Accounting Applications DECA
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Accounting
Language of business. Record, classify, summarize, analyze and communicate a business's financial information and transactions for use in management decision-making.
Bank Reconcilliation
Process performed by a company to ensure that the company's records (Check Register, General Ledger Account, Balance Sheet, etc.) are correct and the bank's record are also correct
1. Compare your ledger and bank statement. Accounts that do not match need to be reconciled
2. Record deposits marked in your ledger but not in your bank statement.
3. Deduct outstanding checks
4. Deduct Bank Fees
5. possibly create new journal entries detailing changes
Special Journals
Designed to facilitate the process of journalizing and posting transactions. Used for most frequent transactions in a business. Three Types:
1. Sales Journal
2. Cash Receipts
3. Purchases
Straight- Line Depreciation
(Cost-Salvage Value)/Useful Life
Salvage Value could also be represent by the phrase "book value." They mean the same thing.
Book Value
AKA Salvage Value
The residual value of plant assets at the end of their useful life
Profit Margin
Net Income/Total Revenue
The profit margin percent indicates how much profit is generated for every dollar in sales. A higher profit margin is more favorable. When evaluating the profit margin, it is best to compare trends over several years, compare it to the industry average or compare it to a competitor. Ex. if X Company's Profit Margin is 8%, it means means that for every dollar in boarding revenue, the company is earning 8 cents in profit.
Generally, what can a company do to increase profit margin?
1. Consider performing a Cost-Volume Profit analysis (or Break-Even Analysis) and target profit analysis
2. Raise the prices of their goods and services (to increase total revenue)
3. Have better advertising or marketing tactics to attract a higher volume of customers
4. Analyze your waste production or other external costs to lower expenses
Trial Balance
a proof of the equality of debits and credits in a general ledger
Annual Report
Comprehensive report on a company's activities throughout the preceding year. Intend to give shareholders information about the company's activities.
Financial Ratios
Useful indicators of a firms performance and financial situation. Most can be calculated from information provided by the financial statements. Can be used to analyze trends and to compare the firm's financials to other firms.
Asset
Balance sheet item representing what a firm owns, tangible or intangible. Cash, Computer Systems, Patents
Equity
The owners value in an asset or group of assets, also called net worth.
Balance Sheet
Financial statement that summarizes a company's assets, liabilities, and owner's equity at a specific point in time. The three segments give investors an idea as to what the company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
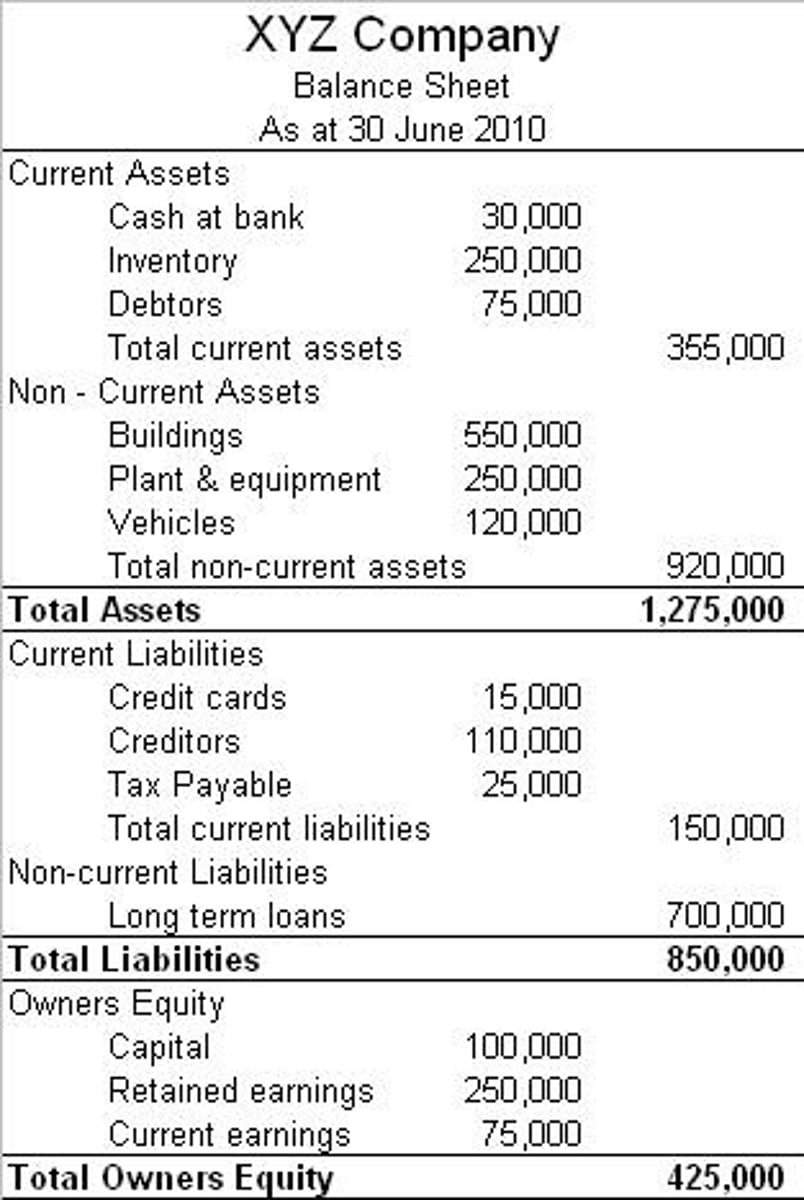
Working Capital
Total Current Assets - Total Current Liabilities
(Total Current aka Current)
Tells the business exactly what their net value is in the short run
Current Ratio
Total Current Assets/ Total Current Liabilities
Measures whether or not a firm has enough resources to pay its debt over the next twelve months.
Debt Ratio
Total Liabilities / Total Assets
Equity Ratio
Total Owners Equity / Total Assets
Financial Statements
Objective is to provide information about the financial position, performance and changes in financial position that are useful in making economic positions
Financial Records
Monitor the progress of business and identify source of receipts
Accounts Receivable
The amount of money owed by your customers after goods or services have been delivered and/or used. An asset to a creditor.
Accounts Payable
The amount of money you owe creditors (suppliers) in return for good and/or services they have delivered. A liability resulting from the sale of goods/services on credit or "on account".
Capital
A financial asset and its value, such as cash or goods. Working Capital is calculated by taking your Current Assets subtracted by Current Liabilities
Costs of Goods Sold (COGS)
The direct expense related to producing the goods or services sold by a company. This can include the cost of the raw materials
Present Value
The value of how much a future sum is worth today. Helps understand how receiving $100 now is worth more than receiving $100 a year from now.
LIFO method (last in first out)
LIFO, short for last-in-first-out, means the last items bought are the first ones sold. Cost of sales is determined by the cost of items purchased the most recently. Because this method assumes that the most recently purchased items are sold, the value of the ending inventory is based on the cost of the oldest items.
FIFO method (first in first out)
FIFO, first in-first out, means the items that were bought first are the first items sold. Cost of sales is determined by the cost of the items purchased the earliest. Ending inventory is valued by the cost of items most recently purchased. FIFO is the most commonly used method in the U.S. A primary reason is that this approach appeals to common sense. Good inventory management would dictate that the oldest goods should be sold first, while the most recently purchased items remain in inventory.
Petty Cash
Businesses generally keep small amounts of cash to meet small miscellaneous payments such as entertainment expenses and stationery costs. Usually kept in a cash box. Cashier must be responsible to keep supporting invoices in respect of payments made through.
Surprise cash counts must be conducted time to time to ensure the accuracy of the cash balance
Overages
When there's more money in a check register than there should be. Written as a Revenue+ Cash in Bank
Shortage
When there's more money in a check register than there should be. Written off as an expense when filing taxes
Sole Proprietorship
a business owned and managed by a single individual
Partnership
a business organization owned by two or more persons who agree on a equal division of profits, assets etc.
Example: if a business has 3 owners and their net income was 30000, each owner receives 10000
limited partnership
a business organization owned by two or more persons who agree on a specific division of profits, assets etc.
ex: 3 owners, ratio of 1:2:1
25% of earnings goes to Owner 1
50% goes to Owner 2
25% goes to Owner 3
Depreciation
Method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life.
Return on Investment
Measure used to evaluate the financial performance relative to the amount of money that was invested.
Simple Interest
I= PRT
I= Interest
P= Principal
R= Rate
T= Time (in this formula it is usually in years)
Ordinary Interest
I= PRT
TIME is x amount of days/360 days
Exact Interest
I= PRT
Time is x amount of days/365 days
Depreciation Schedule
A depreciation schedule breaks down the depreciation of the firm's long-term assets. It calculates the depreciation expense for each asset and allocates the cost of each asset over the useful life.
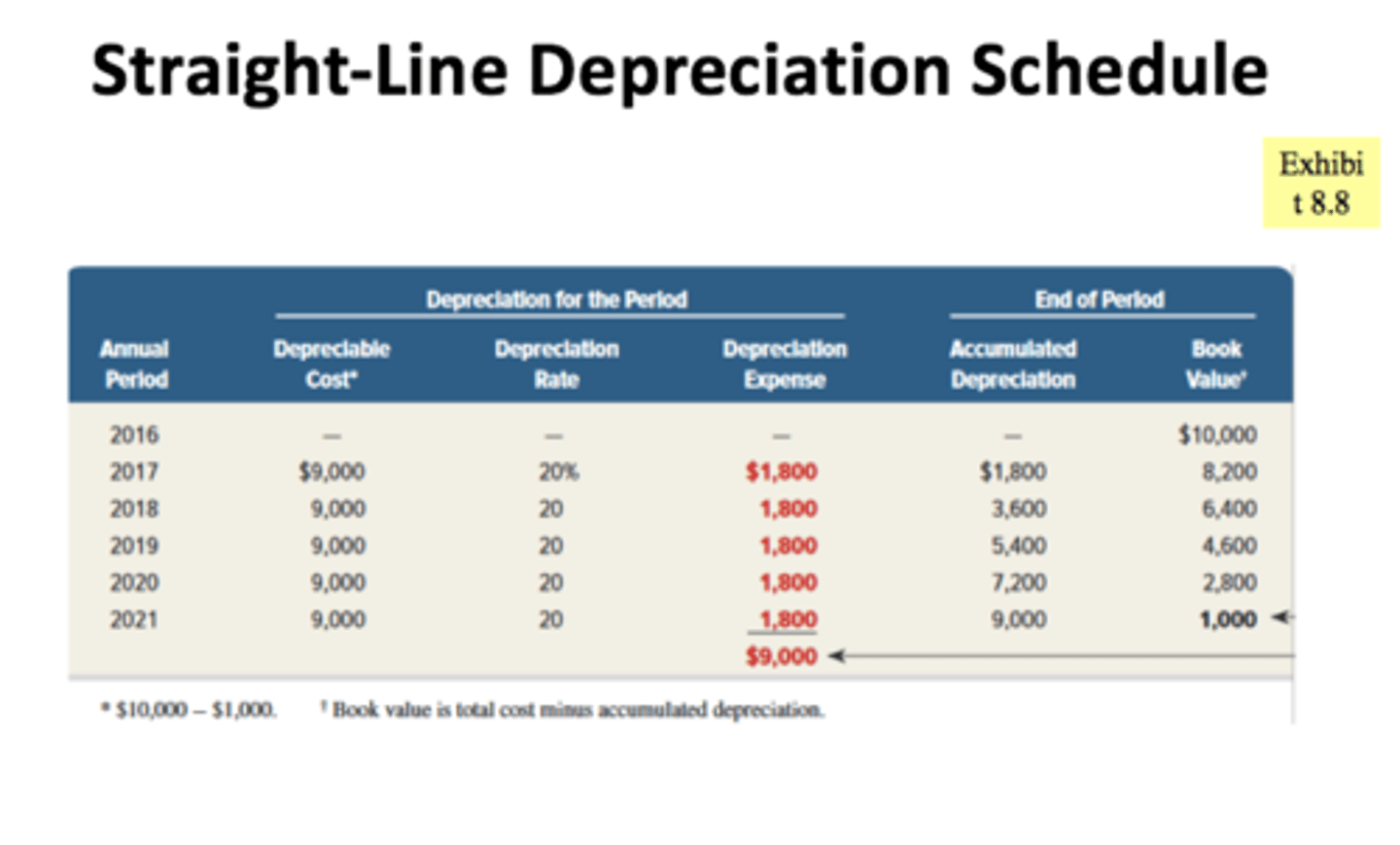
How to record Depreciation in a Journal
Debit to Depreciation Expense
Credit Accumulated Depreciation
Income Statement
A formal report which includes revenue and expenses only. This report is used to evaluate the profitability of the company over a period of time. In this case, it is for a period of 4 months. If the net income is positive, the company has an excess of revenue over expenses. If the net income is negative, the company has more expenses than revenues. This report should be generated monthly for management to make important decisions related to prices, boarding volume and costs.