Bio 119 Exam 3
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Which group is that to which the mighty oaks belong?
Rosids
Which group is that from which we derive pumpkins and chocolate?
Rosids
Which group is that from which we derive coffee?
Asterids
Which group is that from which we derive bay leaves and cinnamon?
Basal Angiosperms
Which group is that from which we derive blueberries?
Asterids
Match the following taxonomic rank name endings with the rank they indicate. Class
-opsida
Match the following taxonomic rank name endings with the rank they indicate. Phylum
-phyta
Match the following taxonomic rank name endings with the rank they indicate. Family
-aceae
Match the following taxonomic rank name endings with the rank they indicate. Order
-ales
Poaceae
Graminae
Fabaceae
Leguminosae
Asteraceae
Compositae
Lamiaceae
Labiaateae
Brassicaceae
Cruciferae
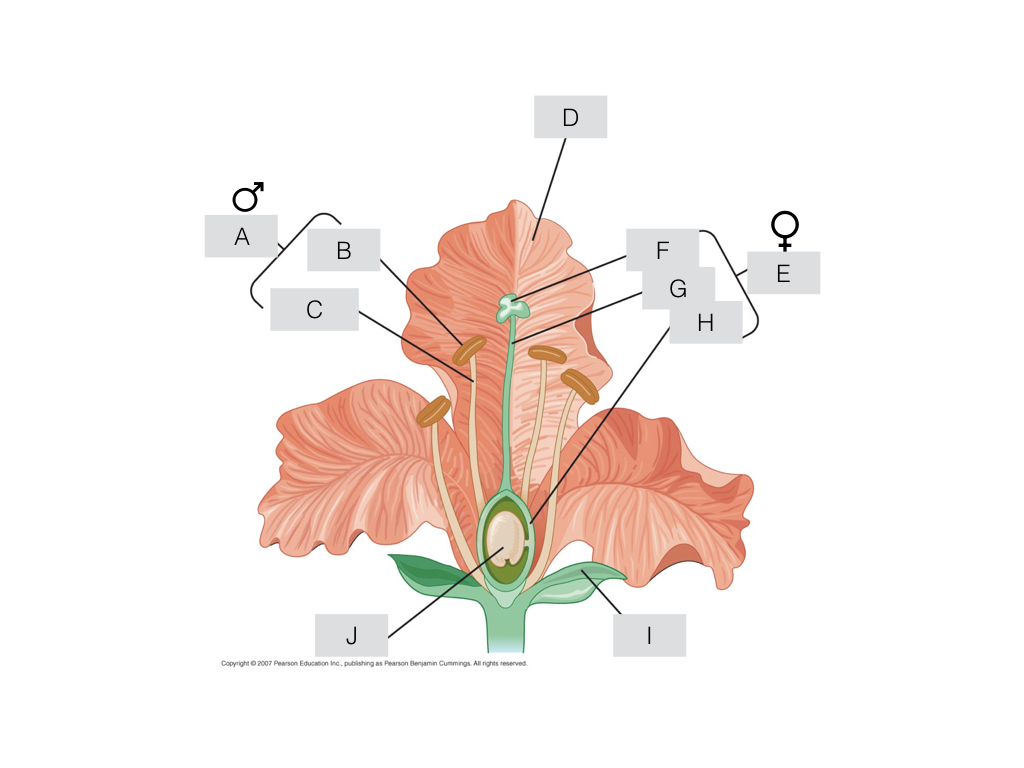
Match the parts of the flower diagram above with its proper name from the list provided below.
filament, stamen, anther, stigma, sepal, carpel, ovule, ovary, style, petal
endosperm
the result of double-fertilization, which serves as the nutrient source for the embryo of an Angiosperm
Polar nuclei
a part of the megagametophyte that fuzes with a sperm cell to create the endosperm
triploid
a cell that contains 3 copies of each of its chromosomes
monocots
a group of Angiosperms that includes the grasses and their relatives
eudicots
a group of Angiosperms that includes the Rosids and the Asterids and their close relatives
biotic
living, used to refer to pollinators that are animals
abiotic
non-living, used to refer to pollinators like wind and water
Angiosperms size order
Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae, Rubiaceae, Poaceae
sepals
protect the flower in bud
petals
serve as advertisement for pollinators
stamen
comprised of the anther and filament, the male reproductive parts
carpel
comprised of the stigma, style, and ovary, the female reproductive parts
Which group is that from which we derive black pepper?
Basal Angiosperms
Which group is that from which we derive wheat, rice, and corn?
Monocots
Which group is that from which we derive potatoes, tomatoes, and peppers?
Asterids
Chytridiomycota
a phylum of fungi that's primarily aquatic with flagellated zoospores; responsible for recent declines in amphibian species
Zygomycota
a phylum of fungi exemplified by bread mold
Ascomycota
a phylum of fungi that includes truffles, morels, and chestnut blight
Basidiomycota
a phylum of fungi that includes mushrooms, rusts, smuts, and puffballs
crustose lichen
a lichen that appears as flat, two dimensional coloring on the substrate it's growing upon
foliose lichen
a lichen that appears leafy, closely appressed to the substrate it's growing upon
fruiticose lichen
a lichen species that appears as a "bushy" clearly three dimensional entity such as reindeer moss or old man's beard
zygotic meiosis
a life cycle in which the organism is largely haploid wherein the zygote undergoes meiosis to restore the haploid state
meiotic gametogenesis
a life cycle in which the organism is largely diploid with specialized structures that produce haploid gametes by meiosis
sporic meiosis
a life cycle in which a diploid phase produces spores by meiosis and a haploid phase produces haploid gametes by mitosis
phycobiont
the algal partner in a lichen
mycobiont
the fungal partner in a lichen
mycorrhiza
a symbiotic relationship between fungi and the roots of plants
lichen
a symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae
Thigmotropism
tropism caused by either the hormone auxin promoting cell elongation or by diffusion and osmosis
(T or F) Tropisms that result from the movement of ions followed by osmosis are reversible as opposed to those that result from differential cell elongation which are non-reversible
true
(T or F) Phototropism involves auxin stimulating cell elongation on the lighted side of a plant resulting in growth of the stem toward the light.
false
(T or F) Phototropism involves auxin stimulating cell elongation on the shady side of a plant resulting in growth of the stem toward the light
true
(T or F) Gravitropism occurs in response to the action of auxin promoting cell elongation.
false
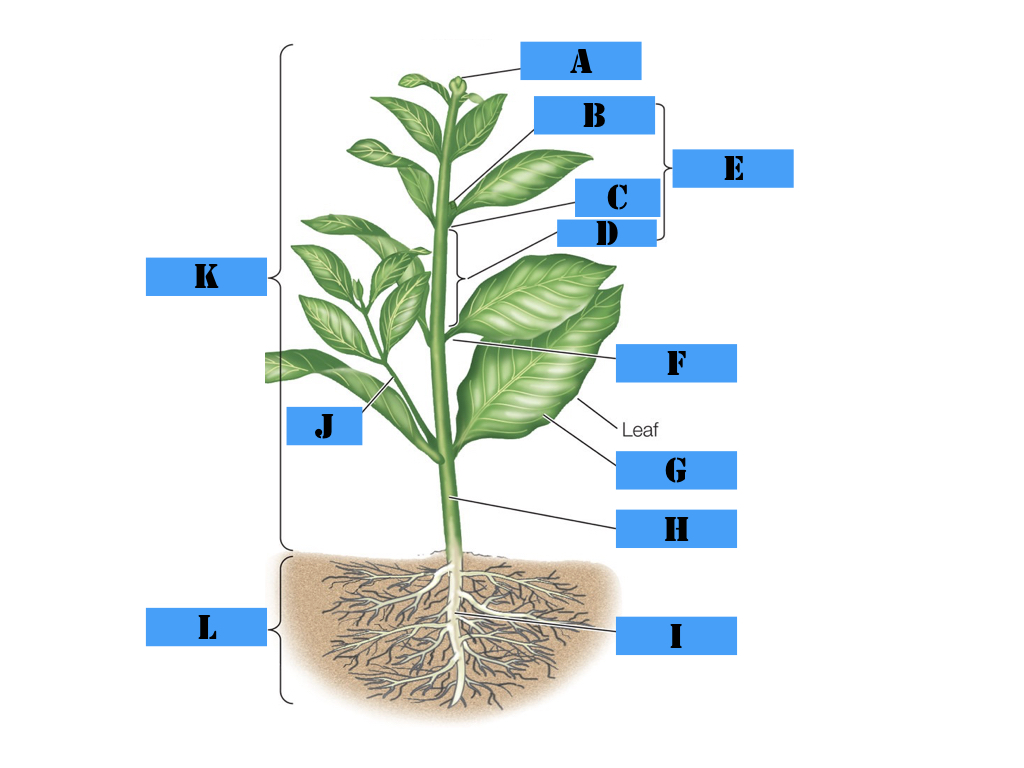
Plant Structure Labeling
axillary bud, petiole, blade, internode, root system, terminal bud, shoot system, node, phytomer
(T or F) Gravitropism occurs in response to the action of auxin inhibiting cell elongation
True
(T or F) When guard cells swell with the influx of water stomata are opened, and the loss of water from guard cells causes stomata to close
True
Tropisms that result from the movement of ions followed by osmosis are non-reversible as opposed to those that result from differential cell elongation which are reversible
False
This tropism is caused by the hormone auxin inhibiting cell elongation
gravitropism