The Skull
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Skull is formed by cranial and facial bone
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Cranium
A hollow cavity in the skull that protects the brain composed of 8 cranial bones
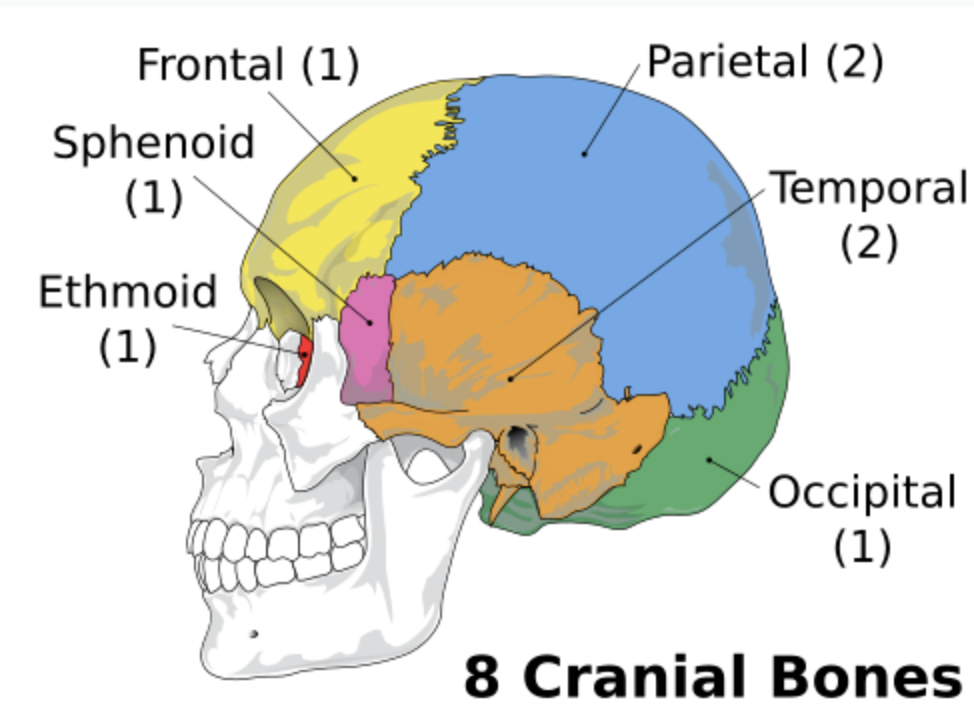
Cranial bones
The cranium is composed of 8 bones
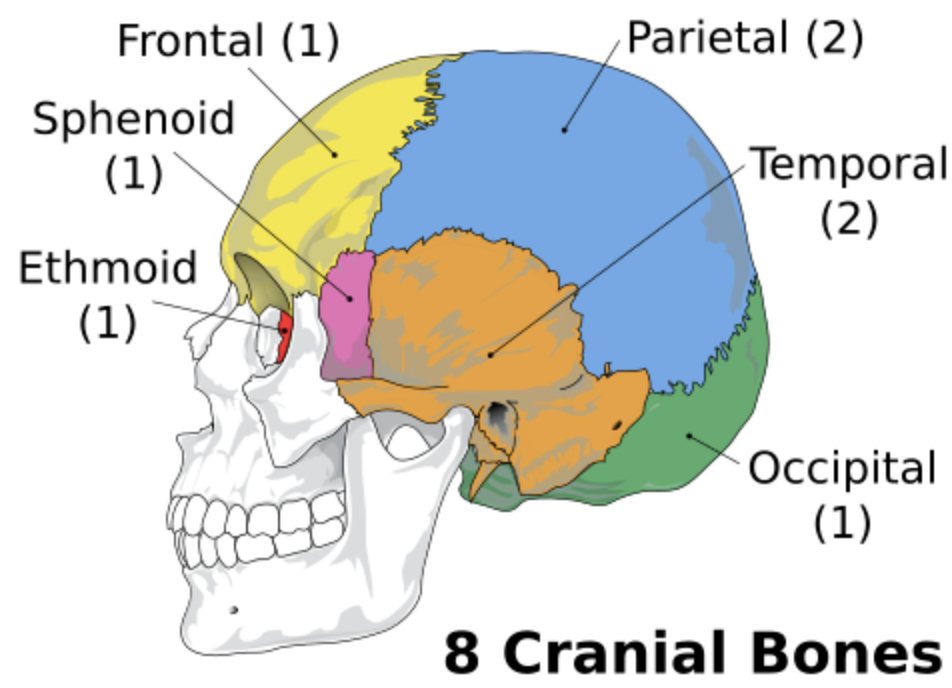
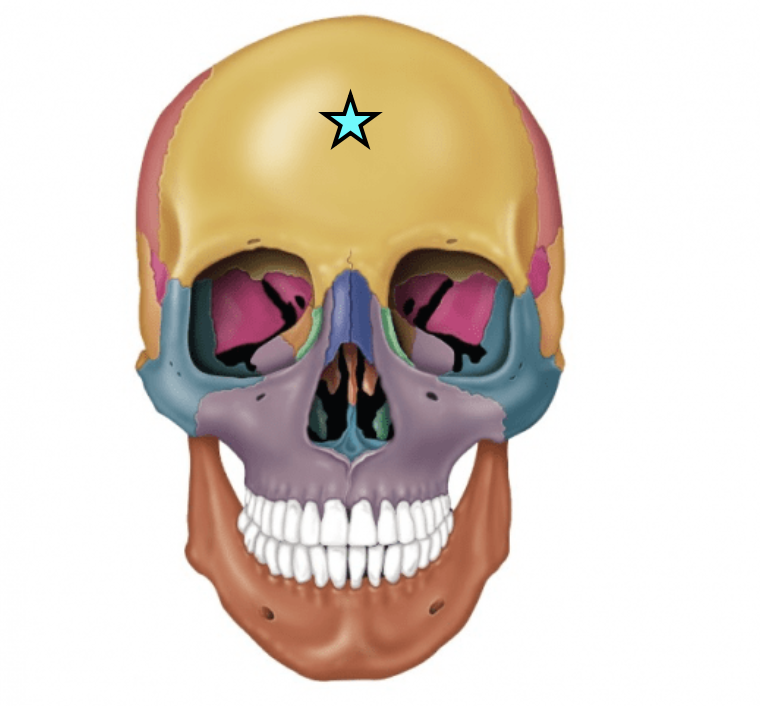
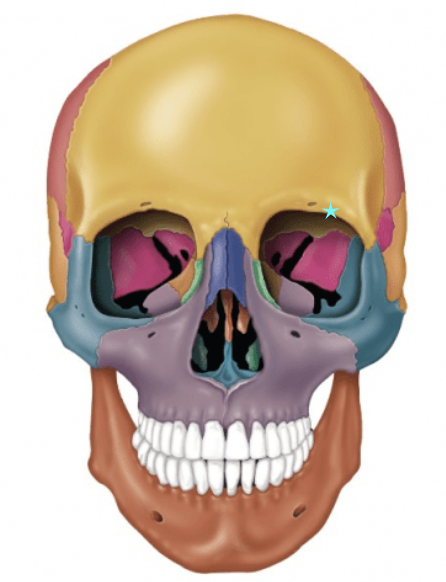
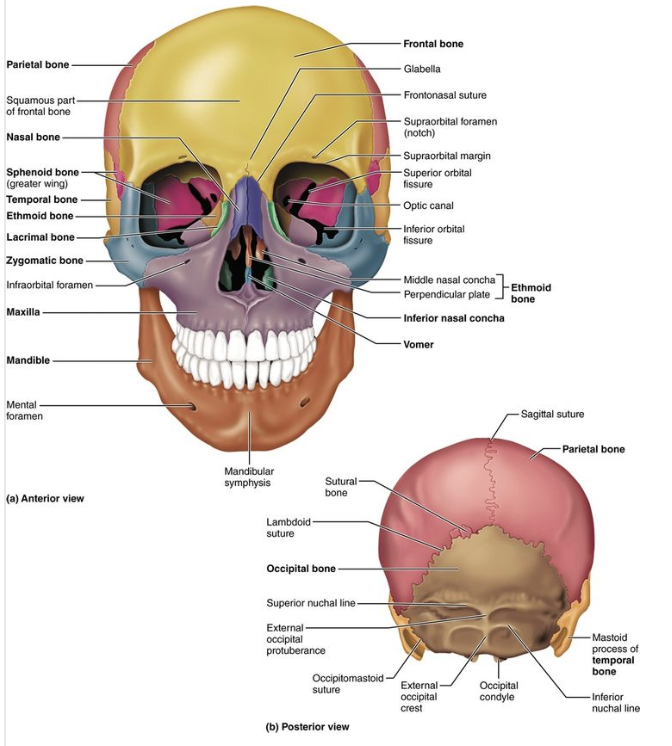
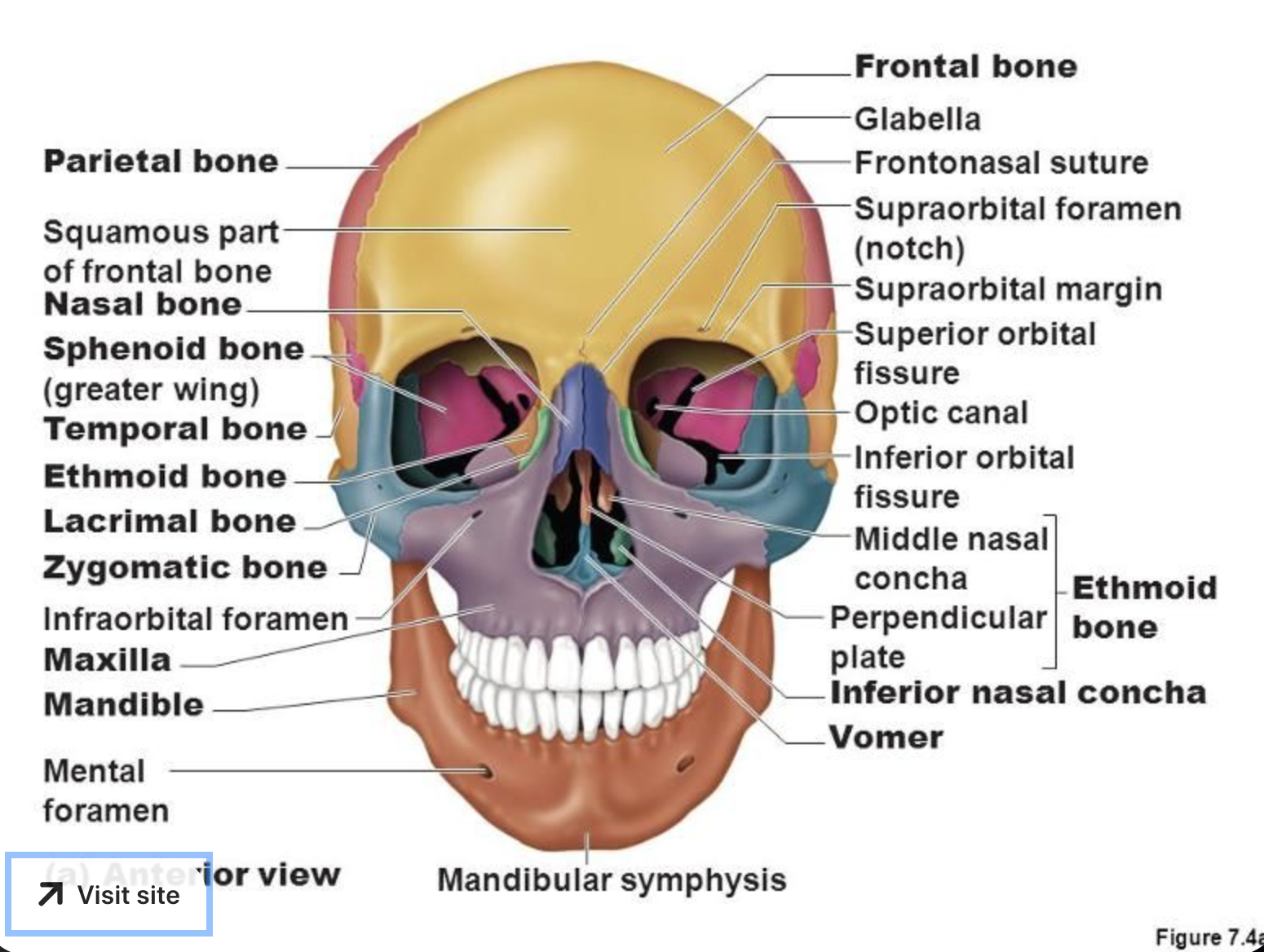
Frontal bone
Protects the frontal lobe of the brain
Parietal bone (Left and Right)
Forms the superior and lateral aspects of the skull
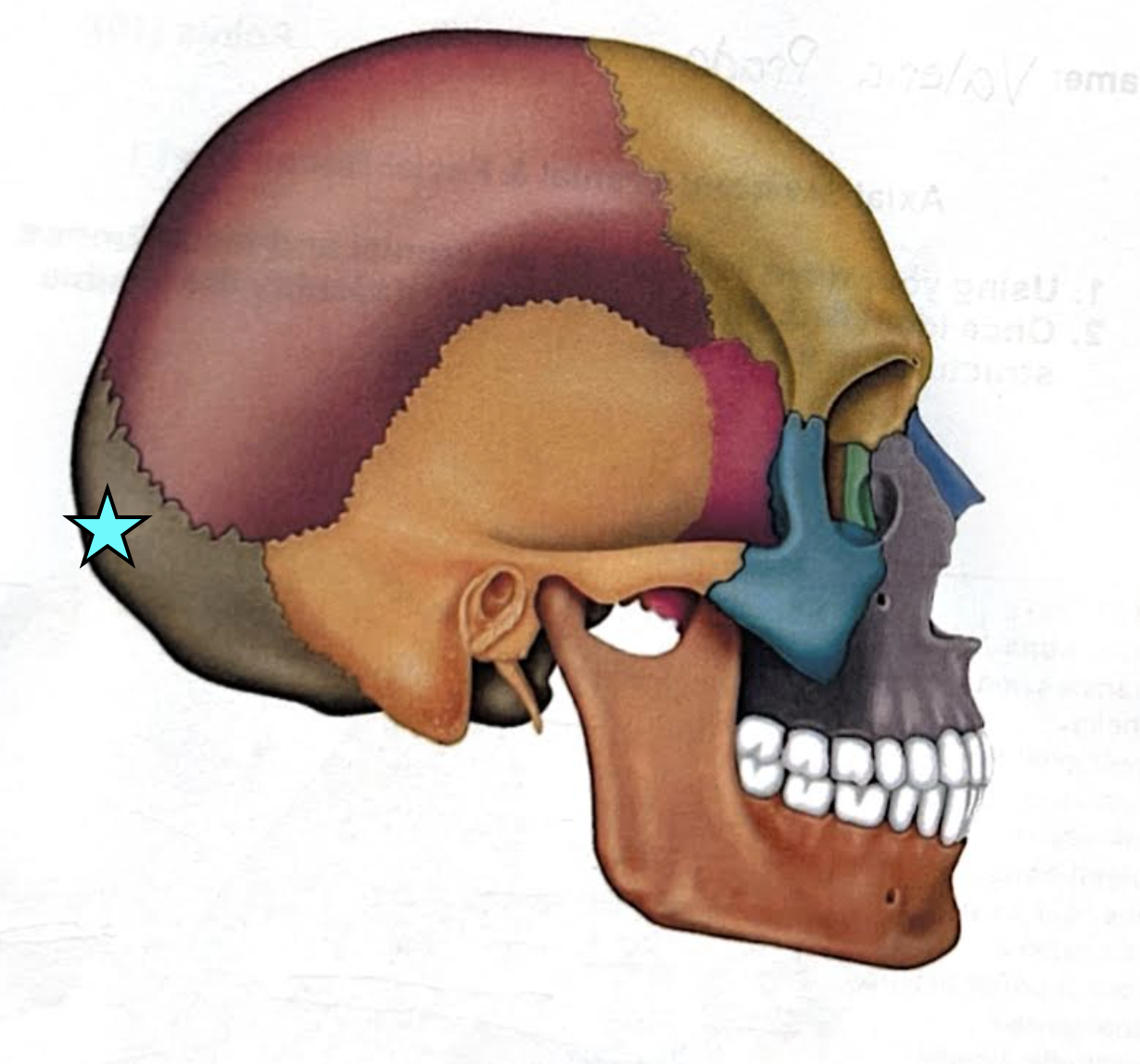
Occipital bone
Forms the posterior aspect and most of the base of the skull
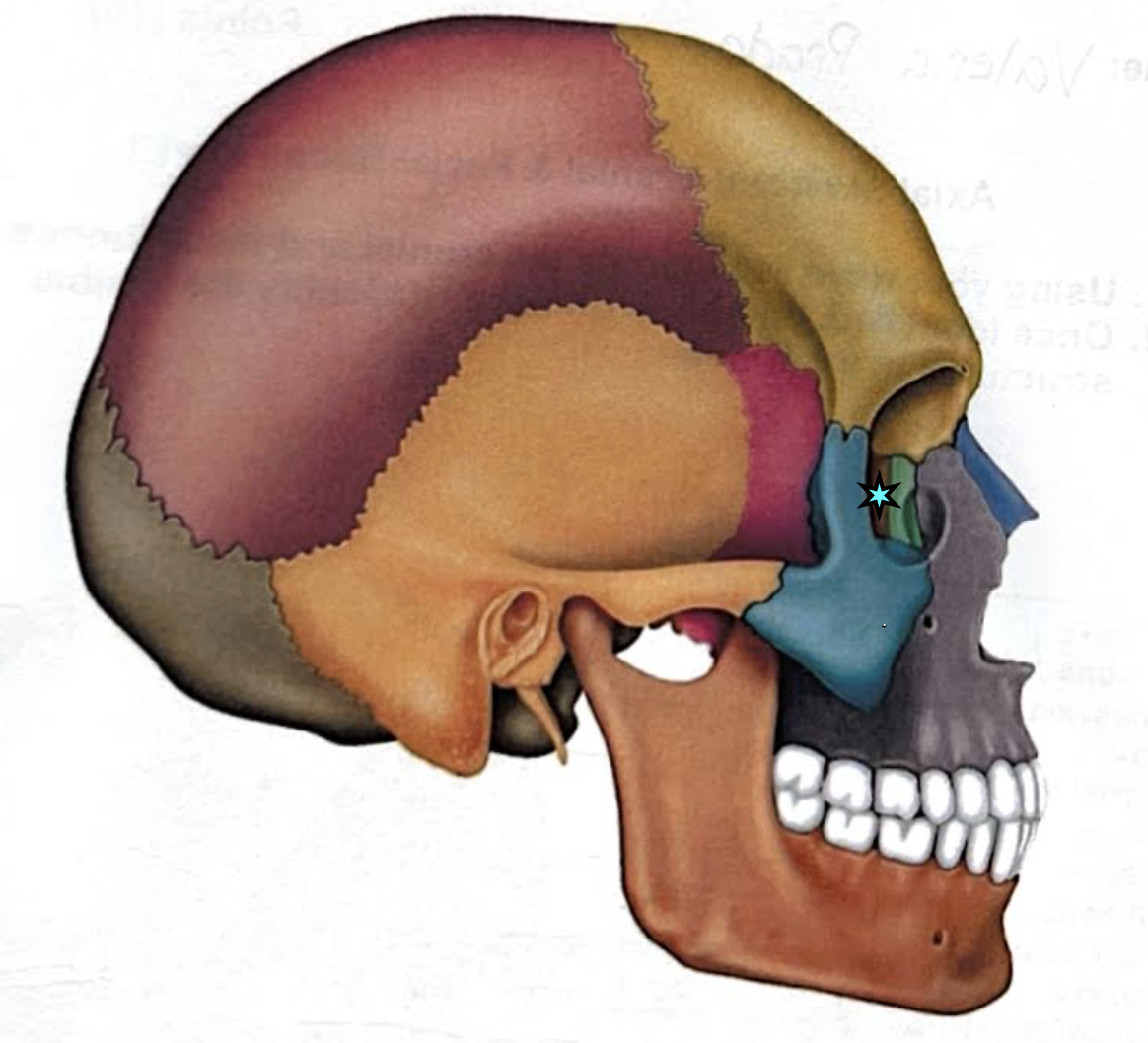
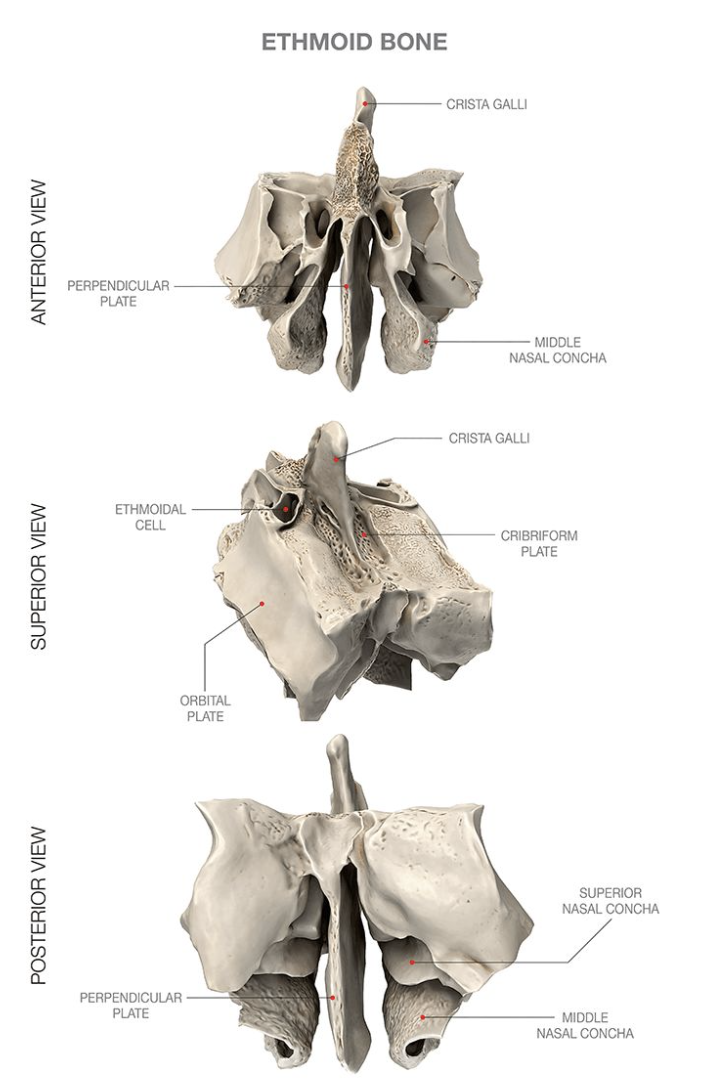
Ethmoid bone
Contributes to the anterior cranial fossa
Forms part of the nasal septum and the nasal cavity
Contributes to the medial wall of the orbit
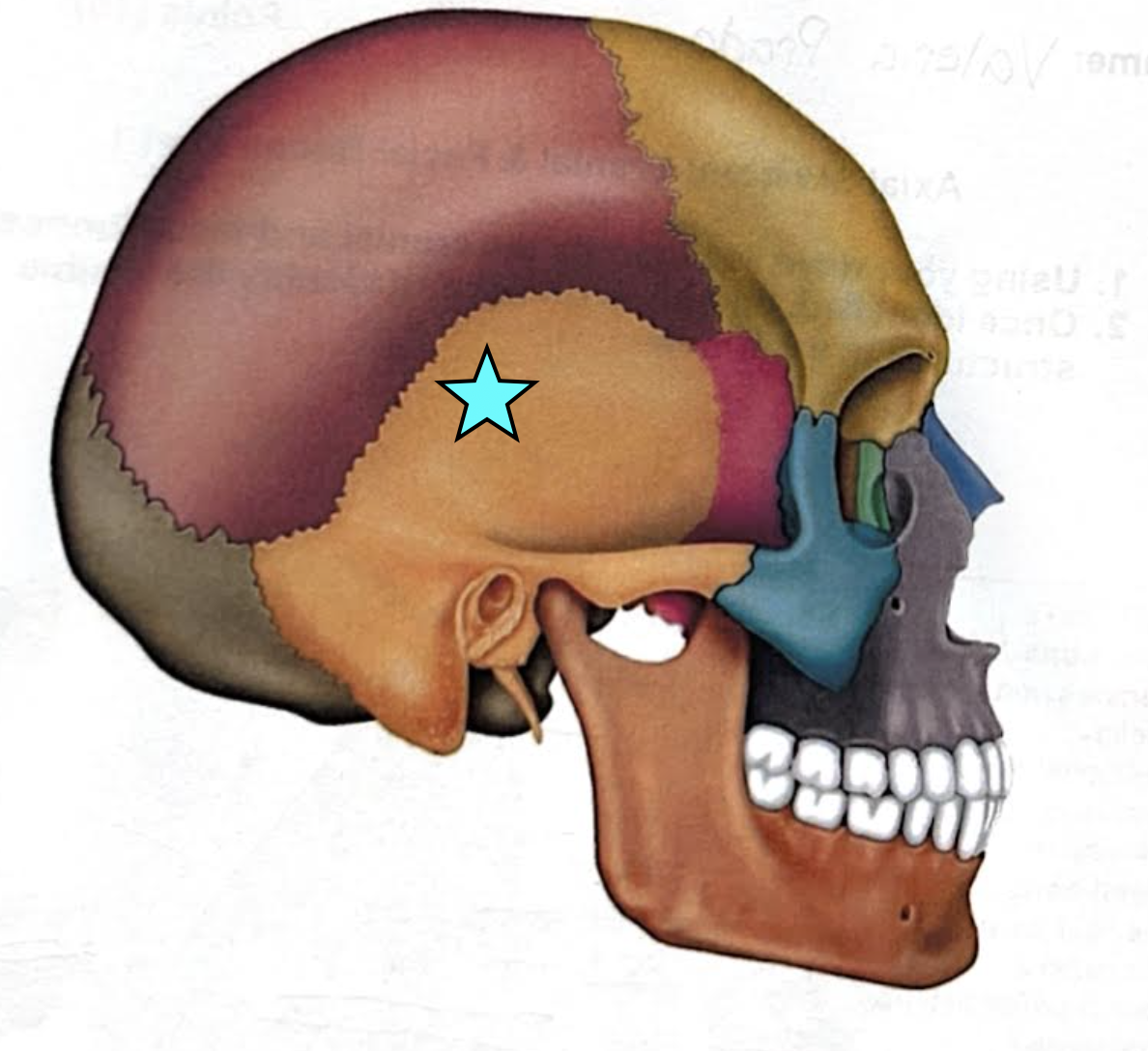
Temporal bones (Left and Right)
Forms the inferolateral aspects of the skull and contributes to the middle cranial fossa
Each has a squamous, tympanic, and petrous part
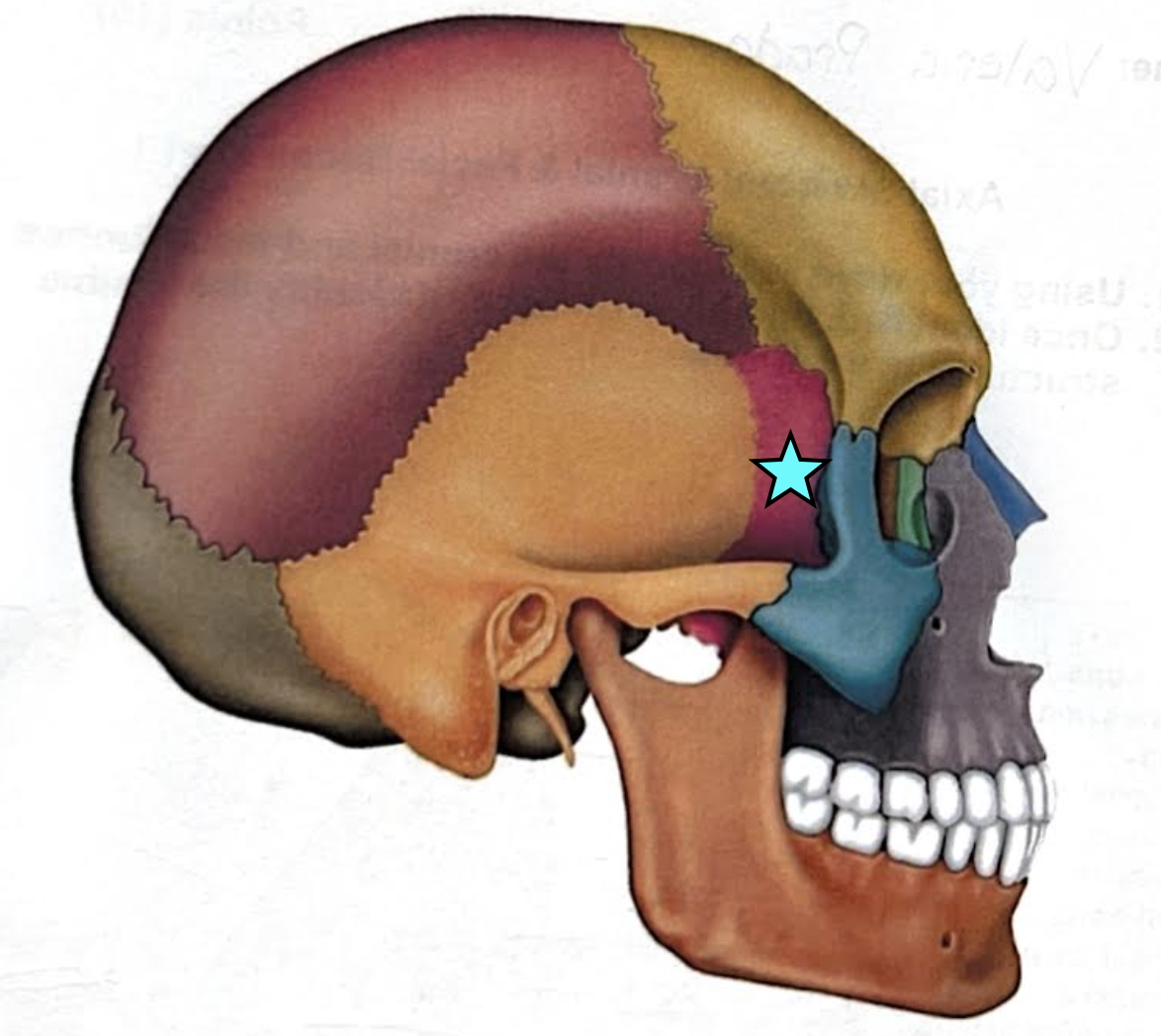
Sphenoid bone
Bat-shaped bone that is described as the keystone bone of the cranium because it articulates with all other cranial bones
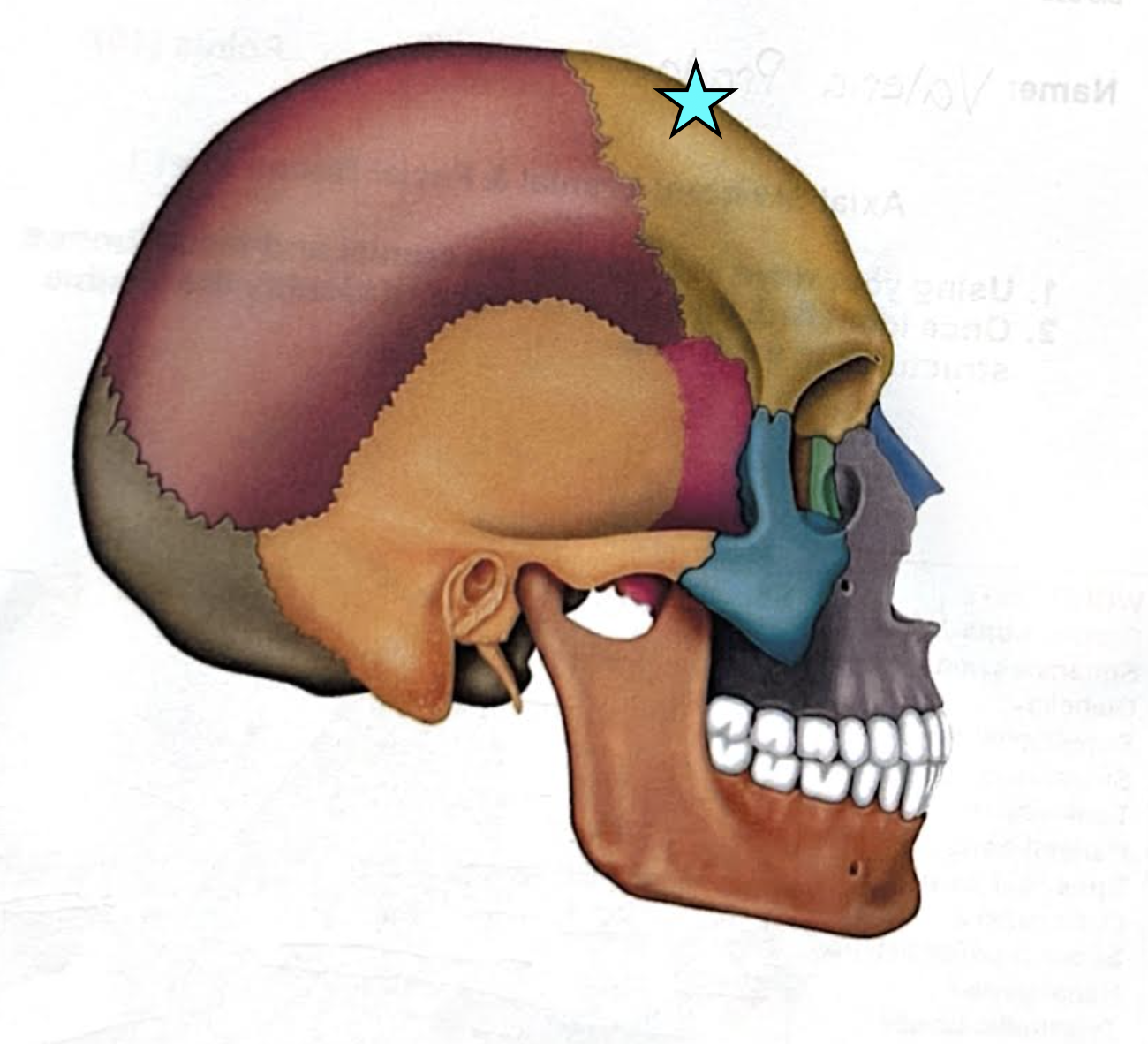
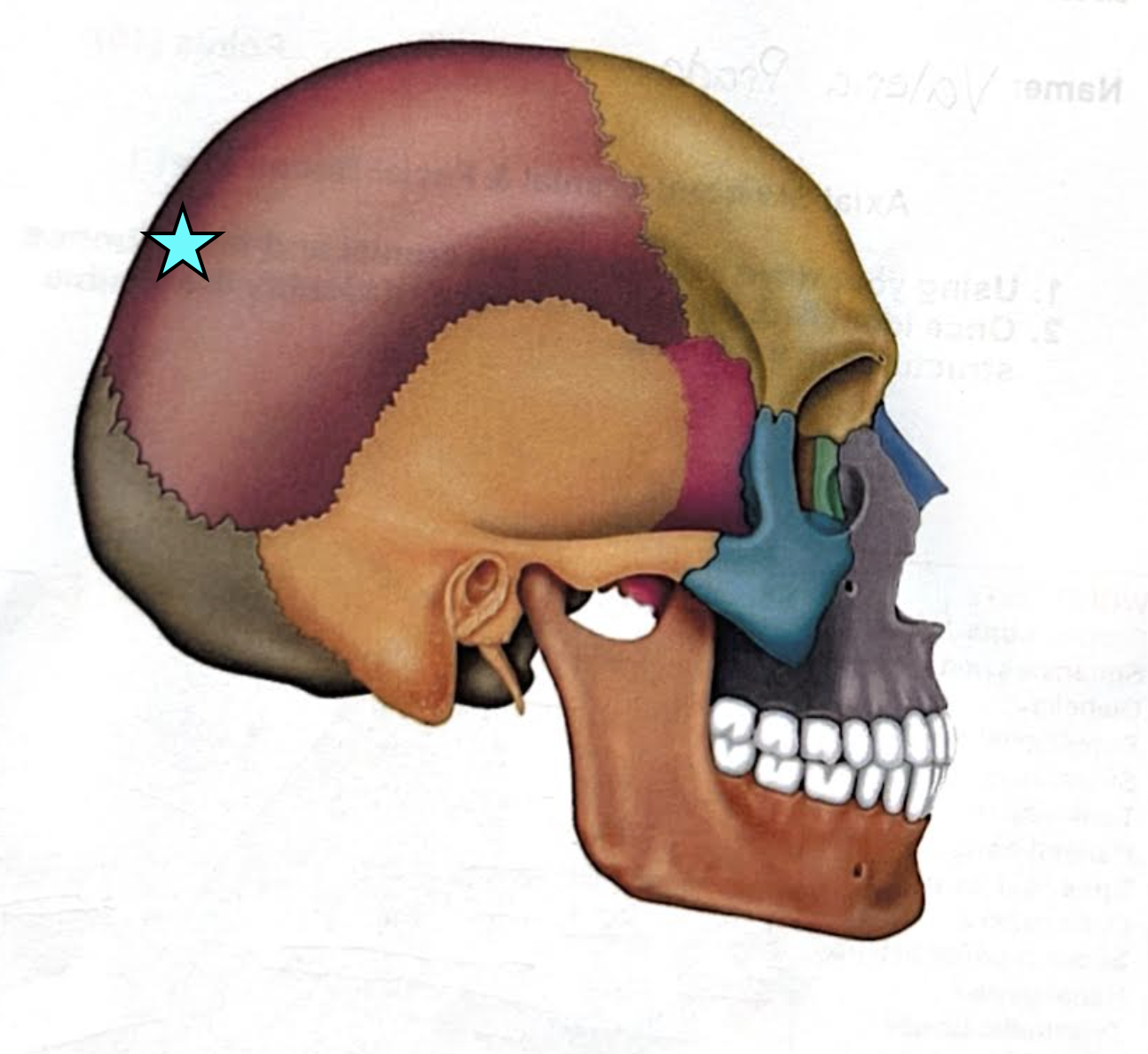
Sutures
Seams that connect skull bones to one another
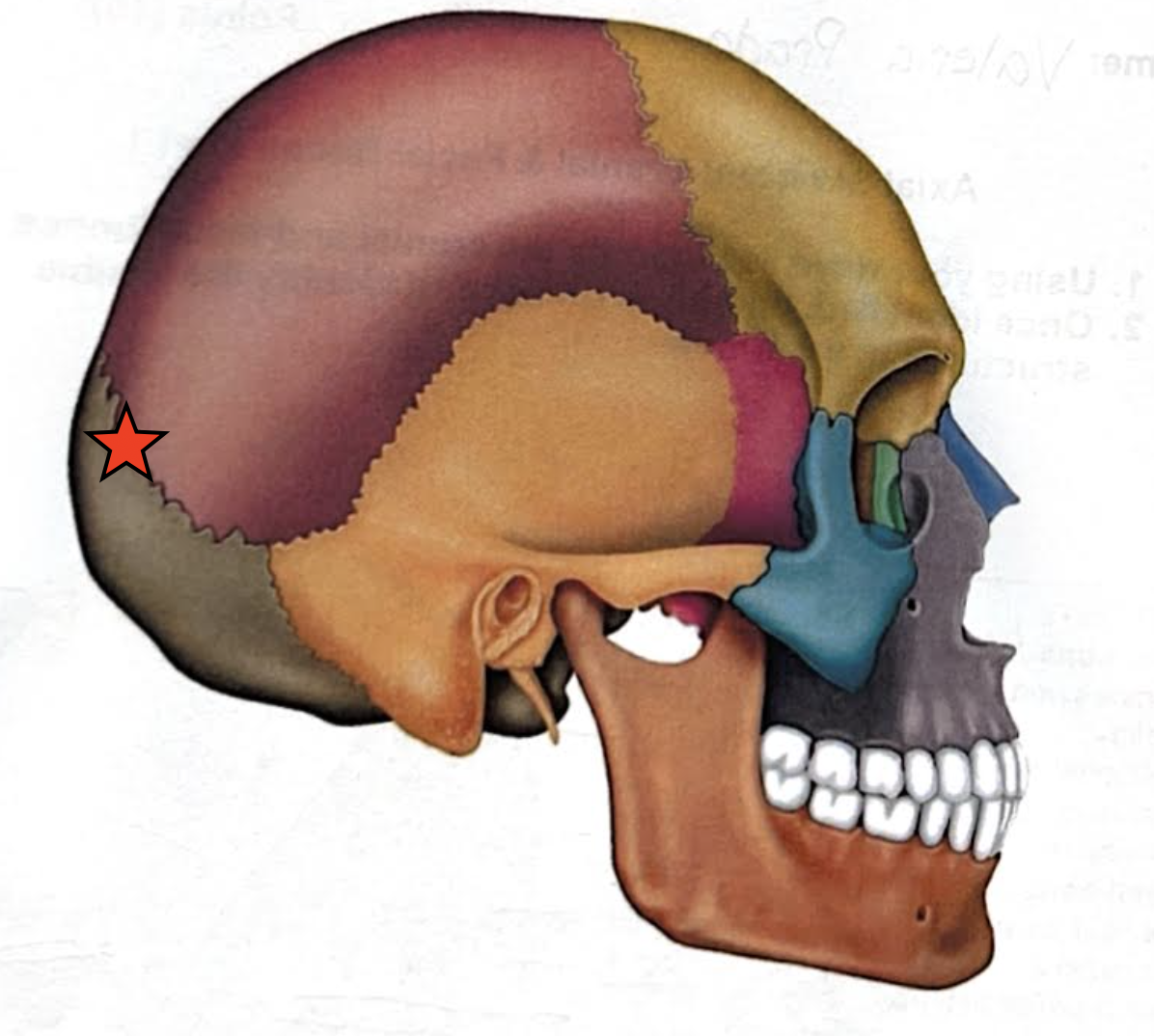
Lambdoid suture
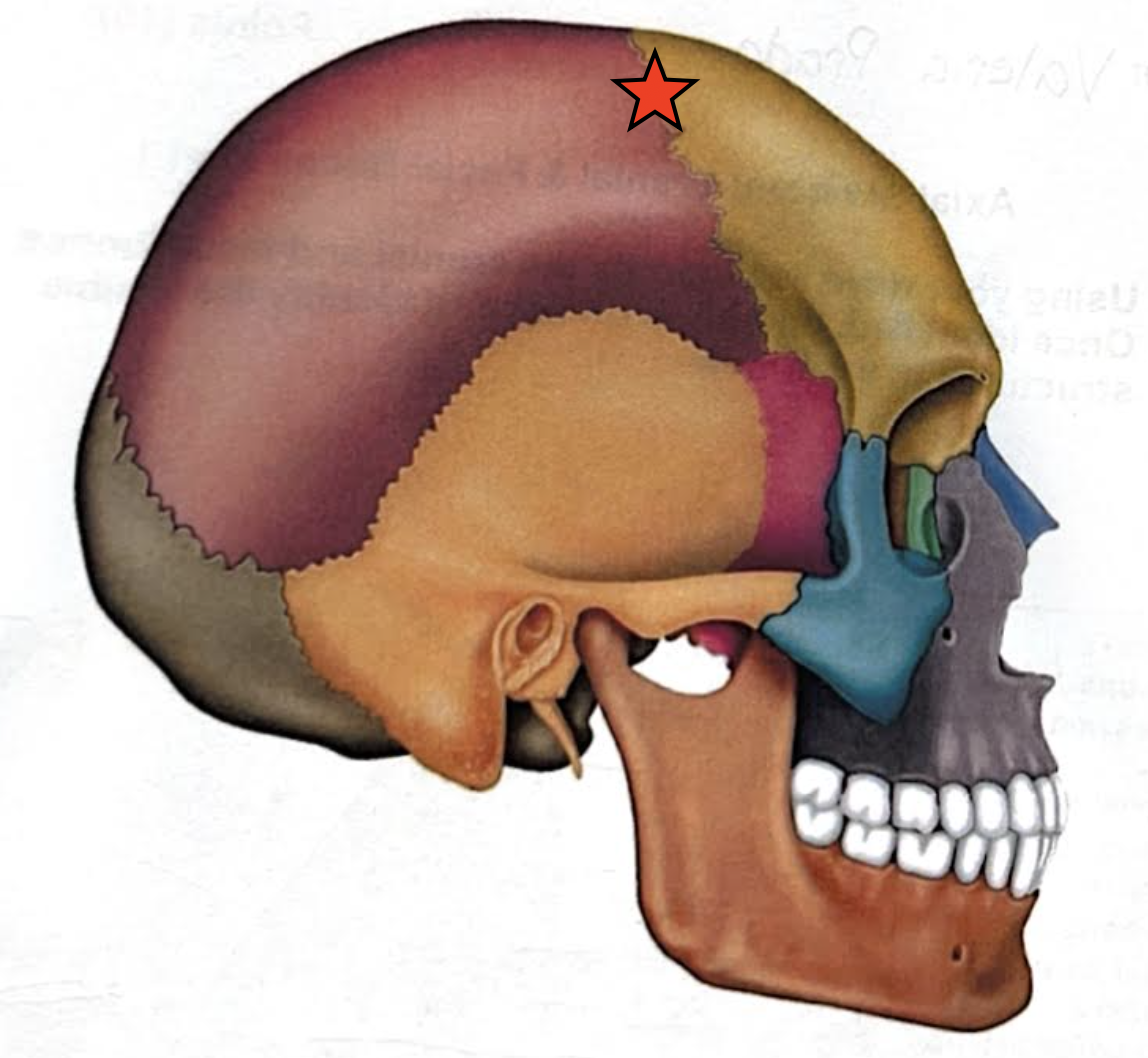
Coronal suture
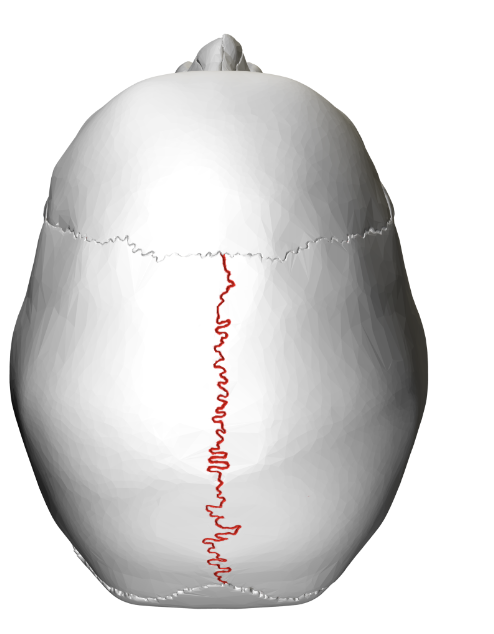
Sagittal suture
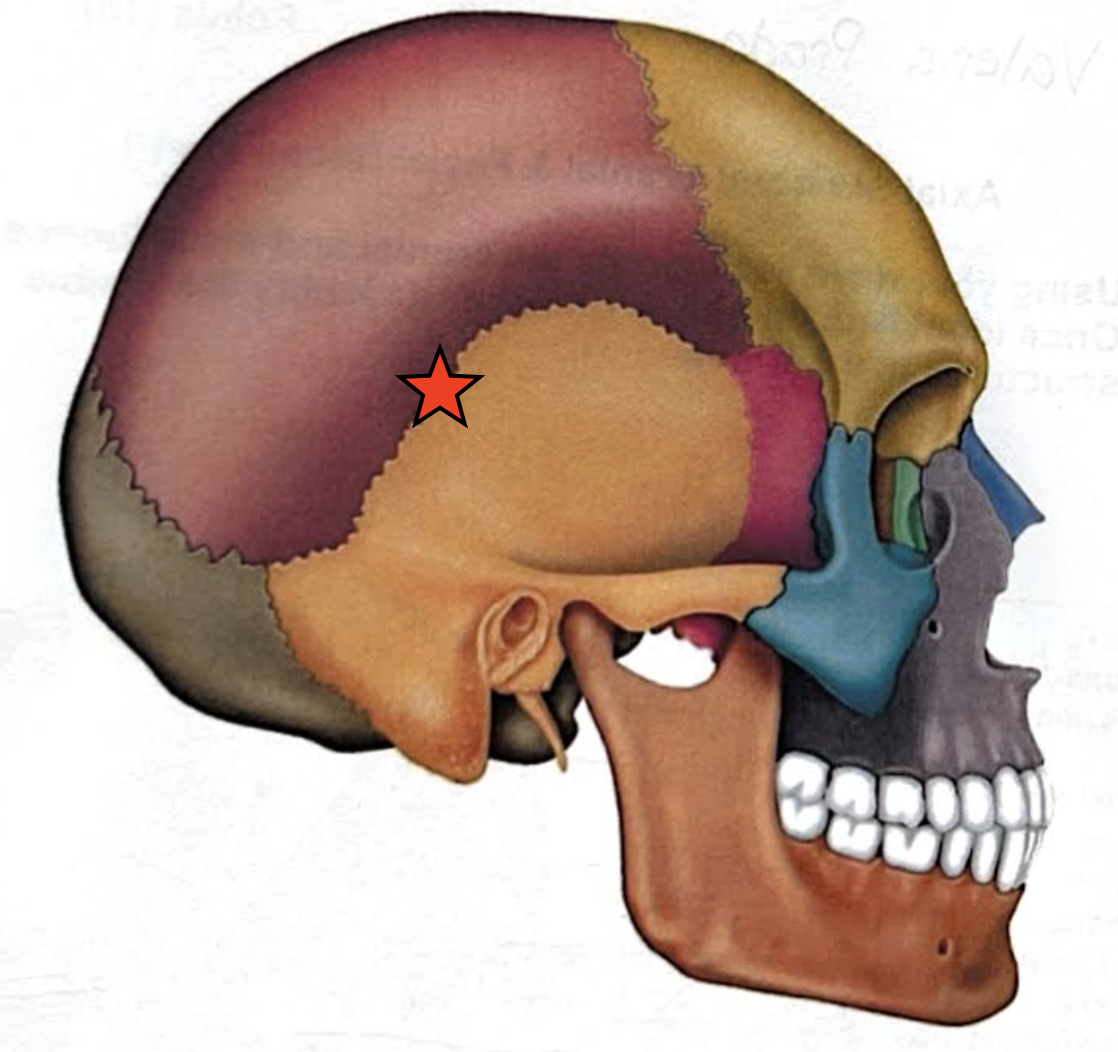
Squamous suture
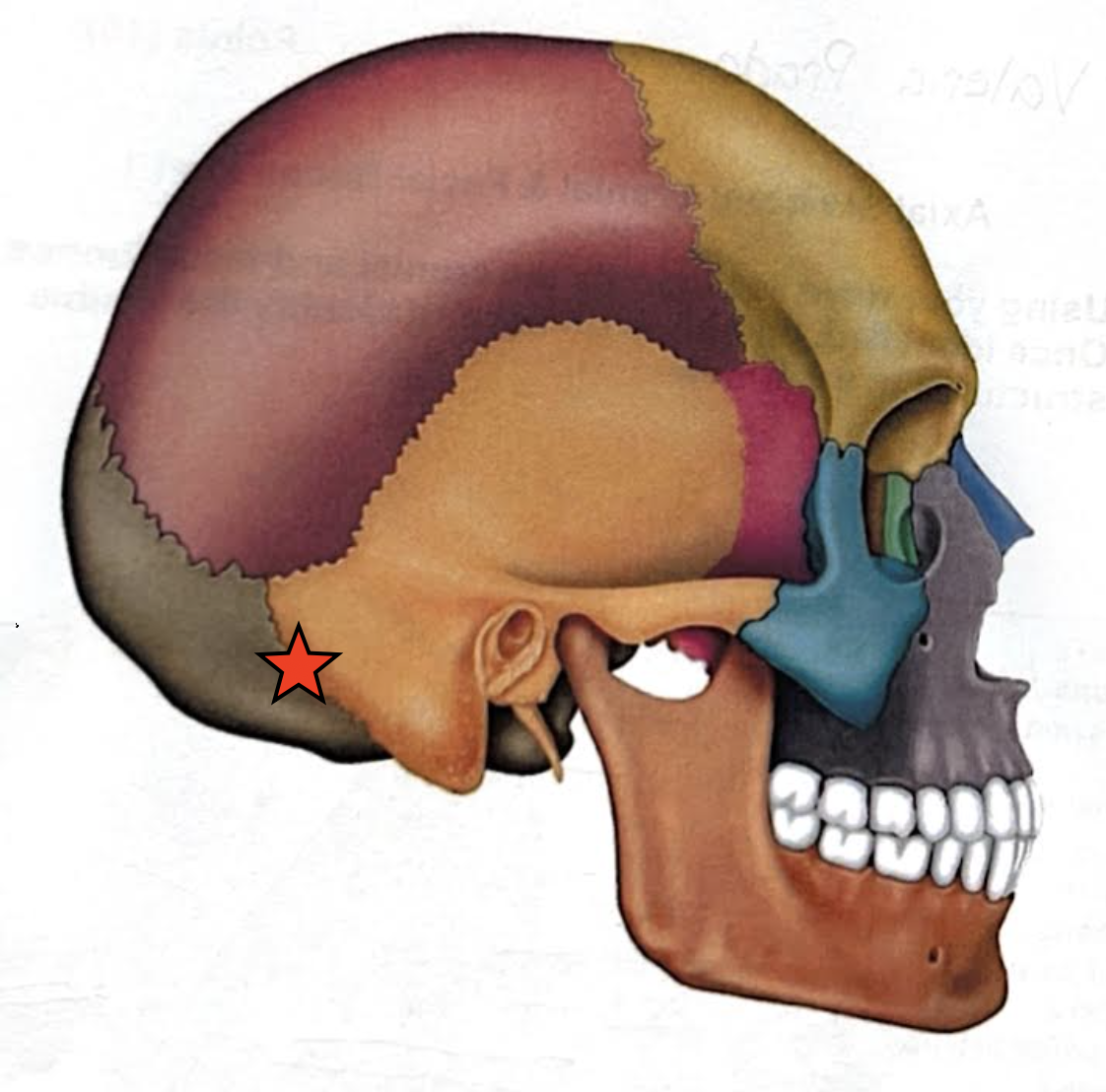
Occipitomastoid suture
Frontal bone structures
Forms the forehead, superior part of the orbit, and the floor of the anterior cranial fossa
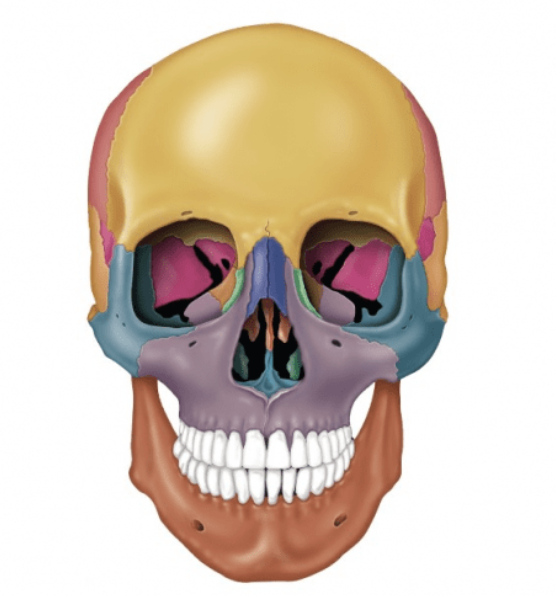
Squamous part
Supraorbital margin
Thick margin of the eye socket that lies beneath the eyebrows
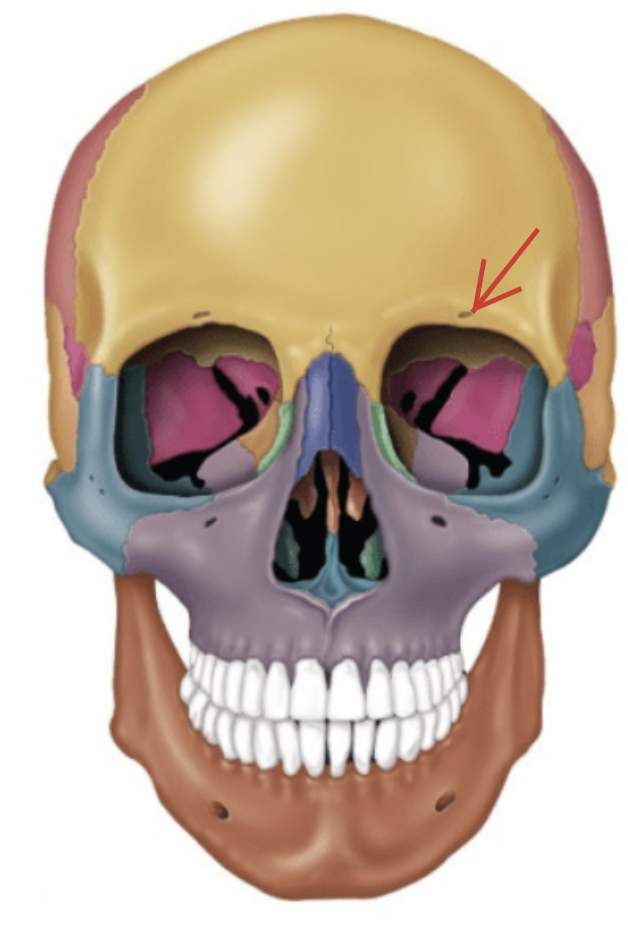
Supraorbital foramen (notch)
Opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass
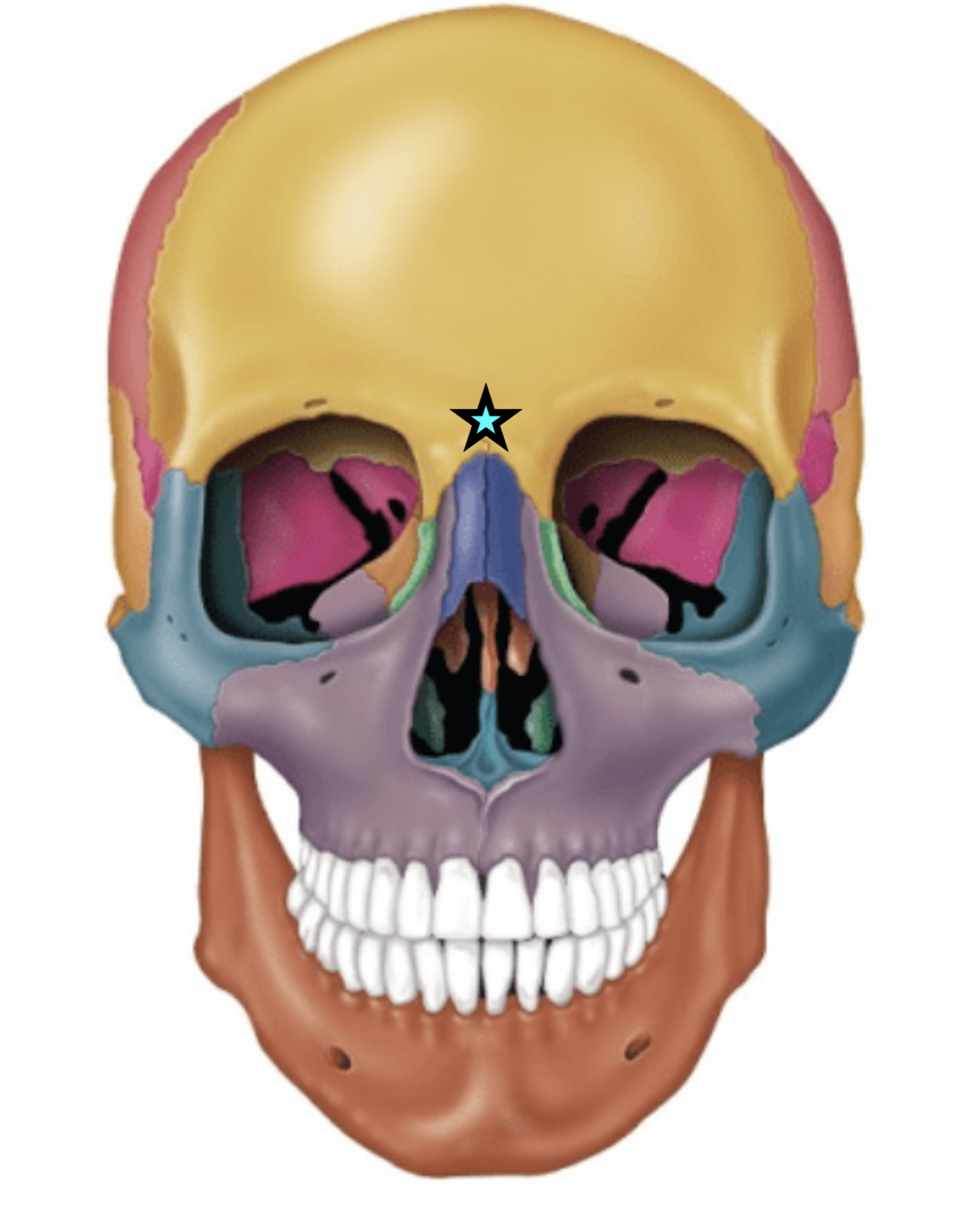
Glabella
Smooth area between the eyes
Occipital bone structures
Forms the posterior aspect and most of the base of the skull
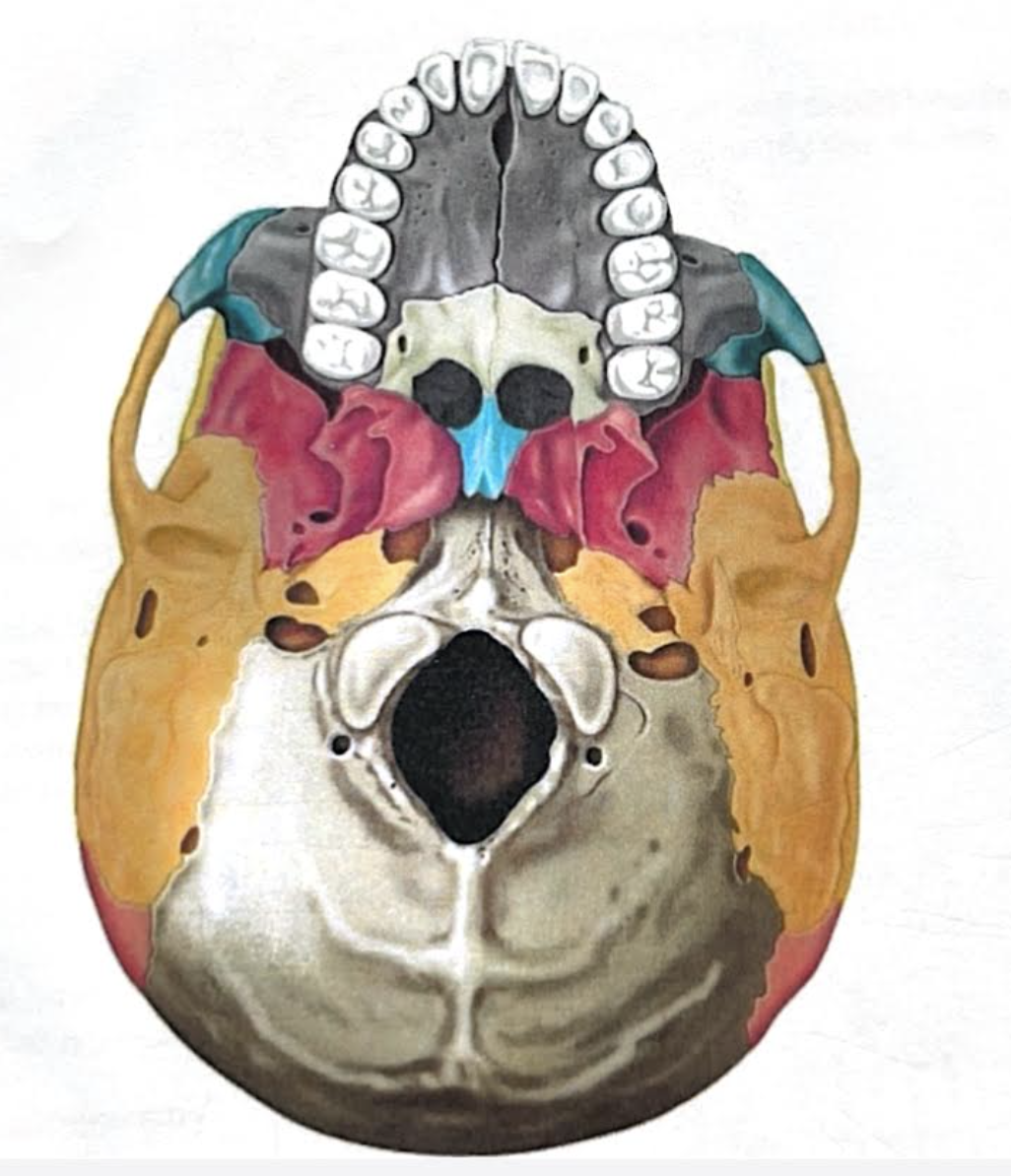
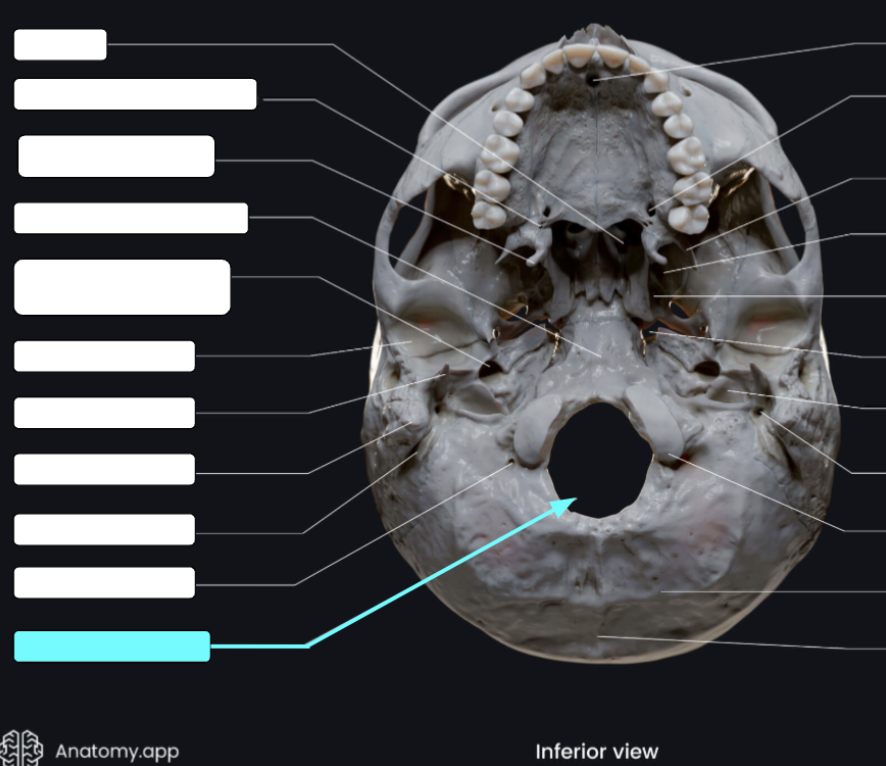
Foramen magnum
Large opening in the base of the bone, which allows the spinal cord to join with the brain stem
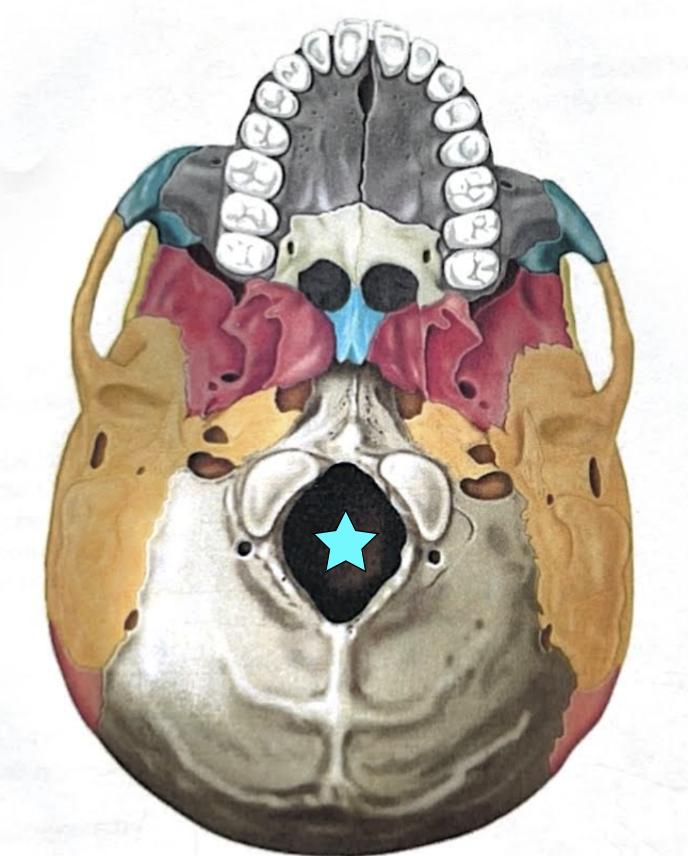
Occipital condyles
Rounded projections lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas)
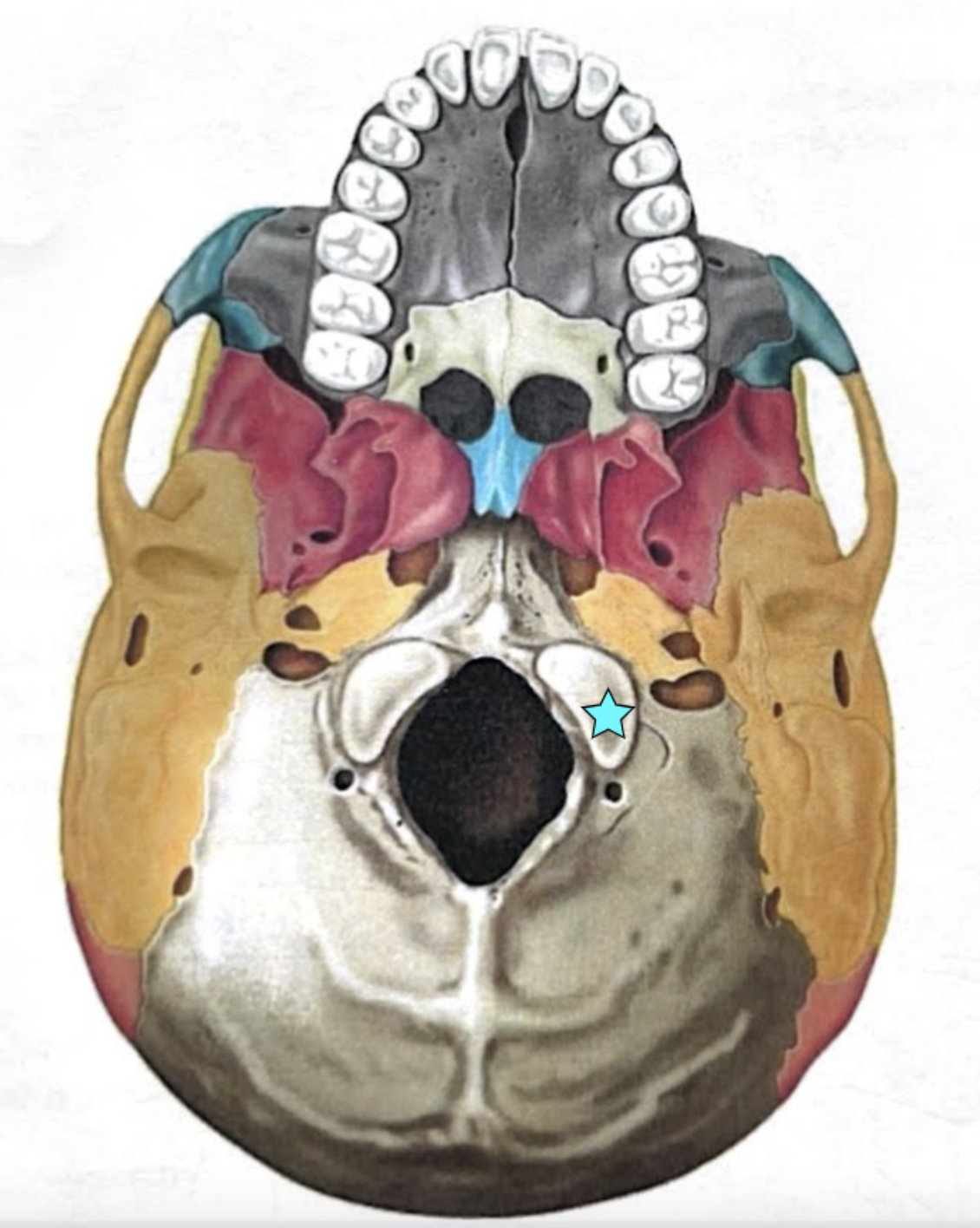
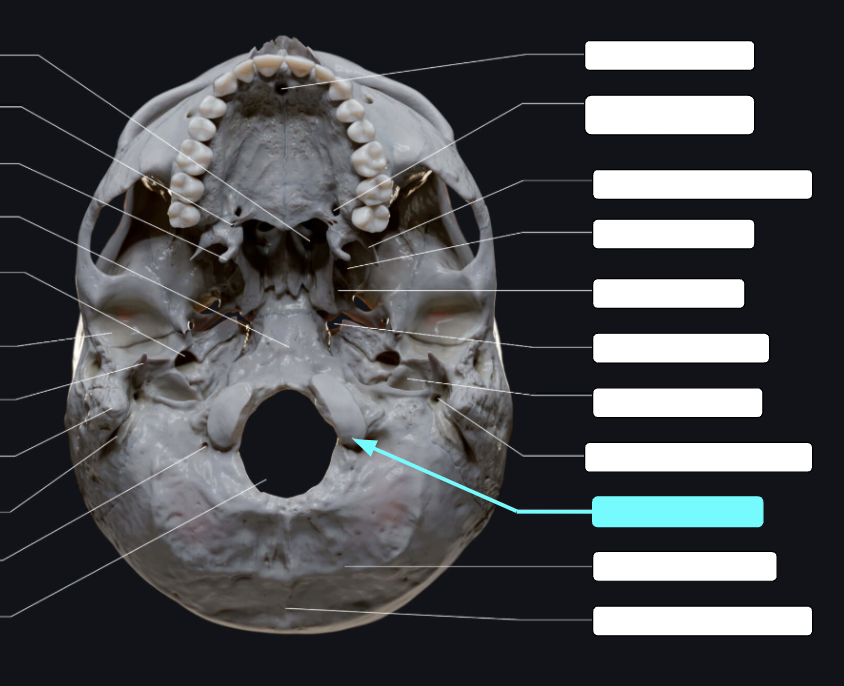
Hypoglossal canal
Opening medial and superior to the occipital condyle through which cranial nerve XII (the hypoglossal nerve) passes
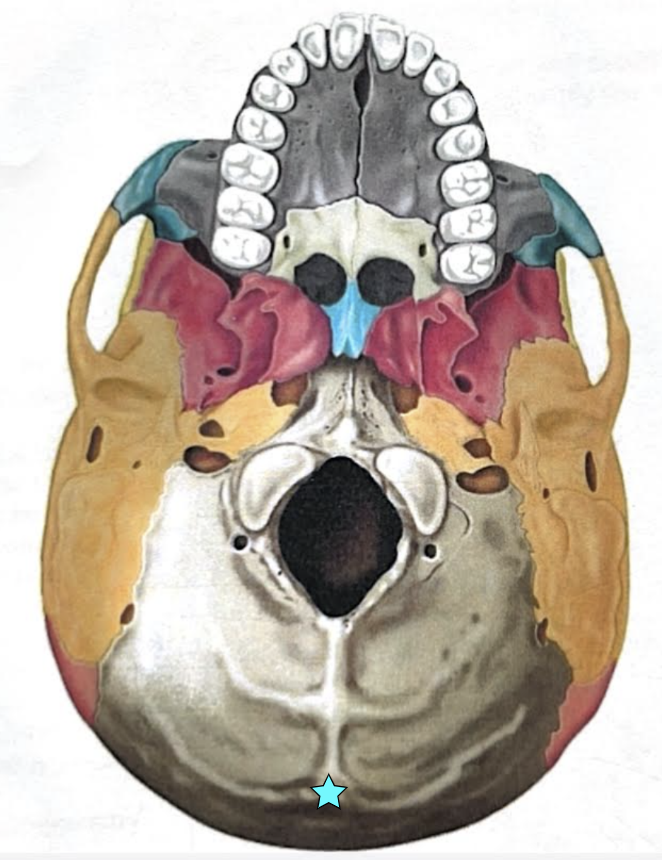
External occipital protuberance
Midline prominence posterior to the foramen magnum
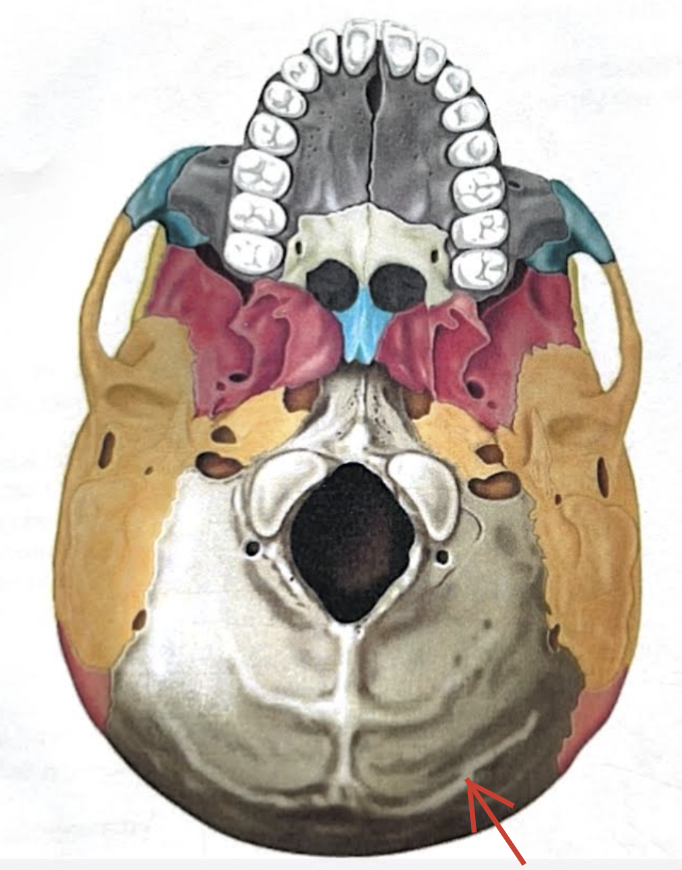
Superior nuchal line
Ethmoid bone structures
Contributes to the anterior cranial fossa
Forms part of the nasal septum and the nasal cavity
Contributes to the medial wall of the orbit
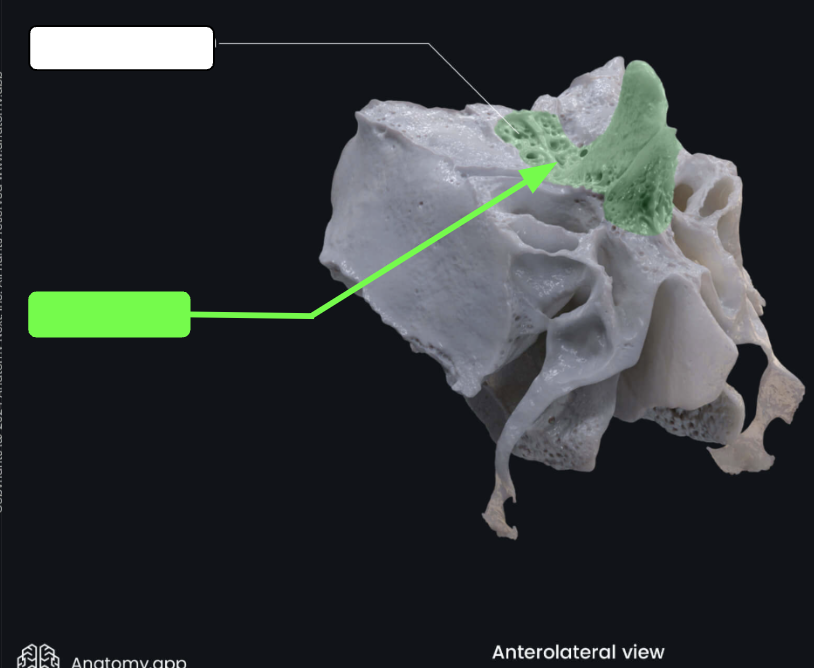
Cribriform plates
Located lateral to the crista galli
Form a portion of the roof of the nasal cavity and the floor of the anterior cranial fossa
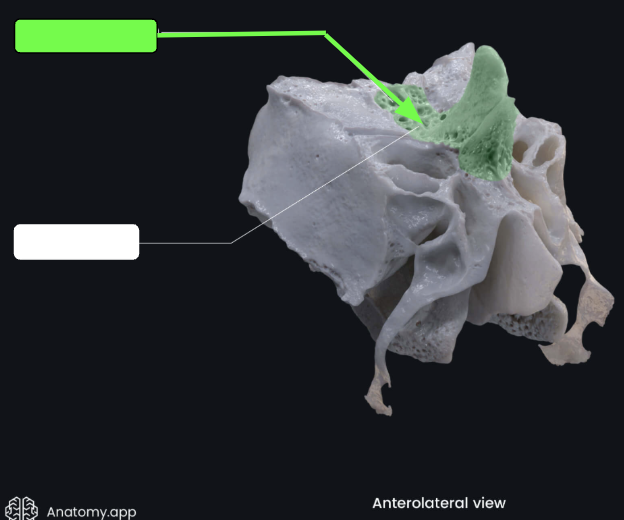
Cribriform (olfactory) foramina
Tiny holes in the cribriform plates that allow for the passage of filaments of cranial nerve I (olfactory nerve)
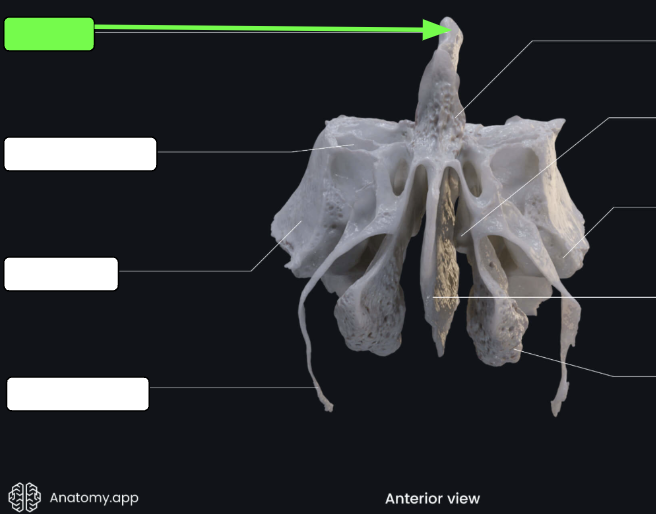
Crista galli
“Rooster’s comb”
A superior projection that attaches to the dura mater, helping the secure the brain within the skull
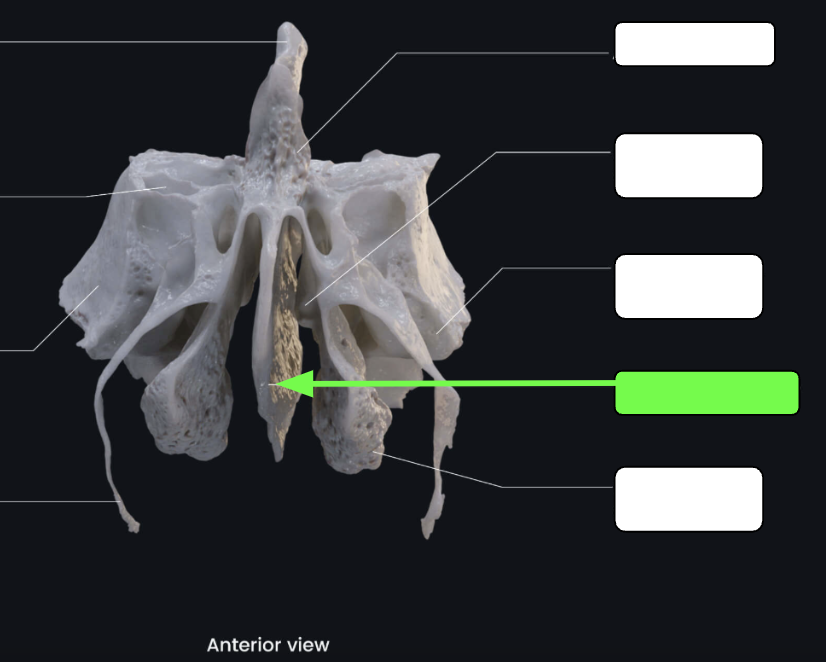
Perpendicular plate
Inferior projection that forms that superior portion of the nasal septum
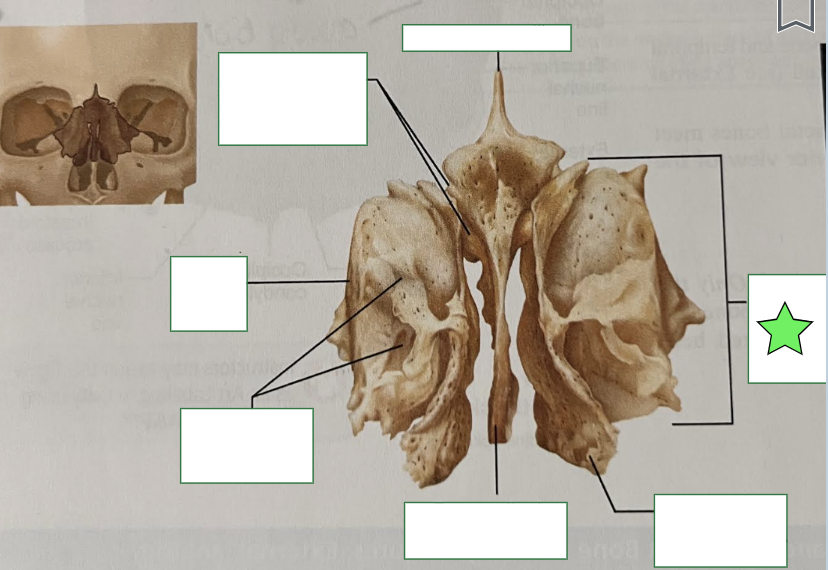
Lateral masses
Flank the perpendicular plate on each side and filled with sinuses called ethmoidal air cells
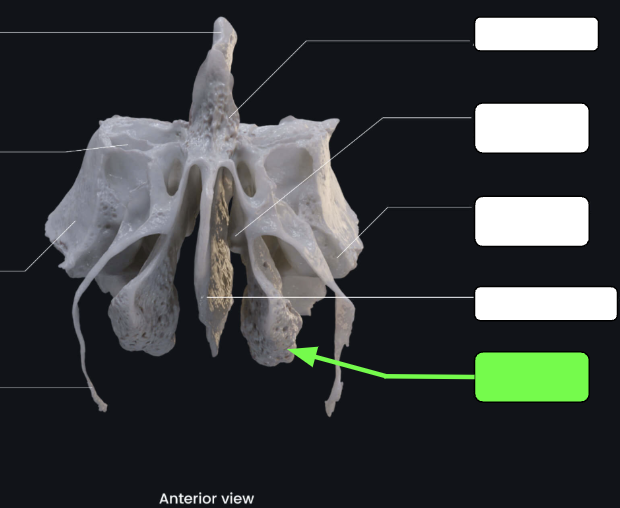
Middle nasal concha
Extend medially from the lateral masses
Act as turbinates to improve airflow through the nasal cavity
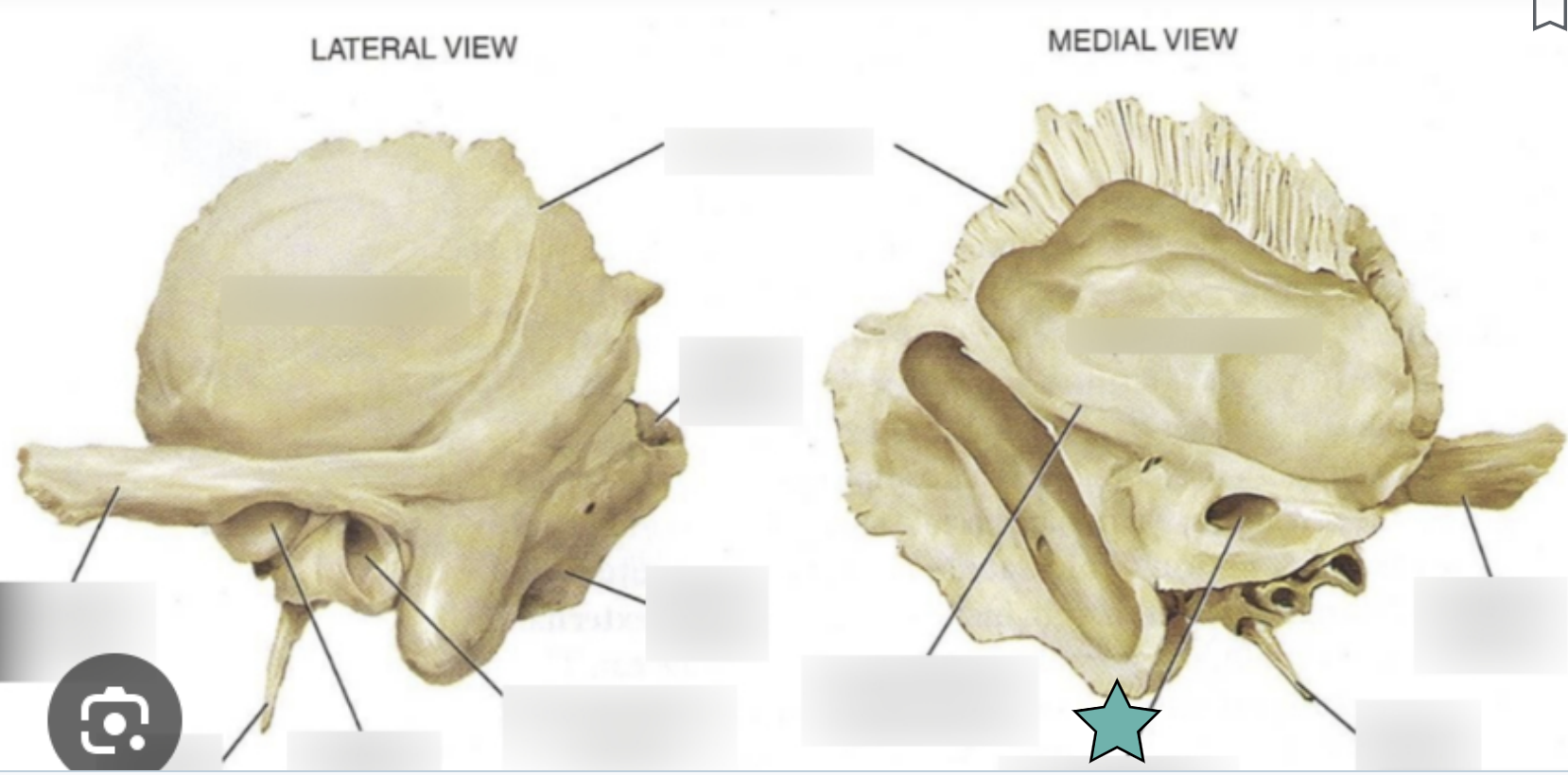
Temporal Bone structure
Forms the inferolateral aspects of the skull and contribute to the middle cranial fossa
Each has squamous, tympanic and petrous parts
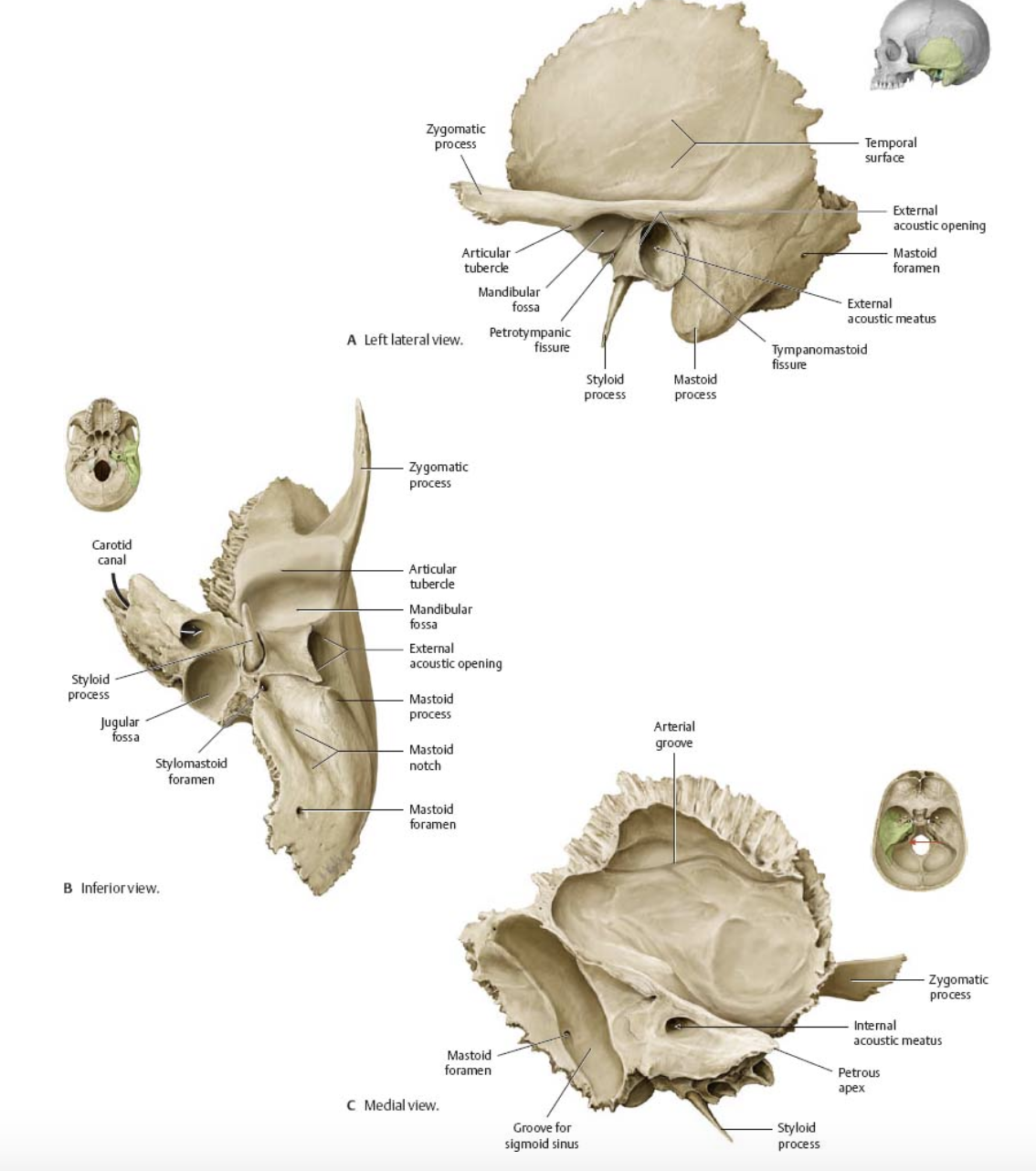
Squamous part
Located inferior to the squamous suture
The next two markings are located in this part
Zygomatic process
A bridge-like projection that articulates with the zygomatic bone to form the zygomatic arch
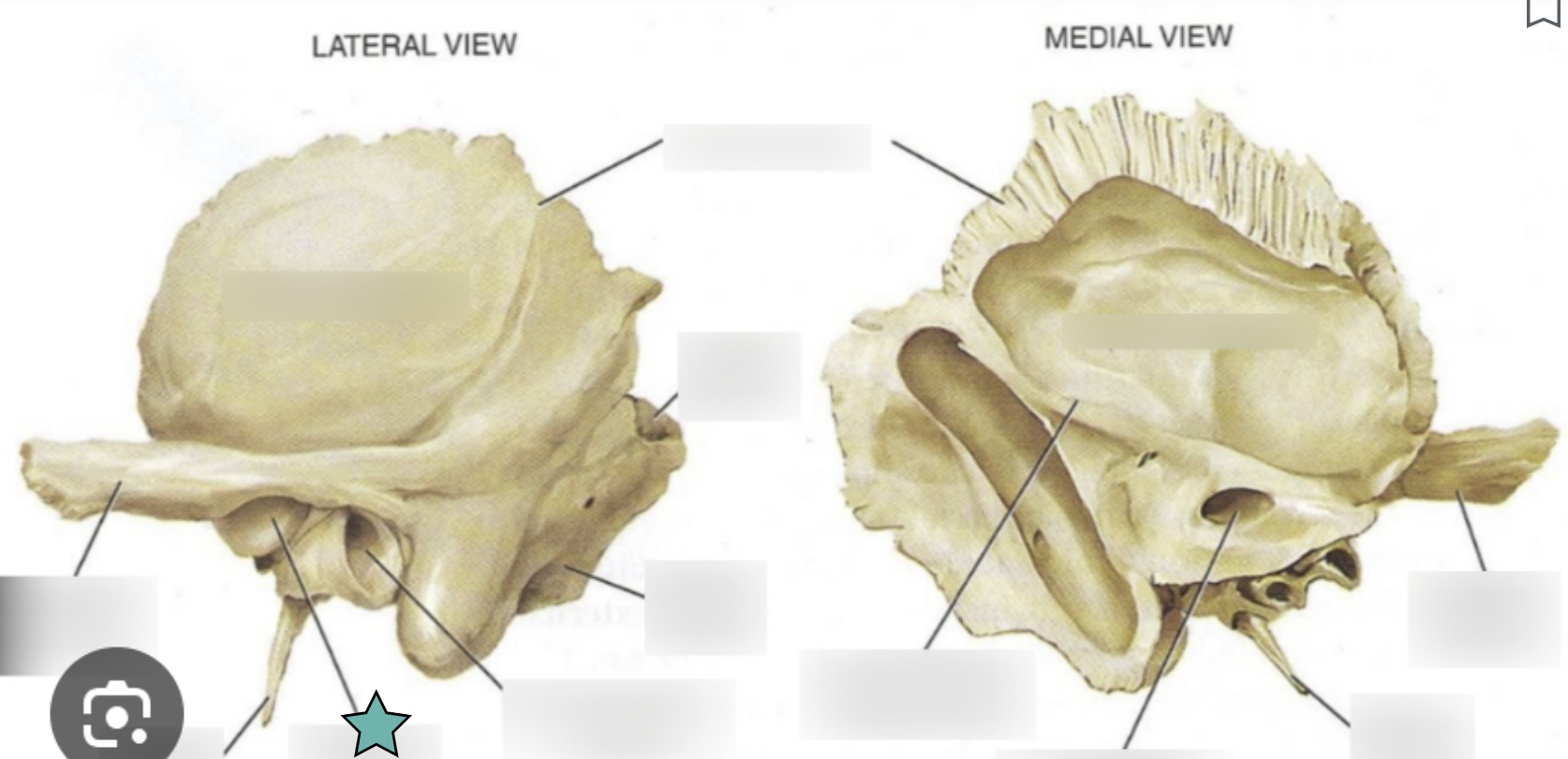
Mandibular fossa
Located on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process
Receives the condylar process of the mandible to form the temporomanidubular joint
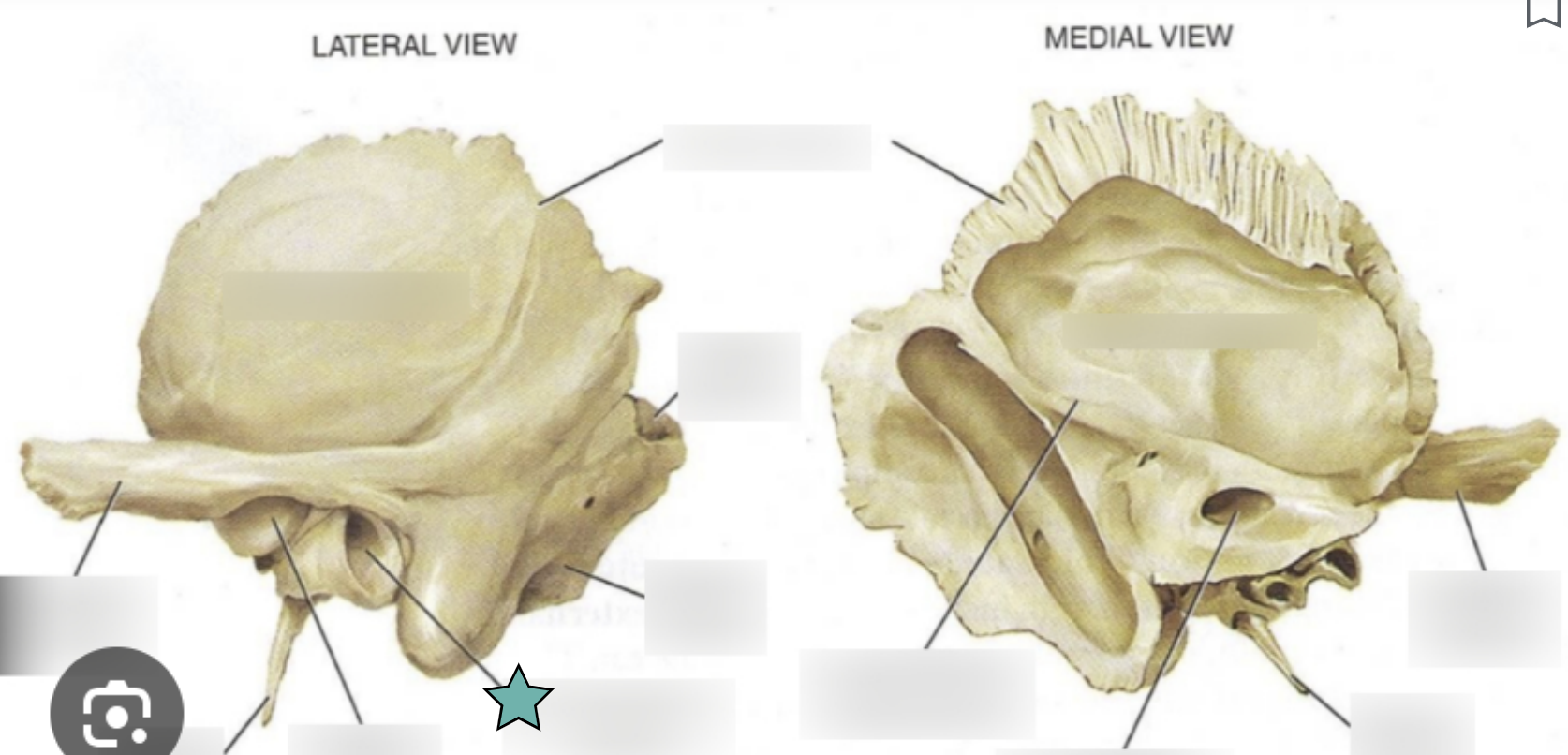
External acoustic meatus
Canal leading to the middle ear and eardrum
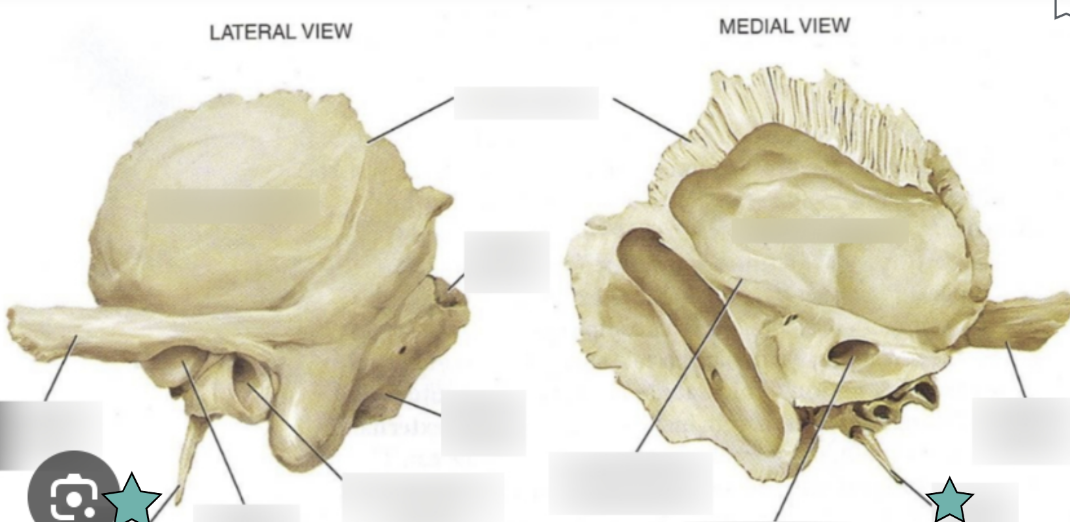
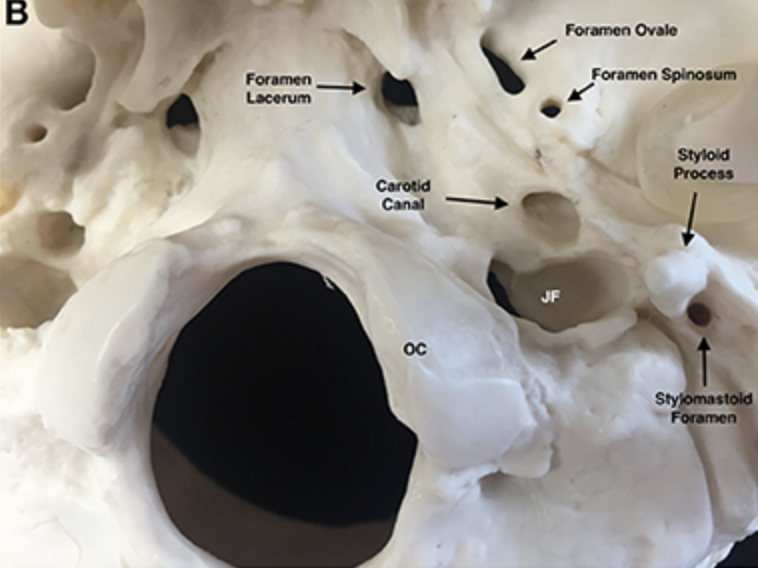
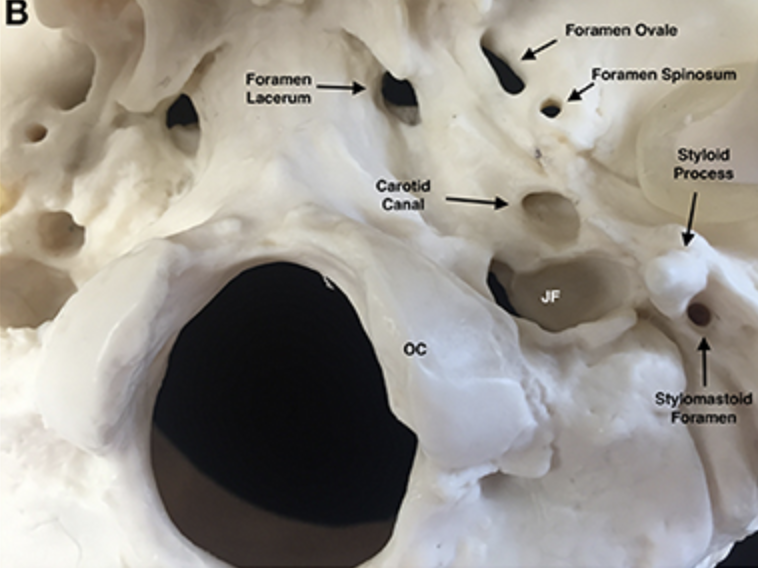
Styloid process
Needle-like projection that serves as an attachment point for ligaments and muscles of the neck
++This process is often missing from demonstration skulls because it has broken off++
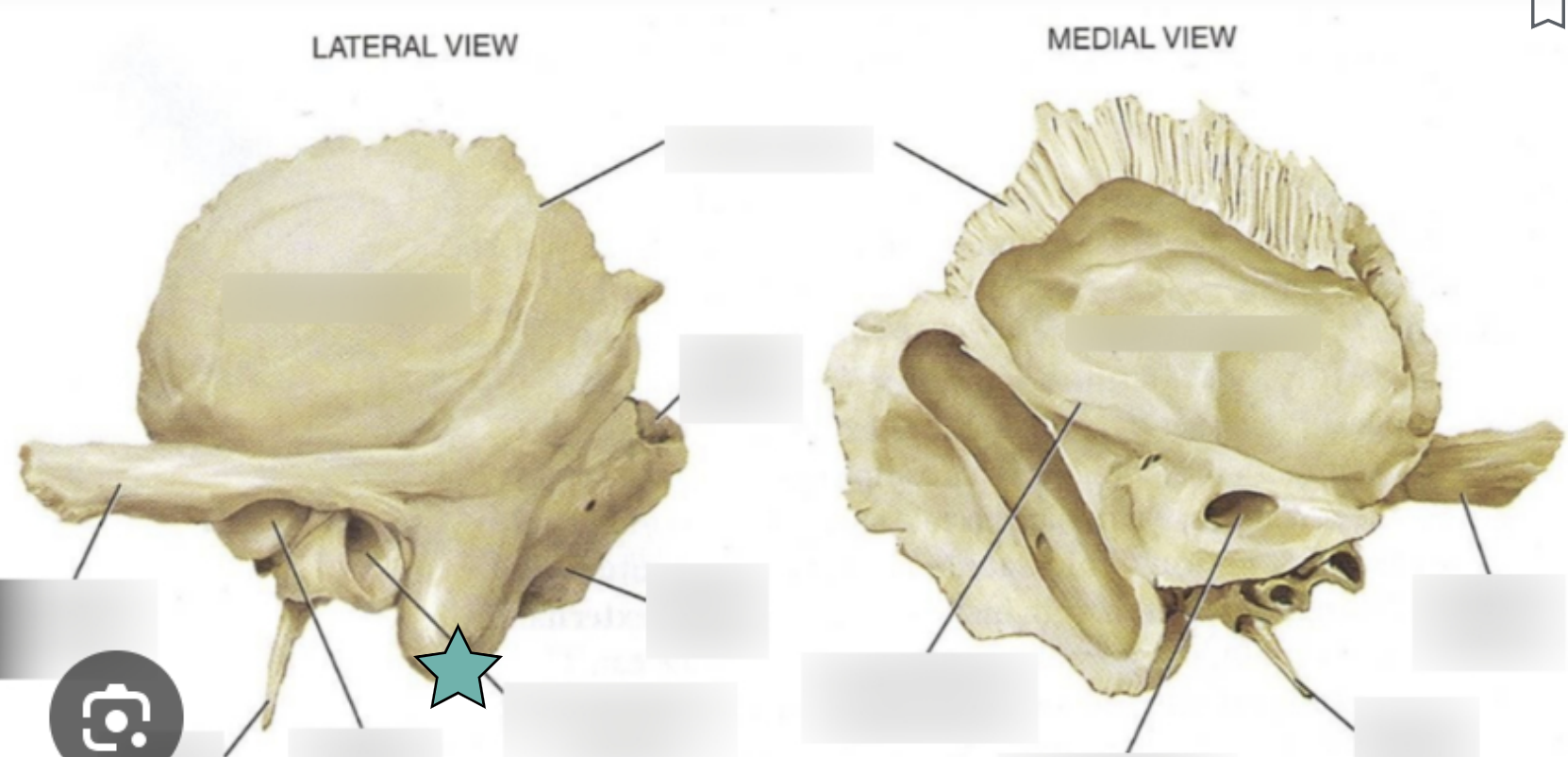
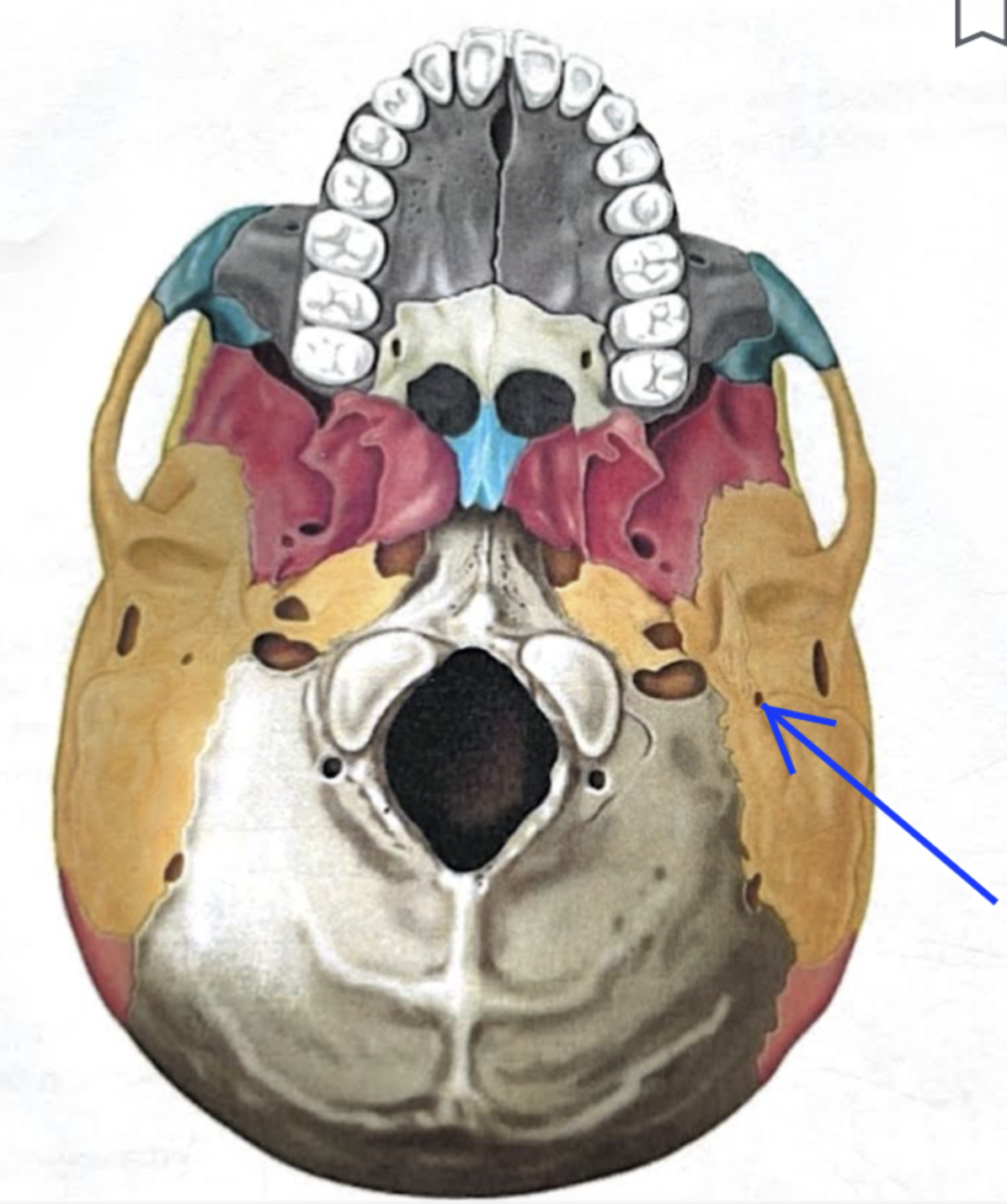
Mastoid process
Located posterior to the external to the external acoustic meatus
Serves as an attachment point for neck muscles
***
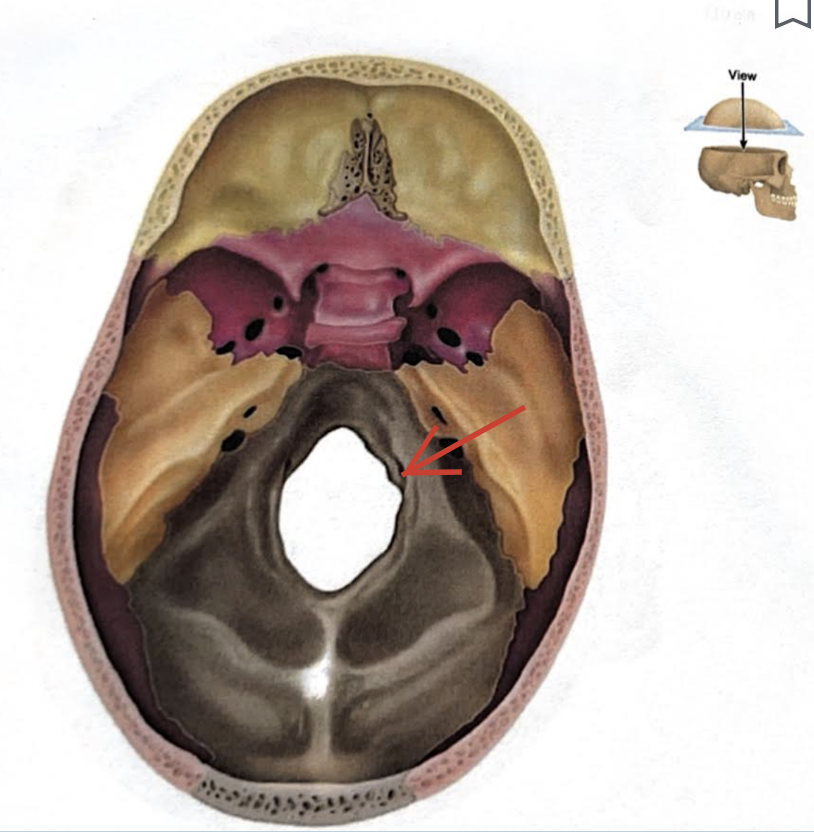
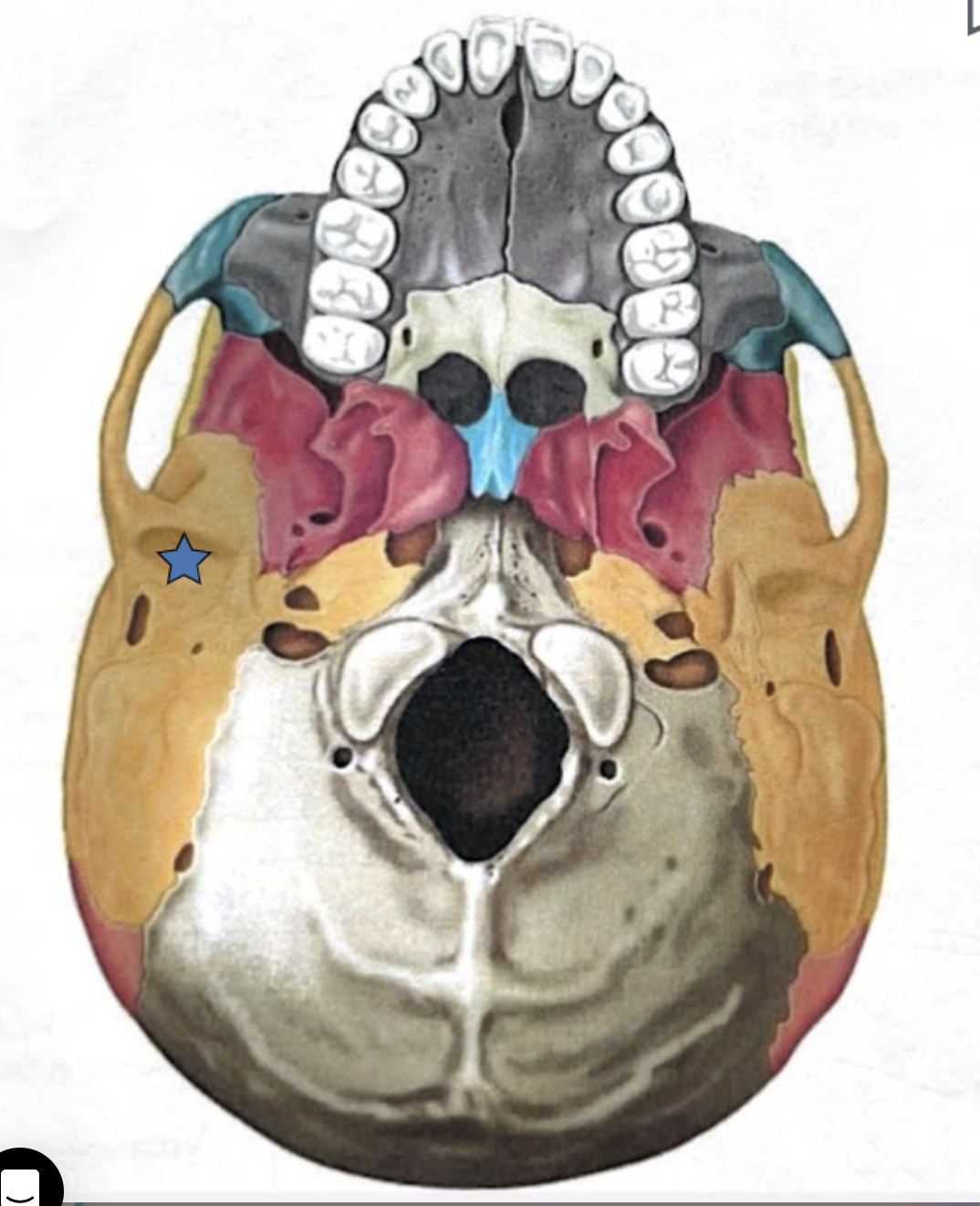
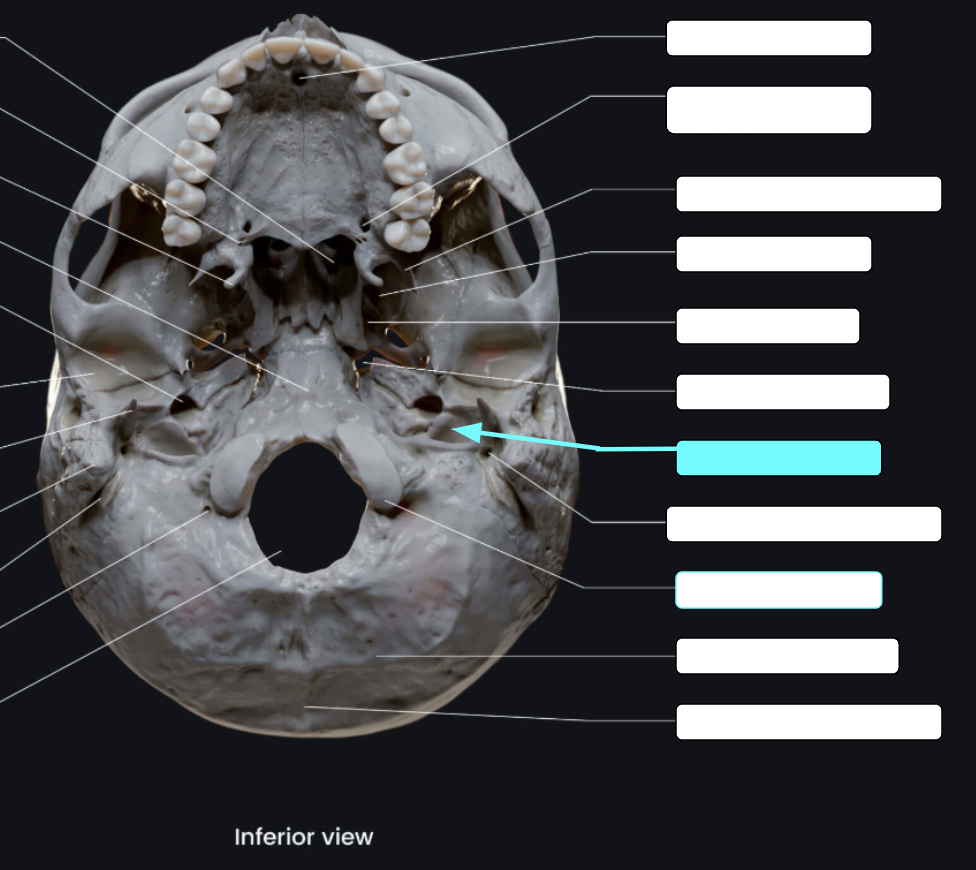
Jugular foramen
Located where the petrous part of the temporal part of the temporal bone joins the occipital bone
Forms an opening which the internal jugular vin and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI pass
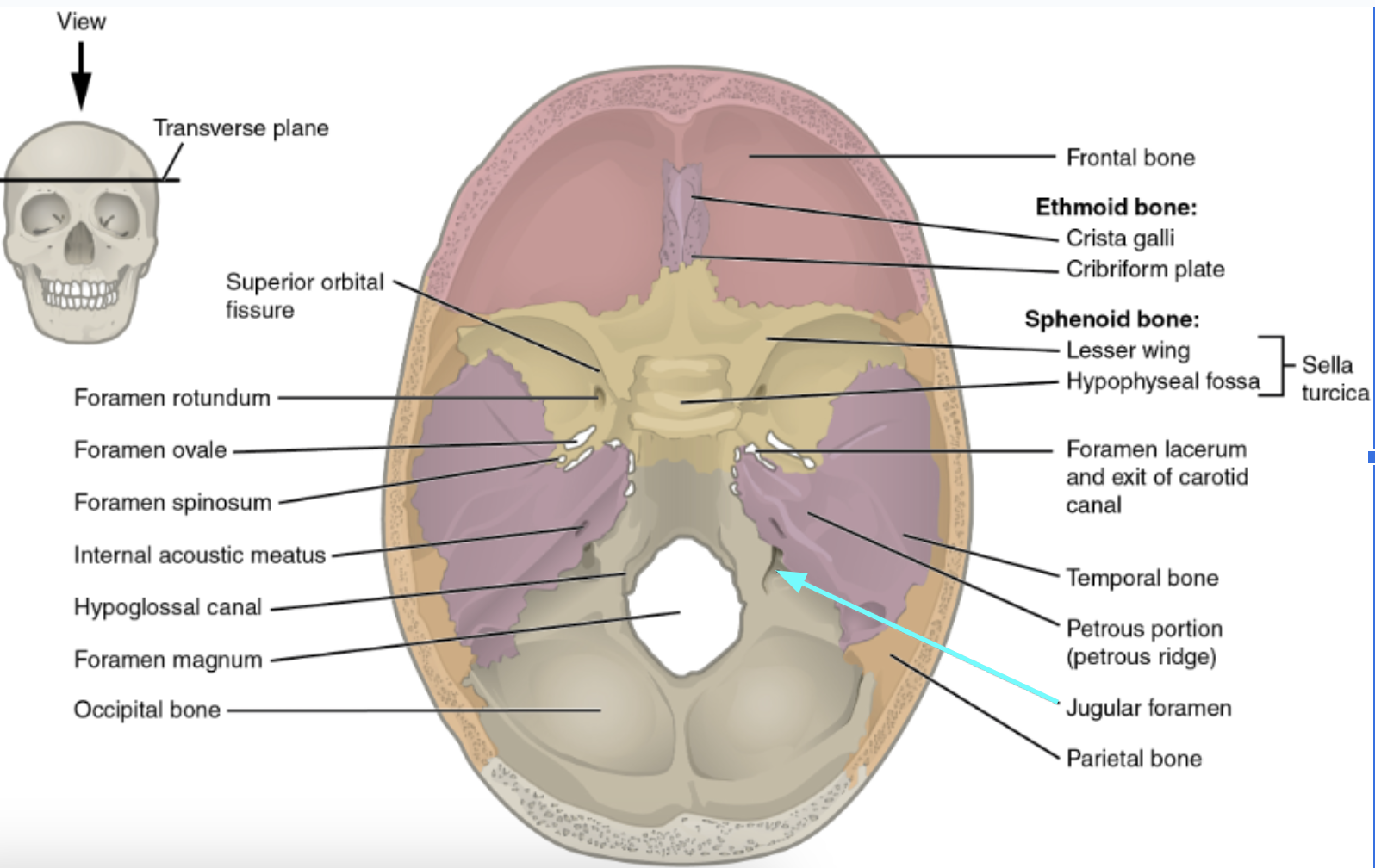
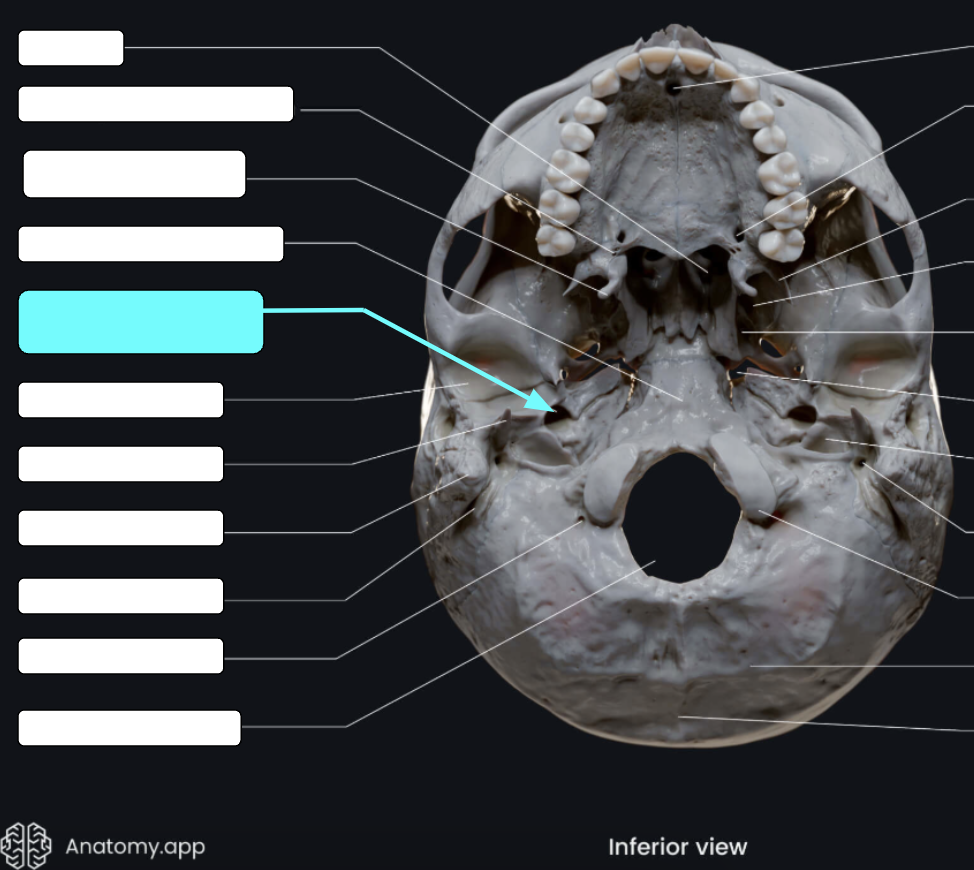
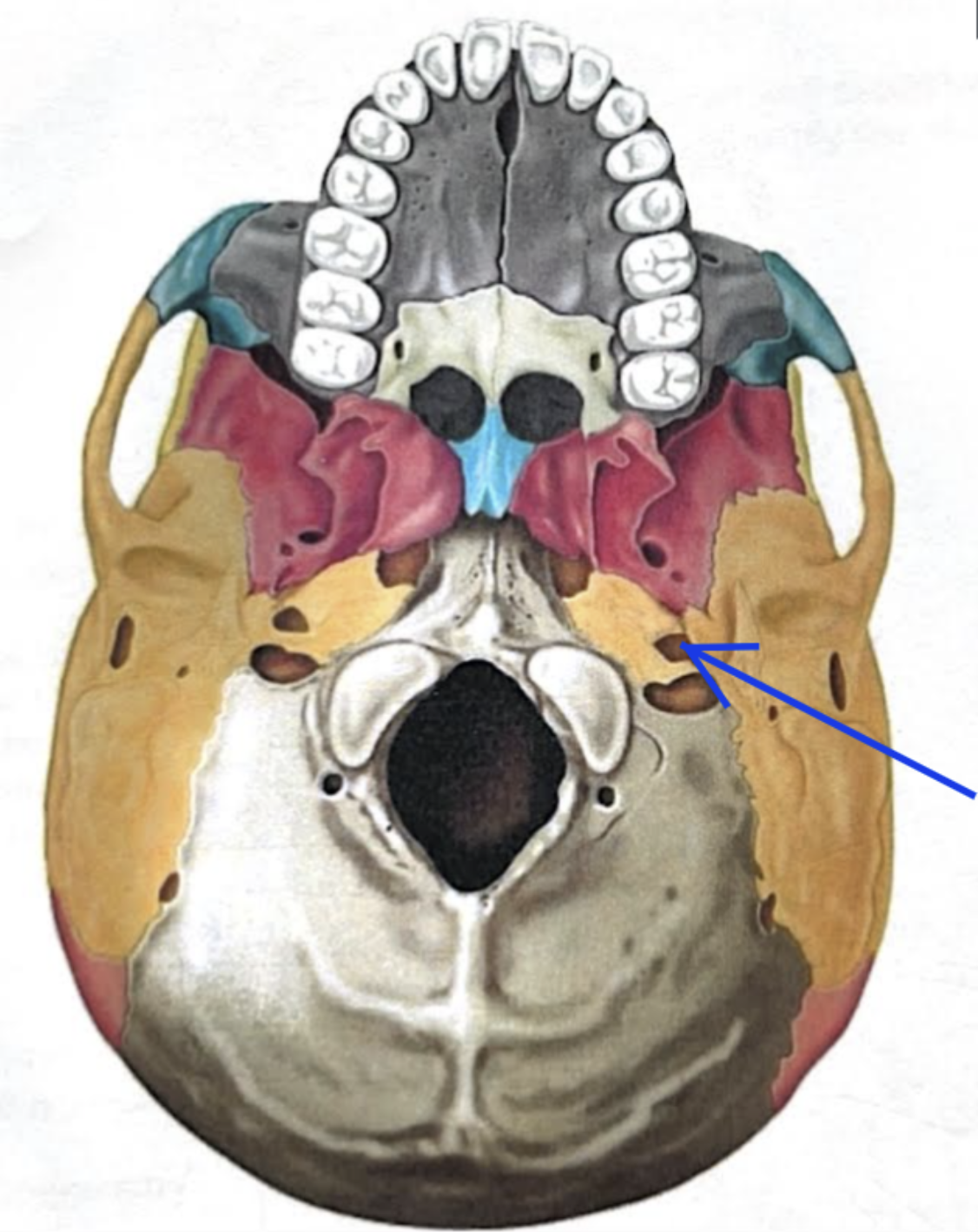
Carotid canal
Opening through which the internal carotid artery passes into the cranial cavity
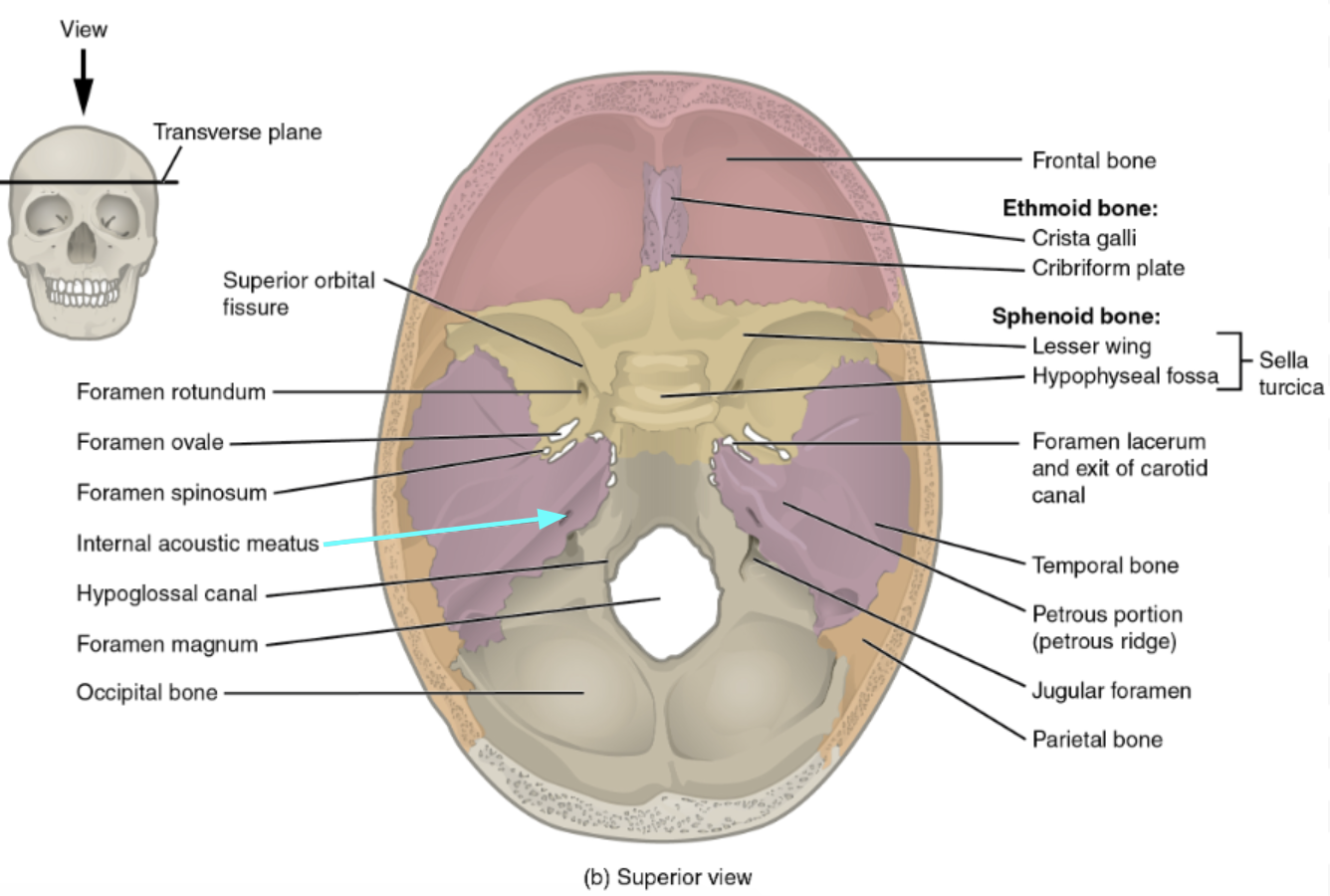
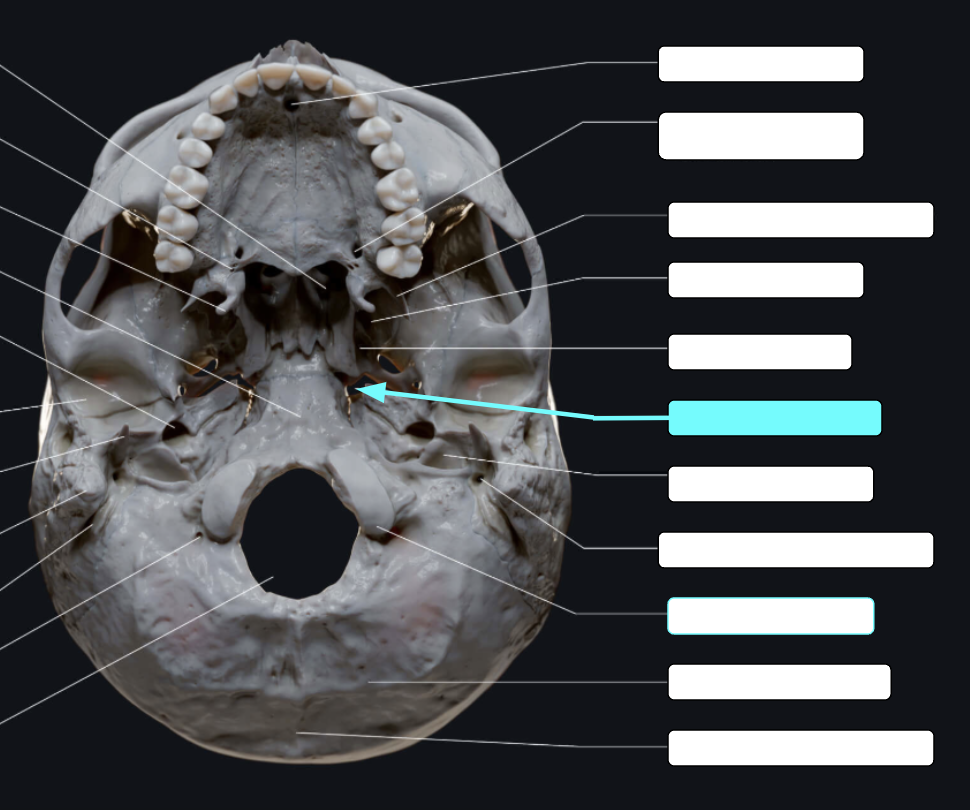
Internal acoustic meatus
Foreamen lacerum
Almost completely closed by cartilage in the living person but forms a jagged opening in dried skulls
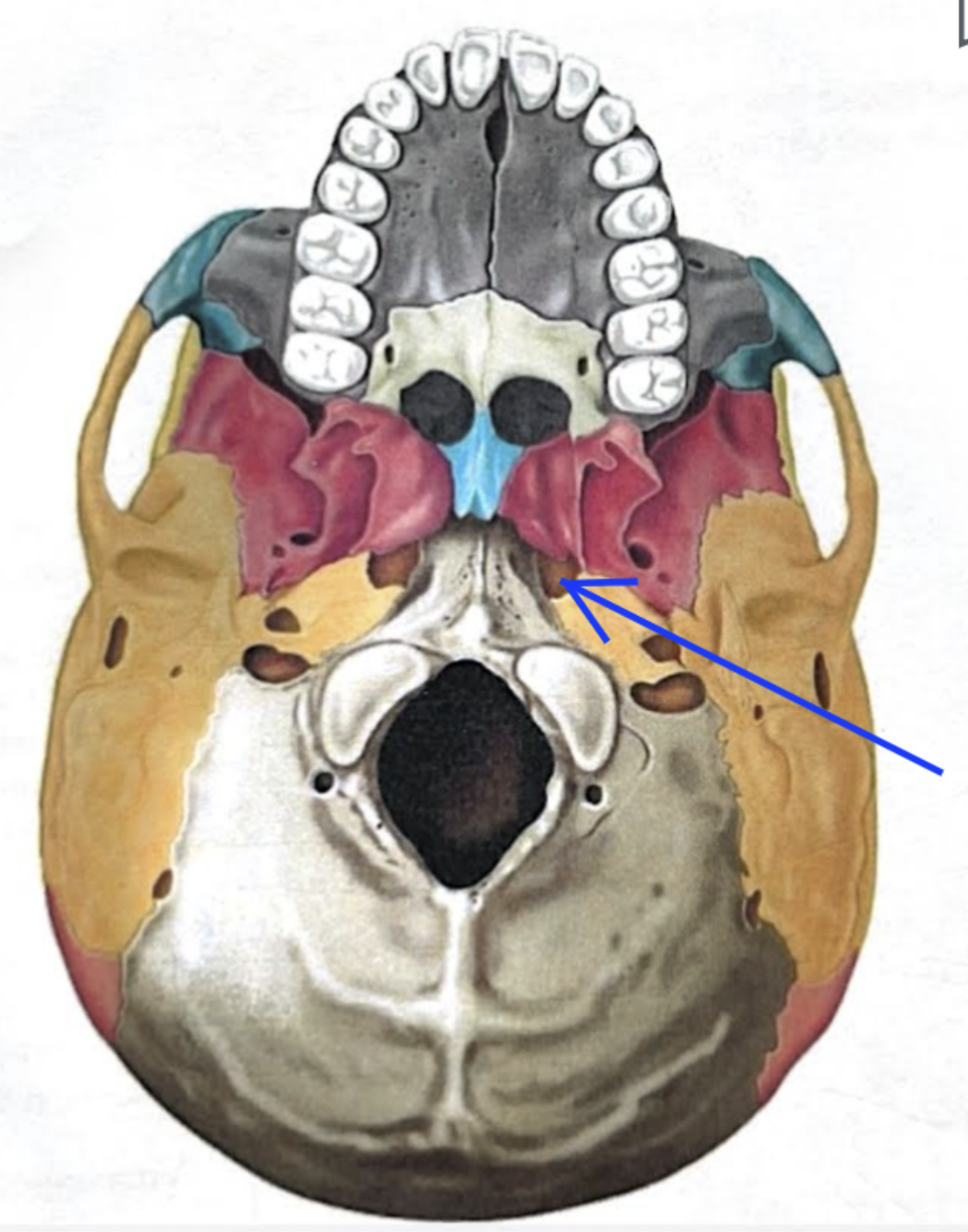
Stylomastoid foramen
Tiny opening between the mastoid and styloid processes through which cranial nerve VII leaves the cranium
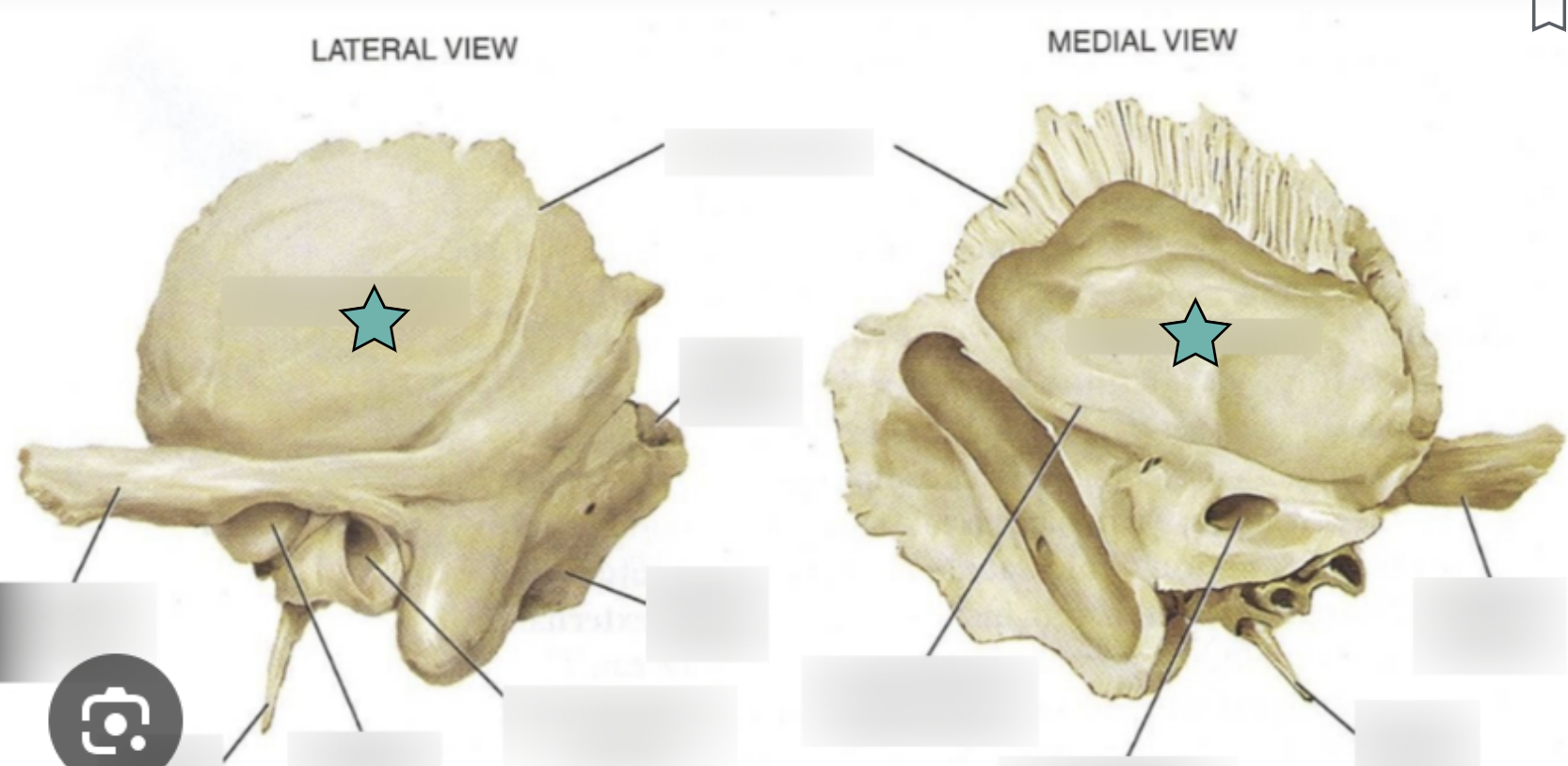
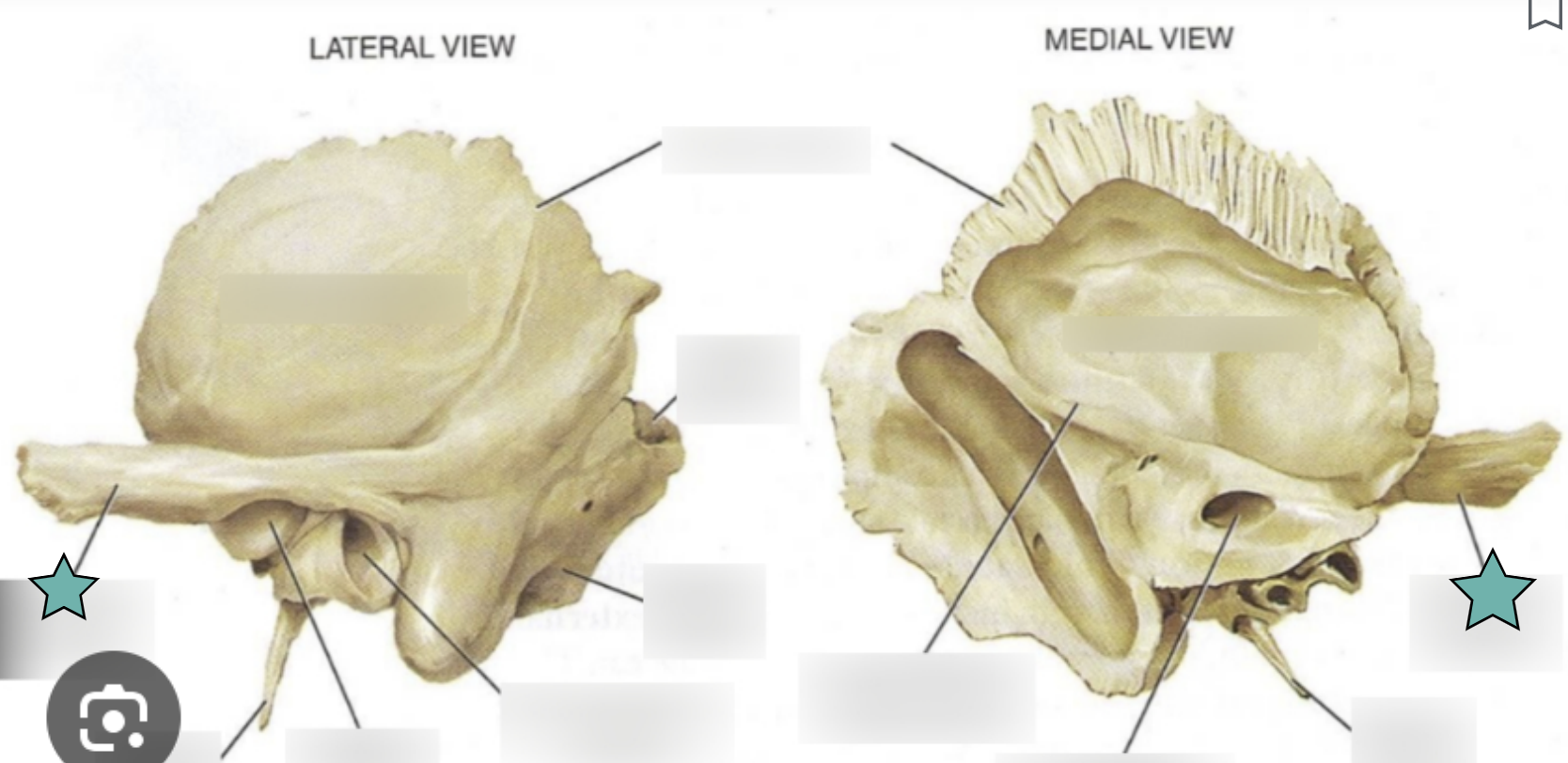
Sphenoid bone structure
Bat-shaped bone that is described as the keystone bone of the cranium because it articulates with all other cranial bones
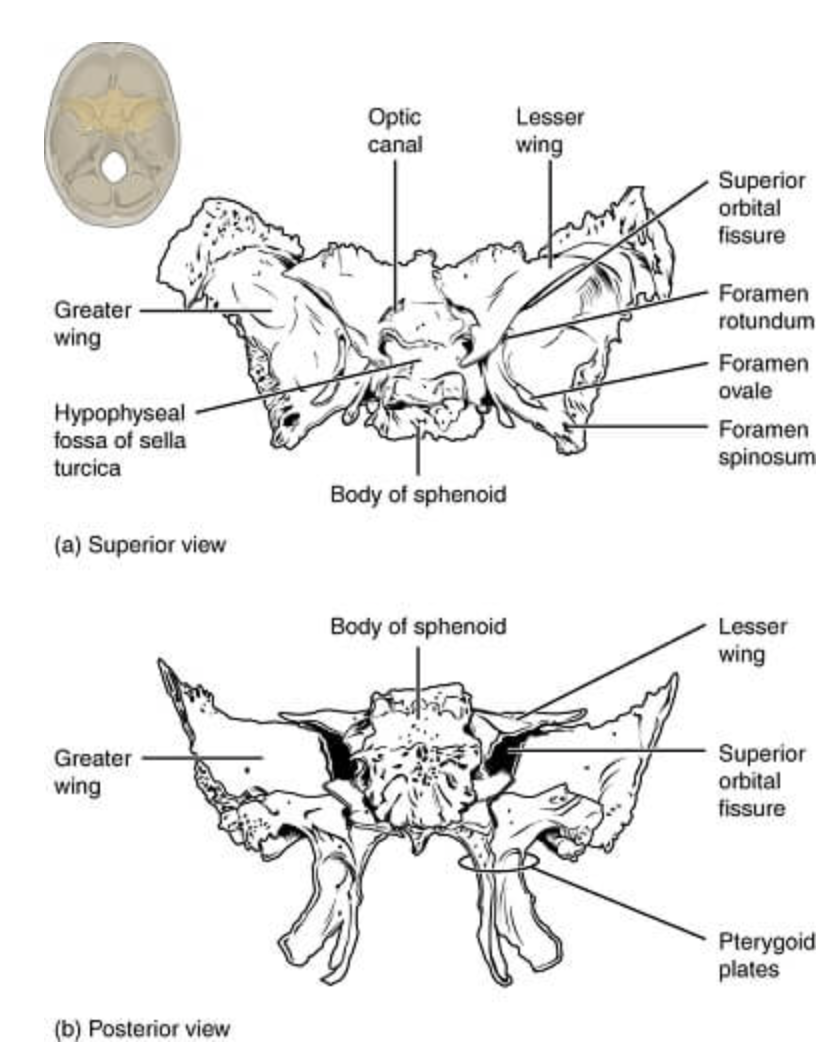
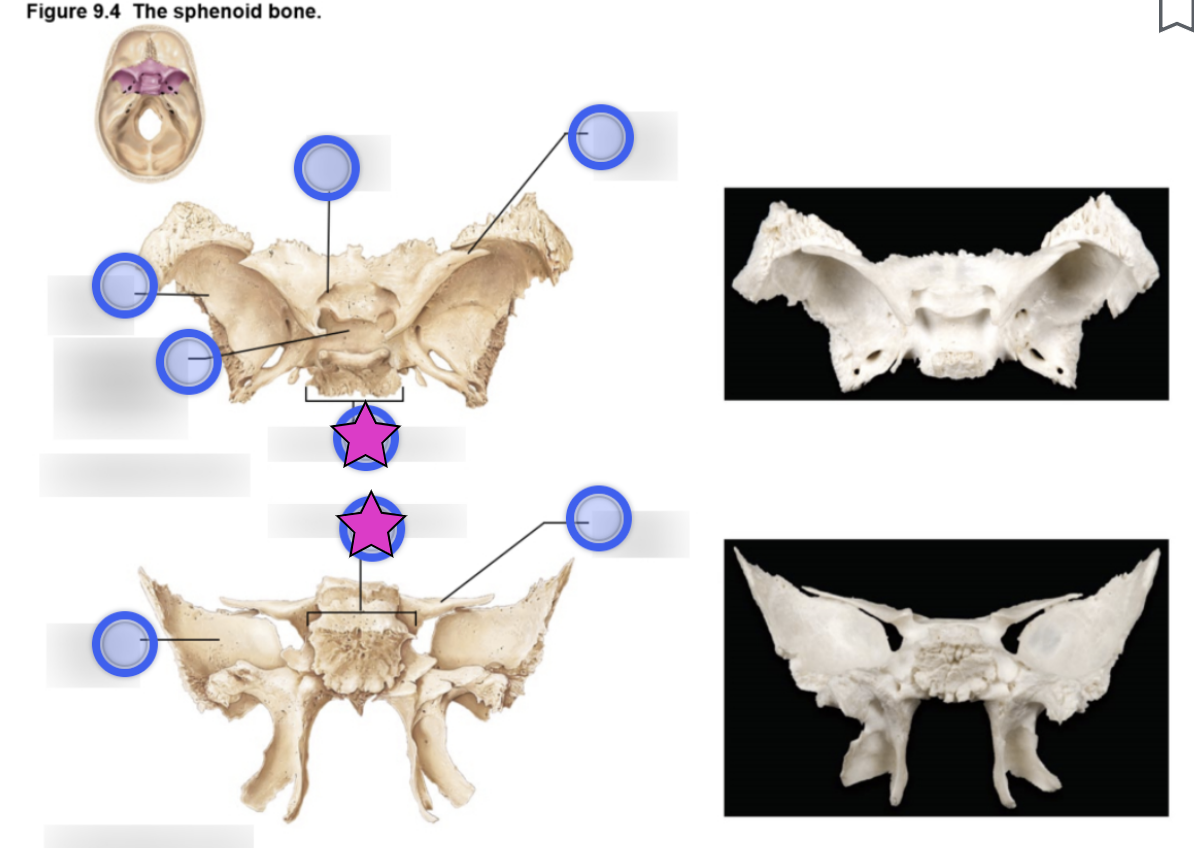
Body
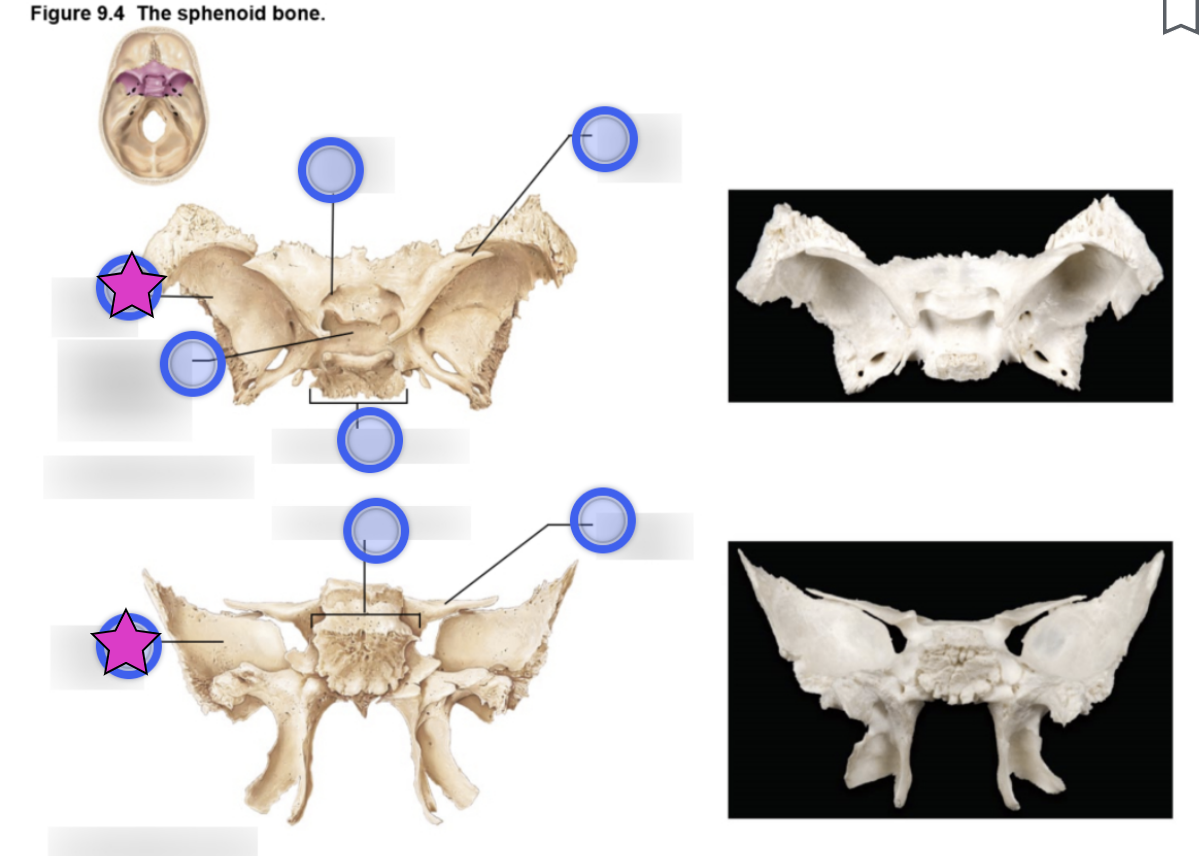
Greater wing
Project laterally from the sphenoid body, forming parts of the middle cranial fossa and the orbits
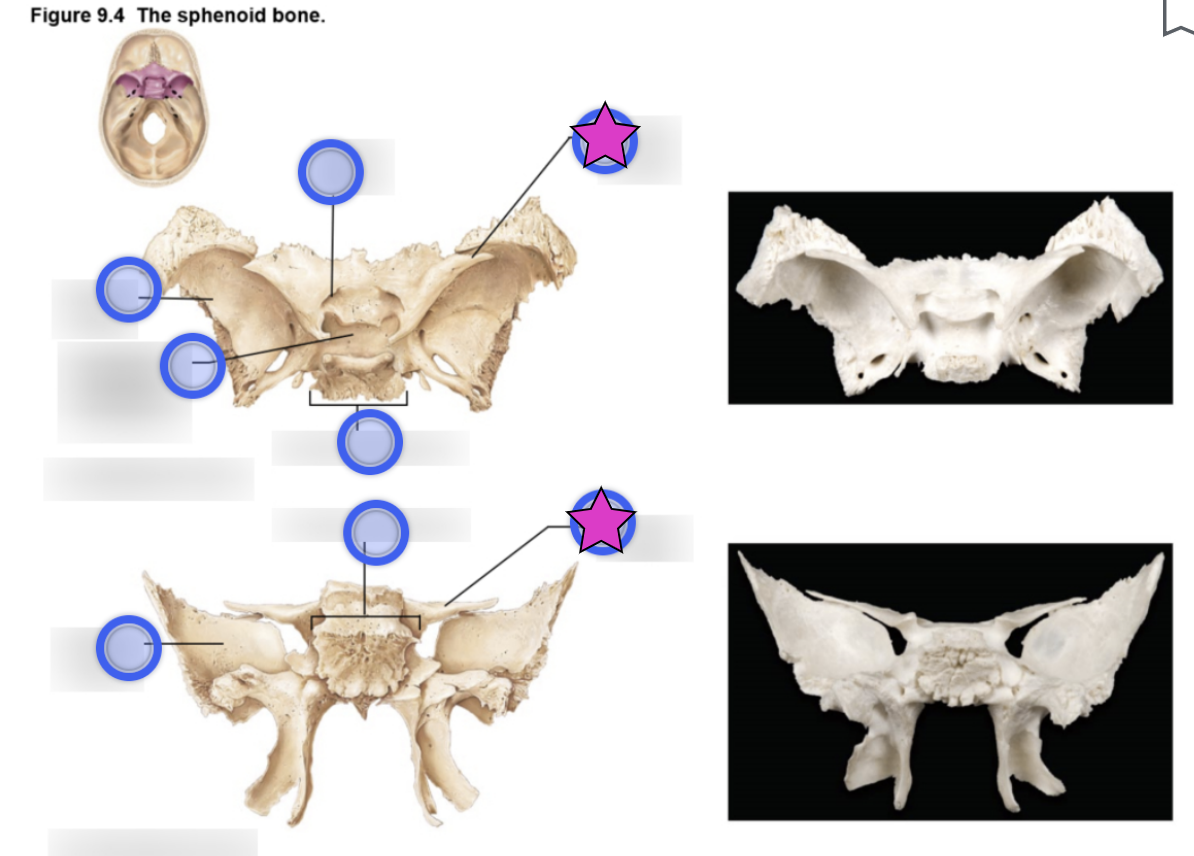
Lesser wing
From parts of the floor of the anterior cranial fossa and part of the orbit
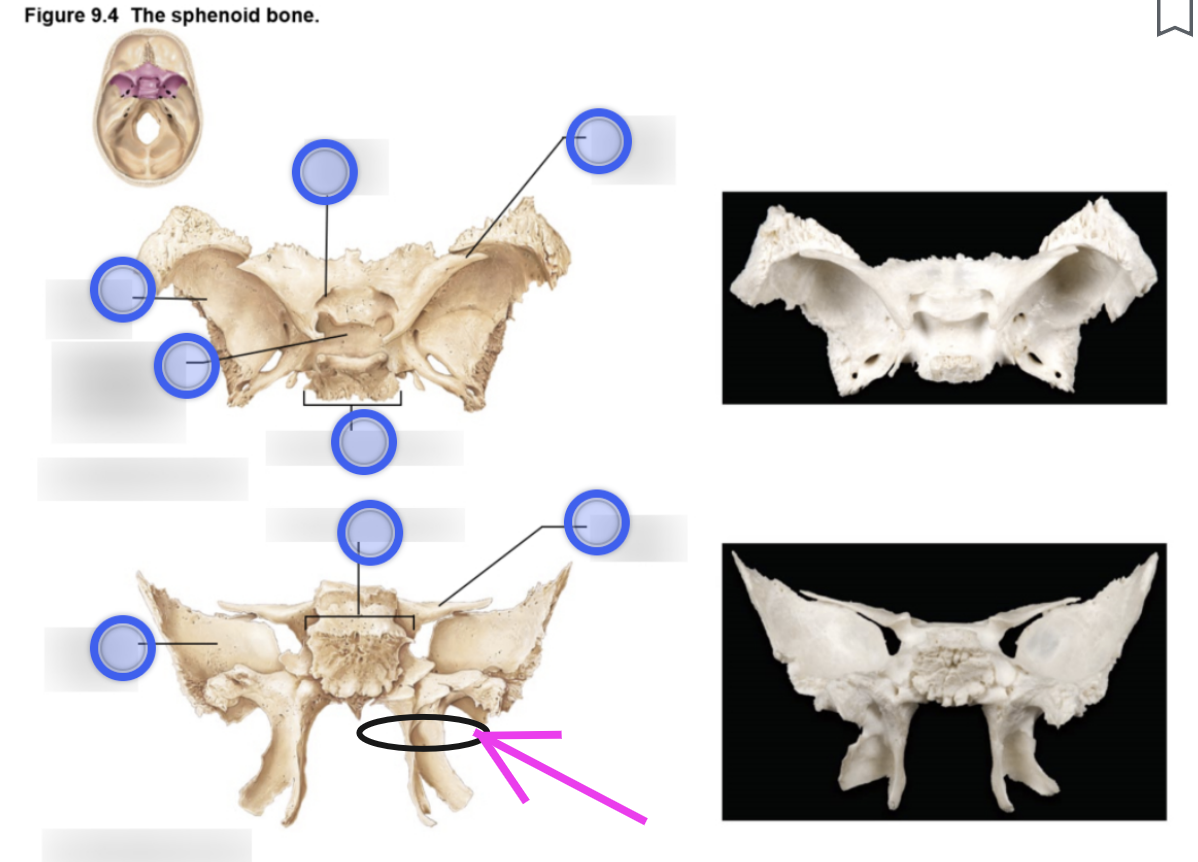
Pterygoid proccess
Project inferiorly from the greater wings n
Attachment site for chewing muscles
Pterygoid muscles
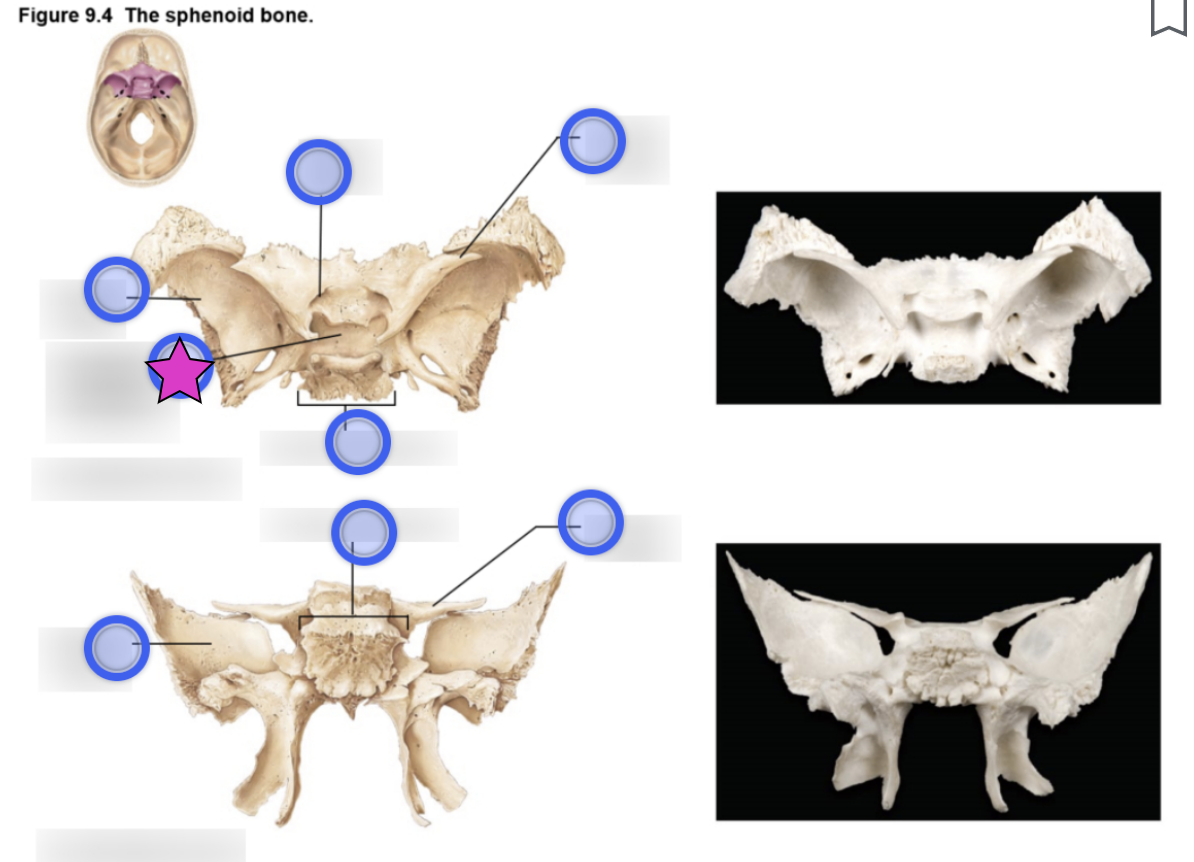
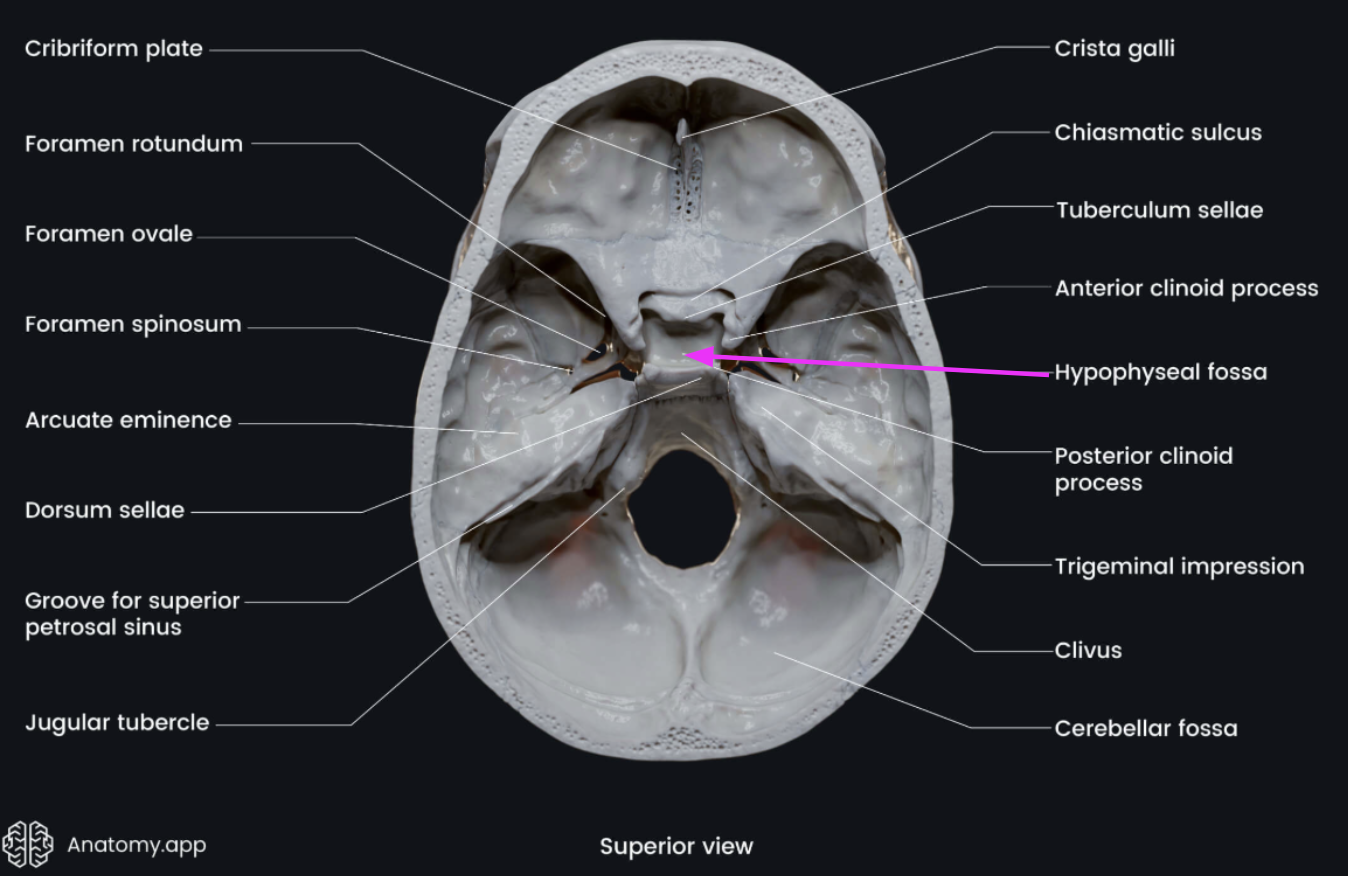
Hypophyseal fossa (aka sella turcica)
“Turkish saddle”
Located in the superior surface of the body
The seat of the saddle, called the hypophyseal fossa, holds the pituitary gland
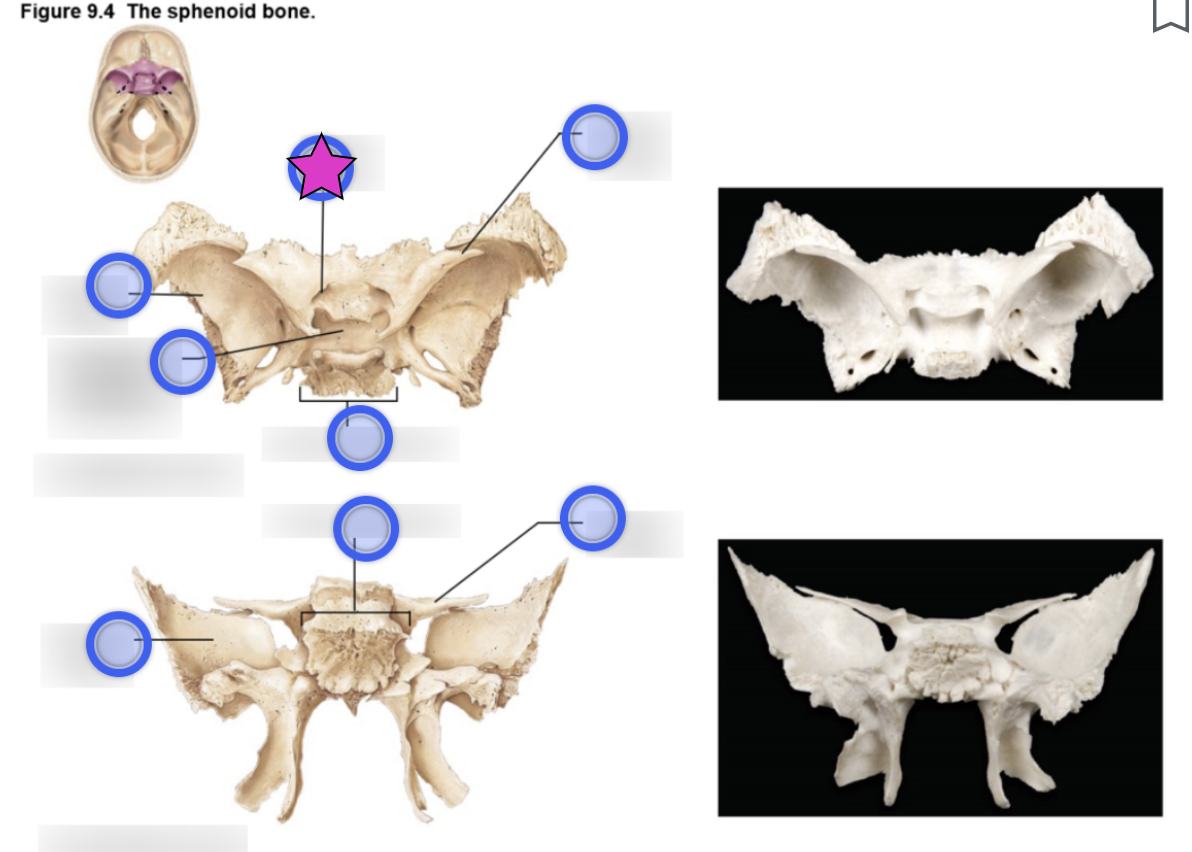
Optic canal
Openings in the base of the lesser wings
Cranial nerve II (optic nerve) passes through to serve the eye
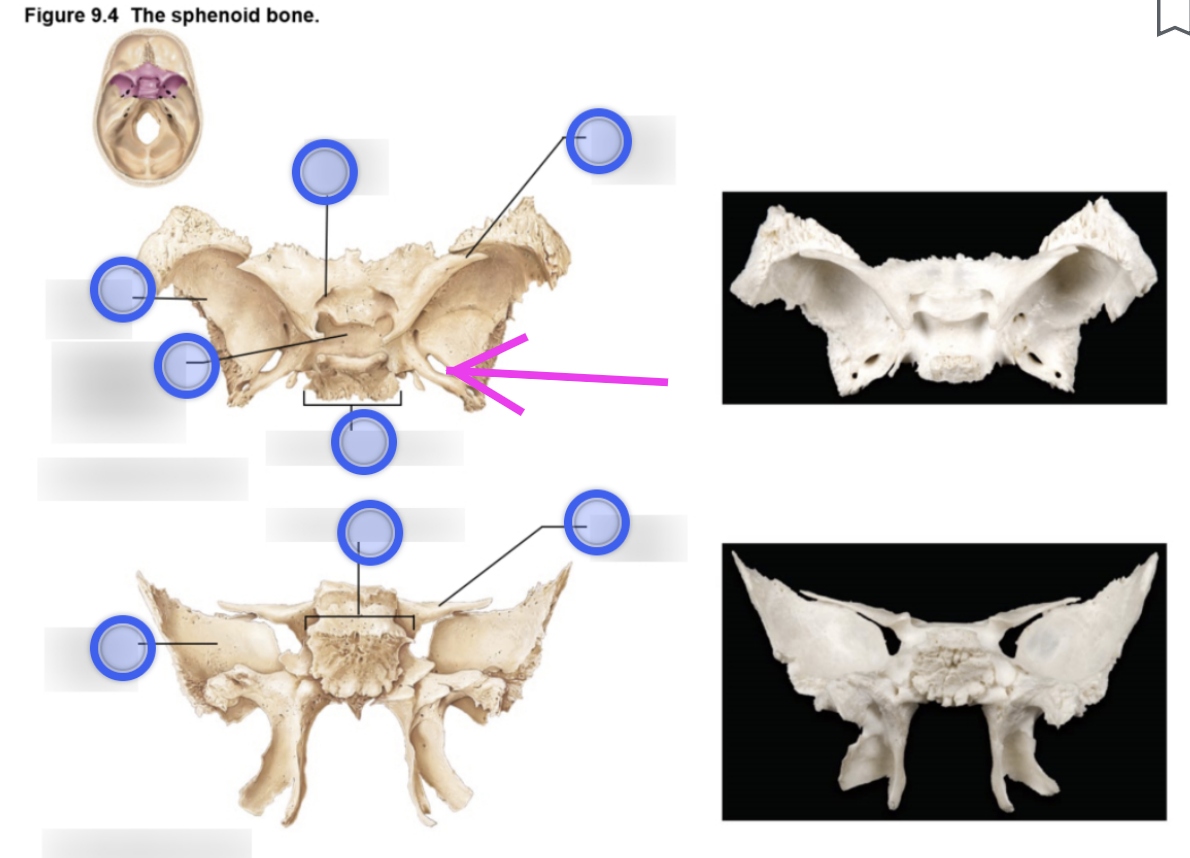
Foramen ovale
Openings located posterolateral to the foramen rotundum
A brancg of cranial nerve V (mandibular division) passes through

Foramen rotundum
Openings located in the medial part of the greater wing
A branch of cranial nerve V (maxillary division) passes through
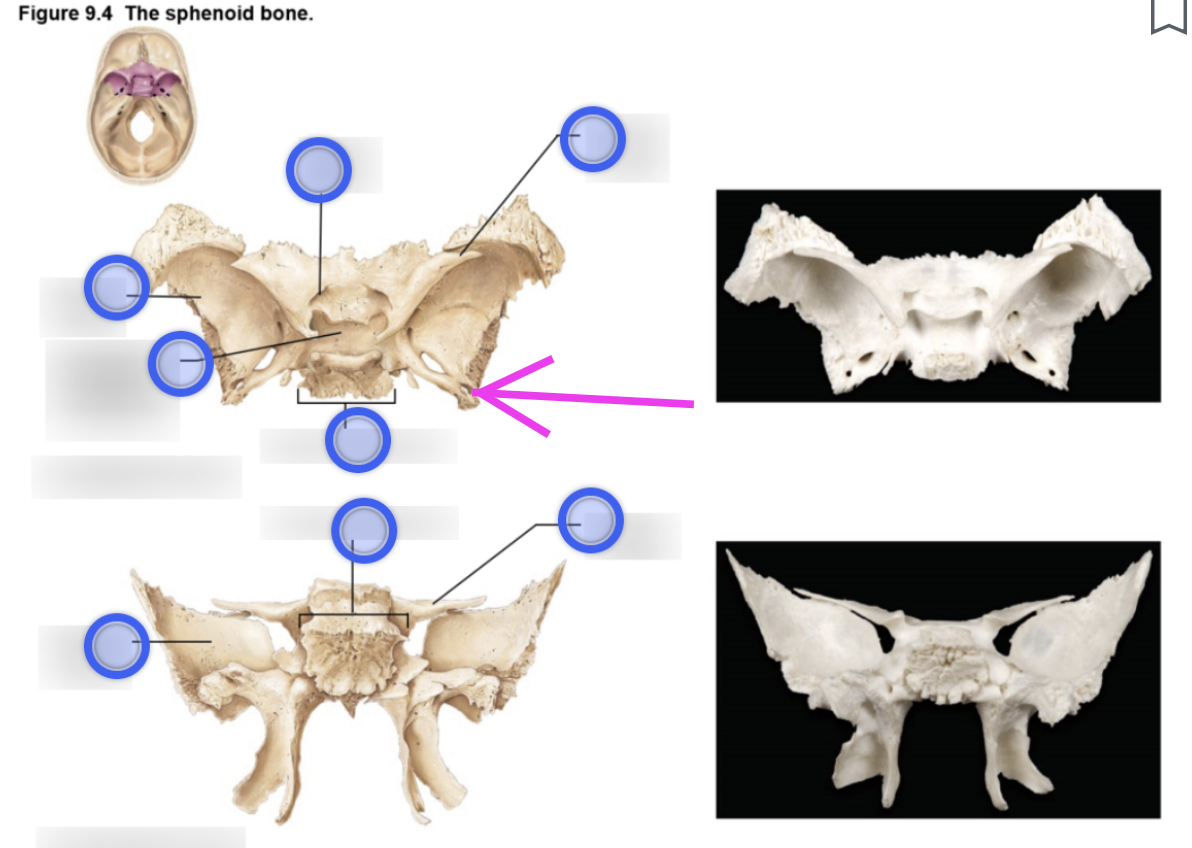
Foramen spinosum
Openings located posterolateral to the foramen spinosum
Provides passageway for the middle meningeal artery
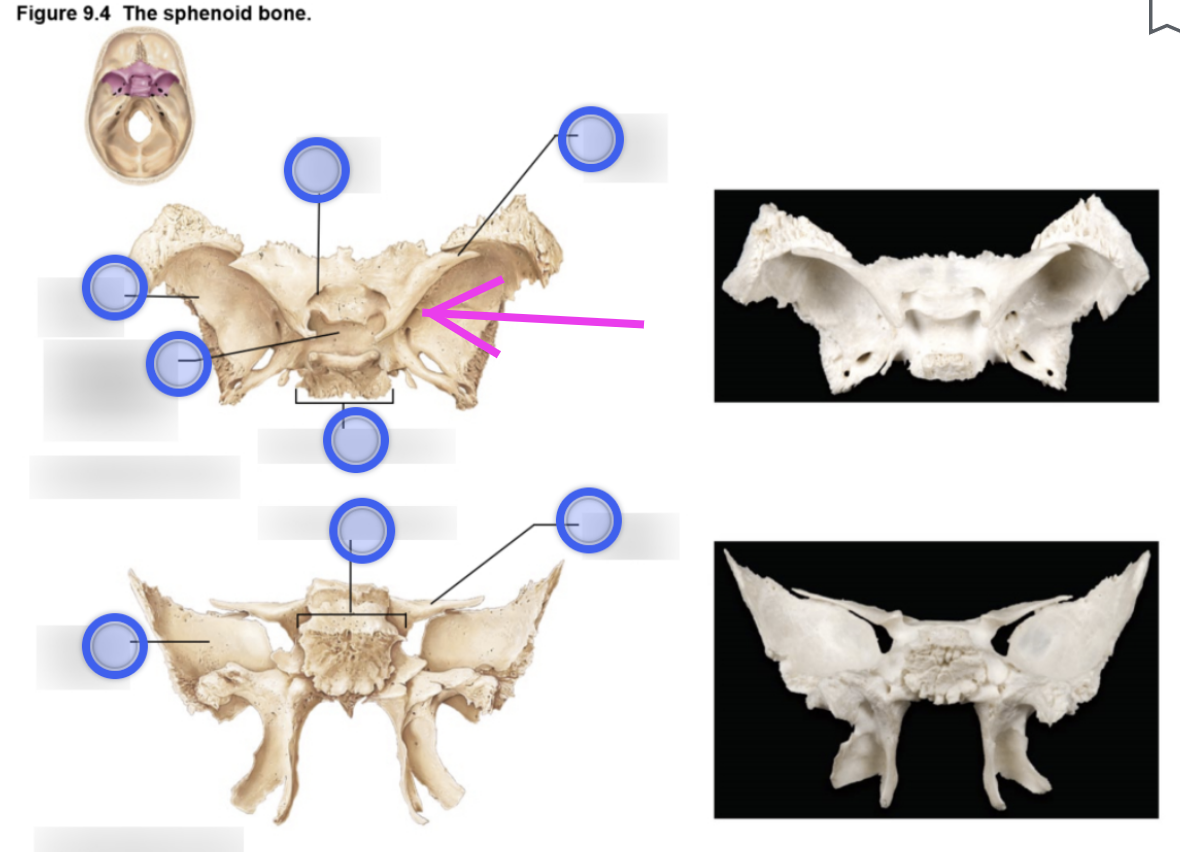
Superior orbital fissure
Slits in the orbits providing passaging of cranial nerves that control eye movements (III, IV, VI, and the ophthalmic division of V)
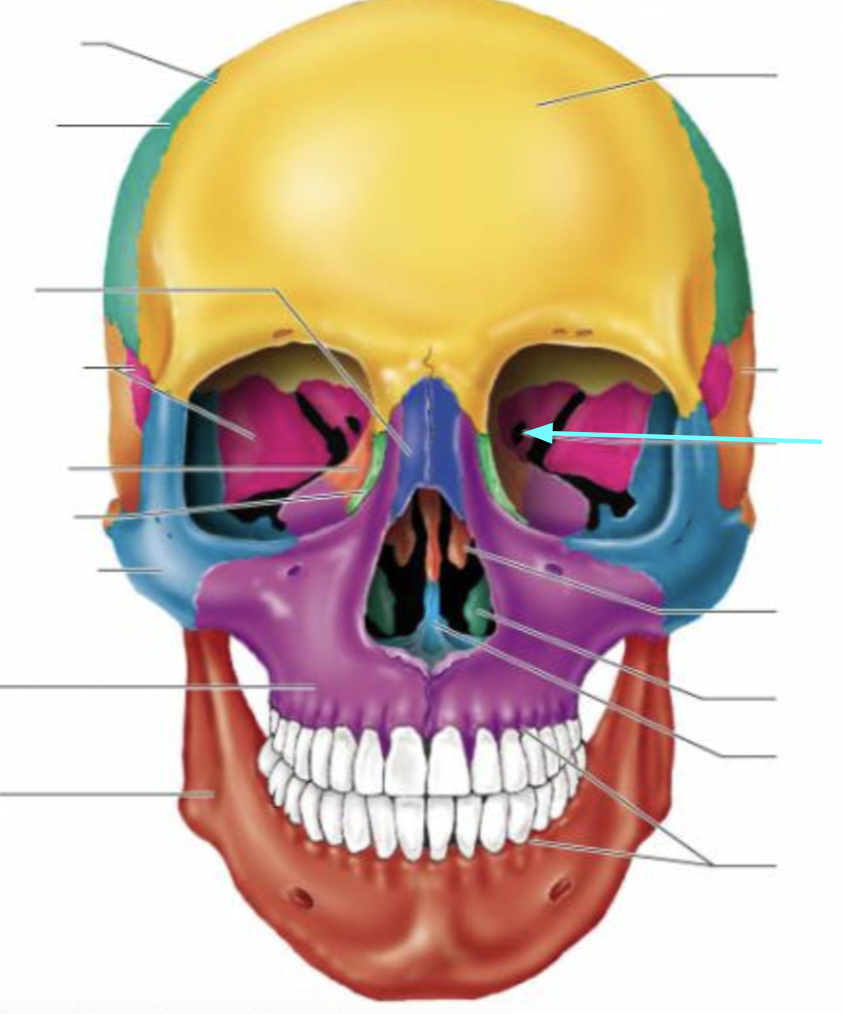
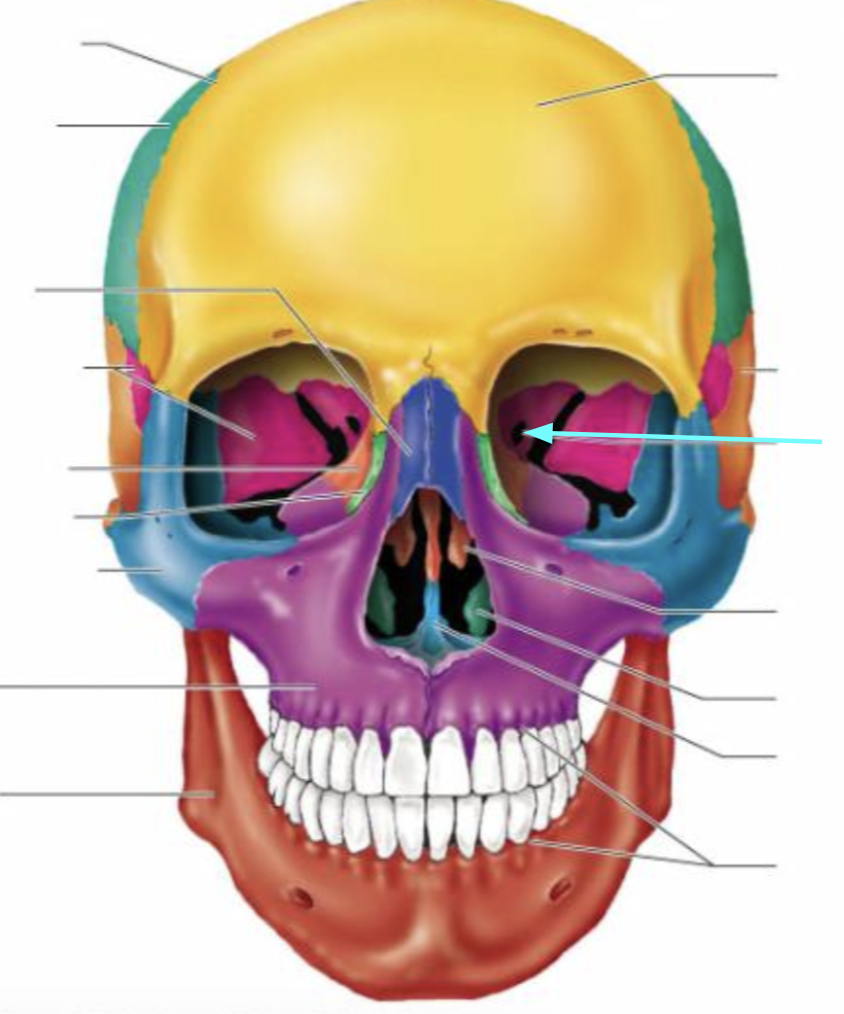
Face
The face makes up the anterior portion of the skull
Facial bones
The bones is composed of 14 bones

Mandible
The lower jawbone, which articulates with the temporal bone to form the only freely moveable joints in the skull (the temporomandibular joint)
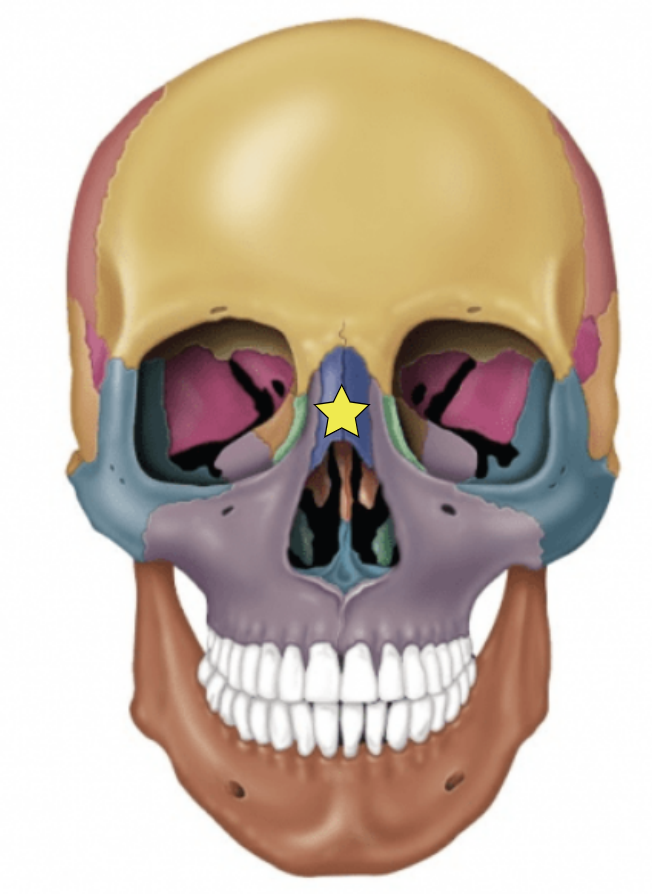
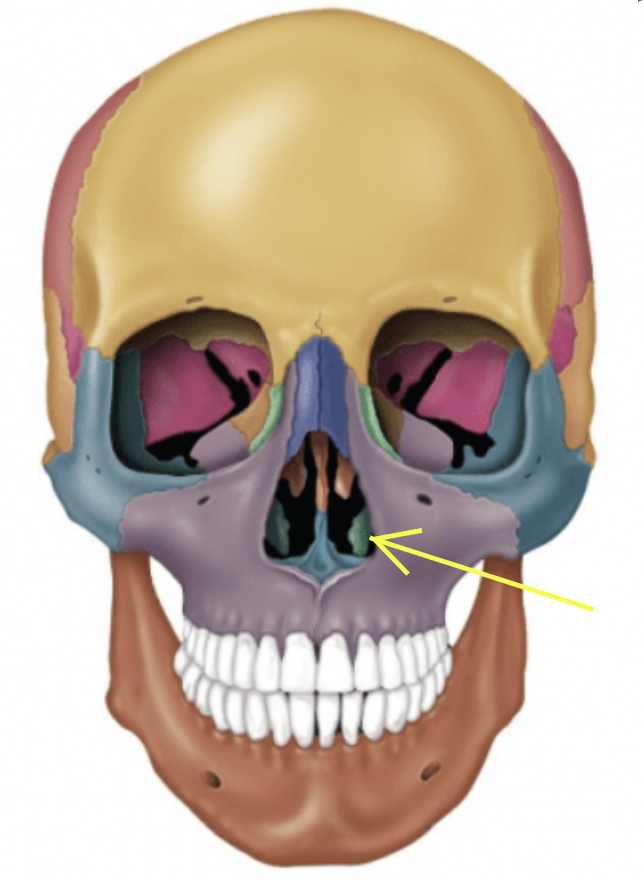
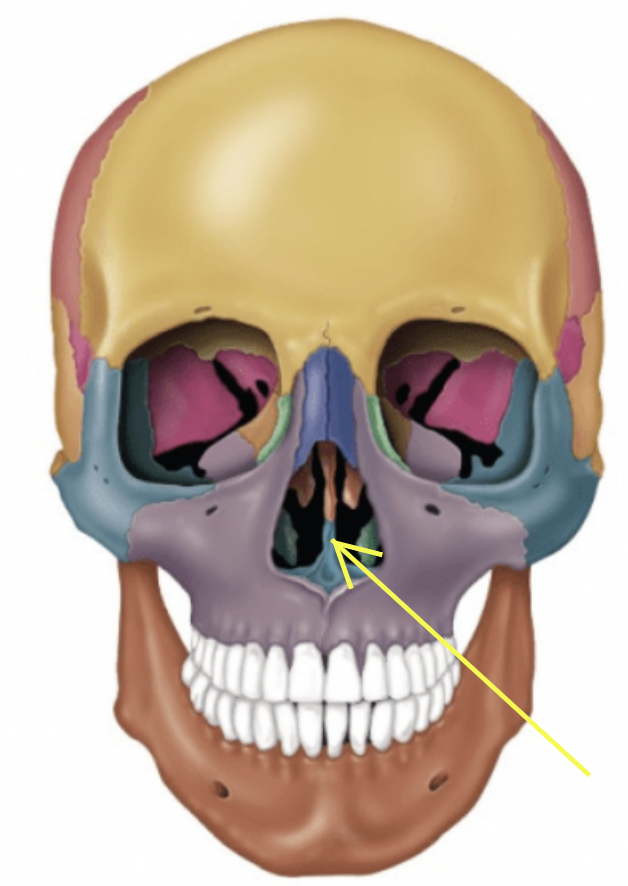
Maxillary bones (Left and Right)
Keystone facial bones because they articulate with all other facial bones except the mandible
Form the upper jaw and parts of the hard palate, orbits, and nasal cavity
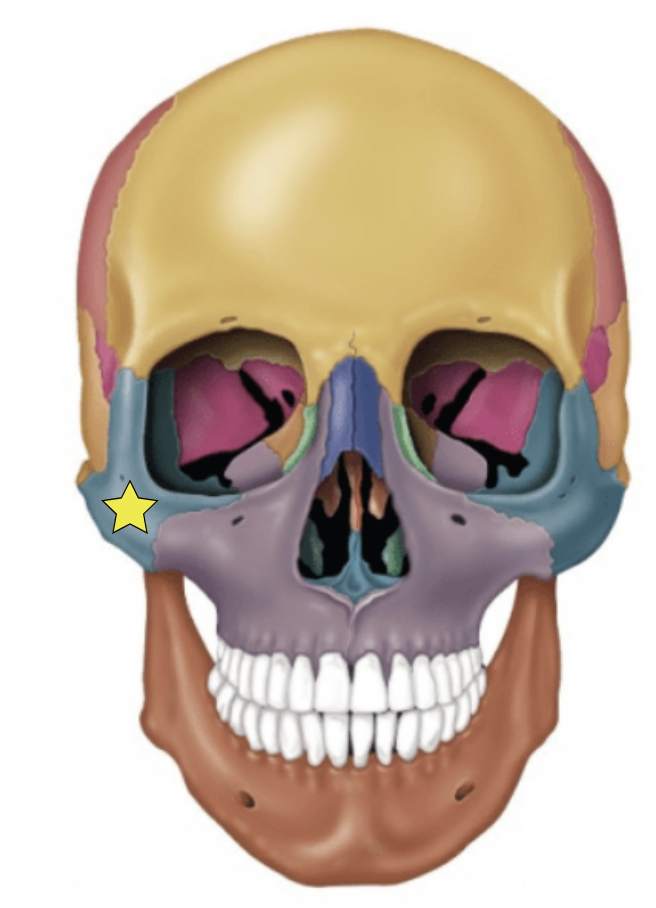
Lacrimal bones (Left and Right)
Each forms part of the medial orbit in between the maxilla and ethmoid bone
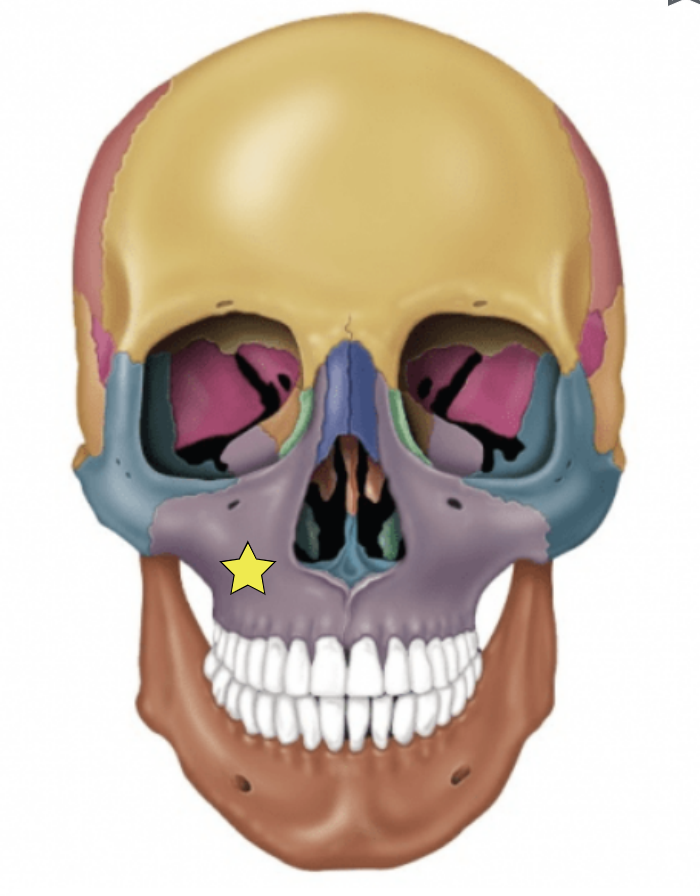
Zygomatic bones (Left and Right)
Commonly called the cheekbones
Each forms part of the lateral orbit
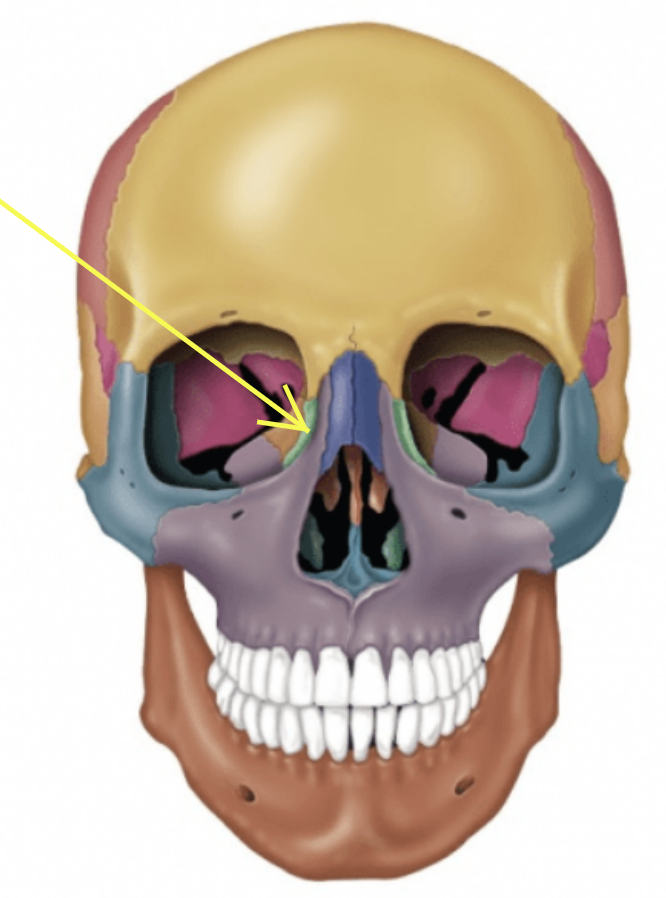
Nasal bones (Left and Right)
Small rectangular bones forming the bridge of the the nose
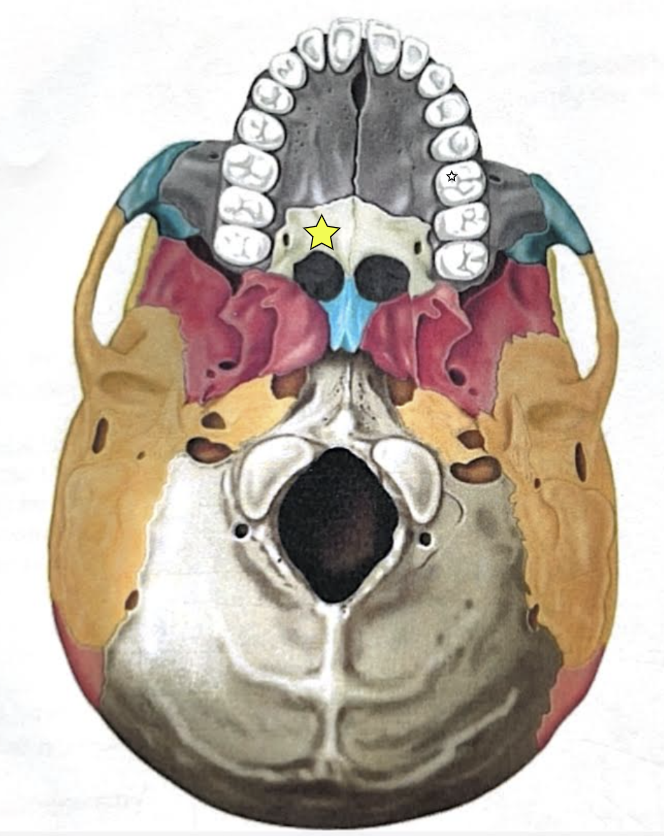
Palatine bones (Left and Right)
Forms the posterior hard palate, a small part of the nasal cavity, and part of the orbit
Inferior nasal conchae (Left and Right)
Inferior turbinate
Each forms part of the lateral walls of the nasal cavities
Improves the airflow through the nasal cavity
Vomer
Thin
Blade-shaped bone that forms the inferior nasal septum
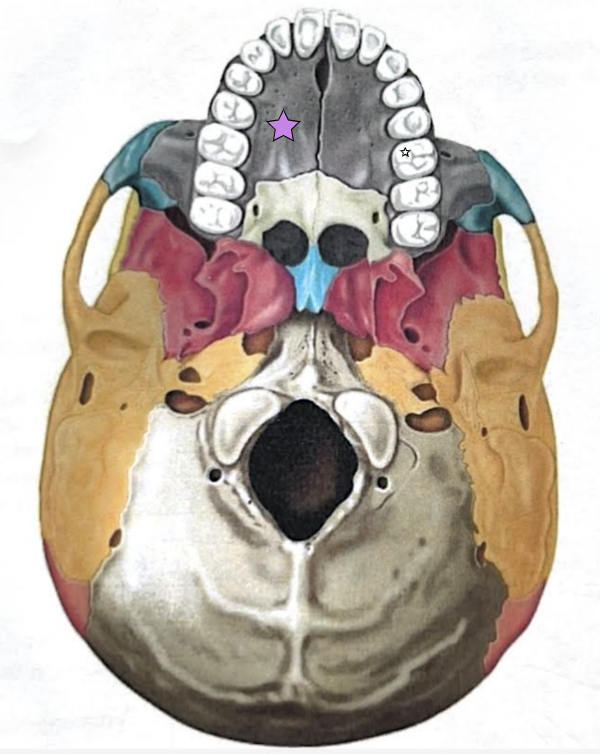
Maxilla structures
Keystone facial bones because they articulate with all other facial bones except the mandible form the upper jaw and the hard palate, orbits, and nasal cavity
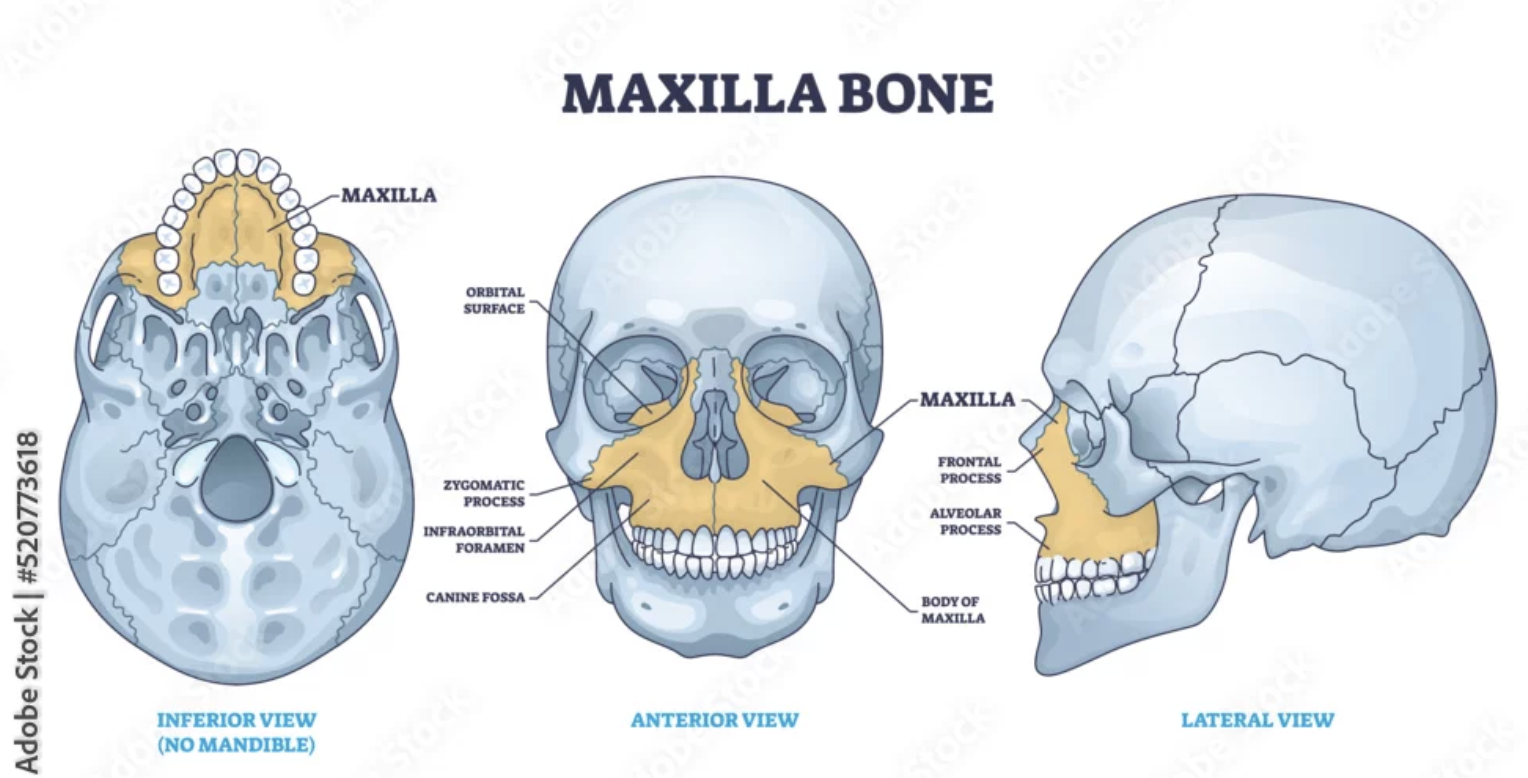
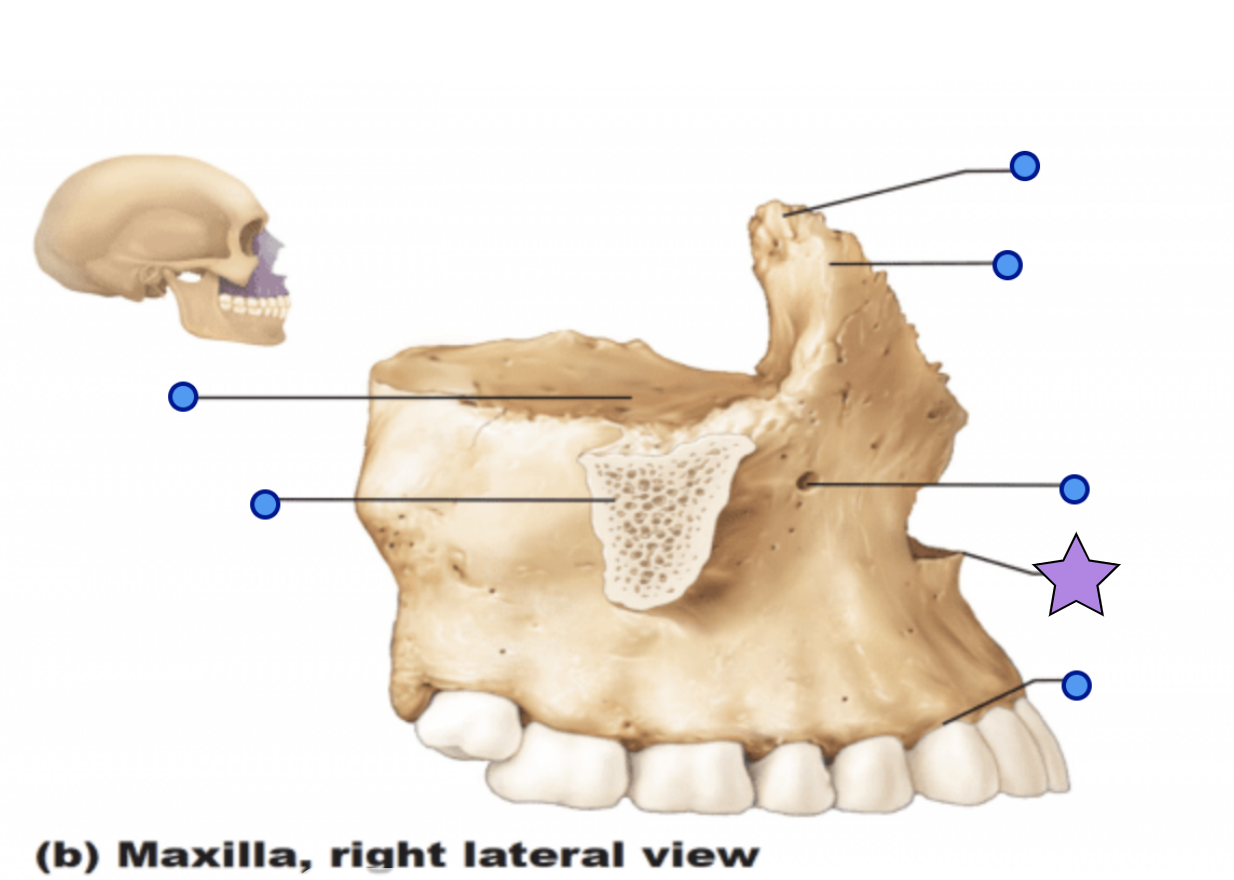
Anterior nasal spine
Palatine process
Forms the anterior hard palate
Meet anteriorly in the inter-maxillary suture
++Seen in the inferior view++
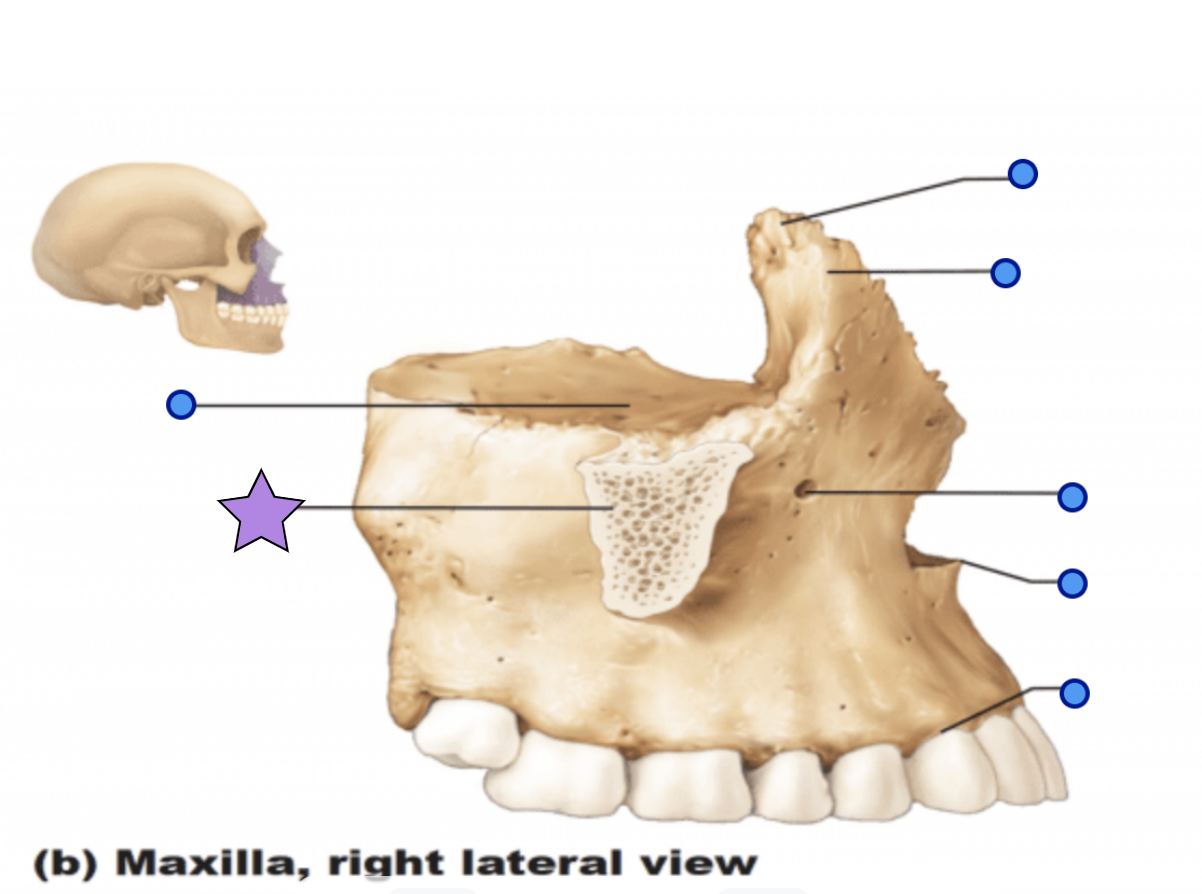
Zygomatic process
Articulation process for zygomatic bone
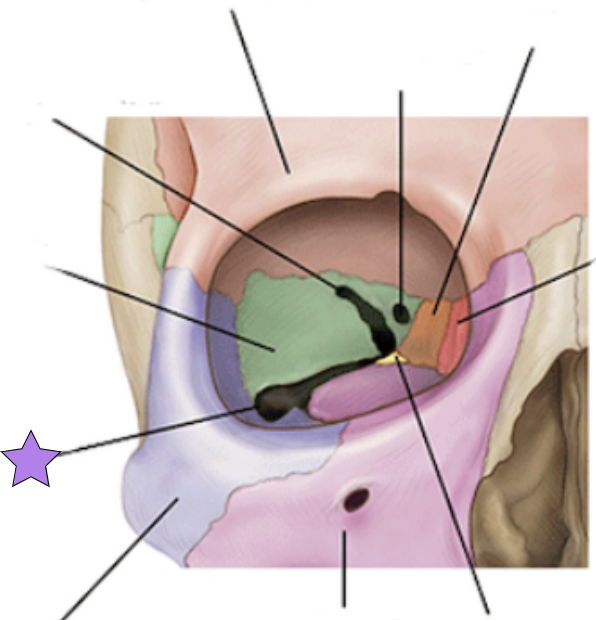
Inferior orbital fissure
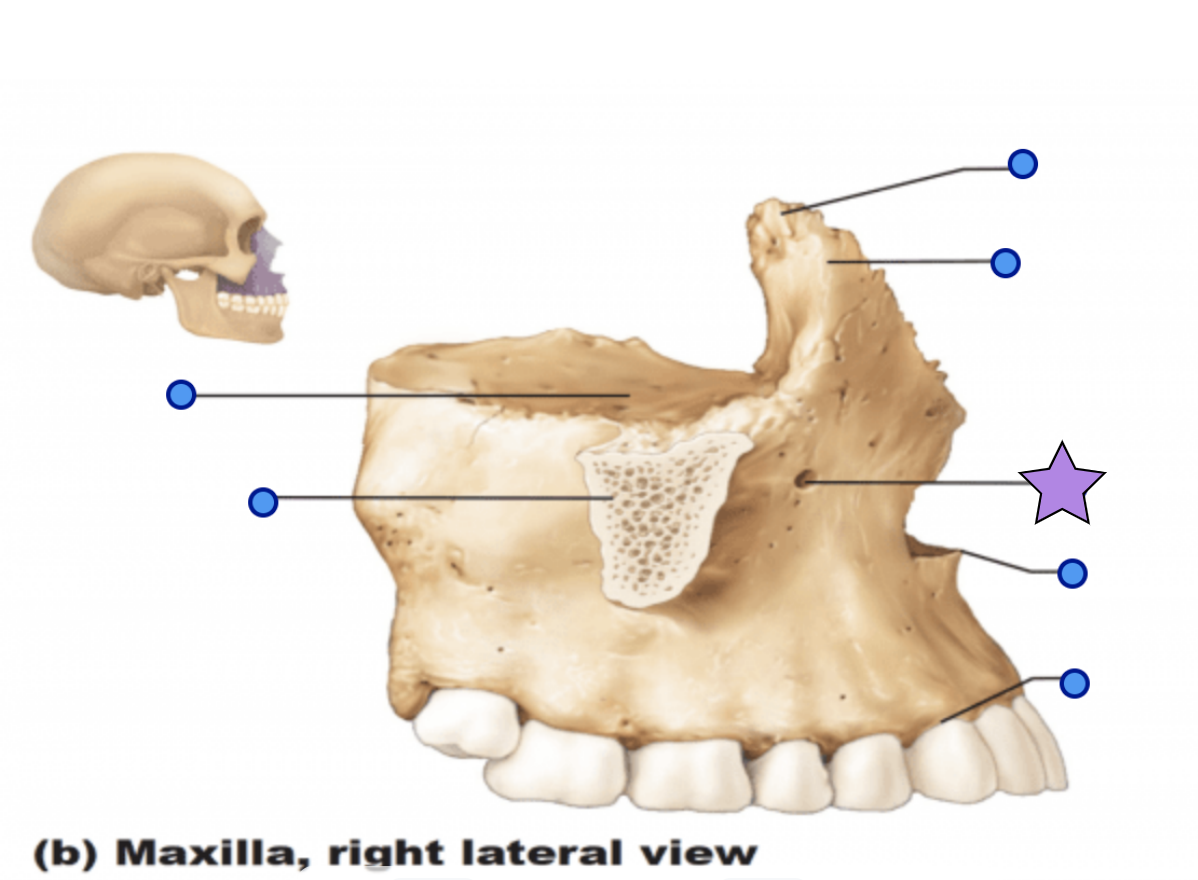
Infraorbital foramen
Opening under the orbit that forms a passageway for the for the infraorbital artery and nerve
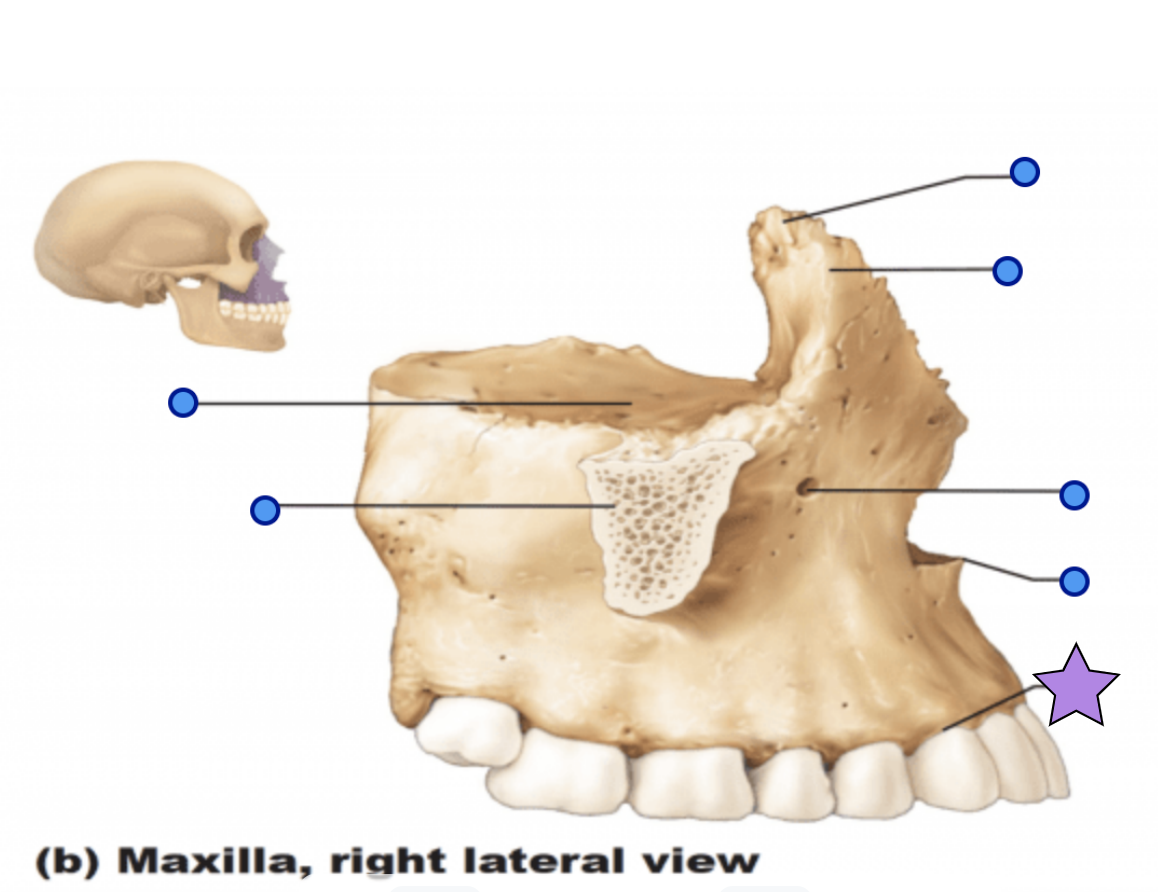
Alveolar process
Inferior margin of the maxilla
Contains sockets in which the teeth lie
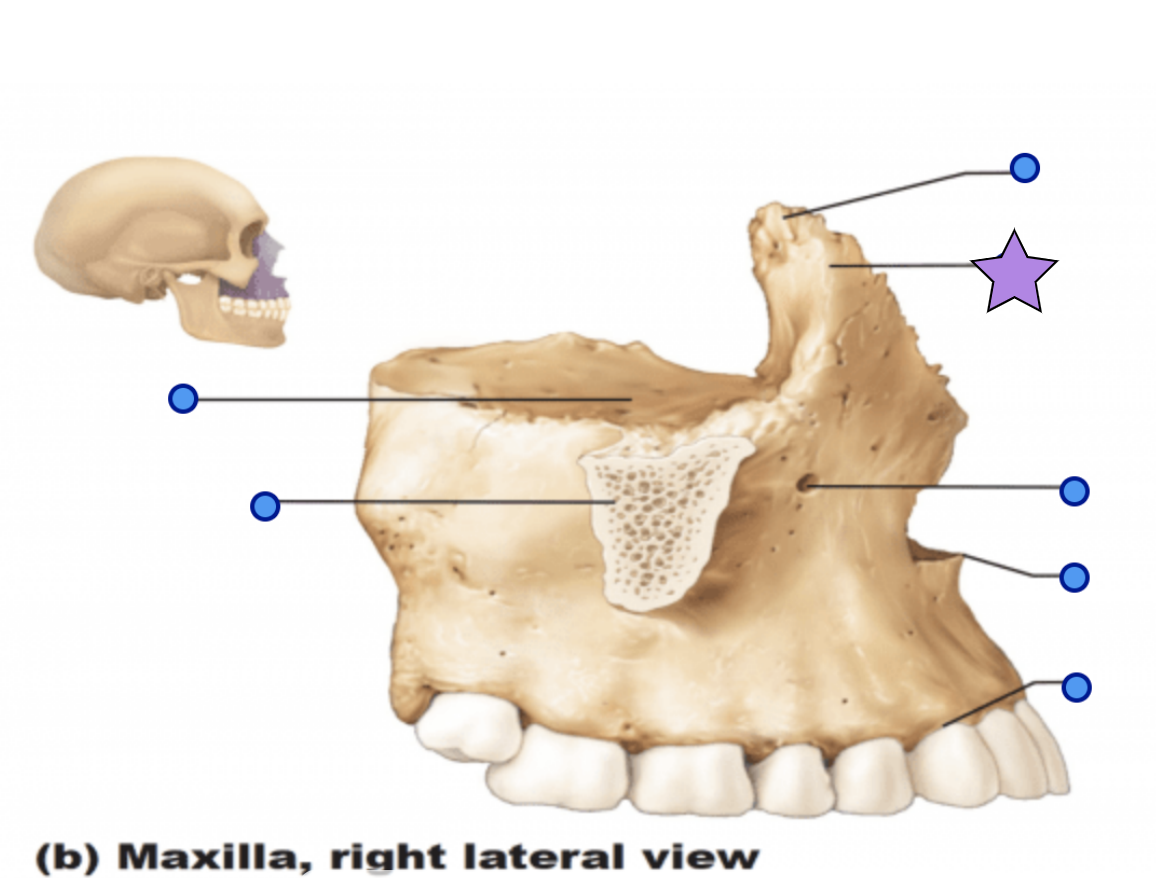
Frontal process
Forms the part the lateral aspect of the bridge of the nose
Mandible structures
The lower jawbone, which articulates with temporal bone to form the only freely moveable joints in the skull (the temporomandibular joint)
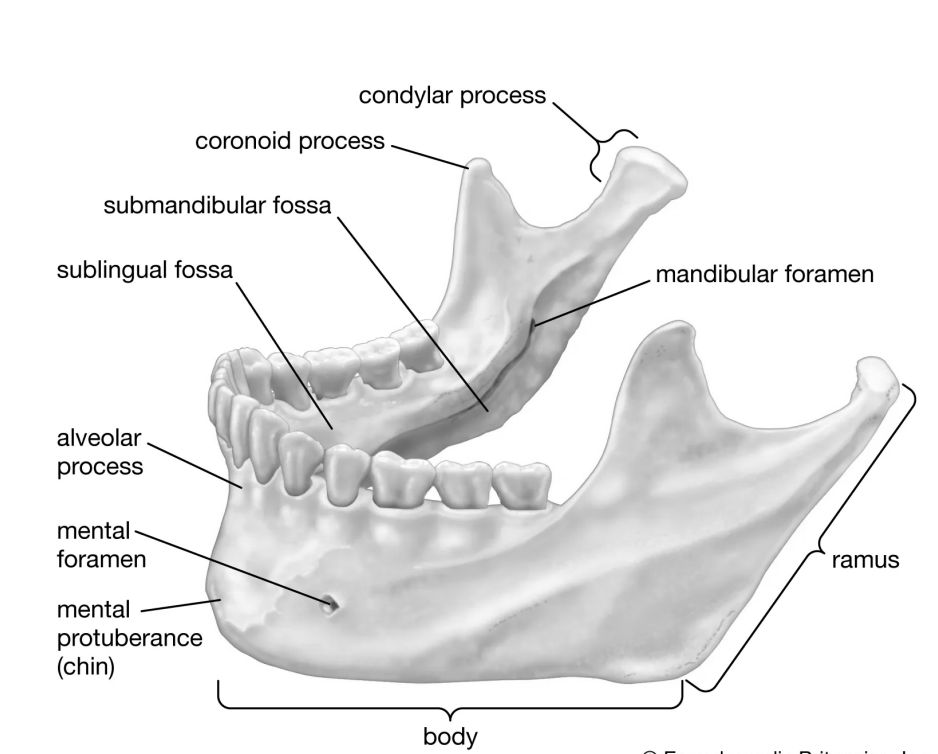
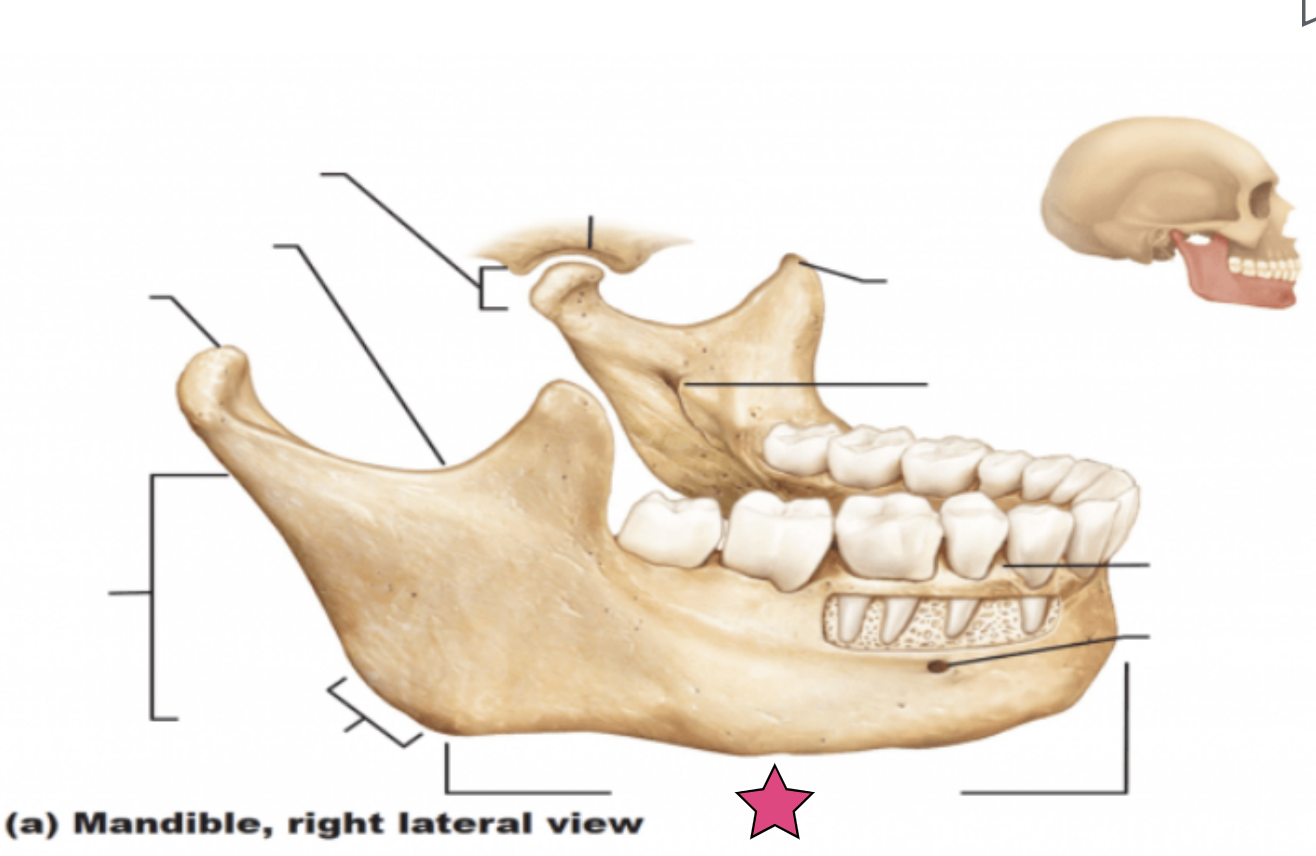
Body
Horizontal portion that forms the chin
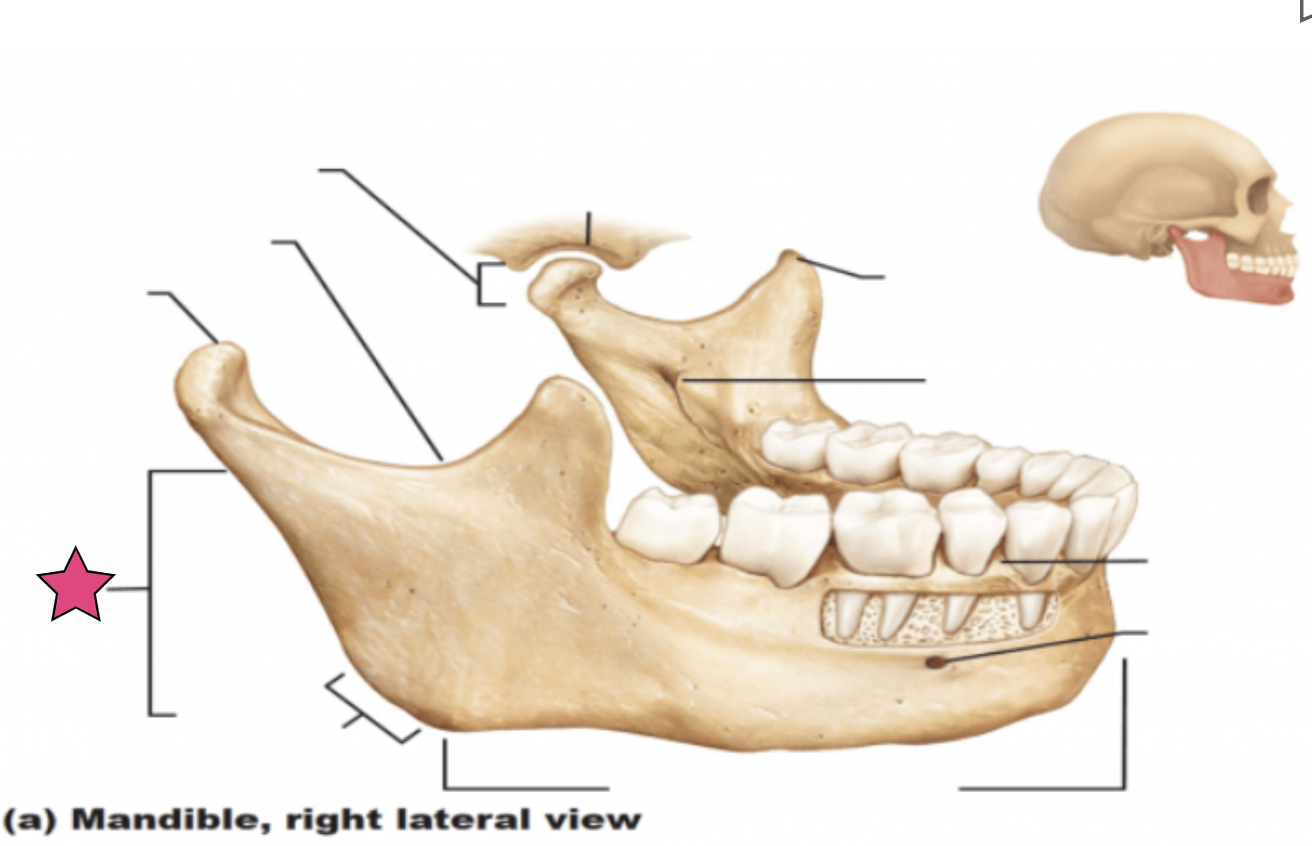
Ramus
Vertical extension of the body
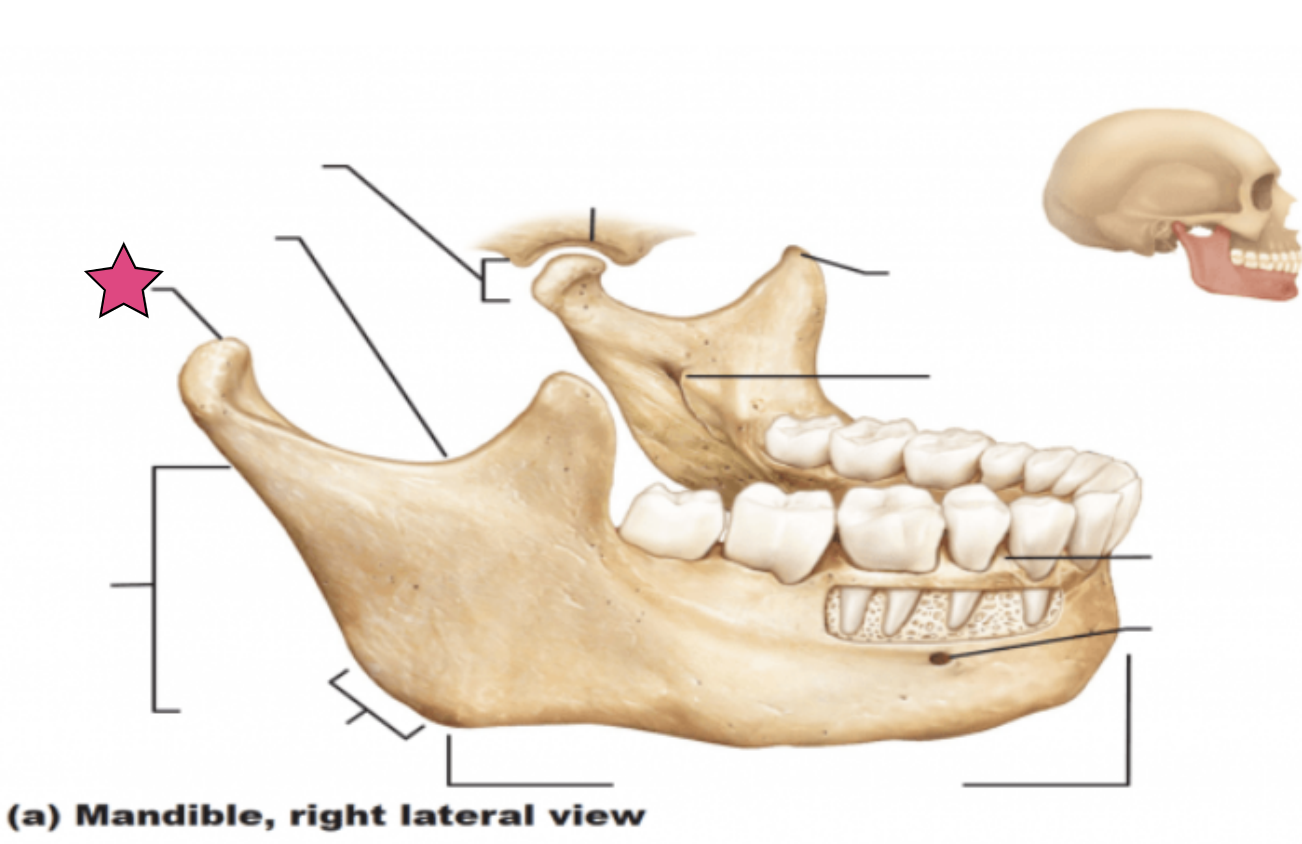
Condylar process
Articulate with the mandibular fossae of the temporal bone
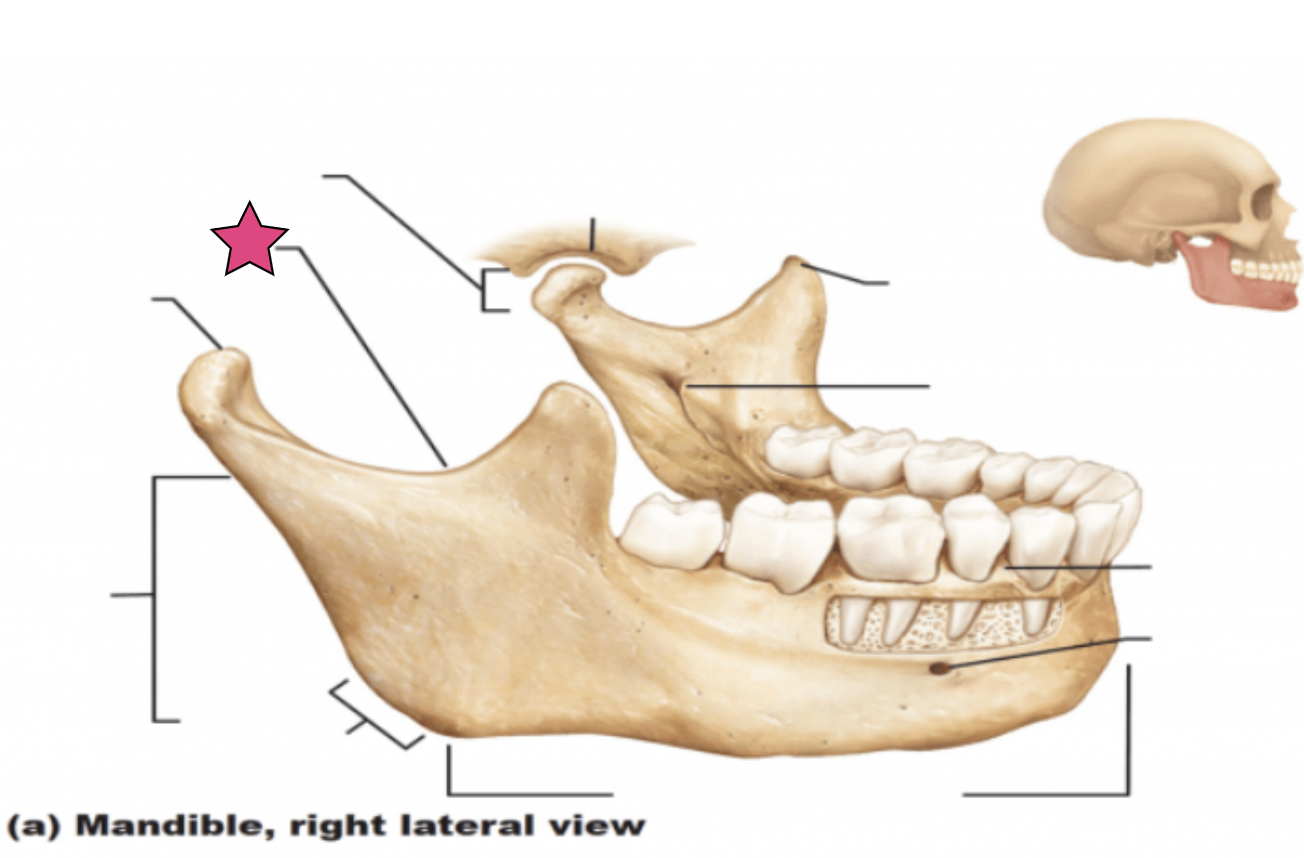
Mandibular notch
Separate the condylar process and the coronoid process
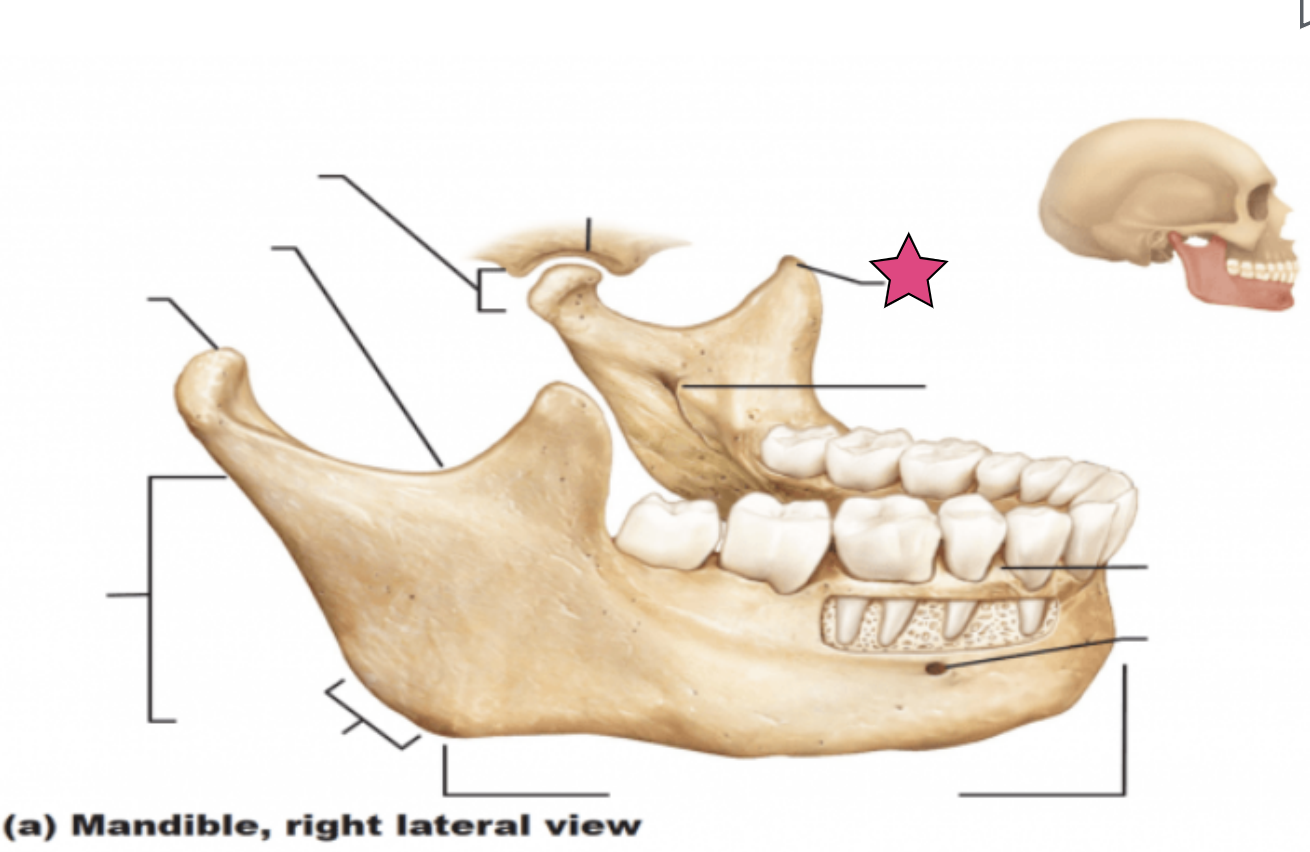
Coronoid process
“Crown-shaped” portion of the ramus for muscle attachment
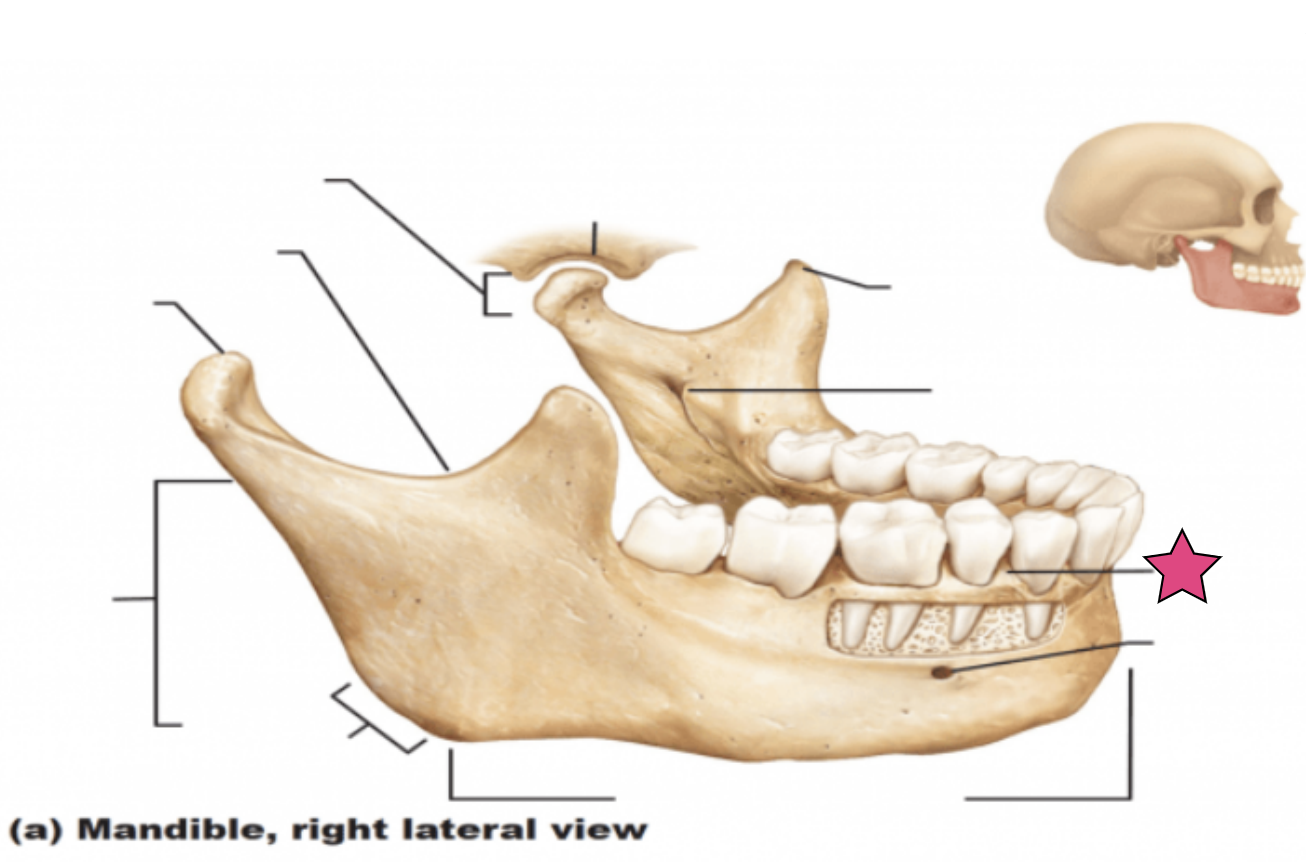
Alveolar process
Superior margin of the mandible
Contains sockets in which the teeth lie
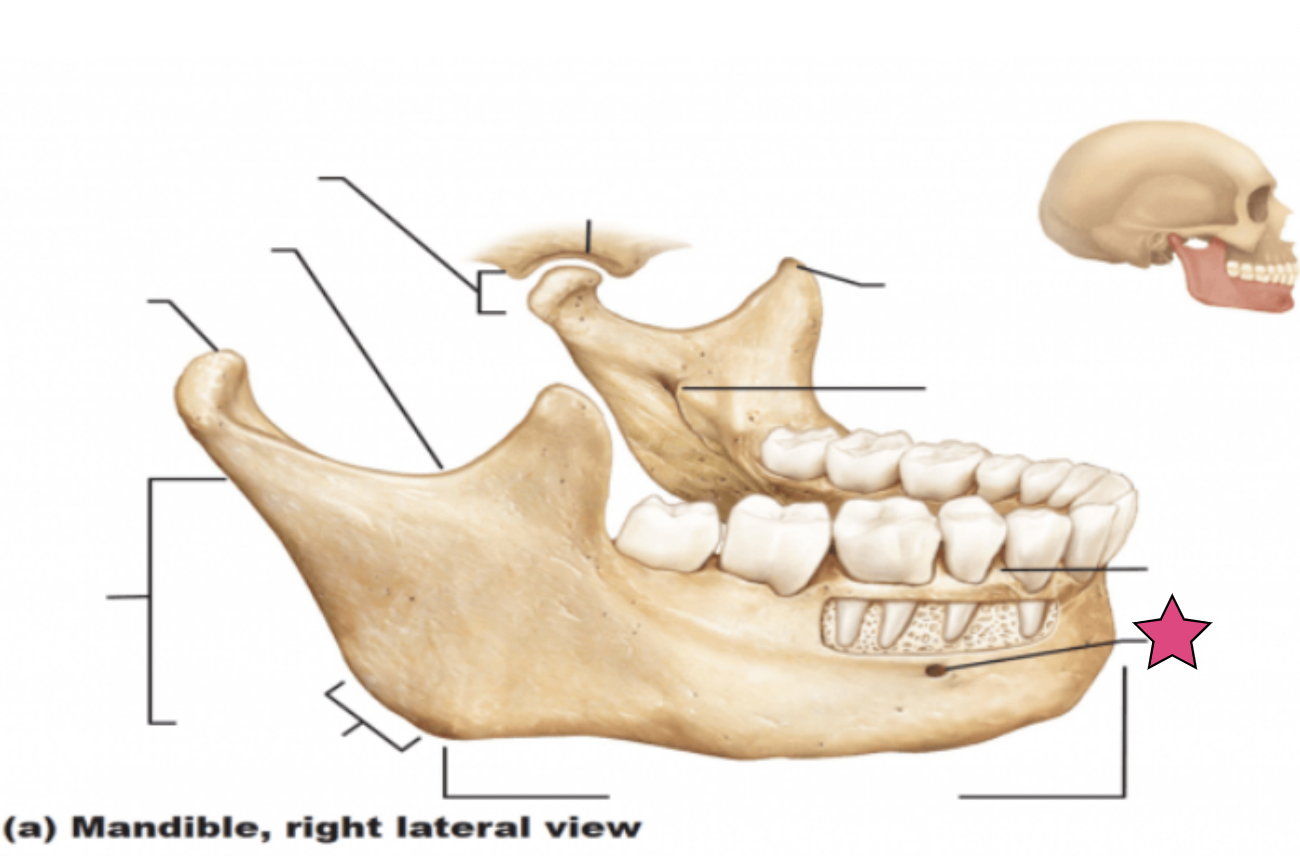
Mental foramen
Mental foramina (openings)
Paired openings on the body (lateral to the midline)
Transmit blood vessels and nerves to the lower lip and skin of the chin
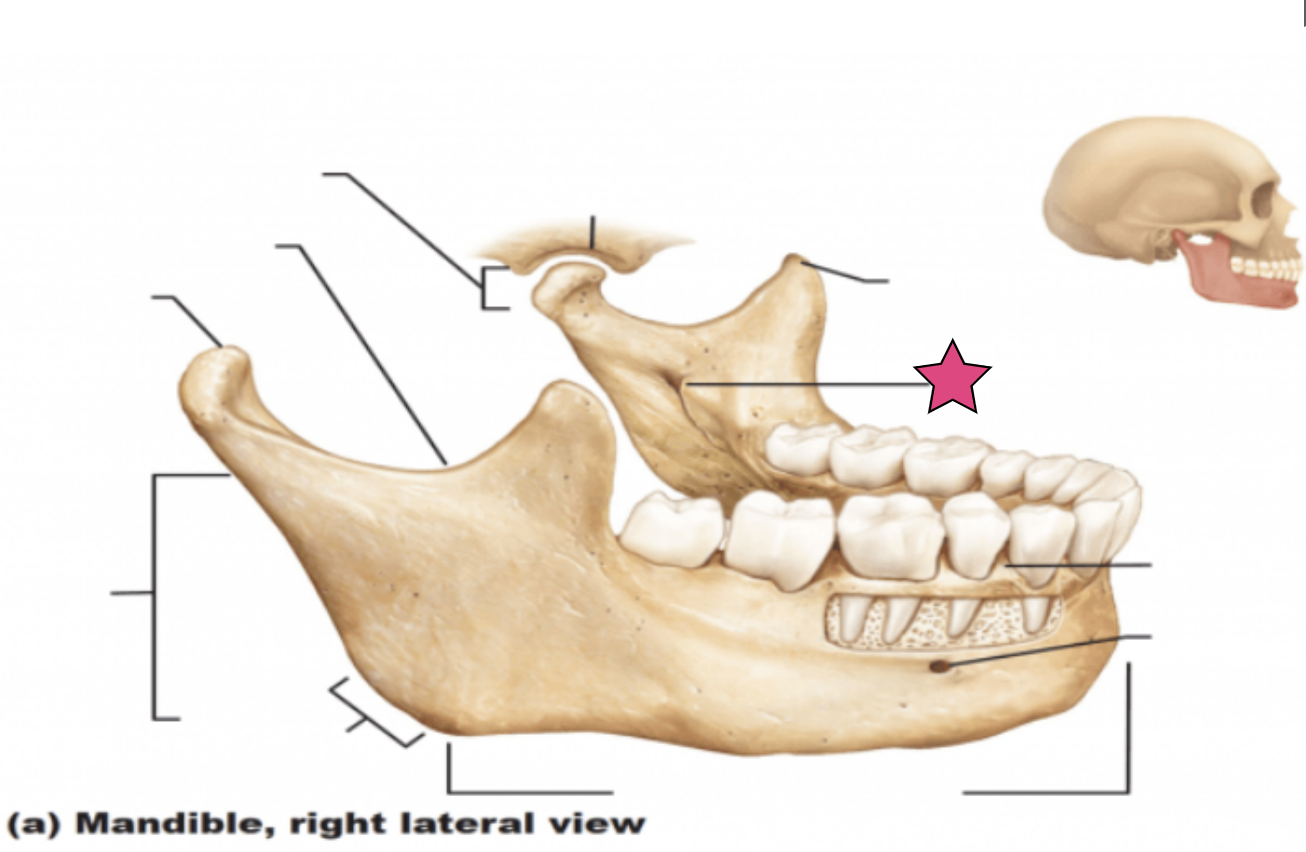
Mandibular foramen
Located on the medial surface of each ramus
Passageway for the nerve involved in tooth sensation
(Dentists inject anesthetic into this foramen before working on the lower teeth)
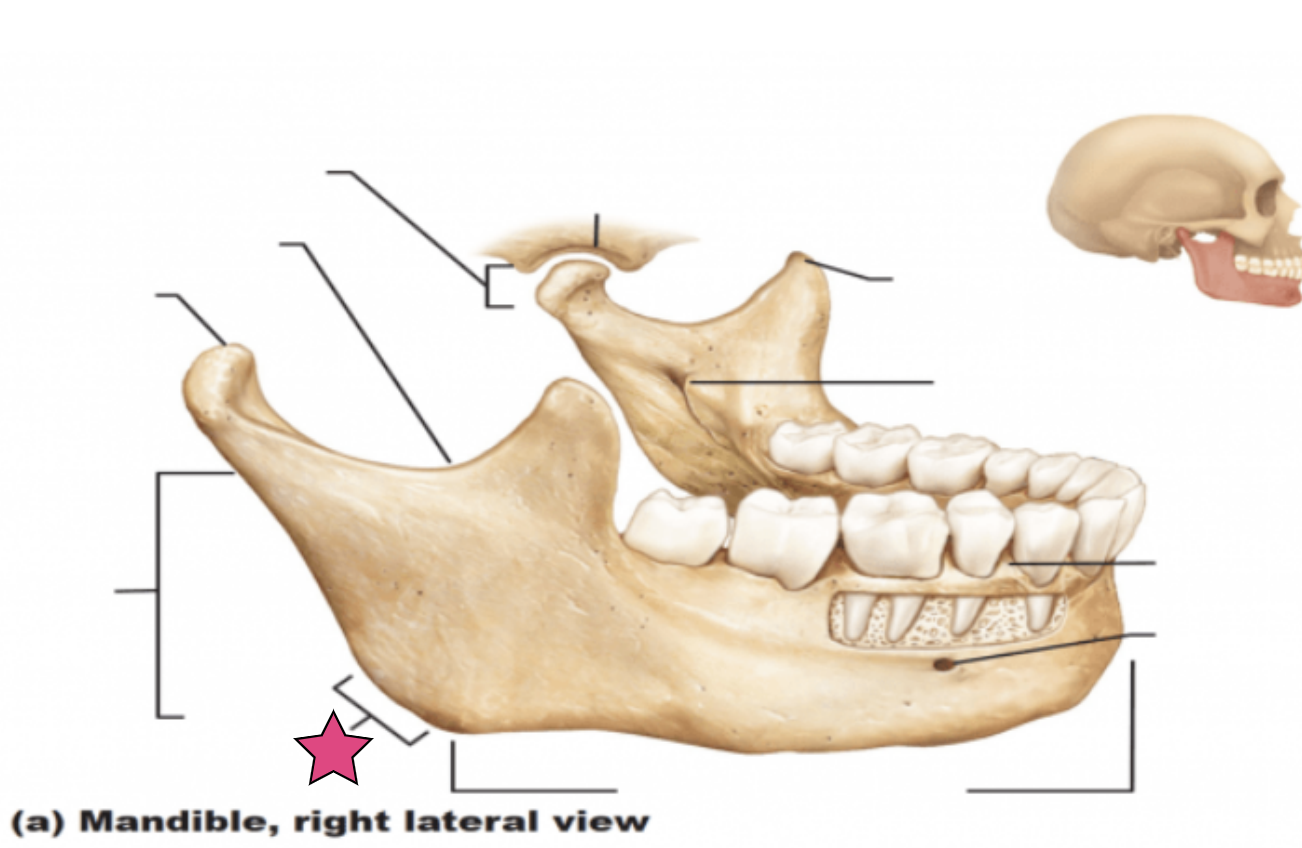
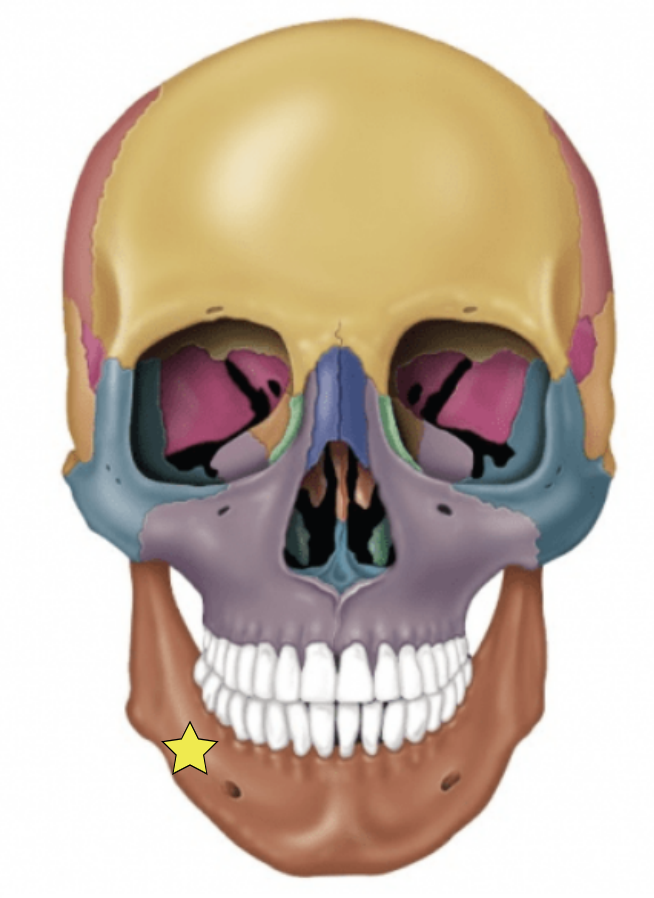
Mandibular angle
Posterior points where the ramus meets the body
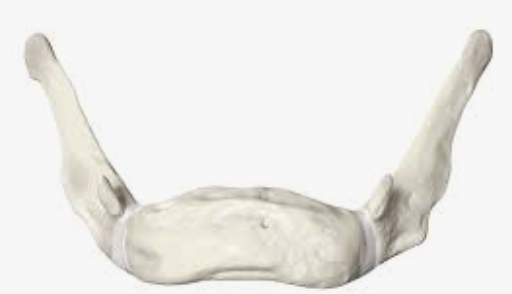
Hyoid bone
Only bone in the body that does not articulate directly with another bone
Found in the neck, below the mandible
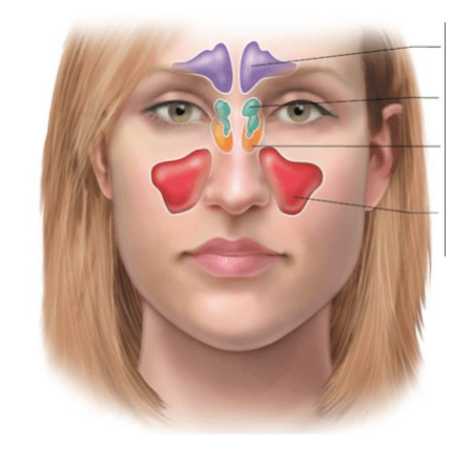
Paranasal sinuses
Some skull bones contain air-filled cavities
Found in five bones
Frontal
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
and each Maxilla