Geography Exam Review
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Demography
Demography is the study of human populations, including their size, distribution, and trends such as birth rates, death rates, aging, and migration.
Dependency load
Dependency load is the part of the population (usually children and seniors) that depends on working-age people for support.
Population pyramid - what 2 factors are displayed? How do you read it?
A population pyramid shows age and sex (gender).
The horizontal bars show how many males and females are in each age group.
The bottom is younger ages, and the top is older ages.
The shape can tell you if the population is growing (wide base), stable (straight sides), or shrinking (narrow base).
Immigration vs Emigration - what’s the difference?
Immigration = people coming into a country to live.
Emigration = people leaving a country to live somewhere else.
A quick memory tip:
Imm = in, Em = exit.
2 Categories of immigration
1. Economic immigrants — people who come for jobs, skills, or business opportunities.
2. Family immigrants — people who come to reunite with close family members already living in the country.
Where do immigrants settle in Canada?
Top 3 provinces:
1. Ontario
2. Quebec
3. Alberta
Top 3 cities:
1. Toronto
2. Vancouver
3. Calgary
4 reasons why immigrants choose to settle in large cities
1. Most immigrants in Canada come from large cities so they are used to city life.
2. The large CMAs have large and growing economies. New immigrants need to find jobs, and
most go where the jobs are good,
3. Most immigrants have family members or friends from Canada, and most of these people are
in the largest cities.
4. It is easier to make the transition to life in Canada. Large cities provide formal and informal
support for this process.
Obstacles to immigration
Cost
Emotional factors
Discrimination
Intraprovincial migration - Interprovincial migration
Intra = Moving within a province
Inter = moving from one province to another
Types of population pyramids
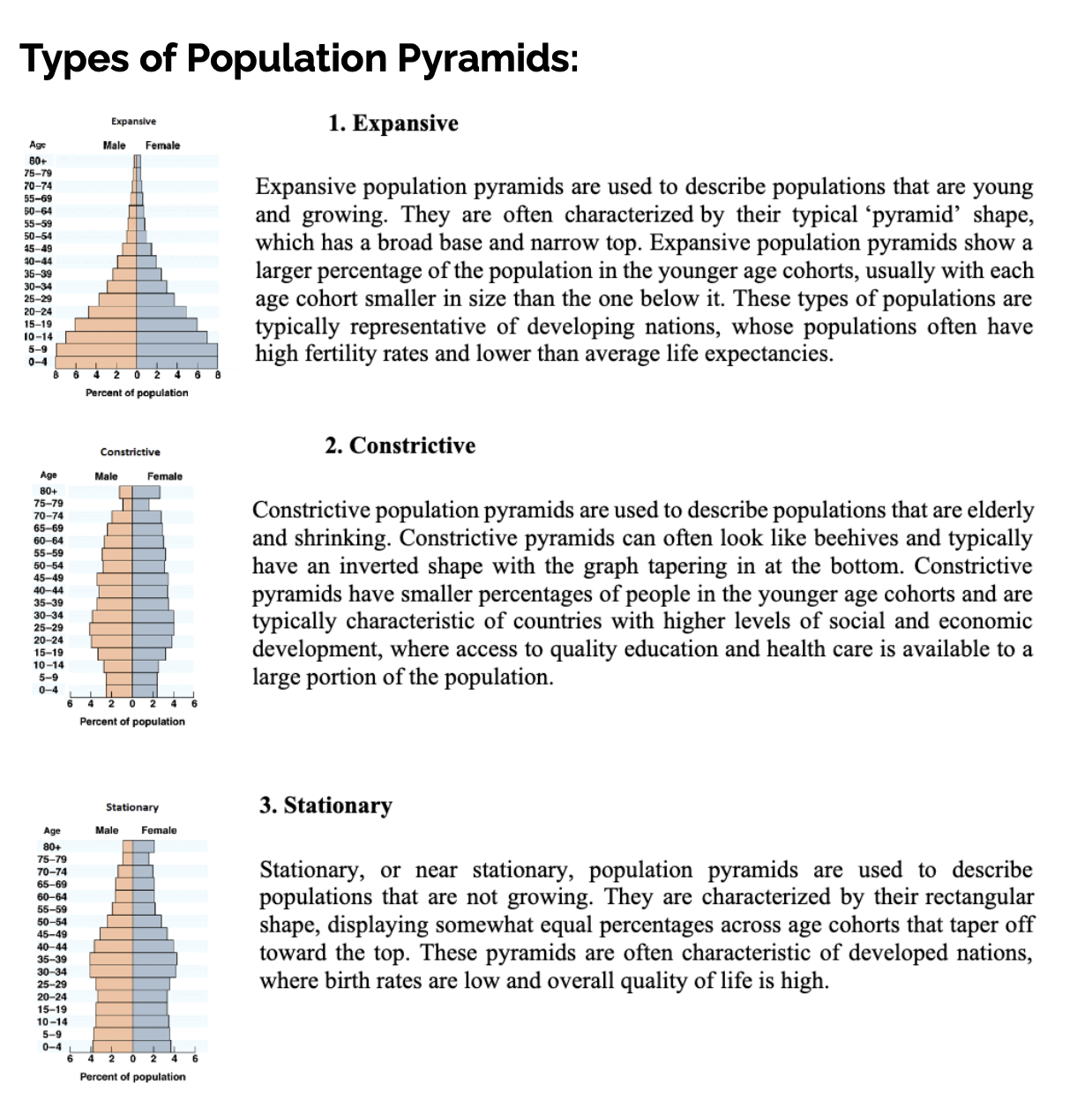
Characteristics of a youthful population vs. an ageing population
Youthful population
Lots of children and young people
High birth rates
Population grows quickly
Can create demand for schools, childcare, and jobs in the future
Ageing population
Lots of older adults/seniors
Low birth rates
Population growth is slow or shrinking
Can create demand for healthcare, pensions, and senior services
Tip for tests:
Youthful = wide base on population pyramid
Ageing = wide top on population pyramid
Push and Pull factors – explain what they are and give examples
Push factors are reasons people leave a place.
Examples: war, unemployment, poverty, natural disasters, or lack of opportunities.
Pull factors are reasons people move to a new place.
Examples: jobs, safety, better schools, freedom, or higher quality of life.
Short version for tests:
Push = pushes you out. Pull = pulls you in.
Characteristics of Canada’s population – diversity, immigration, etc
Diversity: People come from many ethnic, cultural, and religious backgrounds.
Immigration: A major source of population growth; people move for jobs, family, or safety.
Indigenous people: First Nations, Métis, and Inuit communities have unique cultures and histories.
Population distribution: Most people live in cities near the US border; much of Canada is sparsely populated.
Aging population: Growing number of seniors due to low birth rates and longer life expectancy.
Language: Two official languages, English and French, with many other languages spoken because of immigration.
One sentence answer: Canada’s population is diverse, largely shaped by immigration, includes Indigenous peoples, mostly lives in cities near the US border, is aging, and speaks mainly English and French.
Climate vs Weather what’s the difference?
Weather = short-term
What’s happening today or this week
Changes quickly
Example: “It’s raining right now” or “It’s hot this afternoon.”
Climate = long-term
The average pattern of weather over many years
Changes slowly
Example: “Canada has cold winters” or “Brazil has a tropical climate.”
Weather = Week
Climate = Century (not exact, but helps with “long time”)
What is climate?
Climate is the long-term pattern of weather in a place. It describes what the weather is usually like over many years(often 30+).
How can climate influence us?
Climate influences us in many everyday ways, because it affects how we live, dress, eat, build, and travel.
Why Canada has different time zones
Canada has different time zones because the country is very wide from east to west. The Earth rotates, and not every place gets sunlight at the same moment, so time zones help match the clock to the position of the Sun.
Factors that affect climate
Phrase = Lower near water
Latitude: Latitude is how far a place is from the equator
Ocean currents
Ocean currents are large movements of water in the oceans.
Wind and Air Masses
Air masses are large bodies of air that take on the temperature and moisture of the area where they form.
Winds move these air masses around the world.
Elevation
Elevation means how high a place is above sea level.
Near water
Areas near oceans or large lakes have milder climates.
Continental climate vs Maritime Climate
LOOK AT PAPER

Effects of climate change
LOOK AT PAPER

The 4 components of soil

What is humus?
Humus is the dark, organic material in soil that forms from decomposition of plants, animals, and other organic matter. It is very important because:
It adds nutrients to the soil, helping plants grow better.
It improves soil structure, making it easier for roots to spread.
The 3 Rs
Reduce (Best)
Meaning: Use less in the first place.
Why Best: If you don’t use it, there’s nothing to throw out, recycle, or waste.
Reuse
Meaning: Use items again instead of throwing them out.
Why Good: Makes things last longer and saves money/resources.
Recycle (Worst)
Meaning: Break old materials down to make new products.
Why Last: Still uses energy and not everything can be recycled.
Conservation
Protecting resources so they last.
Wants vs Needs
Wants:
Candy
Perfume
Airpods
Makeup
Needs:
Education
Shelter
Food
Clothing
Sustained Yield
Use a resource so it can renew. Mining a resource = using it faster than nature replaces it.
Renewable vs Non- Renewable
Renewable = replaces quickly (trees, wind, water)
Non-renewable = takes millions of years to form (oil, gas, minerals)
Factors affecting farming
Climate, soil, topography (land shape), economics.
GDDs
Growing Degree Days — measure heat for crops.
Land quality ranking
Class 1 = best, Class 7 = worst. Canada has lots of poorer land; less high-quality farmland.
2 types of farming
Intensive (small land, more labor), Extensive (large land, fewer workers).
Forest regions in Canada
Boreal, West Coast, Montane, Mixed, Deciduous, Taiga (main types).
Commercial vs Non-Commercial forests
Commercial = used for industry
Non-commercial = too small/remote to cut.
Pulp & Paper vs Sawmills
Pulp & paper = makes paper
Sawmills = lumber for building.
Types of Forestry Practice
Clear-cutting, Shelter-wood, Selective cutting.
East Coast Fisheries Collapse
Overfishing + tech → cod stocks collapsed.
Inshore vs Offshore Fishing
Inshore = small boats, near shore, more people
Offshore = big boats, far out, fewer workers.
R/P Ratio
Reserves divided by Production — how long a resource will last.
Canada’s Fossil Fuels
Oil, Natural gas, Coal
Canada’s Energy Use vs World
High use because cold climate + big country + industry.
Fossil Fuels Are Organic
Made from ancient plants/animals.
4 Sectors of Energy Use in Canada
Industrial (biggest), Transportation, Residential, Commercial.
Fracking
Method to get oil/gas by cracking rock. Pros: more energy. Cons: environmental damage.
Minerals
Natural substances in rocks. Metallic vs Non-metallic vs Fuels
Mining Methods
Strip mines (surface)
Open pit
Underground.
Two-Step Mineral Separation
Crushing → Concentrating → Smelting.
Energy Source Pros/Cons
Fossil fuels = cheap but polluting
Hydro = clean but needs dams
Nuclear = powerful but waste
Wind/Solar = clean but depends on weather.
Canada’s population situated and why
Most of Canada’s population lives in the southern part of the country, close to the U.S. border — mainly in places like Ontario, Québec, and British Columbia, especially around cities such as Toronto, Montréal, Ottawa, and Vancouver.
Why? (Easy reasons to remember):
Warmer climate — Southern Canada is less cold and easier to live in.
Better farmland — Good soil for early settlement and farming.
Major trade routes — Close to the U.S., which is Canada’s biggest trading partner.
Jobs & cities — Businesses, industry, and big cities grew there, attracting people.
Memory trick:
“South for warmth, farms, trade, and jobs.”
Population density vs Population distribution
Population density = How crowded a place is
Population distribution = Where people live
👉 Density = crowdedness
👉 Distribution = pattern of where people are
Rural settlement patterns
Linear
Houses and farms in a long line (often along a road, river, or coast)
Scattered
Homes spread far apart across the countryside
Clustered
Homes grouped together in a small area (like a village)
Canada’s population vs USA and China
👉 Canada = very low density
👉 USA = medium density
👉 China = high density
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is the idea that Earth’s crust is broken into big pieces called plates that move slowly on top of the hot, soft mantle beneath them.
👉 “Move → Collide → Slide”
(Plates move apart, collide, or slide)
Or:
👉 “Plates move, Earth changes”
Rock cycle
The rock cycle is the process that changes rocks from one type to another over time.
It never stops and has no beginning or end.
👉 “Melt – Cool – Break – Squish – Change”
Or:
👉 “Igneous → Sedimentary → Metamorphic → Igneous” (keeps cycling)
Glaciation
Glaciation is the process where glaciers form, move, and shape the land.
Glaciers are huge masses of ice and snow that move slowly like slow rivers of ice.
👉 “Glaciers Form, Move, Carve, and Drop”
(Form ice → move → carve land → drop materials)
Regions of Canada
Canada is commonly divided into 7 major physical regions:
Western Cordillera
Interior Plains
Canadian Shield
Hudson Bay–Arctic Lowlands
Great Lakes–St. Lawrence Lowlands
Appalachian Mountains
Arctic / Innuitian Mountains
👉 “West Plains Shield, Lowlands, Apps & Arctic”
Or:
👉 “Mountains–Plains–Shield–Lowlands–Apps–Arctic”
(From west to east and north)
What is geography?
Geography = the study of Earth, its land, water, people, and how they interact.
Mapping Skills & Rules (BOLTS)
BOLTS = parts of a good map:
Border
Orientation (compass / direction)
Legend (what symbols mean)
Title
Scale (distance)
Types of maps
Different maps show different info:
Political → countries, cities, borders
Physical → landforms (mountains, rivers)
Thematic → themes like climate, population
Topographic → elevation/height and contour lines
The map of Canada
Know provinces, territories, and capital cities (example: Ontario → Toronto).
Canada’s time zones
Canada has 6 time zones from west to east.
Time moves later as you go east.
Also know:
Daylight savings time
International Date Line → where the date changes
Relative vs. Absolute Location
Absolute = exact location (coordinates)
Relative = where something is in relation to other places (“near the school”)
The 3 W’s of Geography
What is where?
Why there?
Why care?
Geographic Concepts (4)
Patterns & Trends
Spatial Significance
Geographic Perspective
Interrelationships
(Helps explain why things in geography happen.)
Latitude & Longitude
Grid system to find locations.
Latitude = lines run left–right (east/west), measure north–south
Longitude = lines run up–down (north/south), measure east–west
Used for coordinates like 45°N, 79°W