Humanities Final Exam Review: Environmental Impact and Society
1/570
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
571 Terms
Biodiversity
Variety of life on Earth.
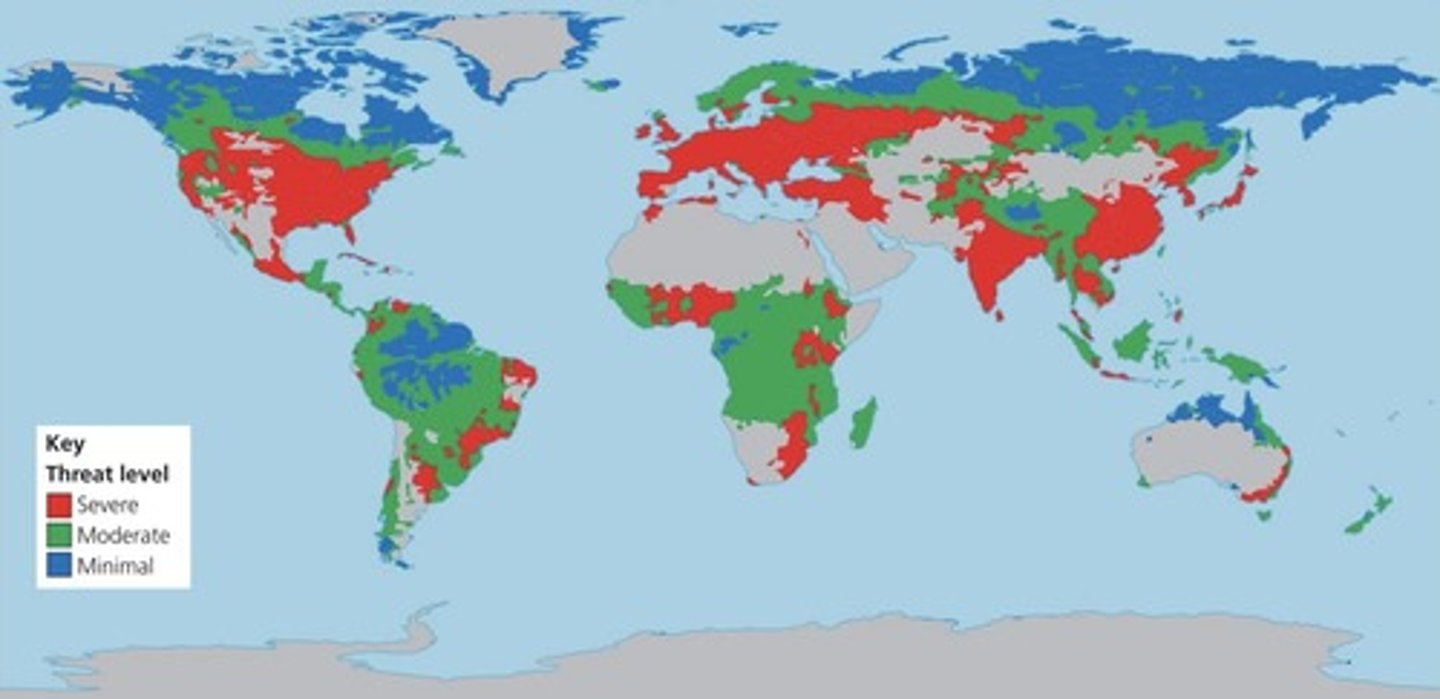
Threats to Biodiversity
Factors endangering species and ecosystems.
Deforestation
Clearing forests for agriculture or urban use.
Marine Environment Depletion
Reduction of ocean resources affecting ecosystems.
Climate Change
Long-term alteration of temperature and weather patterns.
Biome
Group of ecosystems with similar climate and communities.
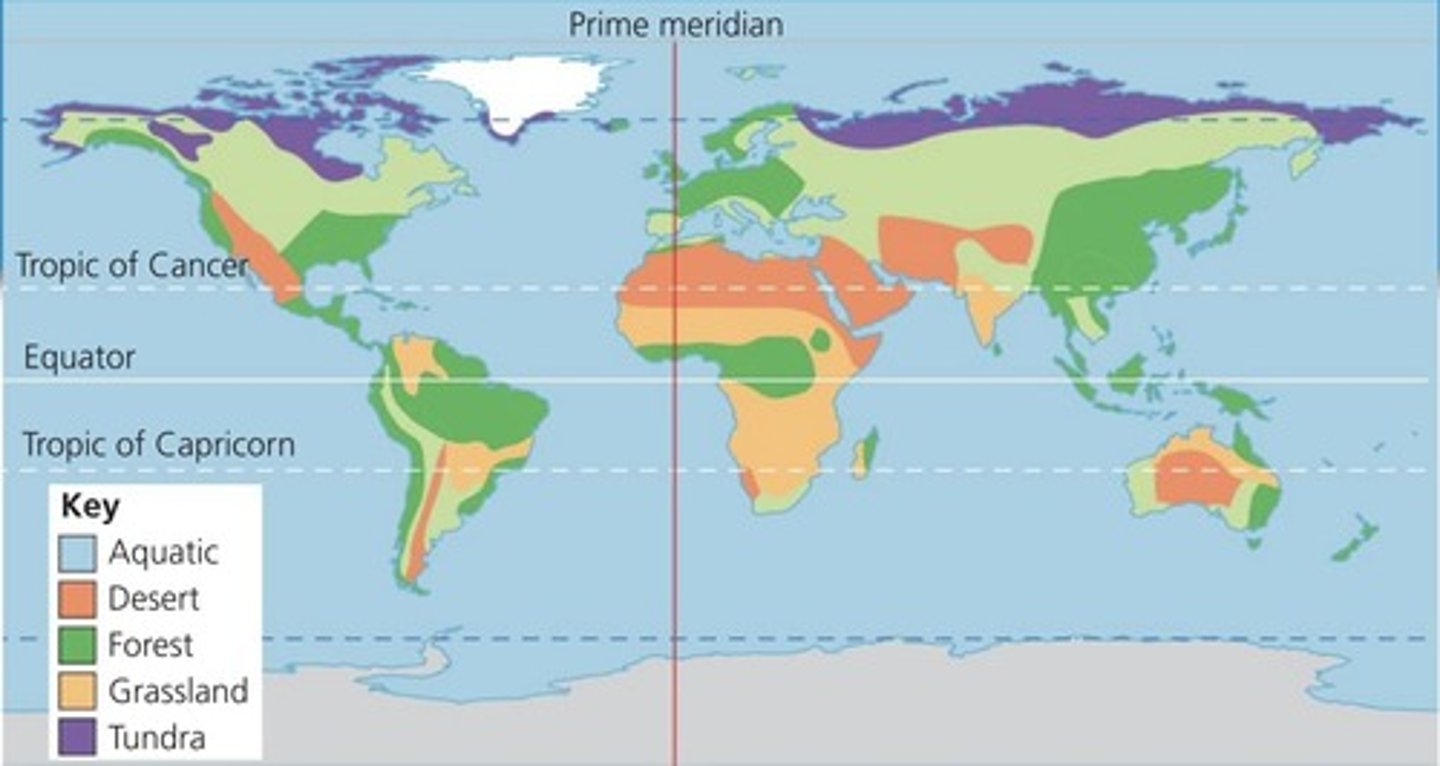
Aquatic Biome
Includes freshwater and marine ecosystems.
Freshwater Biome
Includes ponds, lakes, rivers, and wetlands.
Marine Biome
Includes oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries.
Tropical Rainforest
High biodiversity, warm temperatures, and high rainfall.
Temperate Forest
Seasonal weather with diverse tree types.
Boreal Forest (Taiga)
Cold climate with coniferous trees.
Savanna
Grassland with scattered trees, seasonal rainfall.
Desert
Low precipitation, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation.
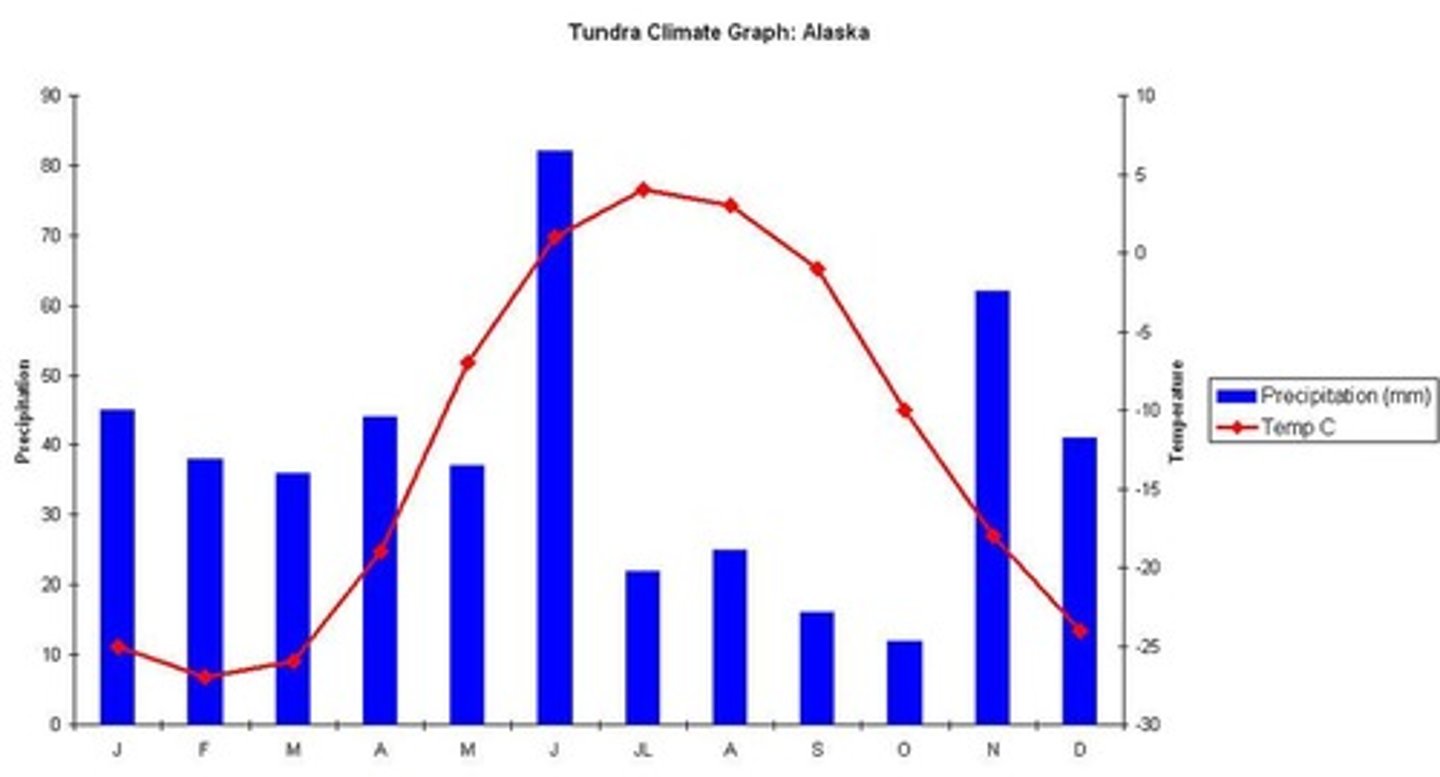
Tundra
Cold, low biodiversity, and permafrost soil.
NPP (Net Primary Productivity)
Rate of energy production in ecosystems.
Climate
Average weather conditions over 30 years.
Weather
Day-to-day atmospheric conditions.
Soil Type
Composition affecting plant growth and ecosystem health.
Species
Group of organisms capable of interbreeding.
Vegetation
Plant life in a specific area.
Wildlife
Animal life in a specific habitat.
Rainforest
Dense forest with diverse plant and animal life.
Forest Floor
Dark, low-light area beneath rainforest canopy.
Flood Absorption
Tiny shrubs absorb floodwater in rainforests.
Climbers (Lianas)
Woody vines that climb trees for sunlight.
Desert
Arid region with extreme temperature variations.
Cactus Adaptation
Stores water and withstands extreme temperatures.
Nocturnal Animals
Active at night to avoid daytime heat.
Camel Adaptation
Thick fur and fat storage for heat resistance.
Serengeti
Ecosystem in Tanzania with diverse wildlife.
Grasslands
Transitional biome between deserts and rainforests.
Vegetation Adaptation
Plants adjust to seasonal climate changes.
Tundra
Cold biome with limited sunlight and warmth.
Hibernation
Dormancy during winter to conserve energy.
Aquatic Environments
Habitats including freshwater and marine ecosystems.
Lakes and Ponds
Still water bodies, smaller than rivers.
Streams and Rivers
Flowing water bodies with diverse wildlife.
Wetlands
Waterlogged areas supporting unique plant and animal life.
Marine Environments
Oceans and coastal areas rich in biodiversity.
Coral Reefs
Marine structures formed by coral organisms.
Biodiversity Factors
Depth, sunlight, salinity, and temperature affect life.
Human Impact
Activities that negatively affect natural ecosystems.
Deforestation
Clearing forests for agriculture or urban development.
Desertification
Land degradation in arid regions due to human activity.
Rhino Poaching
Illegal hunting of rhinos for their horns.
Serengeti Tourism
Tourism in Serengeti impacts local ecosystems.
Overgrazing
Excessive grazing leading to land degradation.
Sustainable Tourism
Tourism that conserves resources and benefits locals.
Eco Tourism
Responsible travel to natural areas conserving environment.
Oil Spills
Accidental release of oil into oceans.
Trans Alaska Pipeline
Pipeline transporting oil across Alaska.
Global Warming
Increase in Earth's average temperature due to emissions.
Tundra
Cold, treeless biome with permafrost.
Eutrophication
Nutrient pollution causing excessive algae growth.
Dead Zones
Areas in water bodies with low oxygen.
Great Pacific Garbage Patch
Large area of marine debris accumulation.
Shark Finning
Removal of shark fins for soup, harming populations.
Coral Bleaching
Loss of color in corals due to stress.
Ghost Fishing
Lost fishing gear continues to catch marine life.
Sustainability
Meeting needs without compromising future generations.
Great Green Wall
8,000 km project to combat desertification in Sahara.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Theory of human motivation based on needs.
Economic Systems
Methods societies use to allocate scarce resources.
Feudalism
Socioeconomic system based on land ownership hierarchy.
Capitalism
Economic system based on private ownership and profit.
Communism
Economic system where resources are shared equally.
Global Culture
Emerging shared culture influenced by globalization.
Sustainability
Three elements: economic, social, environmental.
Economic Sustainability
Focus on financial health and resource management.
Social Sustainability
Ensuring social equity and community well-being.
Environmental Sustainability
Preserving natural resources for future generations.
Empire
A large political unit ruled by a central authority.
Roman Empire
Ancient empire known for extensive territorial expansion.
Mongol Empire
Largest contiguous empire in history, known for conquests.
British Empire
Global empire known for colonial expansion and trade.
Military Conquest
Acquisition of territory through armed forces.
Imperialism
Modern term for empire creation and expansion.
City-State
A sovereign state consisting of a city and surrounding territory.
Central Authority
Recognized governing body in an empire.
Tax Collection
Gathering resources to fund empire operations.
Legal Systems
Framework of laws governing society and governance.
Roman Law
Legal code known as Twelve Tables in Rome.
Infrastructure
Physical structures supporting economic and social activities.
Cultural Exchange
Sharing of ideas, beliefs, and practices between cultures.
Standing Armies
Permanent military forces maintained for defense.
Alliances
Agreements between states for mutual benefit.
Treaties
Formal agreements between nations or empires.
Military Strength
Capability to defend and expand territory.
Leadership
Central force necessary for effective empire governance.
Empire Collapse
Inevitability of empires failing due to various reasons.
Climate Change
Affects agriculture, leading to food shortages.
Invasion
Rival state attacks an empire, destabilizing it.
Innovation
New technologies that can enhance military or economy.
Military Superiority
Having a stronger military than rivals.
Economic Weakness
Financial instability undermining an empire's power.
Taxation Systems
Essential for funding government and services.
Transportation Systems
Infrastructure for moving goods and people.
Corruption
Dishonest behavior undermining governance and stability.
Civil Wars
Internal conflicts leading to fragmentation of power.