Chapter 14 APES (pollution)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is BPA?
A chemical used in the production of plastics.
What is a point source?
specific, distinct location where pollution can be traced to - identifiable
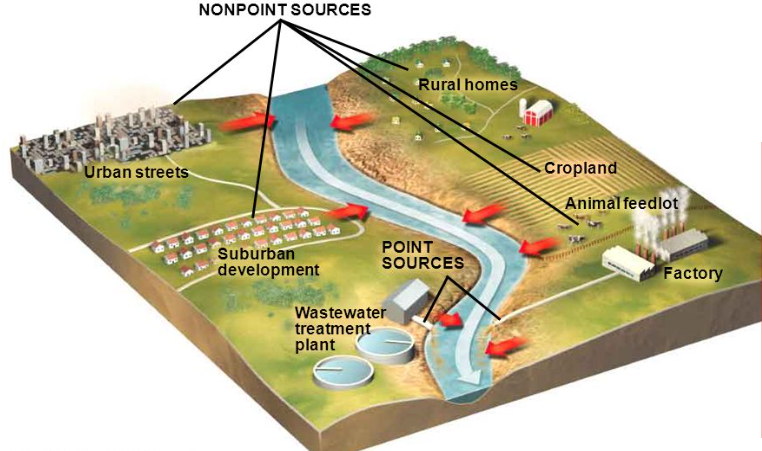
What is non point source?
Pollution not from a distinct location, small things adding up
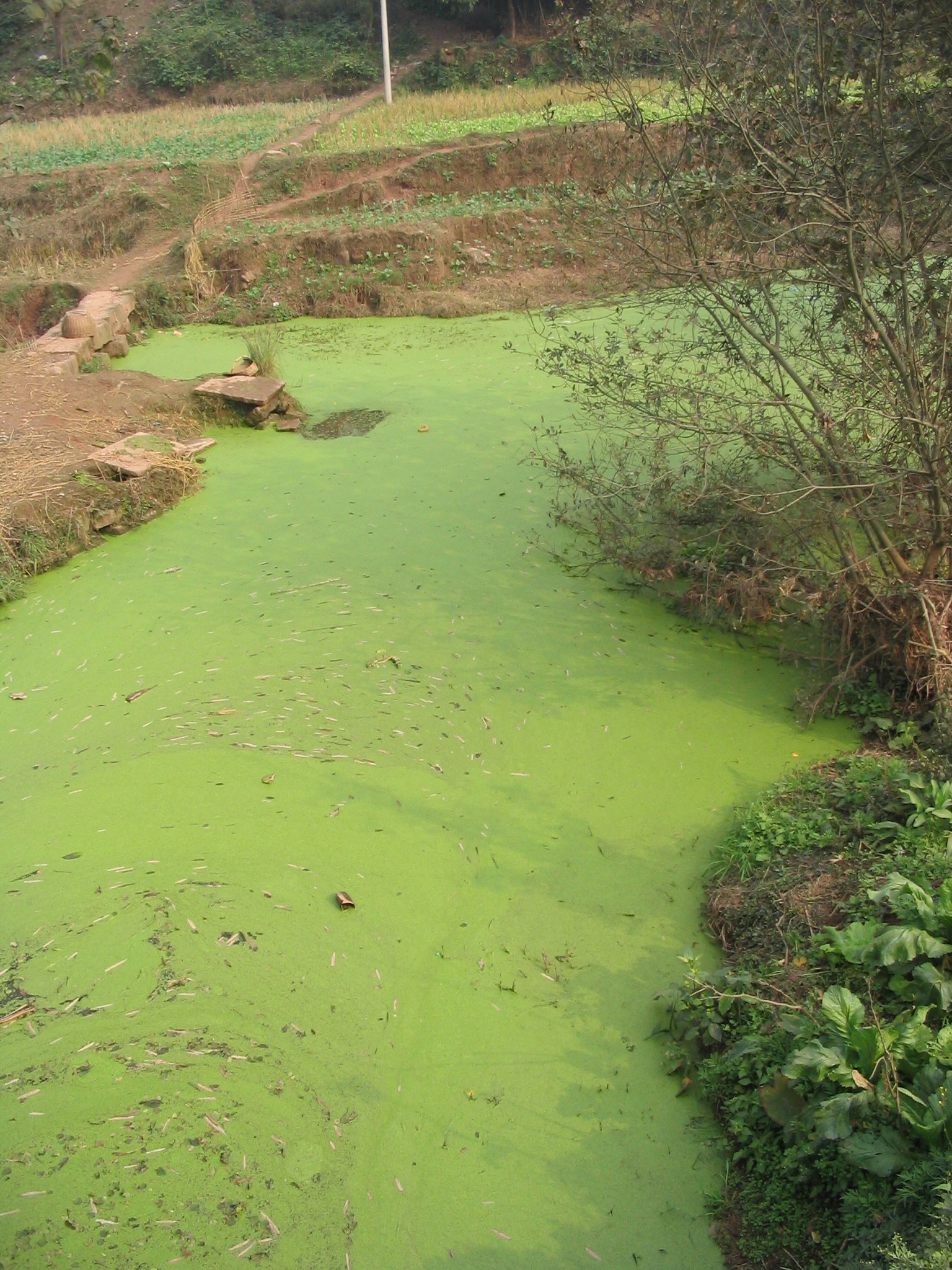
What is eutrophication? (Eutrophic water)
Too rich in nutrience, kills of oxygen causing the water to have a green film

What is Biological Oxygen Demand/ Biochemical oxygen demand? (BOD)
The amount of oxygen a quanity of water uses over a period of time at a specific temperature.
Usually, the colder the water ______ the biological oxygen demand
Higher
Whats an indicator species?
An animal or plant species that can be used to infer conditions in a particular habitat
ex) “if a trout can live in the water then the water is pretty healthy”

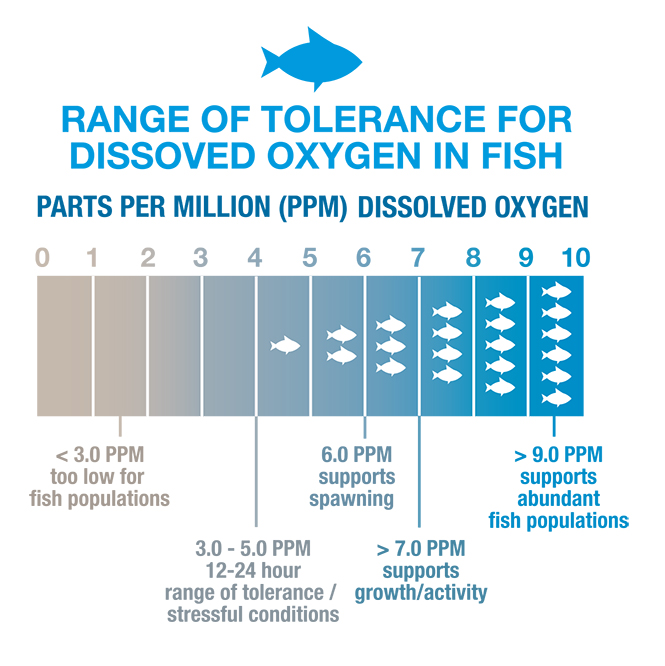
what does dissolved oxygen tests tell us about water quality?
It indicates the amount of oxygen dissolved in water which directly reflects the ability of a water body to support aquatic life
low oxygen levels can be lethal to many organisims
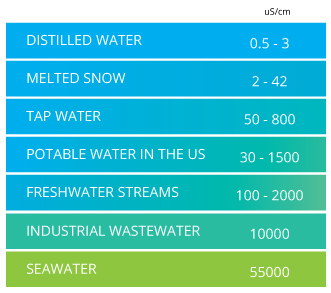
what does the conductivity levels tell us about water quality?
it tells us the amount of salt/minerals in the water
what does the turbidity levels tell us about water quality?
It tells us how clear the water is

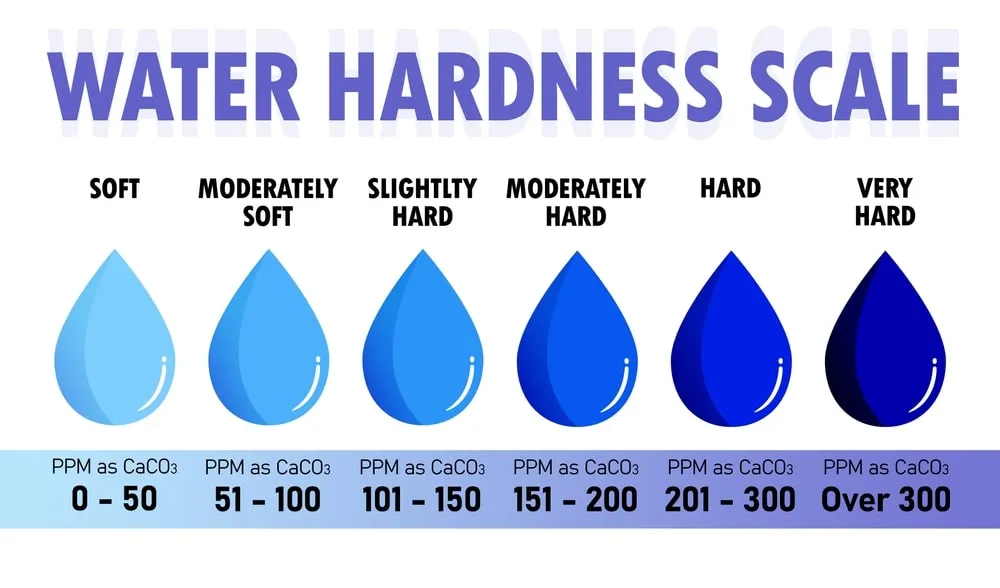
what does the hardness tell us about water quality?
Hard water contains high levels of minerals, while soft water has lower concentrations. Water hardness is an important water quality parameter that can have various effects on plumbing systems.
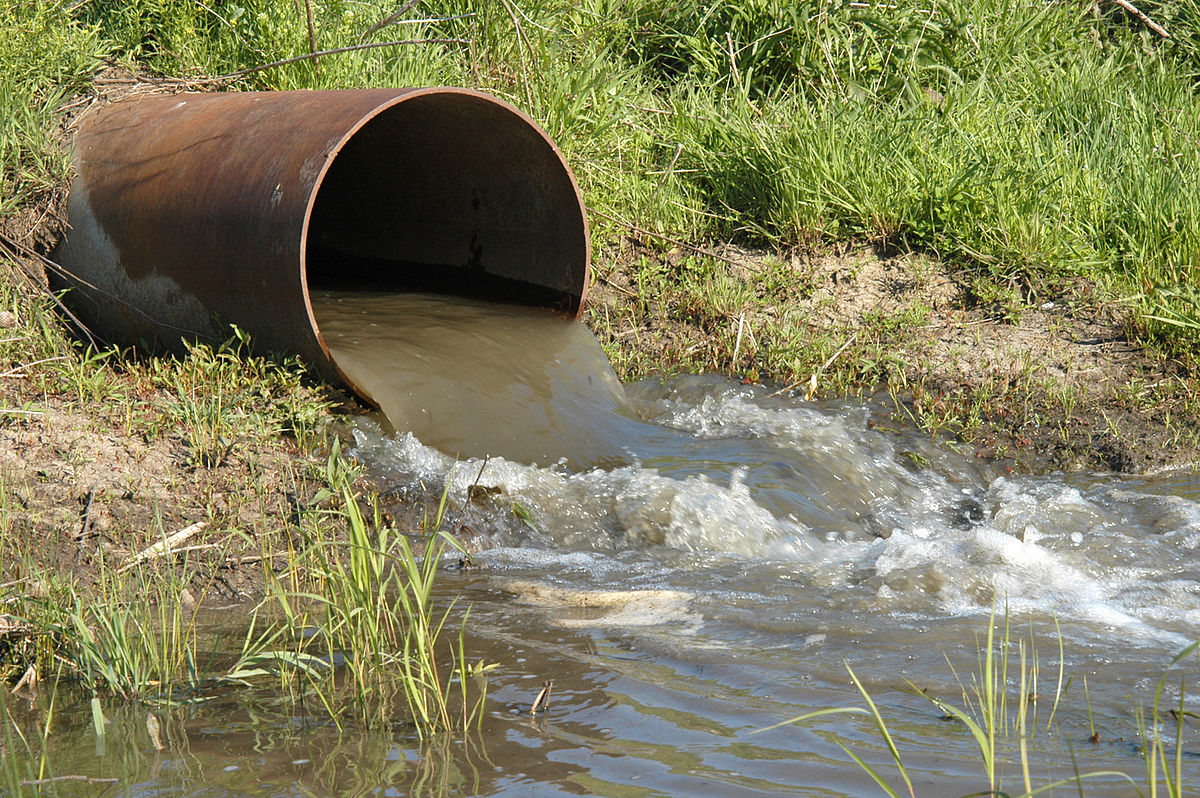
what is effluent?
Waste water


How can we disinfect water at a treatment plant?
chlorine
UV light
ozone
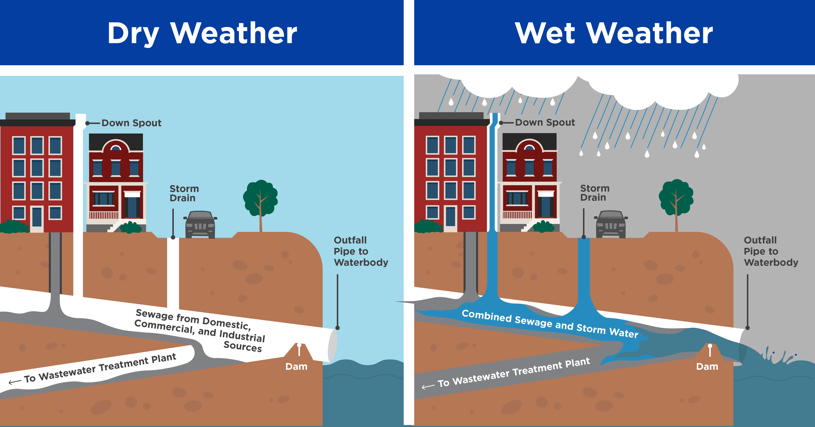
What are combine sewage/ storm water systems?
Older sewage systems allow overflow in rivers/ streams
What are the point sources of lead?
lead pipes- and the solder
lead paint
fuels (cars and airplaines)
toys and ceramics
Used as an additive in many things


How can we remove lead?
replacement of old pipes and paint
water filtration
laws and regulations
What are the health effects of lead?
fetuses and infants are the most sensitive to lead
Brain, nervous system and kidney damage
What are the point sources of arsenic?
natuarly occurring in the ground (dissolves into the groundwater)
mining waste

How can we remove arsenic?
water filtration
What are the health effects of arsenic?
Can cause cancer of the skin, lung, kidney, and bladder
What are the sources of mercury?
coal
garbage
industrial waste
What are the health effects of mercury?
Increases in toxicity as it moves up the food chain (biomagnification)
Damages the central nervous system
How can we remove mercury?
reduce coal usage
filters
electrochemical processes
What is acid deposition?
caused when sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are emitted into our atmosphere due to fossil fuel combustion. Breaks things down and is not good for plants, soils, rocks, and water.

What is acid mine drainage?
Water reaches the surface or subsurface mines, the land, and the acid drainage forms through the chemical reaction of the water with rocks that contain sulfur-bearing minerals, resulting in sulfuric acid.
Contaminated drinking water, disrupted growth/reproduction of aquatic plants/animals, corrosion on infrastructure, like bridges

What is a Persistent Organic Pollutants (POP)
hazardous organic chemical compounds that are resistant to biodegradation and thus remains in the environment for a long time.
(they wont leave you alone)
ex) DDT
What is pharmaceutical water pollution?
Medications and drugs being released into the water and this can have an impact on humans, animals, and the environment
ex) antibiotics, reproductive hormones, steroids, and non prescription drugs
Petroleum is _____ to wildlife and _________ to break down.
toxic, resistant
How can we remidiate oil spills?
vacuuming the oil out
dispurting the chemicals
burning
bioremediation (using biology to create something that would eat/ control the oil spillage)
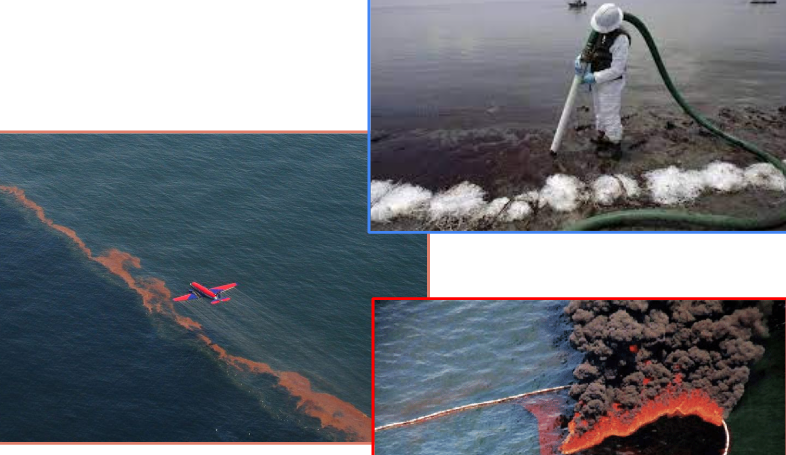


What is the source for solid waste pollutants?
garbage
sludge
plastics
coal ash (byproduct of coal being burned)
What are the effects of solid waste pollutants?
Can entangle ocean organisms and medical waste poses threats to humans on beaches


How can we solve the issue of solid waste pollutants?
Create laws and penalties for dumping
Fine those who violate
Public relations campaign

What is the source for sediment pollutants?
construction sites
poor farming practices
Both causing lots of erosion

What are the effects of sediment pollutants?
Decreases photosynthetic rates
Clogs gills of fish and bottom dwellers

How can we solve the issue of sediment pollutants?
Use silt fences at construction sites
Mandate riparian buffer zones near farms
silt socks
All create barriers to stop the erosion and dispersion of sediments.

What is the source for thermal pollutants?
Electrical power plants

What are the effects of thermal pollutants?
Thermal shock, which causes organisms to increase respiration rate

How can we solve the issue of thermal pollutants?
Monitor and regulate water temperature at power plants and manufacturing facilities
Require cooling towers or discharge lagoons
What is the source for noise pollutants?
The sounds emitted by ships and submarines
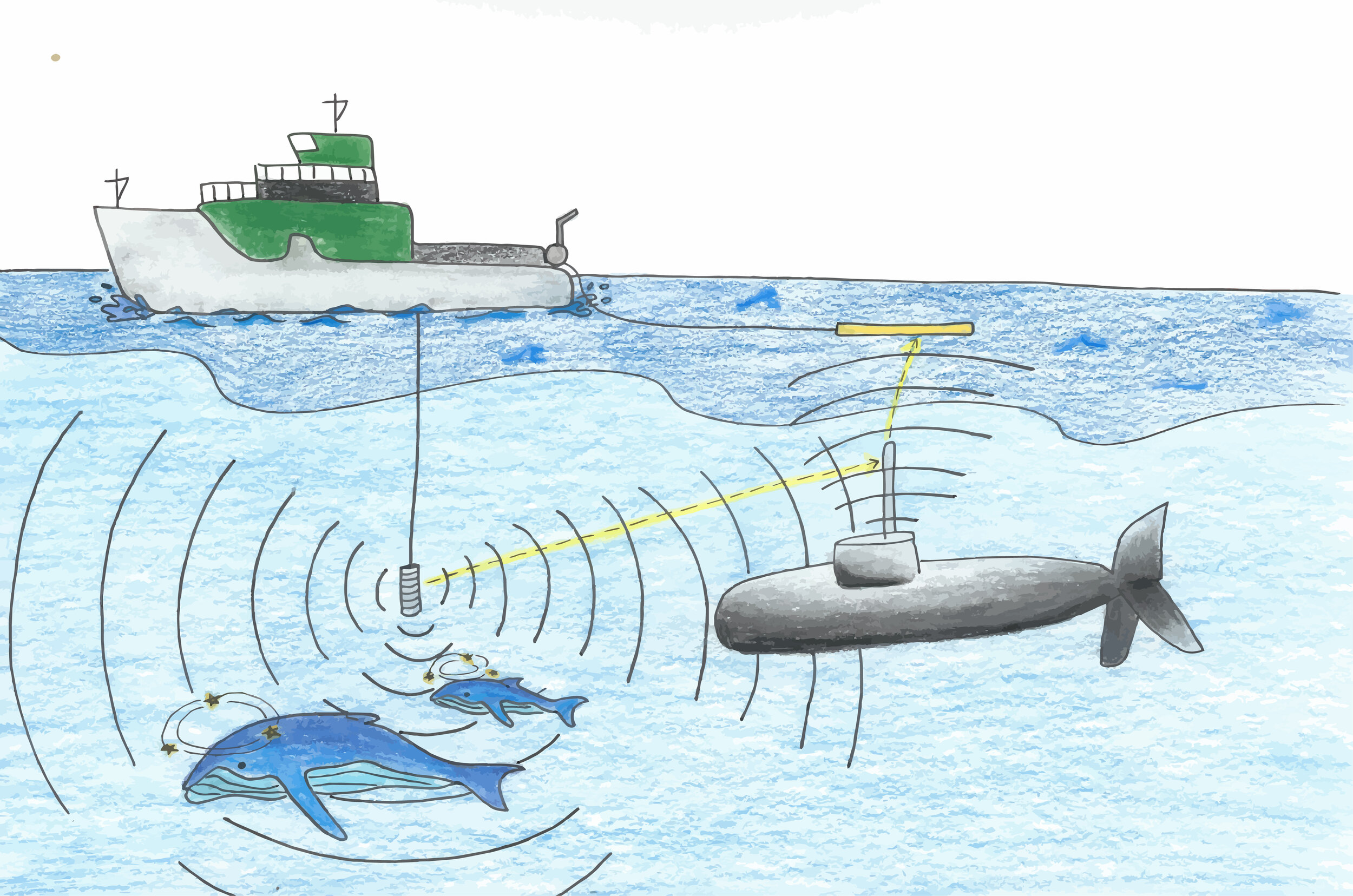
What are the effects of noise pollutants?
Interferes with animal communication
Beaching of dolphins and whales
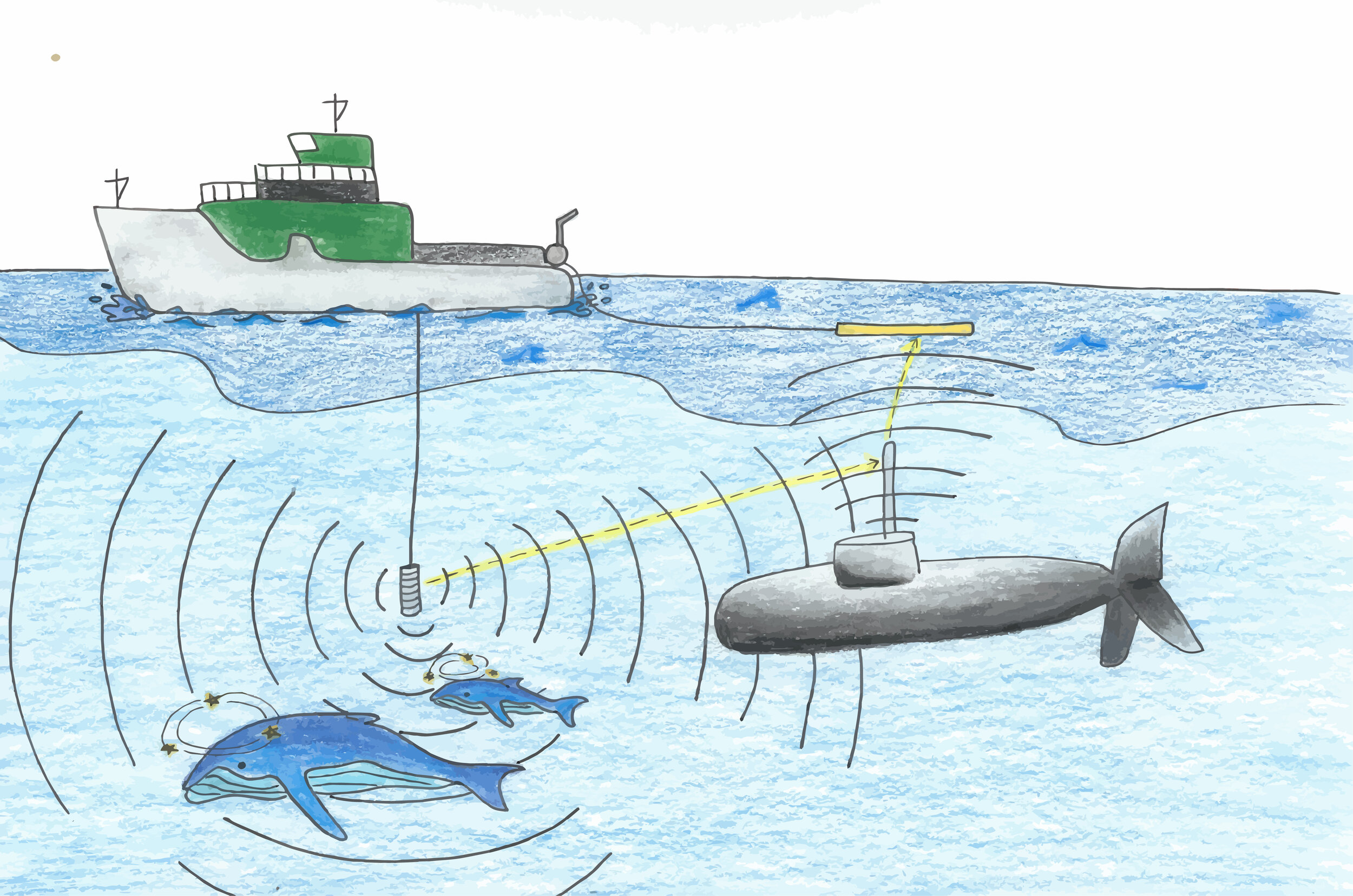
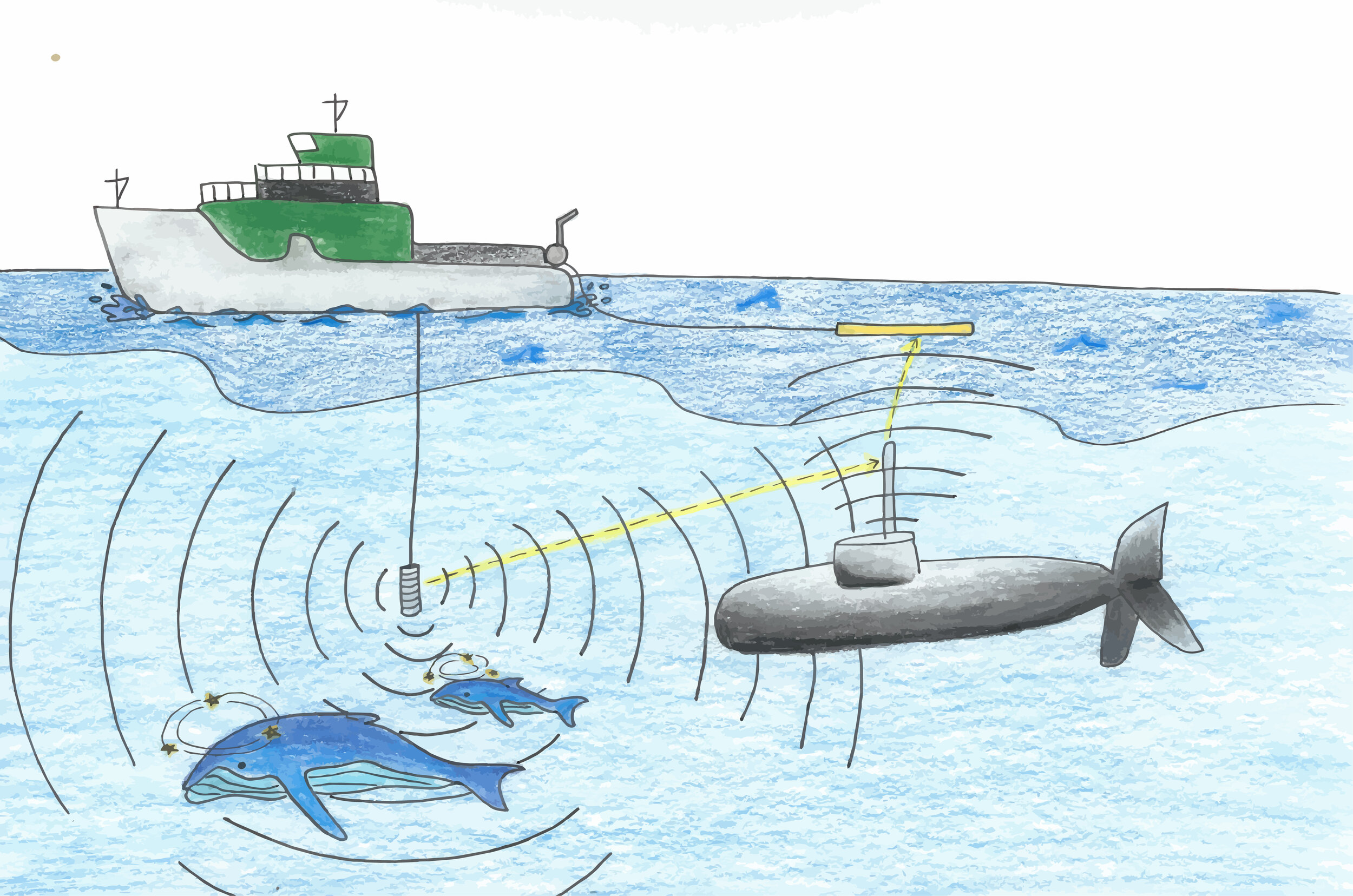
How can we solve the issue of noise pollutants?
require large ships to use quieter propellers
Describe the action of an endocrine disruptor.
Blocks the receptor protein binding site of a hormone so that the cell cannot receive a signal.
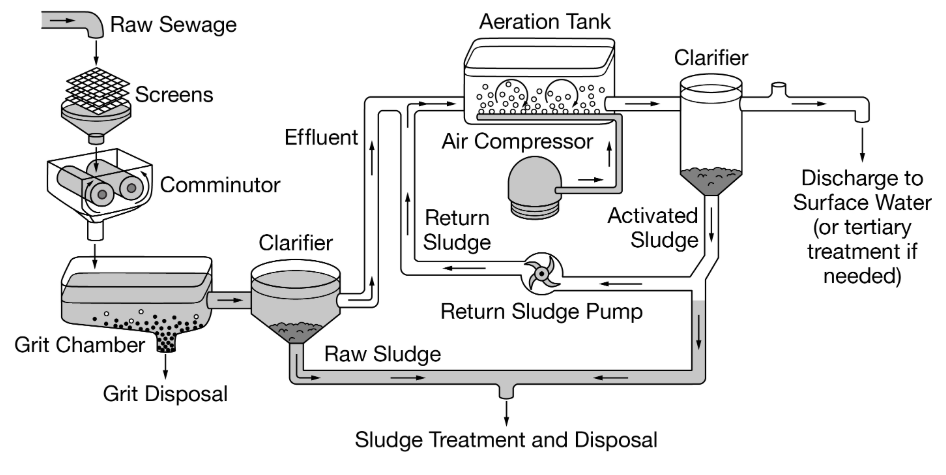
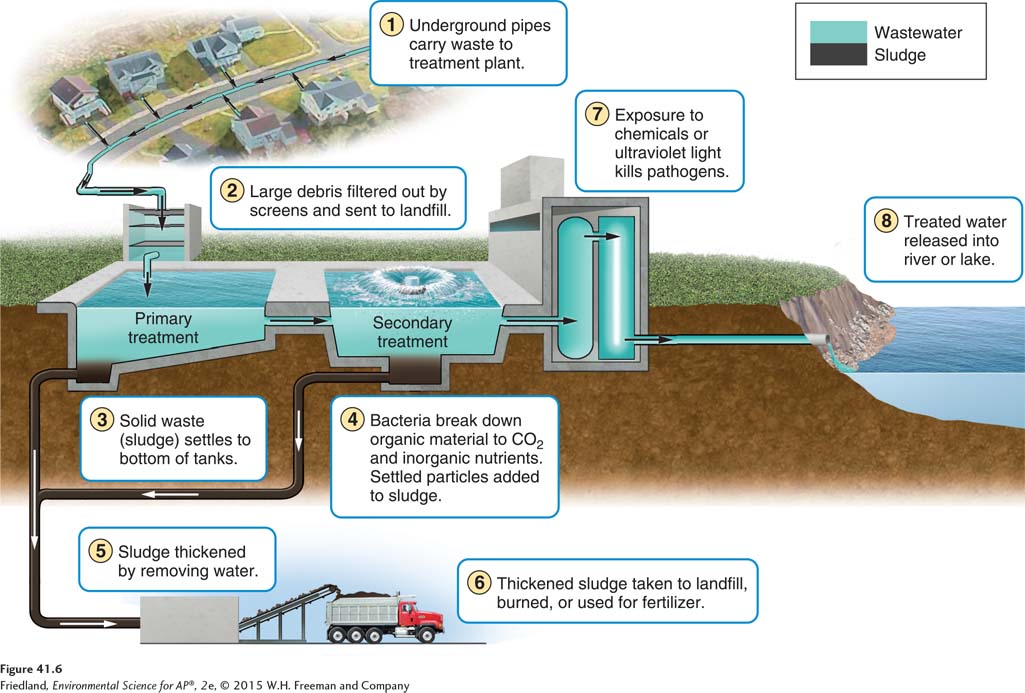
Based on the diagram, what is associated with the primary treatment of sewage?
Grit chamber
When water used to cool power plants during normal plant operations is released into adjacent waterways what will occur as a result?
The dissolved oxygen in the adjacent waterways would decrease causing fish and other organisms near by to die off

Give three reasons why Environmental scientists are concerned about wastewater as a pollutant.
1) large oxygen demand
2) makes the water more fertile
3) variety of disease-causing organisms
Inorganic Mercury is not super harmful, but when released into the environment, it becomes _____________ which is.
Methylmercury
Oligotrophic
low productivity
clear and little to no aquatic plants
high drinking water capability

Mesotrophic
average productivity
clear, with some aquatic plants

What is the clean water act?
Defines water quality standards that limit the amount of pollution that you put into waterways NOT ground water → created due to rivers catching on fire
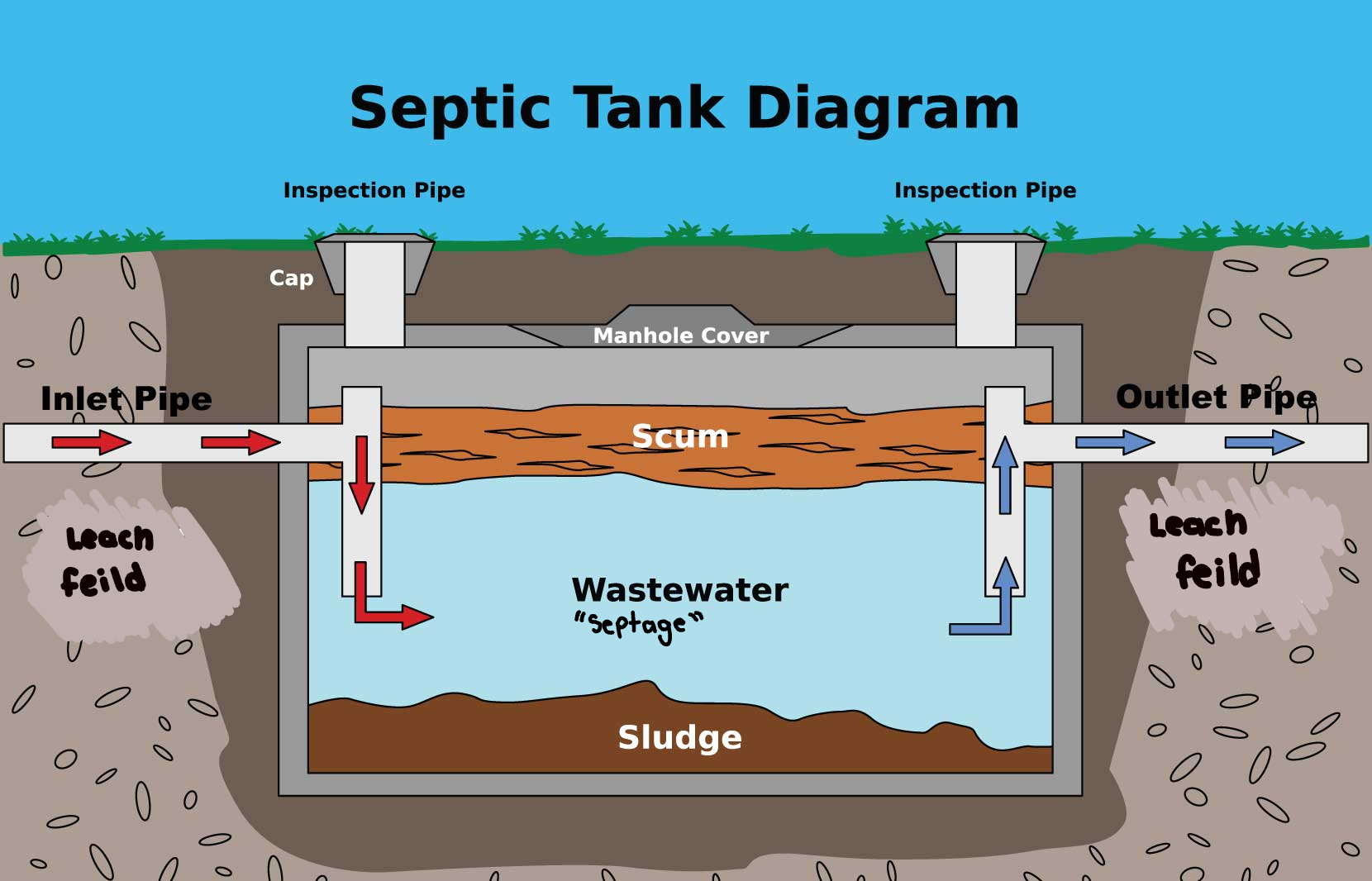
what are the names of the 3 layers in a septic tank?
1) scum (what is at the top of the tank)
2) septage (bacteria filter)
3) sludge (solid waste)
What is primary treatment in sewage treatment plants?
Sewage enters a treatment plant and first passes through a screen that removes large items like rags and sticks to prevent clogs. Then, it goes into a grit chamber where sand and small stones settle to the bottom.
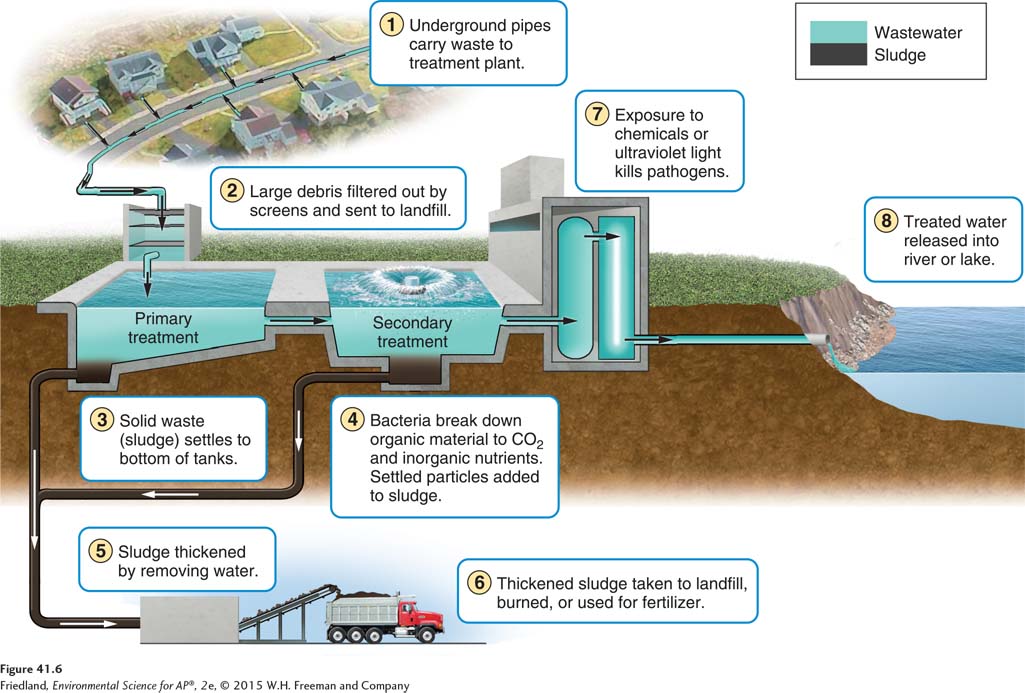
what is secondary treatment in sewage treatment plants?
Bacteria breaks down the solid waste
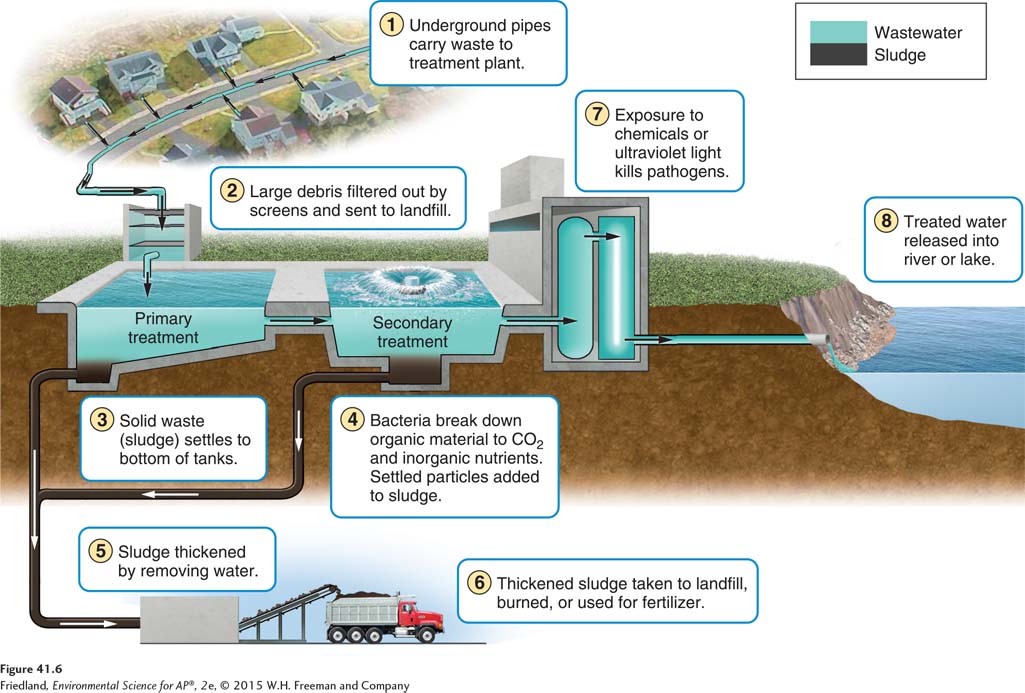
The final step before water is released is disinfection which
kills the pathogens using chemicals or ultraviolet light