SBI4U - Unit One - Biochemistry
1/84
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Ionic Bonds
Bonds formed by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms with an electronegativity greater than 1.7, resulting in cations and anions.
Covalent Bonds
Bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Polar Covalent Bonds
Bonds where electrons are shared unequally, resulting in partial charges; electronegativity between 0.41 and 1.7 (e.g., H2O).
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Bonds where electrons are shared equally, with electronegativity less than 0.4 (e.g., H2, O2).
Amphiphilic
Molecules that have both polar and nonpolar parts (e.g., fatty acids).
Electronegativity
A measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons, influencing bond strength.
Hydrogen Bonds
Attractive forces between a partially positively charged hydrogen atom and a partially negative charge in another molecule (e.g., between water molecules).
Dehydration Reaction
A chemical reaction that removes an OH and H to join smaller molecules, producing water.
Hydrolysis Reaction
A reaction that adds water to split a larger molecule into smaller units.
Neutralization Reaction
A reaction between acids and bases that produces water and salt.
Redox Reaction
A reaction involving the transfer of electrons, where one atom loses electrons (oxidation) and another gains them (reduction).
Cohesion
The attraction between water molecules, contributing to surface tension.
Adhesion
The attraction of water molecules to other polar molecules.
Capillary Action
The ability of water to climb inside tubules due to adhesion and cohesion.
Surface Tension
The result of water molecules bonding more at the surface than below, creating a "skin" effect.
Lower Density Solid
Water expands when frozen, making ice less dense than liquid water, allowing it to float.
High Heat of Vaporization
The amount of heat required to convert water from liquid to vapor, aiding in cooling through sweat evaporation.
High Heat Capacity
The large amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of water, affecting climate and ecosystems.
Universal Solvent
Water's ability to dissolve ionic and polar substances.
Carbon Chains
The backbone of biochemistry, allowing for complex molecules due to carbon's ability to form four bonds.
Functional Groups
Specific groups of atoms within molecules that determine their chemical properties and reactions.
Macromolecules
Large biological molecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars with a chemical formula of CHO in a 1:2:1 ratio (e.g., glucose).
Disaccharides
Formed from two monosaccharides through a dehydration reaction (e.g., sucrose).
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides, serving as energy storage or structural support (e.g., cellulose).
Lipids
Nonpolar molecules that include fats, oils, and phospholipids, with functions in energy storage and membrane formation.
Nucleic Acids
Macromolecules (DNA and RNA) made of nucleotides, essential for genetic information storage and transfer.
Proteins
Polymers made of amino acids, serving various functions such as enzymes, hormones, and structural support.
Protein Denaturation
The process where proteins lose their functional shape due to changes in temperature, pH, or salt concentration.
Properties of Water
Key properties of water include low density solid, universal solvent, high heat capacity, heat of vaporization, adhesion/cohesion, capillarity, and surface tension.
Monosaccharide example
Glucose, Fructose
Disaccharide example
Sucrose, Lactose
Polysaccharide example
Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose
Saturated fatty acid
Straight chain fatty acid - no double bonds
Unsaturated fatty acid
“Kinked” chain fatty acid - at least one double bond
Eukaryotic Cell
Plant and animal cells.
Have organelles, the amount of which varies by cell type
Prokaryotic Cell
Bacteria Cell
No organelles
Cell Membrane Functions
Maintains cell shape
Semi-permeable
Between-cell communication
Show cell identity
Fluid Mosaic Model
flexible and made with many different parts; molecules are attracted to each other but float freely
Phospholipids
form a bilayer spontaneously; hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails line up with heads facing out and tails facing in
Primary Protein Stage
sequence of amino acids coded by DNA (peptide bonds)
Secondary Protein Stage
alpha helix and beta sheet (H- bonds between polar R’s)
Tertiary Protein Stage
3D shape is globular or fibrous and defined by various bonds
Quaternary Protein Stage
2 or more polypeptides join, making it a functional protein
Cell Carbohydrates
markers that identify the cell
Glycoprotein
“person specific” marker; lets immune system recognize invaders
Glycolipids
“tissue specific” marker; tells cells to stop multiplying and stay put
Cholesterol
contributes to the fluidity of the membrane; in moderate temperatures, reduces fluidity, but at low temperatures hinders solidification
Globular Proteins
receptors for communication
transport substances in and out
speed up reactions
anchors cells and their parts
Types of globular proteins
Integral and Peripheral
Integral
embedded in protein
Peripheral
attached to surface
Fibrous Proteins
form a cytoskeleton to maintain cell shape
Shape of Fibrous Proteins
shape is closely tied to function
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a membrane
simple diffusion
movement of molecules from [high] to [low] across a membrane (small, nonpolar molecules only)
Facilitated Diffusion
requires a specific protein channel, moving down concentration gradient.
It requires no energy and works for large, polar molecules
Ions require channel proteins
Hypotonic
Lower concentration of solute than inside the cell
Hypotonic Effects on Animal Cells
highly dangerous - can cause cell to burst
Hypotonic Effects on Plant Cells
beneficial - causes cell membrane to push against the cell wall, increasing pressure to make cell turgid (firm, healthy)
Hypertonic
higher concentration of solute than inside the cell
Hypertonic Effects on Animal Cells
cell shrinks and becomes flaccid
Hypertonic Effects on Plant Cells
highly dangerous - cell membrane tears away from cell wall, causing plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
Occurs only in plant cells; cell membrane ruptures after tearing away from the cell wall, killing the cell
Active Transport
The movement of particles from low concentration to high concentration, requiring ATP
Carrier Proteins
certain membrane proteins use ATP to change their shape, allowing particles to be taken in or out against natural diffusion
Endocytosis
the cell membrane folds around a substance, bringing it into the cell
Phagocytosis
cell “eating” - taking in solids
Pinocytosis
cell “drinking” - taking in liquids
Receptor-mediated Endocytosis
substances attach to membrane receptors, causing the membrane to fold inward and create a coated vessicle
Exocytosis
vacuoles containing wastes, to be removed or cell products for export. The vacuole approaches the cell membrane, fuses with it, and expels its contents.
Enzyme
biological catalyst that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed
Active Site
a pocket or groove in an enzyme that binds to a substrate
Substrate
a substance that is recognized by and binds to an enzyme
Anabolic Enzyme
pulls molecules together
Catabolic Enzyme
pulls molecules apart
Induced-Fit Hypothesis
enzymes are somewhat flexible and can change shape to better accommodate a substrate
Activation Energy…
is lower when enzymes are present
Cofactors and coenzymes
bind to an enzyme in order to make space for the correct substrate
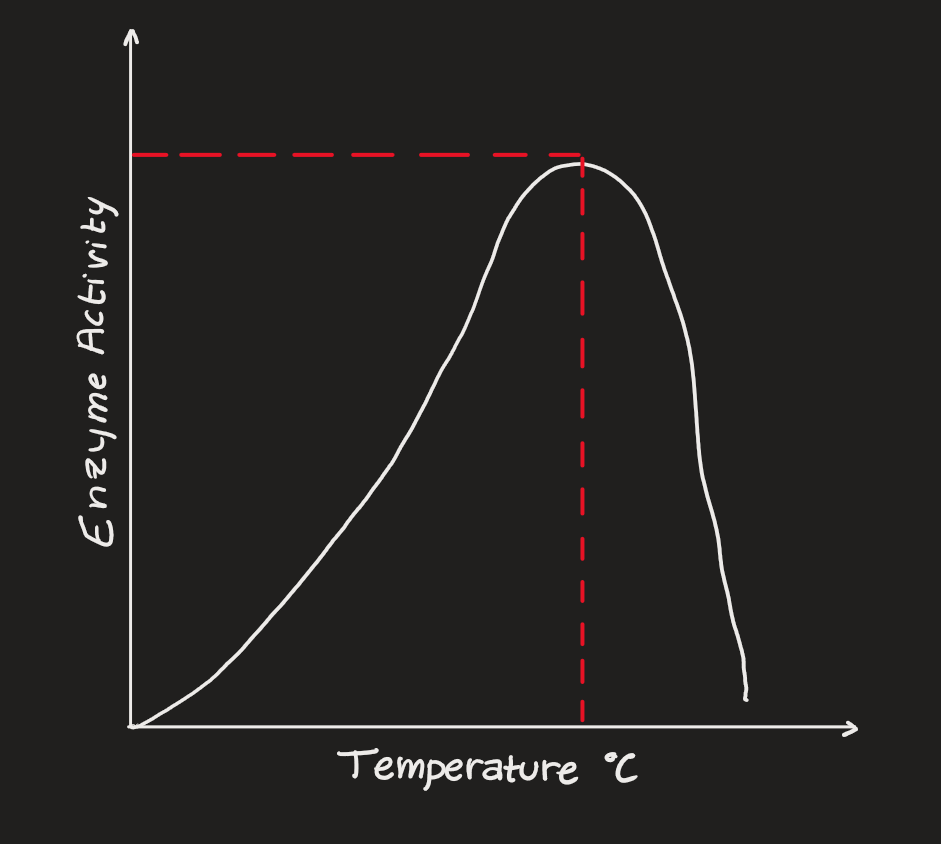
Temperature
enzymes @ low temperatures - inactive
enzymes @ high temperatures - denatured
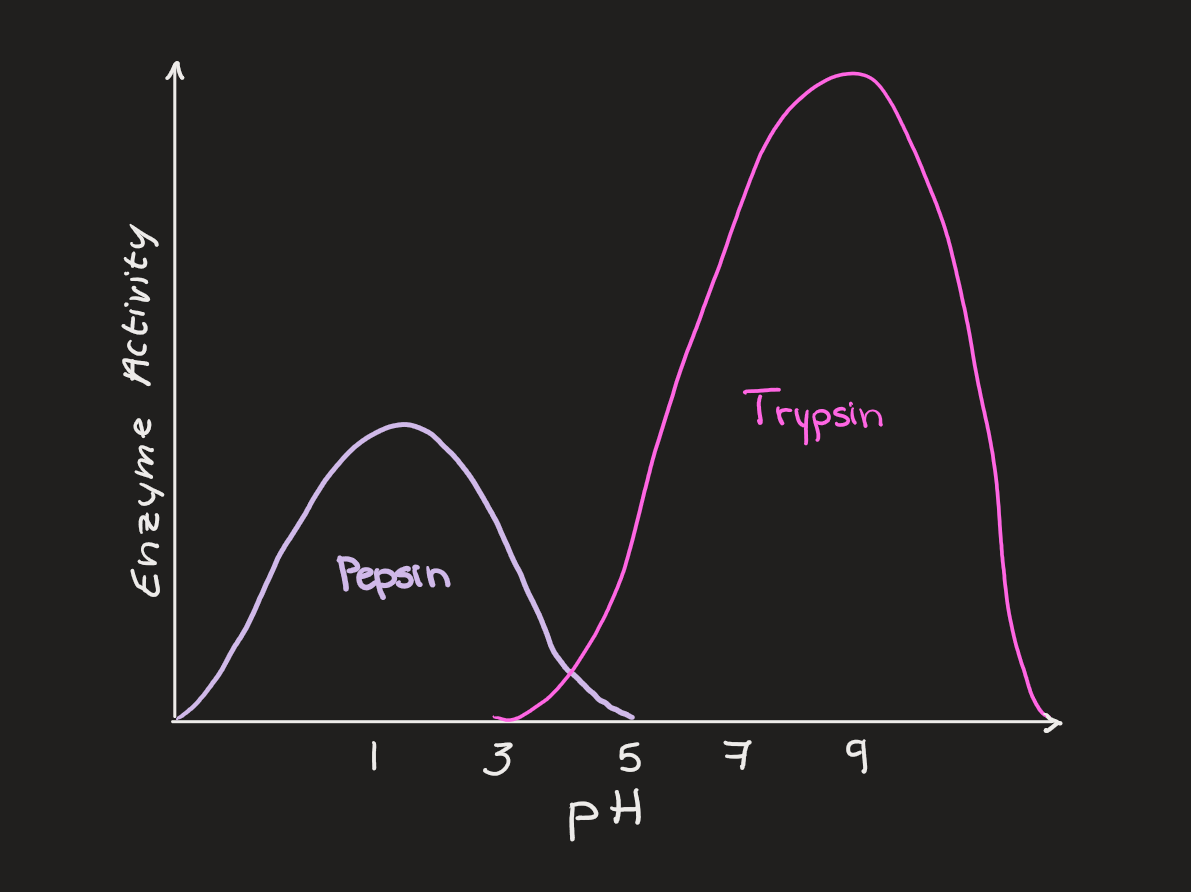
pH
different enzymes have different ideal pH
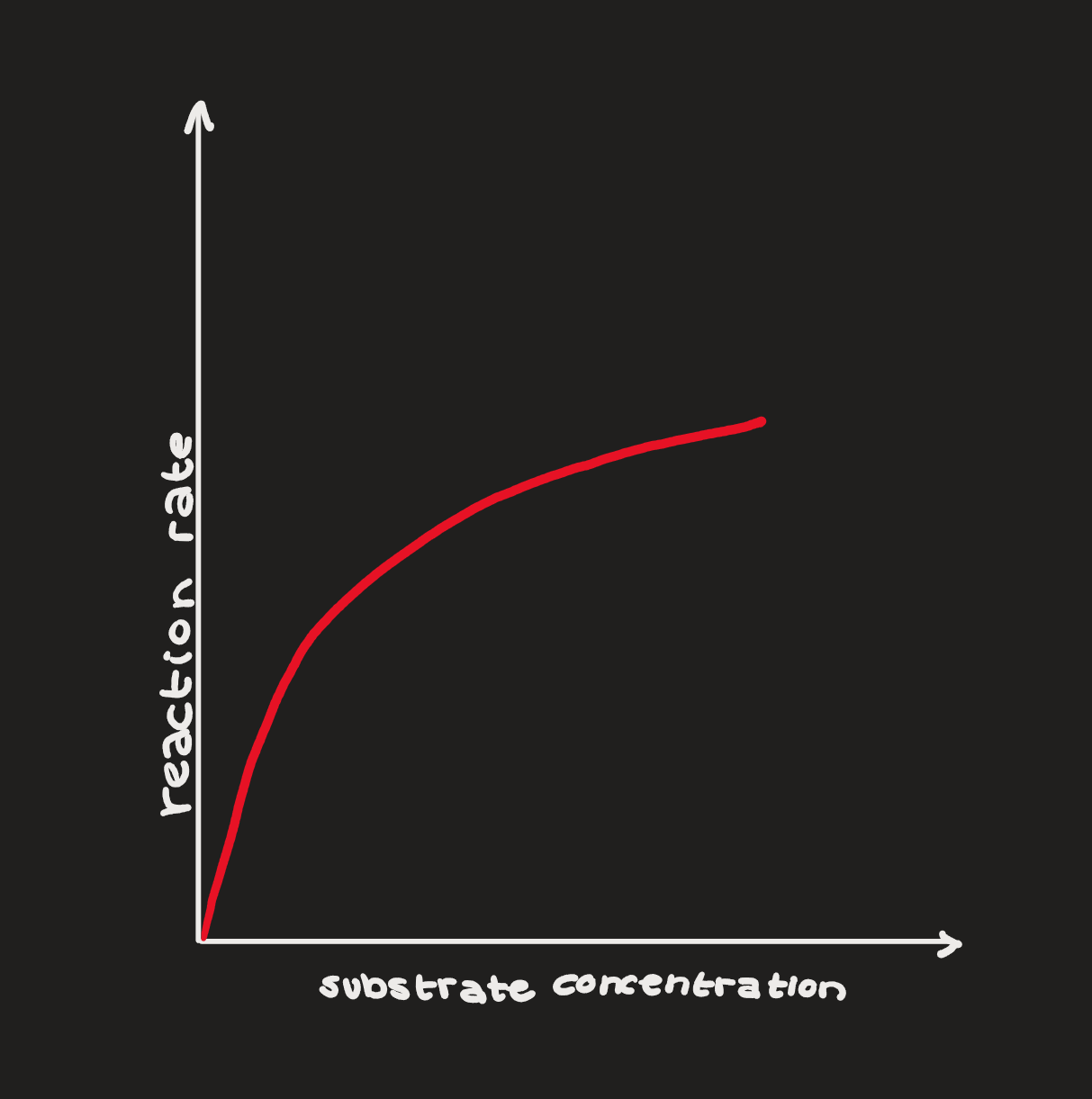
Substrate Concentration
enzymes can only do so much - as substrate concentration increases, reaction rate increases, until it reaches a maximum
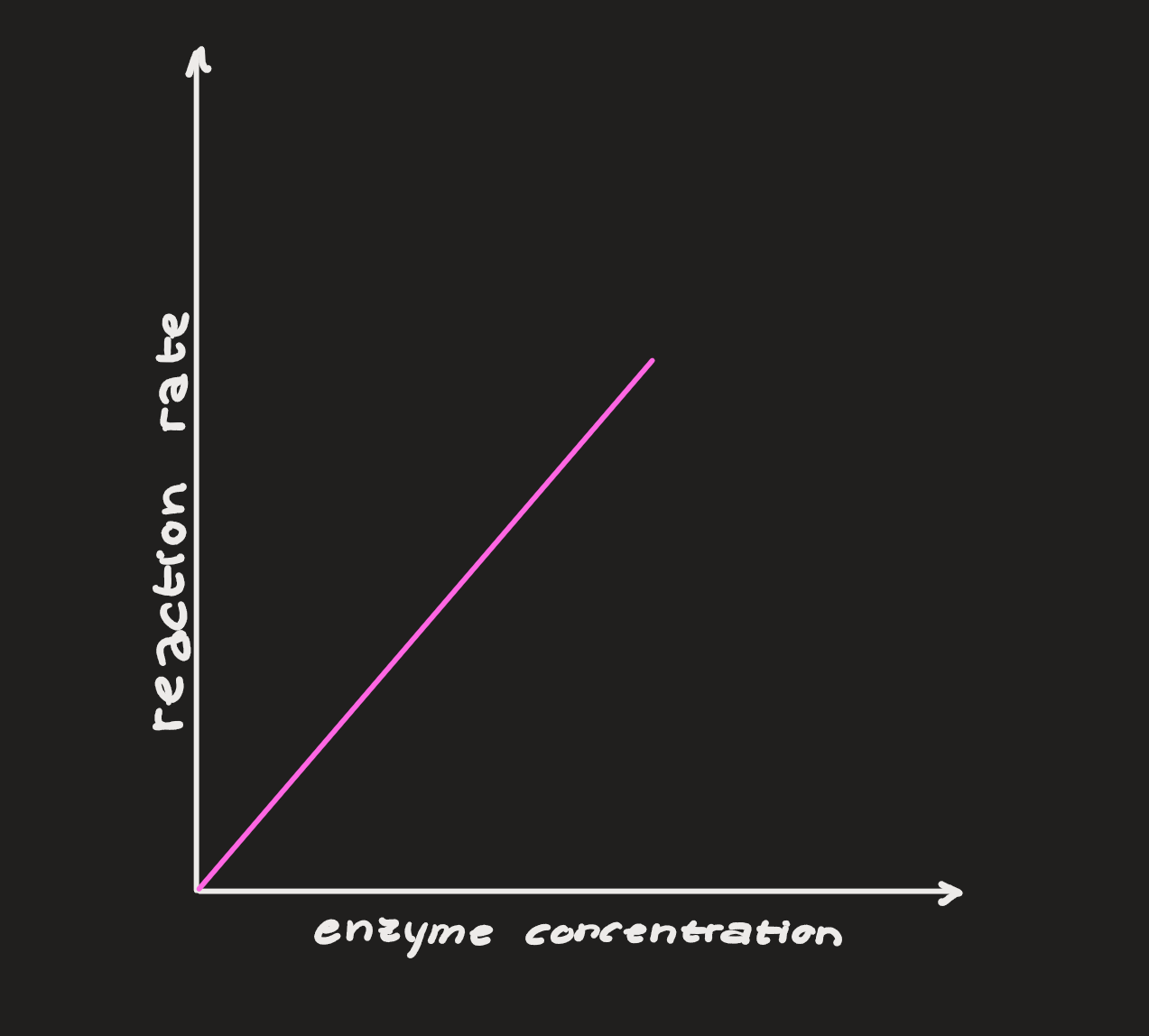
Enzyme Concentration
As enzyme concentration increases, the reaction rate increases. these are directly proportional
Competitive Inhibitors
interference by a molecule (inhibitor) binding to the active site
Non-Competitive Inhibitor
a molecule binds to another place on the enzyme, causing a change in the shape of the active site