AQA Psychology - Agression
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:58 AM on 6/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
Which **neural mechanism** is implicated in agression?
Limbic System
2
New cards
What is the **Amygdala?**
* Responsible for **emotion** & **agression**
* If damaged, aggressive behaviour results
* If damaged, aggressive behaviour results
3
New cards
Show **research support** for the riole of the Amygdala in agression
**Pardini et al. (2014)**
↳ Londitudinal study of 56 males w/ a history of violence
* Found a **negative correlation** between the **volume** of their amygdala + **higher levels** of **violence**
* *Also the* ***case study*** *of* ***Phineas Gage***
↳ Londitudinal study of 56 males w/ a history of violence
* Found a **negative correlation** between the **volume** of their amygdala + **higher levels** of **violence**
* *Also the* ***case study*** *of* ***Phineas Gage***
4
New cards
Name **one** neurotransmitter linked to agression levels
Serotonin
5
New cards
Explain the role of **serotonin** on **agression**
* Normal levels of serotonin are **inhibitory,** so lead to **greater self-control** (reduced aggression)
* Decreased Serotonin **disturbsthis mechanism** + reduces **self-control,** increasing impulsive behaviours (including aggression)
* Decreased Serotonin **disturbsthis mechanism** + reduces **self-control,** increasing impulsive behaviours (including aggression)
6
New cards
Give **research support** for the role of **serotonin** in aggressio/n
\
###
### Berman et al. (2009)
↳ found that **low** levels of serotonin are associated with increased aggression
* Higher levels of serotonin are associated with decreased aggression.
* Serotonin plays a crucial role in regulating aggressive behavior, according to the study.
###
### Berman et al. (2009)
↳ found that **low** levels of serotonin are associated with increased aggression
* Higher levels of serotonin are associated with decreased aggression.
* Serotonin plays a crucial role in regulating aggressive behavior, according to the study.
7
New cards
Give an issue with the **neural** explanation of aggression
## %%Nomothetic%%
↳ The research evidence is nomothetic, based on a universal evidence which disregards the need for idiographic insight. This is an issue as it doesn’t account for unique individual experiences
↳ The research evidence is nomothetic, based on a universal evidence which disregards the need for idiographic insight. This is an issue as it doesn’t account for unique individual experiences
8
New cards
Give **one** example of a **hormonal mechanism** involved with aggression
Testosterone
9
New cards
Outline the **role** of Testosterone
* Responsible for the development of **masculine features**
* Males are **more aggressive** to other males at \~20yrs
* Males are **more aggressive** to other males at \~20yrs
10
New cards
Give an example of **research** which **supports** the role of **testosterone** in aggression
### @@Wagner et al. (1979)@@
↳ Measured aggression levels in male mice before castrating them making agression levels
* Testosterone was restored through HRT, and agression reached pre castration levels
* Male mice given testosterone showed increased aggression towards other males
* The amount of aggression was related to the dose of testosterone given
↳ Measured aggression levels in male mice before castrating them making agression levels
* Testosterone was restored through HRT, and agression reached pre castration levels
* Male mice given testosterone showed increased aggression towards other males
* The amount of aggression was related to the dose of testosterone given
11
New cards
Give research evidence for **hormones** in **female aggression**
### Ziomkiewicz et al. (2012)
↳ Low levels of the hormone **progesterone** have been linked to female aggression.
* A **negative correlation** was found between progesterone levels and self reported aggression
↳ Low levels of the hormone **progesterone** have been linked to female aggression.
* A **negative correlation** was found between progesterone levels and self reported aggression
12
New cards
Give an **issue** with the **hormonal** explanation of **aggression**
### Biological Reductionism
↳ Oversimplifies a complex behaviour down to high levels of testosterone, which doesn’t look **holistically** at all factors that can influence aggression
↳ Oversimplifies a complex behaviour down to high levels of testosterone, which doesn’t look **holistically** at all factors that can influence aggression
13
New cards
How do **Twin Studies** show evidence of the role of genetics in aggression?
### Berkowitz (1993)
↳ Measured the concordance rate for aggressive behaviour in MZ and DZ twins
* **87%** for **MZ twins**
* **72%** for **DZ twins**
↳ Measured the concordance rate for aggressive behaviour in MZ and DZ twins
* **87%** for **MZ twins**
* **72%** for **DZ twins**
14
New cards
Give an issue with using **twin/adoption** studies to explain agression?
Lacks **validity** as it is very difficult to separate environmental and genetic factors
15
New cards
What is the **MAOA** gene?
Gene that break down neurotransmitters, meaning if it doesn’t work properly a build up of excess neurotransmitters cause people to stress aggressively.
16
New cards
What is **poor MAOA** function?
People show agression due to a **low function** MAOA gene that is unable to produce enough of the MAOA-L gene
17
New cards
How can MAOA-L gene be triggered?
**Diathesis-Stress**
↳ It can be triggered into low function through **diathesis-stress,** such as **prolonged abuse** in childhood
↳ It can be triggered into low function through **diathesis-stress,** such as **prolonged abuse** in childhood
18
New cards
Give **supporting evidence** of genetics in agression
* Caspi's New Zealand Study is a **longitudinal study** that provides evidence of **genetics** in aggression.
* The study followed a cohort of 1,037 individuals from birth to age 26.
* Those with a **specific genotype** were more likely to exhibit aggressive behavior when exposed to stressful life events.
* This suggests that genetics play a role in the development of aggression.
* The study followed a cohort of 1,037 individuals from birth to age 26.
* Those with a **specific genotype** were more likely to exhibit aggressive behavior when exposed to stressful life events.
* This suggests that genetics play a role in the development of aggression.
19
New cards
Summarise Brunner’s study into aggression in families
* Brunner's Dutch family study investigated the genetic basis of aggression in families with a history of violent behavior.
* The study found that a mutation in the MAOA gene was associated with increased aggression in males.
* However, the increased aggression was only observed in males who had experienced childhood maltreatment.
* The study suggests that genetic and environmental factors interact to influence aggressive behavior.
* The study found that a mutation in the MAOA gene was associated with increased aggression in males.
* However, the increased aggression was only observed in males who had experienced childhood maltreatment.
* The study suggests that genetic and environmental factors interact to influence aggressive behavior.
20
New cards
Give an **issue** with the genetic explantion of aggression
### Hard Determinism
↳ The MAOA-L gene suggetss that if a person has the gene + a childhood of abuse, the **will** be **aggressive** meaning they are not responisble for their actions
↳ The MAOA-L gene suggetss that if a person has the gene + a childhood of abuse, the **will** be **aggressive** meaning they are not responisble for their actions
21
New cards
What is meant by **ethological explanations** of aggression?
Study of animal behaviour which helps us understand human aggression
22
New cards
According to **ethology,** aggression is…
* Adaptive
* Ritualistic
* Innate
* Ballistic
* Universal
* Specific
* Ritualistic
* Innate
* Ballistic
* Universal
* Specific
23
New cards
Why is aggression **adaptive**?
* Reduces competition
* Establishes dominance
* Establishes dominance
24
New cards
Why is aggression **ritualistic?**
* The behaviour is in a set order, to show dominance without causing death
25
New cards
What is an IRM?
**Innate Releasing Mechanism**
↳ A neural network that is triggered by a **sign stimulus** activates the Fixed Action Pattern
↳ A neural network that is triggered by a **sign stimulus** activates the Fixed Action Pattern
26
New cards
What is FAP?
**F**ixed **A**ction **P**attern - innate sequence of movements that cannot be altered once triggered
27
New cards
Give **research** support for the **ethological** explanation of **aggression**
* **Tinbergen (1951)** supports the ethological explanation of aggression
* Stickleback fish have an IRM for other males who have a **red belly.**
* They attack other males when they see their red belly, so Tinenberg put colour clay models in the water
* Sticklebacks attacked all red belly objects regardless of the fact they looked nothing like fish
* He proposed that aggression is an innate behavior that has evolved through natural selection
* Stickleback fish have an IRM for other males who have a **red belly.**
* They attack other males when they see their red belly, so Tinenberg put colour clay models in the water
* Sticklebacks attacked all red belly objects regardless of the fact they looked nothing like fish
* He proposed that aggression is an innate behavior that has evolved through natural selection
28
New cards
What does the **evolutionary explanation** suggest the purpose of human aggression is?
* Individual Survival
* Procreation
* Procreation
29
New cards
Show evidence for agression in **Sexual Competition**
* Men have 75% more muscle mass than females (Lassek & Gaulin, 2009)
* Men are *far* more likely to die violently (Buss, 2005)
* Men have more **robust** skulls and brow bridges than females
* Men are *far* more likely to die violently (Buss, 2005)
* Men have more **robust** skulls and brow bridges than females
30
New cards
What is **anti-cuckoldry** behaviours?
Men avoiding raising a child who is not biologically his
31
New cards
What is **Sexual Jealousy?**
### Responses to possible infidelity
↳ Sexual jealousy is stronger in males (compared to females) due paternity uncertainty
↳ For females, they can be certain of maternity but worry about a **loss of time** and **emotional infidelity**
↳ Sexual jealousy is stronger in males (compared to females) due paternity uncertainty
↳ For females, they can be certain of maternity but worry about a **loss of time** and **emotional infidelity**
32
New cards
Give **research support** for
33
New cards
What are **Mate Retention Strategies?**
* Direct guarding + vigilance
* Negative Inducements
* Negative Inducements
34
New cards
What is **direct guarding?**
Insisting on knowing where your partner is and who she is with
35
New cards
What are **negative inducements?**
Threatening behavoiurs to prevent straying from the relationship
↳i.e threats of suicide to avoid infidelity
↳i.e threats of suicide to avoid infidelity
36
New cards
**Male Bullying**
* **Physical**
↳ bullying ensures access to females and reduces threats from males
↳ bullying ensures access to females and reduces threats from males
37
New cards
**Femal Bullying**
* **Verbal**
↳ By insulting other women, she helps to secure the partner’s fidely by insulting other women
↳ By insulting other women, she helps to secure the partner’s fidely by insulting other women
38
New cards
Give **research support** for sexual jealousy and aggression
**Shackleford**
↳ **Mate retention strategies are associated wih sexual jealousy and aggression**
* Shackelford's (2005) research found a positive correlation between men who used mate retention strategies (MRS) and their use of violence against their partners in heterosexual relationships.
* The study surveyed 461 men and 560 women.
* There was also a positive correlation in women between those who had jealous partners and being the victims of violence.
* The research suggests that aggression may have arisen as another mate retention strategy, used to deter infidelity, and so supports the evolutionary explanation.
↳ **Mate retention strategies are associated wih sexual jealousy and aggression**
* Shackelford's (2005) research found a positive correlation between men who used mate retention strategies (MRS) and their use of violence against their partners in heterosexual relationships.
* The study surveyed 461 men and 560 women.
* There was also a positive correlation in women between those who had jealous partners and being the victims of violence.
* The research suggests that aggression may have arisen as another mate retention strategy, used to deter infidelity, and so supports the evolutionary explanation.
39
New cards
Outline the research of Dobash & Dobash
* Dobash and Dobash's study in 1979 focused on sexual jealousy as a common trigger for violence in domestic relationships
* They interviewed women who had experienced violence from their partners.
* The violence was often triggered by the man's belief that the woman had not **fulfilled** her duties as a wife.
* The violence was often part of a pattern of control and domination within the relationship.
* They interviewed women who had experienced violence from their partners.
* The violence was often triggered by the man's belief that the woman had not **fulfilled** her duties as a wife.
* The violence was often part of a pattern of control and domination within the relationship.
40
New cards
Give one **issue** that is dealt with by the evolutionary explanation
**Gender Differences**
↳ Males engage in physically aggressive acts whereas women often enagein verbally aggressive acts which accounts for the gender differences in behaviour
↳ Males engage in physically aggressive acts whereas women often enagein verbally aggressive acts which accounts for the gender differences in behaviour
41
New cards
What are the **three** Social Psychological explanations of human aggression?
* De-individuation
* Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis
* Social Learning Theory
* Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis
* Social Learning Theory
42
New cards
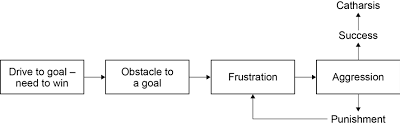
Outline the Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis
### @@Dollard et al. (1939)@@
1. We attempt to achieve something and have a goal
2. Our efforts to reach a goal are **blocked** leading to frustration
3. This creates an aggressive drive which can lead to aggression
4. If we express trhis anger physically, verbally or by fantasizing, we experience **catharsis**
↳ *This reduces our emotional tension*
5. If the target of aggression is unavailable, we could **displace** our emotions leading to **punishment**
6. This then leads to further frustration
1. We attempt to achieve something and have a goal
2. Our efforts to reach a goal are **blocked** leading to frustration
3. This creates an aggressive drive which can lead to aggression
4. If we express trhis anger physically, verbally or by fantasizing, we experience **catharsis**
↳ *This reduces our emotional tension*
5. If the target of aggression is unavailable, we could **displace** our emotions leading to **punishment**
6. This then leads to further frustration
43
New cards
How does **proximity** affect the likelihood of aggression happening?
* Harris (1974) conducted a study on the effect of proximity on aggression.
* Participants were placed in a room with either a confederate or no one.
* The confederate was either in close proximity or far away from the participant.
* Results showed that participants were more likely to behave aggressively towards the confederate when they were in close proximity.
* Proximity can increase the likelihood of aggression happening.
* Participants were placed in a room with either a confederate or no one.
* The confederate was either in close proximity or far away from the participant.
* Results showed that participants were more likely to behave aggressively towards the confederate when they were in close proximity.
* Proximity can increase the likelihood of aggression happening.
44
New cards
How does **justification** affect the likelihood of aggression?
### @@Pastore (1952)@@
↳ Suggested that **only unjustified frustrations** produce aggressive reactions
* He asked his students to how they’d react if a city bus failed to pick them up
* The students would **not be angry** if the bus **seemed full**
* The source of the frustration is key to whether it leads to aggression or not
↳ Suggested that **only unjustified frustrations** produce aggressive reactions
* He asked his students to how they’d react if a city bus failed to pick them up
* The students would **not be angry** if the bus **seemed full**
* The source of the frustration is key to whether it leads to aggression or not
45
New cards
How does **displacement** affect the likelihood of aggression?
* It is not always appropriate to respond aggressively to the source of frustration
* By displacing the aggression onto a scapegoat, catharsis is achieved
* By displacing the aggression onto a scapegoat, catharsis is achieved
46
New cards
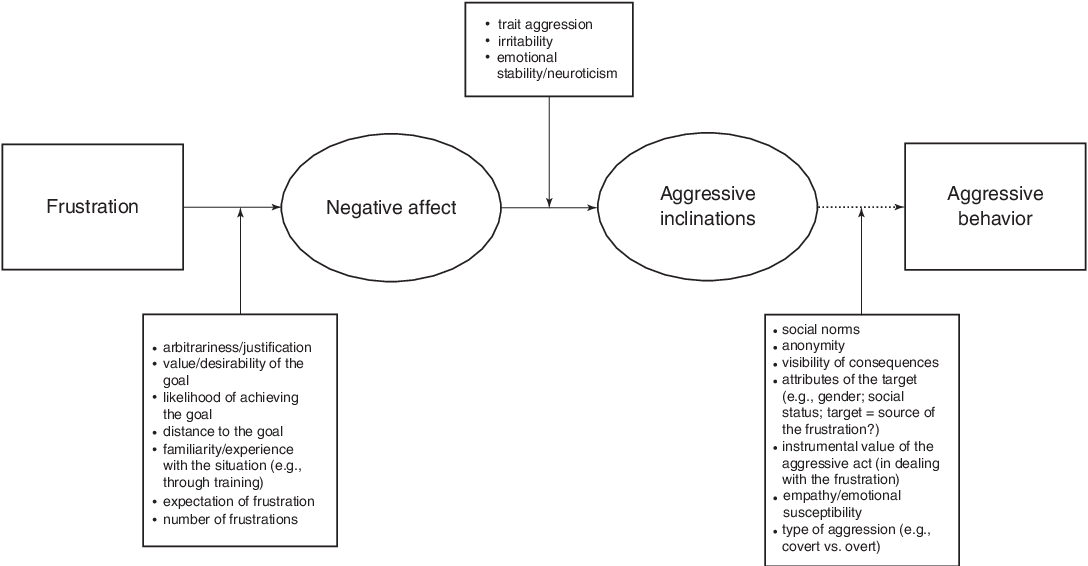
How did **Berkowitz** revise the Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis?
* According to Berkowitz (1989), it is the **negative** **feelings** that causes us to be aggressive **not** the **frustration**
* Unanticipated interference is more likely to provoke an **aggressive** **response** than an anticipated interference as the latter is experience is less unpleasant.
* Unanticipated interference is more likely to provoke an **aggressive** **response** than an anticipated interference as the latter is experience is less unpleasant.
47
New cards
What does **SLT** suggest about aggression?
* Agression is learned
* Agression is copied by observing others
* We copy behaviours from models (**parents**, **friends** and **celebrities**)
* Agression is copied by observing others
* We copy behaviours from models (**parents**, **friends** and **celebrities**)
48
New cards
What are the **4 components** of observaional learning?
1. Attention
2. Retention
3. Production
4. Motivation
49
New cards
What increases the likelihood of an individual copying a modelled behaviour?
1. It results in an outcome (reward) they value
2. The model is powerful, respected and admired (by the learner)
3. The model is seen as similar to the learner (age, sex, interests).
4. The task to be imitated is neither too easy nor too difficult
5. The learner has low self-esteem or lacks confidence in their own abilities.
50
New cards
How does **Bandura’s (1961)** research show support for Transmission of Aggression through Imitation of Aggressive Models?
* Children in the aggressive condition showed significantly higher scores than the non-aggressive or control groups
* 70% of children in non-aggressive and control groups showed **no aggression towards Bobo**
* **Boys were more influenced by a male model**
* Girls showed more **physical** aggression with a **male model**, and more **verbal** aggression with a female model
* ^^Modelling and observational learning were seen to lead to aggressive behaviour^^
* 70% of children in non-aggressive and control groups showed **no aggression towards Bobo**
* **Boys were more influenced by a male model**
* Girls showed more **physical** aggression with a **male model**, and more **verbal** aggression with a female model
* ^^Modelling and observational learning were seen to lead to aggressive behaviour^^
51
New cards
Give an example of research that **challenges** the SLT explanation of aggression
\
### Charlton et al. (2000)
* Children (aged three to eight years) were observed through cameras set up in the playgrounds of two primary schools on the island
* In 1994 (before the introduction of television), the researchers filmed free play in the school playgrounds and observed behaviour again in 2000
* The researchers analysed the children’s aggressive behaviour and compared it to the amount of television that children were exposed and conducted interviews
* Very little difference was found in children’s behaviour after the introduction of television to the island
* This implies that children may learn aggressive behaviour but they may not exhibit it.
### Charlton et al. (2000)
* Children (aged three to eight years) were observed through cameras set up in the playgrounds of two primary schools on the island
* In 1994 (before the introduction of television), the researchers filmed free play in the school playgrounds and observed behaviour again in 2000
* The researchers analysed the children’s aggressive behaviour and compared it to the amount of television that children were exposed and conducted interviews
* Very little difference was found in children’s behaviour after the introduction of television to the island
* This implies that children may learn aggressive behaviour but they may not exhibit it.
52
New cards
Give an **issue** with the **SLT** explanation of **aggression**
* **Socially Sensitive** to teach children aggressive behaviour
* **Environmental Reductionism**
* **Nurture side** of the N/N debate
* **Environmental Reductionism**
* **Nurture side** of the N/N debate
53
New cards
What factors increase de-individuation?
* Uniforms
* Groups/Crowds
* Masks
* Hoods/hats
* Intoxication
* The Dark
* Bieng Online
* Groups/Crowds
* Masks
* Hoods/hats
* Intoxication
* The Dark
* Bieng Online
54
New cards
What is meant by **De-Individuation**?
A **diffusion of responsibility** leading to disinhibited behaviour reducin
55
New cards
What is **Disinhibited Behaviour?**
* Occurs in any situation wsere **identification is restricted**
* Blame + Responsibility cannot be given to **specific individuals**
* Lower Inhibitions leads to no longer conforming to social roles
* Blame + Responsibility cannot be given to **specific individuals**
* Lower Inhibitions leads to no longer conforming to social roles
56
New cards
What is **Public/Private** self-awareness?
**Private:** A cincern we have for our own thoughts and feeling (when we forget ourselves)
**Public**: A concern about the impressiomn resented to other people - This can be reduced by anonymity
**Public**: A concern about the impressiomn resented to other people - This can be reduced by anonymity
57
New cards
Give an example of research that featured **deindividuation**?
**Zimbardo Prison Experiment (1971)**
Gergen, Gergen & Barton (1973) Dark Room Arousal
**Real Life:** Abu Ghraib (Iraq)
Gergen, Gergen & Barton (1973) Dark Room Arousal
**Real Life:** Abu Ghraib (Iraq)
58
New cards
What is menat by **Institutional Agression?**
Agression in institutions (schools, prisons, military compunds)
59
New cards
Outline the **Importation Model/ Dispositional Model**
Prisoners bring in their own social histories + traits into the prison environment
* The traits influence their subsequent behaviour in the institution
* For many prisoners, these traits are the reaosn they’ve been imprisoned in the first place
* Some pre-existing conditions such as **Alcoholism** can affect the levels of aggression (Weeks, 1998)
* The traits influence their subsequent behaviour in the institution
* For many prisoners, these traits are the reaosn they’ve been imprisoned in the first place
* Some pre-existing conditions such as **Alcoholism** can affect the levels of aggression (Weeks, 1998)
60
New cards
Give **research support** for why the **Dispositional/Importation Model** holds
**Kane & Janus (1981)**
* These groups are likely to become **disenfranchised** and separate from **mainstream norms and values** that promote less aggressive ways of resolving interpersonal conflict
* Many will live in in a subculture where aggression is valued, respected and reinforced
* These groups are likely to become **disenfranchised** and separate from **mainstream norms and values** that promote less aggressive ways of resolving interpersonal conflict
* Many will live in in a subculture where aggression is valued, respected and reinforced
61
New cards
What is the **Situational Model?**
Recognises the **environment** of the institution plays a key part in aggression exhibited due to **organisational factors, physical factors + Staff Factors**
62
New cards
What did **Sykes (1958)** believe caused aggression within institutions?
**Deprivation**
1. Deprivation of **liberty**
2. Deprivation of **heterosexual relationships**
3. Deprivation of **goods and services**
4. Deprivation of **adequate living conditions**
5. Deprivation of **security**
6. Deprivation of **autonomy**
1. Deprivation of **liberty**
2. Deprivation of **heterosexual relationships**
3. Deprivation of **goods and services**
4. Deprivation of **adequate living conditions**
5. Deprivation of **security**
6. Deprivation of **autonomy**
63
New cards
What did **Folger + Skarlicki (1995)** suggets made prisons aggressive?
**The Popcorn Model**
* When an individual becomes heated, other prisoners become angry to and begin to ‘pop’
* To reduce the aggression levels, the prison must find the intiial ‘heat’ that caused them to ‘pop’ in the first place
* When an individual becomes heated, other prisoners become angry to and begin to ‘pop’
* To reduce the aggression levels, the prison must find the intiial ‘heat’ that caused them to ‘pop’ in the first place
64
New cards
What did **Dilulio (1987)** suggest caused aggression in prisons?
**The Mangement Model**
* Aggression in prisons occurs as the reult of failed maagement, high staff turnover + lack of staff discipline
* McCorkle et al. (1995) found that educative programs within prisons had positive effects for both prisoners and staff
* Aggression in prisons occurs as the reult of failed maagement, high staff turnover + lack of staff discipline
* McCorkle et al. (1995) found that educative programs within prisons had positive effects for both prisoners and staff
65
New cards
Evidence for Situational Model
Zimbardo
I/D - Nurture v. Nature + Environmental reductionism
I/D - Nurture v. Nature + Environmental reductionism
66
New cards
What are **media influences?**
Findings of research looking at the correlation of aggression and TV/Video Games
67
New cards
What 2
68
New cards
Give **research support** for Gaming and its role in
69
New cards
How does **desensitisation** show evidence for media?
* Normally, when we witness violent actions we experience physilogical arousal associated with the SNS
* When children reperatedly view aggression on TV or play aggressive computer games, they become habituated to its effects
* **Negative attitudes towards violence weaken, less empathy is felt for victims, and their injuries are minimised/dissmissed** (*Funk, 2004)*
* When children reperatedly view aggression on TV or play aggressive computer games, they become habituated to its effects
* **Negative attitudes towards violence weaken, less empathy is felt for victims, and their injuries are minimised/dissmissed** (*Funk, 2004)*
70
New cards
Give **research support** for **desensitisation**
Krahe (2011)
showed participants violent (and non-violent) film clips, while measuring physiological arousal using skin conductance tests.
* Participants who were habitual viewers of violent media showed lower levels of arousal when they watched the violent clips
* They also reported higher levels of pleasant arousal and lower levels of anxious arousal
* Lower arousal in habitual violent media users reflects desensitisation to the effects of violence, and a greater willingness to be **aggressive**.
showed participants violent (and non-violent) film clips, while measuring physiological arousal using skin conductance tests.
* Participants who were habitual viewers of violent media showed lower levels of arousal when they watched the violent clips
* They also reported higher levels of pleasant arousal and lower levels of anxious arousal
* Lower arousal in habitual violent media users reflects desensitisation to the effects of violence, and a greater willingness to be **aggressive**.
71
New cards
How does **disinhibition** explain **aggressive behaviours?**
* Disinhibition explains that social inhibitions against using aggression as a means to resolve conflict are loosened after exposure to violent media
* Aggressive behaviour is often made to appear **normative** and **socially sanctioned**
* Aggressive behaviour is often made to appear **normative** and **socially sanctioned**
72
New cards
Give an example of a study whihc supports the **disinhibition explanation**
\
* Berkowitz & Alioto (1973) found that participants who saw a film depicting aggression as vengeance gave more (fake) electric shocks of longer duration to a confederate.
* This suggests that media violence may disinhibit aggressive behaviour when it is presented as justified (therefore socially acceptable).
* Berkowitz & Alioto (1973) found that participants who saw a film depicting aggression as vengeance gave more (fake) electric shocks of longer duration to a confederate.
* This suggests that media violence may disinhibit aggressive behaviour when it is presented as justified (therefore socially acceptable).
73
New cards
Outline how **Congitive Priming** explains aggression
Cognitive priming is when a stimulus affects a person's response to another stimulus. Aggressive cognitive priming happens when exposure to aggressive stimuli, like violent media, can make a person more likely to act aggressively
↳ The process is automatic and unconscious
↳ The process is automatic and unconscious
74
New cards
Outline research into **cognitive priming**
* BJ Bushman's (1995) research found that exposure to violent media can prime aggressive thoughts and increase aggressive behavior.
* Participants who played a violent video game in Bushman's study were more likely to deliver loud and long blasts of noise to a confederate than those who played a non-violent game.
* This suggests that exposure to violent media can have a priming effect on aggressive behavior.
* Participants who played a violent video game in Bushman's study were more likely to deliver loud and long blasts of noise to a confederate than those who played a non-violent game.
* This suggests that exposure to violent media can have a priming effect on aggressive behavior.