bodily systems
Skeletal system
The skeleton is the internal framework of the human body
Is composed of 270 bones at birth and decreases to approximately 206 bones by adulthood after some fuse together
Bones to know
Cranium
Mandible
Clavicle
Pelvis
Fibula
Ulna
Calcaneus
Cervical
Sternum
Phalanges (of the feet)
scapula
Humerus
Femur
Tarsals
Sacrum
Coccyx
Ribs
Thoracic
Radius
Carpals
Metacarpals
patella
metatarsals
lumbar
phalanges (of the hands)
tibia
Vertebrae
Small bones making up the spine
Each vertebrae increases in size as you move down from the head to the waist
Each vertebrae has a hollow centre through which is the spinal cord passes
The spinal cord relies on the vertebrae for protection
Skeletal system functions
Allows movement
The skeleton allows movement of the body
Bones provide surfaces for the attachment of muscles
Bones allow muscles to pull on them to produce movement
Shape and protection
The skeleton gives the correct shape to our body
Bones protect internal organs and reduce the risk of injury on impact
rib cage protect the heart and lungs
Cranium protects the brain
Vertebra protects the spinal cord
Mineral storage
Bones store minerals such as calcium, iron, potassium and phosphorus
minerals will be released into the blood when the body needs them
Production of blood cells
Red and white blood cells are produced in the bone marrow (centre of most bones)
Red blood cells
Carry oxygen to muscles
Are red in colour due to haemoglobin
haemoglobin is a protein containing iron
Production is very high during growth years and decreases with age
White blood cells
Fight infection in the body
Muscular System
The muscular system is an organ system consisting of approximately 600 muscles
Muscles to know
Trapezius
Wrist flexors
Soleus
Biceps
Gluteus Maximus
Rectus abddonminus
deltoid
hamstrings
tibialis anterior
triceps
obliques
erector spinae
pectoralis major
gastrocnemius
quadriceps
latissimus dorsi
adductors
abductors
Muscular system functions
Create movement
muscles are responsible for the movements we make
muscles pull on bones to produce movement
Posture
Flexibility and strength are ket to maintaining proper posture
Poor posture can lead to joint pain and weaker muscles
Heat production
when muscles contract, they generate heat
the heat produced is vital for maintaining body temperature
Musculoskeletal system
Refers to the bones, ligaments, tendons and muscles
The collaboration between the skeletal and muscular systems gives the body it’s ability to move
Ligaments
Are a fibrous tissue that connect bone to bone
Ligaments provide stability at the point where the movement occurs
Tendons
Tendons are tough bands that connect muscles to bones
To create movement, muscles pull on tendons which pull on bones
Muscles contract (shorten) and pull on tendons which poll on bones
the pulling on the bones is what creates the movement
Flexion
A movement that decreases the angle between the bones at a joint
Extension
A movement that increases the angle between two body parts
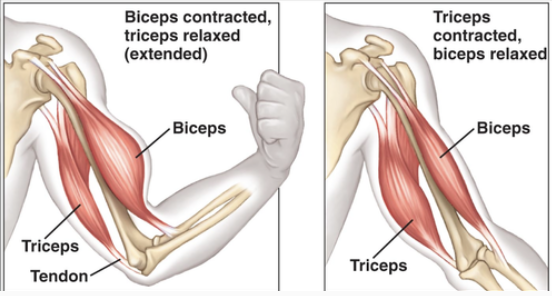
Reciprocal Inhibition
Skeletal muscles work in pairs to enable movement
When one muscle contracts, it’s pair relaxes
Agonist describes the muscle that contracts (shorten)
Antagonist describes the muscle that relaxes (lengthens)
Cardiovascular System
Also known as the circulatory system
Consists of the heart and blood vessels working together to transport gases and nutrients around the body
Functions of the cardiovascular system
circulates blood around the body
transports oxygen and nutrients to the cell
transports wastes (carbon dioxide) away from the cells
Maintains stable body temperatures
Blood vessels
Types of blood vessels include:
Arteries
Generally carry oxygen rich (oxygenated) blood
Always transport blood away from the heart to the body
Have elastic walls so they can expand to accommodate more volume
An artery has a thick, elastic, muscular walls
The Aorta is the largest artery in the body
the left ventricle pushes blood into the aorta and on to the rest of the body
Capillaries
The smallest type of blood vessel
The site where nutrients and waste are exchanged between the blood and the body cells
the exchange is extremely fast because of the thin capillary walls
A capillary has very thin walls that allows oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients to pass into the cells
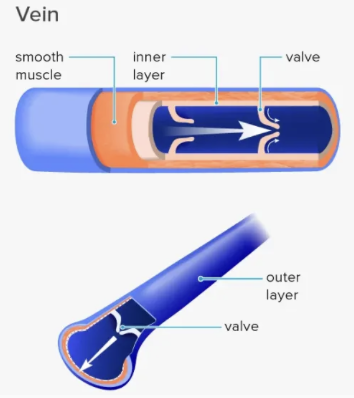
Veins
Generally carry blood with lower oxygen content and higher carbon dioxide content (deoxygenated)
Always transports blood from the body back to the heart (towards the heart)
Have thin walls and not as elastic as the walls of the arteries
Rely on skeletal muscles contracting to transport blood back to the heart
One-way valves prevent blood flowing in the wrong direction
The heart
is a pump designed to push blood throughout the cardiovascular system
Located slightly to the left of the chest (between the 2 lungs)
Protects by the rib cage
The adult heart is about the size of a large fist
Heart structure
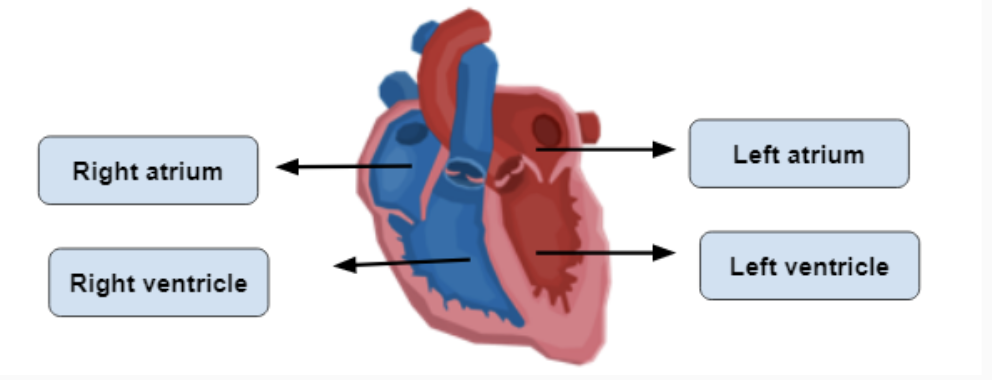
When looking at the heart, the left and right sides are opposite
The heart has four chambers - 2 atria and 2 ventricles
the atria are the upper chambers that receive blood
the ventricles are the lower chambers that pump blood
The septum divides the heart into 2 sides
the left has oxygenated blood for the body
the right has deoxygenated bloods that travels to the lungs for the removal of carbon dioxide
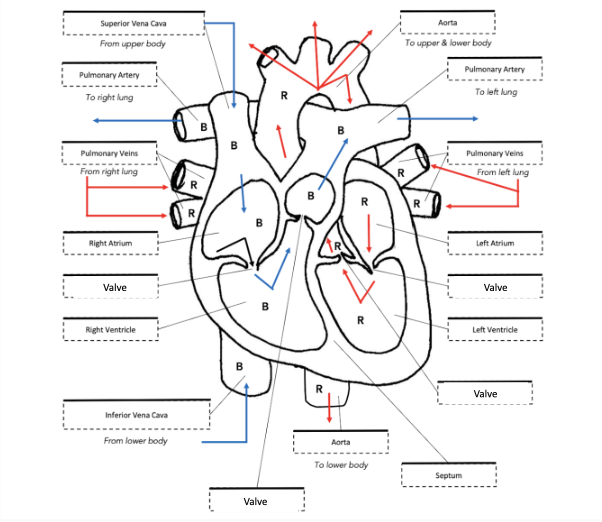
Pathway of blood
Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the vena cava
the superior vena cava collects blood from the upper regions of the body
the inferior vena cava collects blood from the lower regions of the body
Blood moves from the right atrium to the right ventricle
a valve between the atrium and ventricle opens to allow blood to move into the ventricle
The right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary artery to the lungs
a valve between the atrium and ventricle closes to prevent blood from moving in the wrong direction (i.e. back into the right atrium)
at the lungs, carbon dioixide, carbon dioixide is removed from the blood and oxygen is added
the blood is now oxygenated
the exchange of CO2 and O2 between the lungs and blood is called gas exchange
Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary vein into the left atrium
Blood moves from the left atrium to the left ventricle
A valve between the atrium and ventricle opens to allow blood to move into the ventricle
The left ventricle pumps blood through the aorta to the body
A valve between the aorta and ventricle closes to prevent blood from moving in the wrong direction (i.e. back into the left atrium)
Oxygenated blood is transported around the body delivering oxygen and nutrients to the bodies cells and collecting waste (CO2)
The exchange of CO2 and O2 between the blood and body cells occurs in capillaries and is called gas exchange
The blood is now deoxygenated and begins its journey back to the heart via veins
Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the vena cava
the superior vena cava collects blood from the upper regions of the body
the inferior vena cava collects blood from the lower regions of the body
Respiratory system
Includes the mouth, nose, throat, voice box, windpipe and lunch
It is specialised for gas exchange
Functions of the respiratory system
Brings air from the atmosphere into the lungs
transfer oxygen from the air into the blood
removes carbon dioxide from the blood
expels heat in the air exhaled
allows the vocal cords to create speech as is exhaled
The lungs
the lungs are the major organ of the respiratory system
lungs are located in the chest cavity behind the ribs
allows oxygen in the air to be taken into the body, while also letting the body get rid of carbon dioxide
Alveoli
are tiny air sacs within the lungs
the site where the lungs and blood exchange oxygen and carbon dioixde during breathing
The diaphragm
The diaphragm is a muscle of the respiratory system
it helps to inhale and exhale (breathe in and breathe out)
Breathing
Is the process of taking air into and expelling it from the lungs
Is broken into two phases
inspiration
expiration
Concentration
Breathing relies on the tendency for air particles to naturally move from areas where there is a high amount of them (high pressure) to areas where there is a lower amount of them (low pressure)
Inspiration
Also known as inhalation
The process where air is drawn into the lungs
the diaphragm muscle contracts, moving downwards
the muscles between ribs (intercostal muscles) contract, increasing the size of the chest cavity
Steps 1 and 2 cause the pressure in the lungs to decrease
Air is drawn into the lungs as gases move from low to high pressure areas
Expiration
Also known as exhalation
the process where air is expelled from the lungs
the diaphragm muscle moving upwards
the muscles between ribs (intercostal muscles) relax, decreasing the size of the chest cavity
steps 1 and 2 cause the pressure in the lungs to increase
air is forced out of the lungs as gases move from high to low pressure areas
Gaseous Exchange
The process where gases move across a surface without the use of energy
Examples:
between the alveoli and capillaries at the lungs
between the capillaries around skeletal muscles and muscle cells
Concentration
Gas exchange relies on the tendency for gas molecules to naturally move from areas molecules to naturally move from areas where they are in a high concentration (lots of them) to areas of a lower concentration (less of them)
Gaseous exchange
Between the alveoli and capillaries at the lungs
allows deoxygenated blood to oxygenated
carbon dioxide moves from the capillaries to the alveoli
oxygen moves from the alveoli into the capillaries
between the capillaries around skeletal muscles and muscle cells
oxygenated blood becomes deoxygenated
carbon dioxide moved from the muscle cells to the capillaries
oxygen moved from the capillaries into the cells
Menstruation
the female body is biologically designed to have babies
A period signifies that the body has prepared itself to to be able to hold a ertilised egg and make a baby
The menstrual cycle
is the time between one period and the next
on average lasts 28-30 days
everyone’s cycle is different a cycle can range from 21-35 days
stages
mensuration
follicular phase
ovulation
luteal phase
Stage 1: Menstruation phase
the stage where people get their period (bleed)
considered the beginning of the menstrual cycle
commonly lasts for around five days, but can be as short as 2 days or as long as 7
the uterus is shedding its lining that has built over the last 28 days.
All hormone levels are low
it’s common to feel tired, irritable and moody
Low intensity movement, such as swimming, yoga, walking or cycling
reduce salt intake - to reduce fluid retention, abdominal bloating, breast swelling and pain
reduce caffeine intake - can reduce irritability, poor sleep and menstrual cramps
increase consumption of omega - 3 fatty acids (fish, calcium and vitamin D)
drink more water
Products:
people can use period products to abdosrb bleeding
e.g:
pads
tapons
menstrual cups
period underwear
Stage 2 follicular Phase
around 11 to 20 ovarian follicles begin developing, but only one fully matures into an ovum (egg)
uterus lining (endometrium) begins to thicken
hormones are realsed
common to feel more energetic and happy
the body is primed for maximal training efforst, such as high intensity training
appetite may be reduced
intake more healthy carbs and fats support higher energy demands
iron rich foods such as freen leaft vegetables, legumes and lean meats - nourish reproductice organs and support r4egular mensturation
Stage 3 : ovulations phase
usually happens once each month, about 2 weeks before the next period
can last from 16-32 hours
an ovum (egg) is released from an ovary and moves along a fallopian tube towards the uterus
occurs when a sperm fertilises an ovum
an ovum will survive up to 24 hours
if sperm reaches the ovum during this time, pregnancy may occur
people may feel more sensitive to emotional trigger which can lead to feelings of irritability or sadness
similar to follicular phase
the body is primed from maximal training efforts, such as high-intensity training
appetite may be reduced
healthy carbohydrates and fats - support higher energy demands while also maintaining stable blood glucose levels
foods high in fibre - can reduce levels of oestrogen
stage 4 luteal phase
caused by increase in hormon levels:
thickening of uterus lining (endometrium)
slight increase in overall body temperature
irritability, depressed mood, anxiety and mood swings.
some people will also feel sluggish and absent-minded.
Switch to low-intensity movement with more recovery time than usual.
Appetite may be increased and cravings are common.
Complex carbohydrates and high fibre foods - will increase the sense of fullness for longer.
Consume dark chocolate, fruit and nuts - effective substitutes for sweet cravings.