1.1 Introduction to business management
Introduction - what is a business?
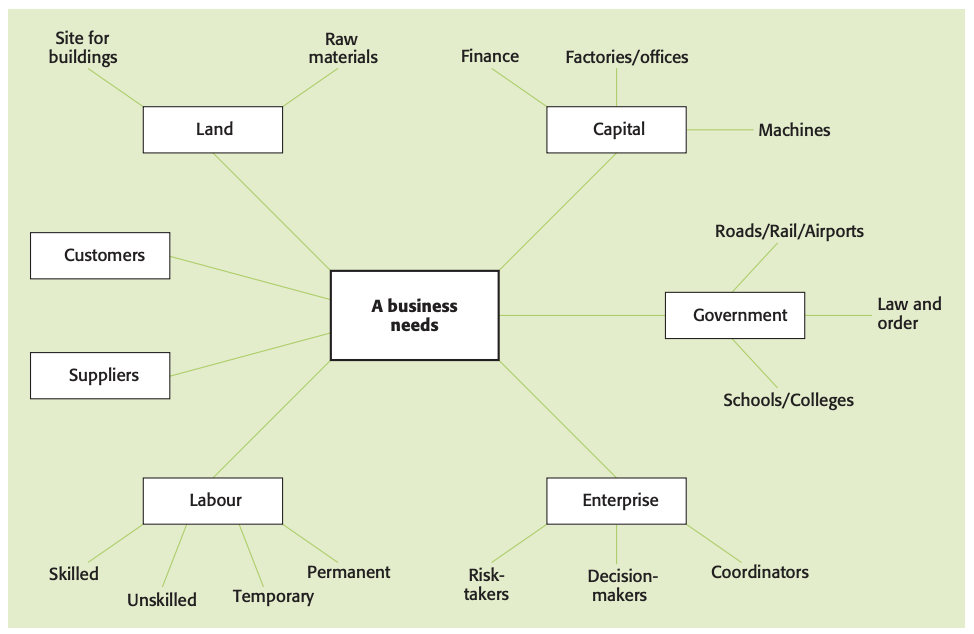
Business: any organization that uses resources to meet the needs of customers by providing a product/service that they demand.
The role of businesses
Role of businesses:
- Identifying the needs of consumers or other firms.
- Then purchasing resources, which are the inputs of the business, or factors of production, in order to produce output. The “outputs” of a business are the goods and services that satisfy consumers’ needs, usually with the aim of making a profit.
Consumer goods: physical and tangible goods sold to the general public.
Consumer services: non tangible products that are sold to the general public and include hotel accommodation, insurance services and train journeys.
Capital goods: physical goods that are used by industry to aid in the production of other goods and services such as machines and commercial vehicles.
What are business “inputs”?
Business functions
Human resource (HR) management identifies the workforce needs of the business, recruits, selects and trains appropriate employees and provides motivational systems to help retain workers and encourage them to work productively.
- Goal: manage human resources to help the business achieve its overall objectives.
Finance and accounts department has responsibility for monitoring the flow of finance into and out of the business, keeping and analyzing accounts and providing financial information to both senior management and other departments.
Marketing department is responsible for market research and for analyzing the results of such research so that consumer wants can be correctly identified. This information will then be discussed with other departments of the business so that the right product decisions are made. Once a product is available for sale, the marketing function will have to make important decisions concerning its pricing, how and where to promote it and how to sell it and distribute it for sale.
Operations management department has responsibility for ensuring adequate resources are available for production, maintaining production and quality levels and achieving high levels of productive efficiency.
Economic sectors
Primary sector business activity: firms engaged in farming, fishing, oil extraction and all other industries that extract natural resources so that they can be used and processed by other firms.
Secondary sector business activity: firms that manufacture and process products from natural resources, including computers, brewing, baking, clothing and construction.
Tertiary sector business activity: firms that provide services to consumers and other businesses, such as retailing, transport, insurance, banking, hotels, tourism and telecommunications.
Quaternary sector business activity: focused on information technology (IT) businesses and information service providers such as research and development, business consulting and information gathering.
Starting a business
Why start a business?
- Losing a job encourages many people to set up business by themselves, either providing their former employer’s product or another product, perhaps based on an interest or skill they have.
- Desire for independence - some people do not like the idea of being told what to do! By creating their own business, they have work flexibility and control over their working lives.
- By talking to friends/family, it might become clear that a business opportunity exists that an entrepreneur could take advantage of.
- A wish to make more money than in the current job many people setting up their own business believe that a they will earn a higher income working for themselves.
Entrepreneur: someone who takes the financial risk of starting and managing a new venture.
Intrapreneur: someone within a large corporation who takes direct responsibility for turning an idea into a profitable finished product through using “entrepreneurial talents” such as risk-taking and innovation.
Impact of enterprise (and intrapreneurship) on business activity
Employment creation
- In setting up a new business an entrepreneur is employing not only themselves (“self-employment”), but, very often, will employ other people too.
Economic growth
- Any increase in output of goods/services from a start-up business will increase the gross domestic product (GDP) of the country.
- If enough small businesses are created, it will lead to increased living standards for the population.
- Increased output and consumption will also lead to increased tax revenues for the government.
Firms’ survival and growth
- Although high proportion of new firms fail, some survive and a few expand to become really important businesses. These will employ large numbers of workers, add considerably to economic growth and will take the place of declining businesses that may be forced to close due to changing consumer tastes or technology.
Innovation and technological change
- New businesses tend to be innovative and this creativity adds dynamism to economy.
- Many new business start-ups are in the technology sector, e.g. website design. The increased use of IT by these firms and the IT services they provide to other businesses, can help a nation’s business sector become more advanced in its applications of IT and therefore more competitive.
Common steps in starting a business/enterprise
Identifying market opportunities
- Sourcing capital (finance)
- Determining a location
- Building a customer base
Problems faced by start-ups
- Competition
- Lack of record-keeping
- Lack of finance and working capital
- Poor management skills
- Changes in the business environment
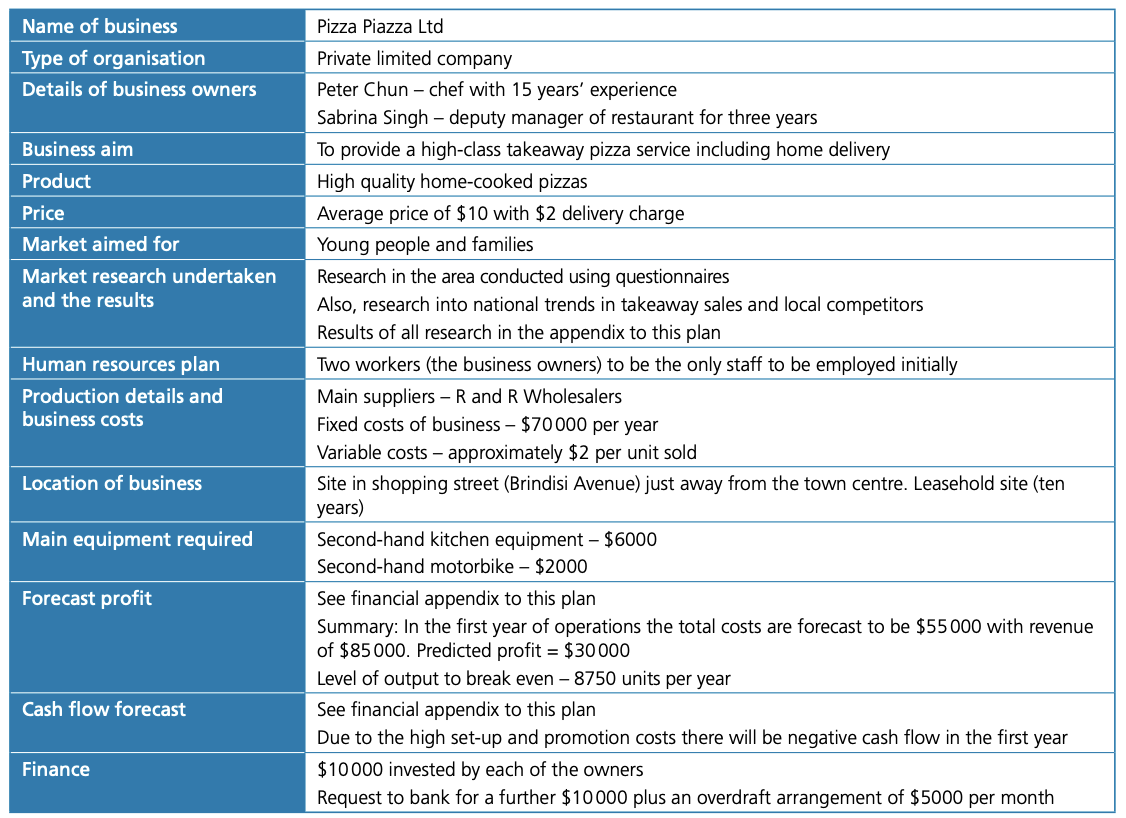
Business plans
Business plan: written document that describes a business, its objectives and its strategies, the market it is in and its financial forecasts.
Contents of a typical business plan:
- Executive summary
- Description of the business opportunity
- Marketing and sales strategy
- Management team and personnel
- Operations
- Financial forecasts
Importance of business plans:
- Obtaining finance for the start-up when setting up a new business
- Planning process
- Financial and other forecasts contained in the plan can be used as the targets that the business should aim for.