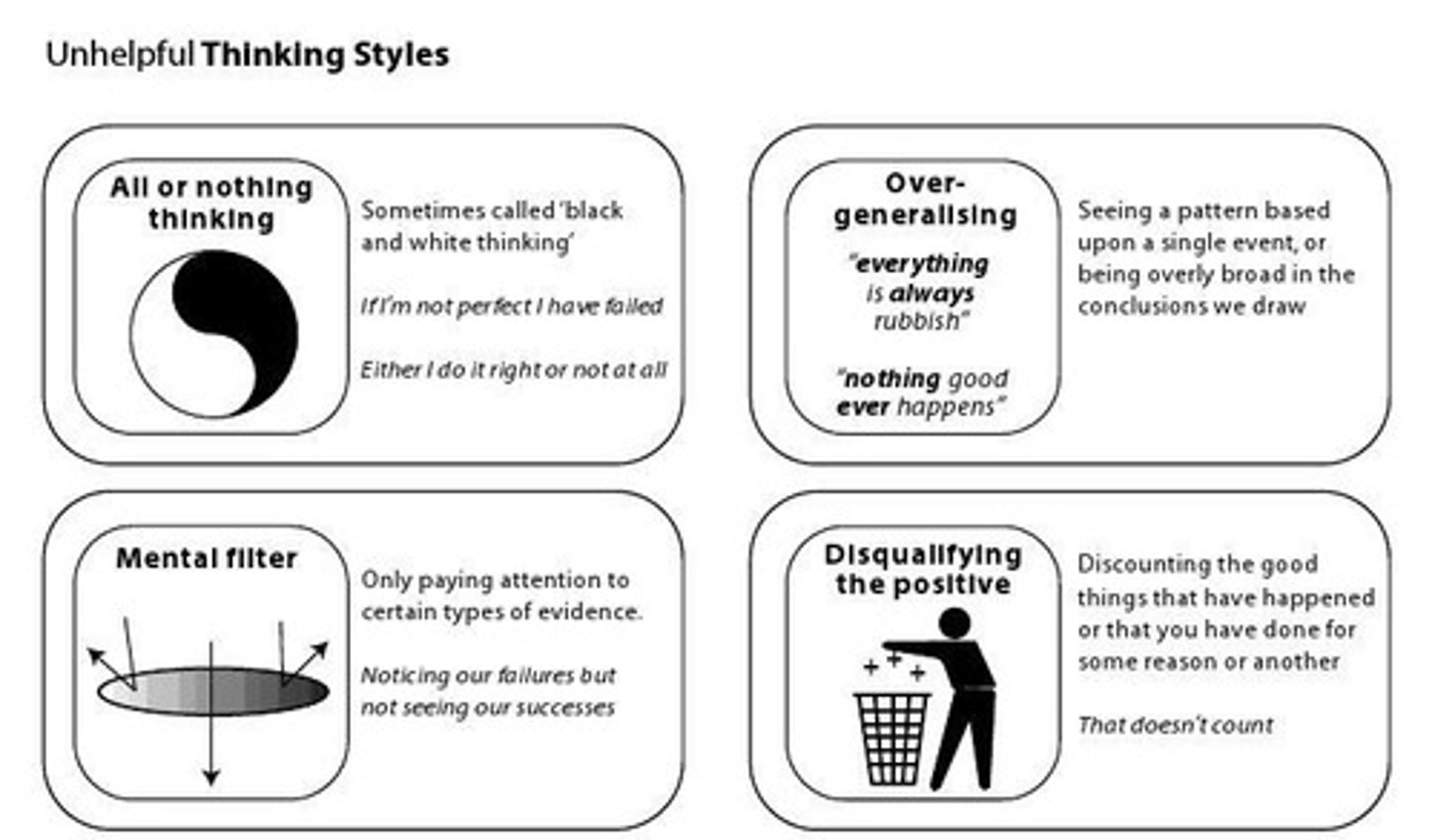
Cognitive Errors
Mistakes in thinking leading to negative conclusions.
Longitudinal Studies
Research tracking changes over time.
Negative Thinking Styles
Consistent patterns of pessimistic thought.
Point Prevalence
Percentage of population with mood disorder at specific time.
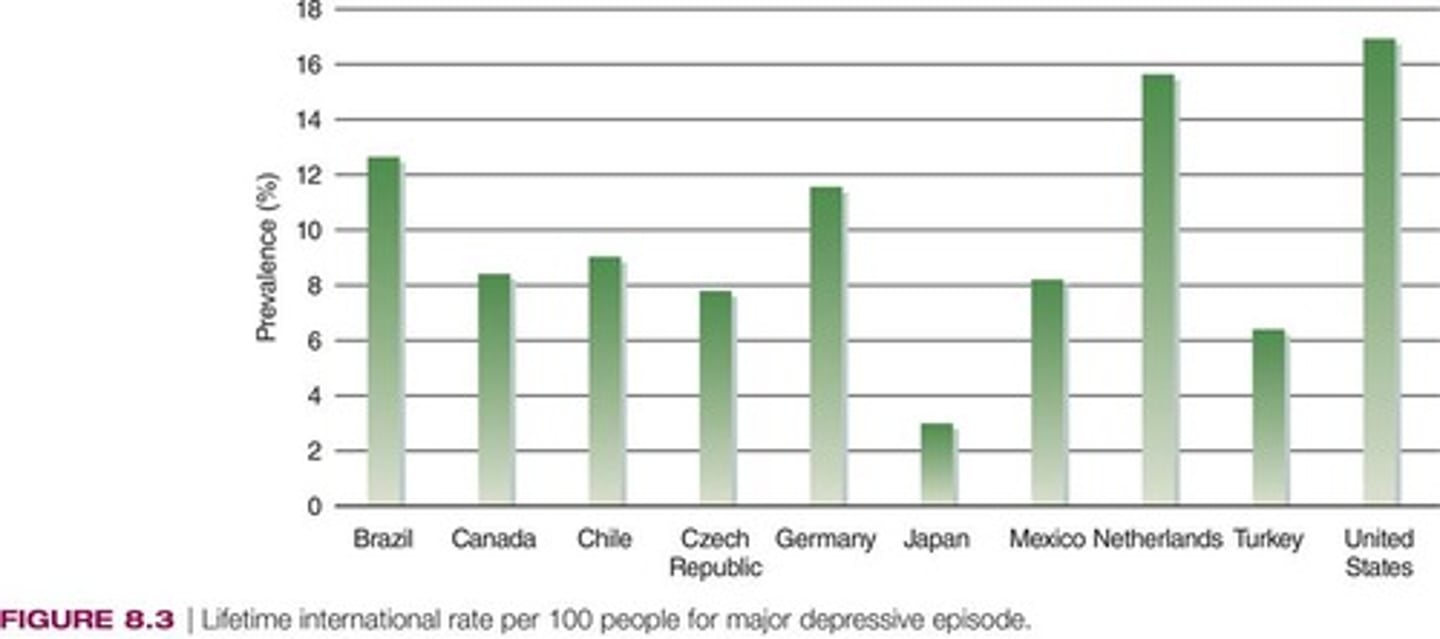
Lifetime Prevalence
Probability of having major depressive episode in lifetime.
12-Month Prevalence
Percentage of population with mood disorder in past year.
Bipolar Disorder Prevalence
Lifetime prevalence for bipolar I and II is 2.6%.
Gender Differences in Depression
Females are twice as likely to have depression.
Chronic Major Life Stress
Associated with onset of mood disorders.
Anxiety Disorder Comorbidity
Major depressive episodes often co-occur with anxiety disorders.
Depression Diagnosis Across Cultures
Bipolar disorder prevalence consistent across diverse cultures.
Meta-Analysis on Indigenous Depression
No prevalence difference in Indigenous versus general population.
Treatment Seeking Rate
Only 60% of those with depression seek treatment.
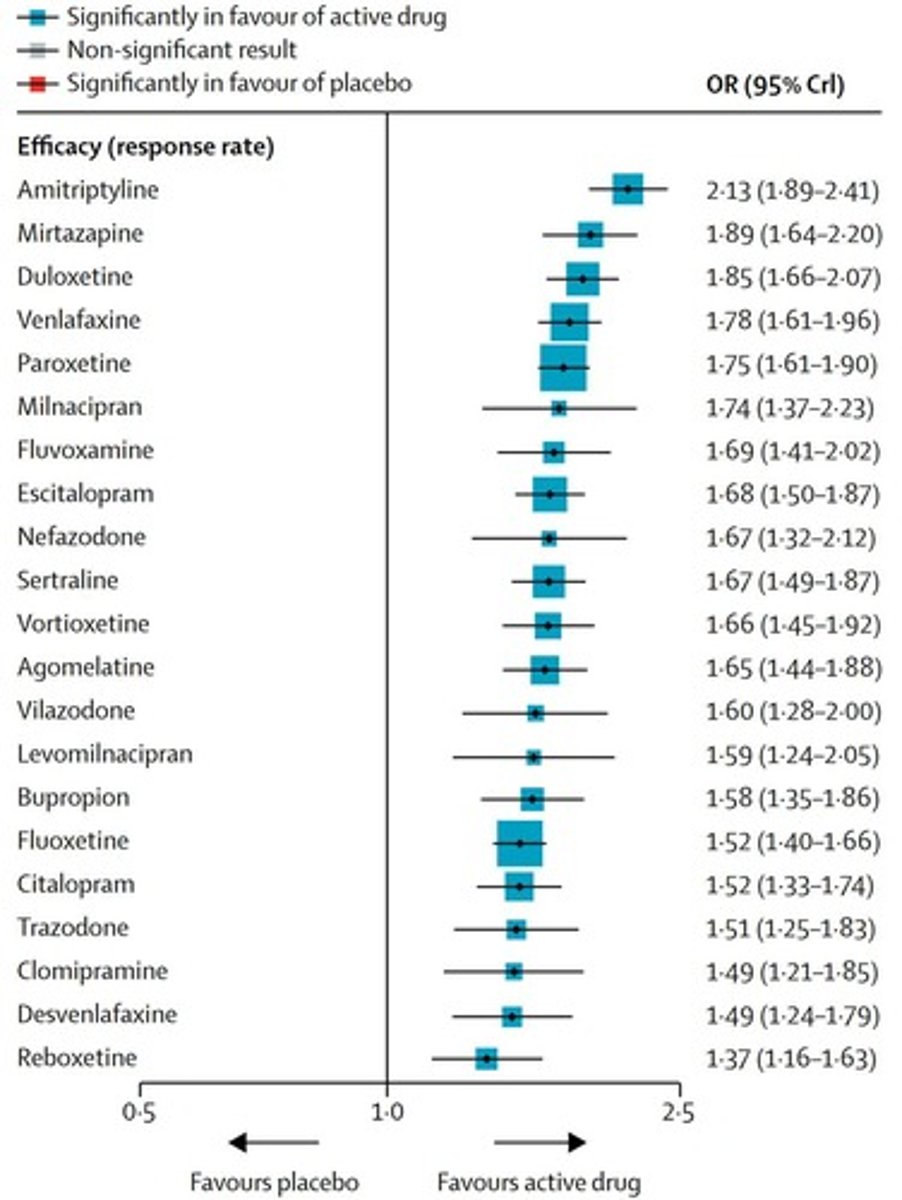
Biological Treatments
Includes drugs and brain stimulation techniques.
Psychotherapy
Commonly used alone or with drug therapy.
Seasonal Affective Disorder Treatment
Light treatment is effective for seasonal affective disorder.
Cognitive Processes
Rumination ties up cognitive resources for school work.
Low Self-Esteem
Can prevent pursuit of scholarships and awards.
Older Adults and Depression
Less prevalent but more disabling due to health issues.
Racial Discrepancies in Diagnosis
Mixed evidence on depression diagnosis across races.
Sociodemographic Correlates
Being female and unmarried correlates with depression.