Reproductive Strategies and Cell Division Processes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
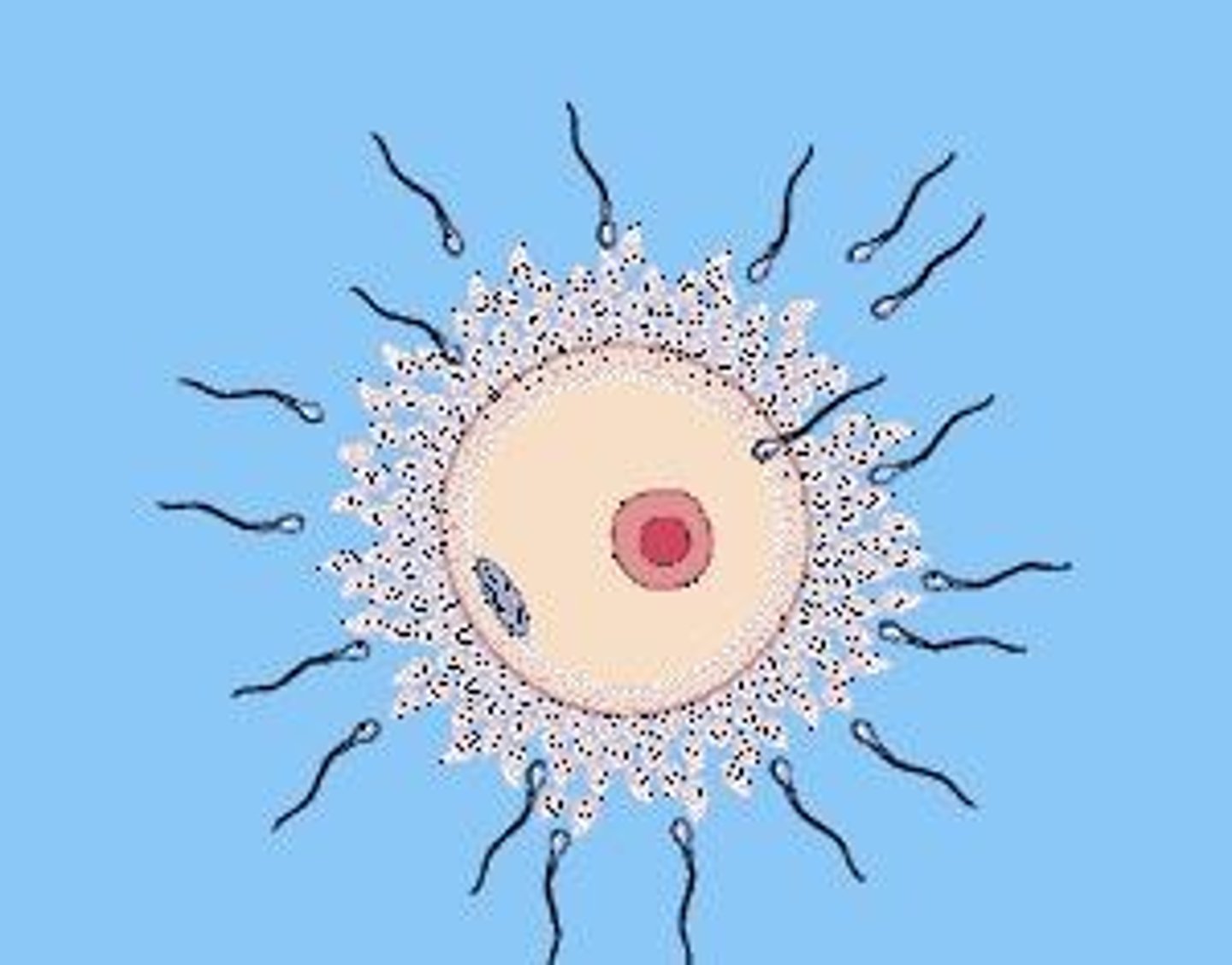
Sexual Reproduction
TWO different reproductive cells, usually from male and female, unite to form new offspring.
Asexual Reproduction
ONE parent; needs much less energy than sexual reproduction and occurs much faster.
Lower Reproductive Potential
Able to have FEW offspring that will be able to reproduce too.
Greater Reproductive Potential
Able to have MANY offspring that will be able to reproduce too.
Zygote
Egg combines with sperm to form a zygote.
Binary Fission
Organism splits into 2 equal parts; examples include amoeba and bacteria.
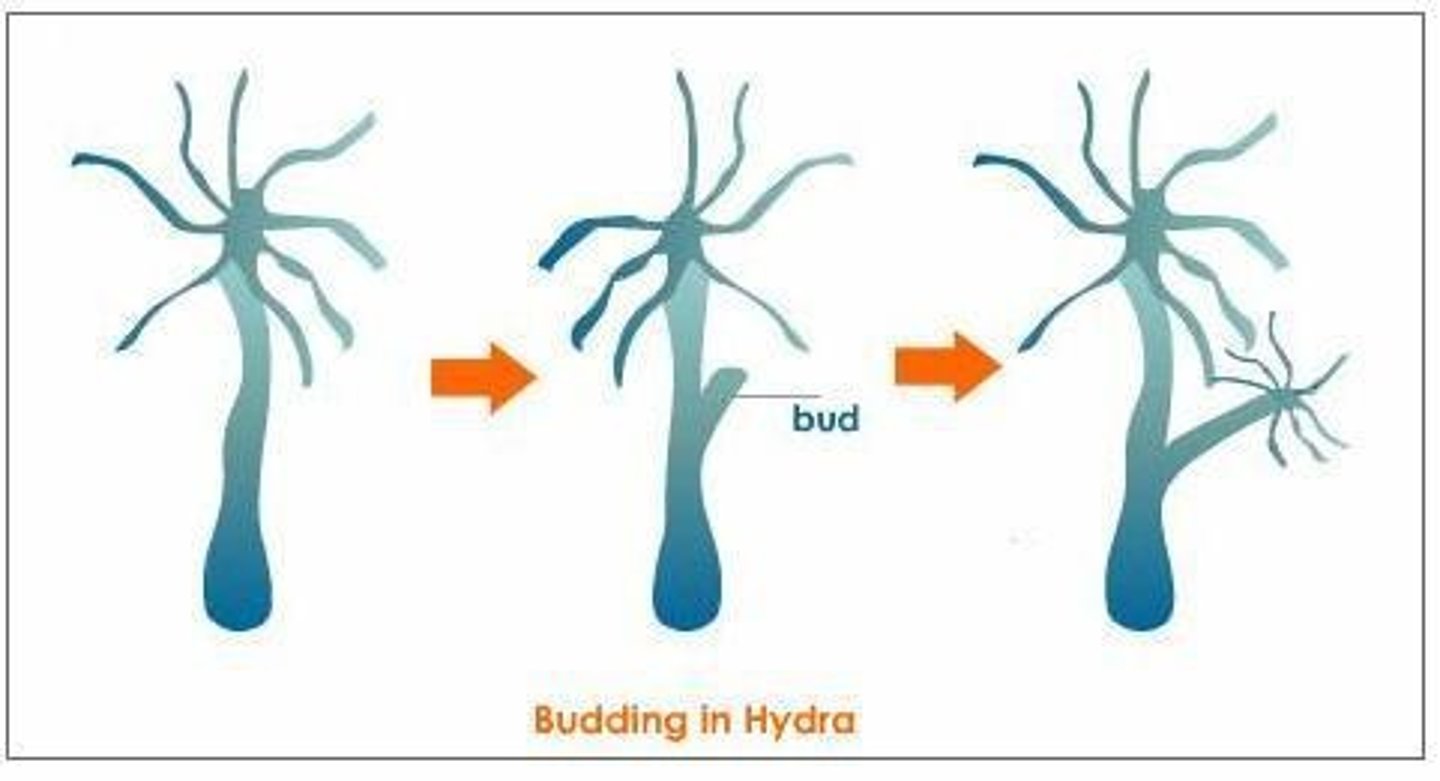
Budding
Offspring grows as outgrowth from parent and breaks off; examples include yeast and hydra.
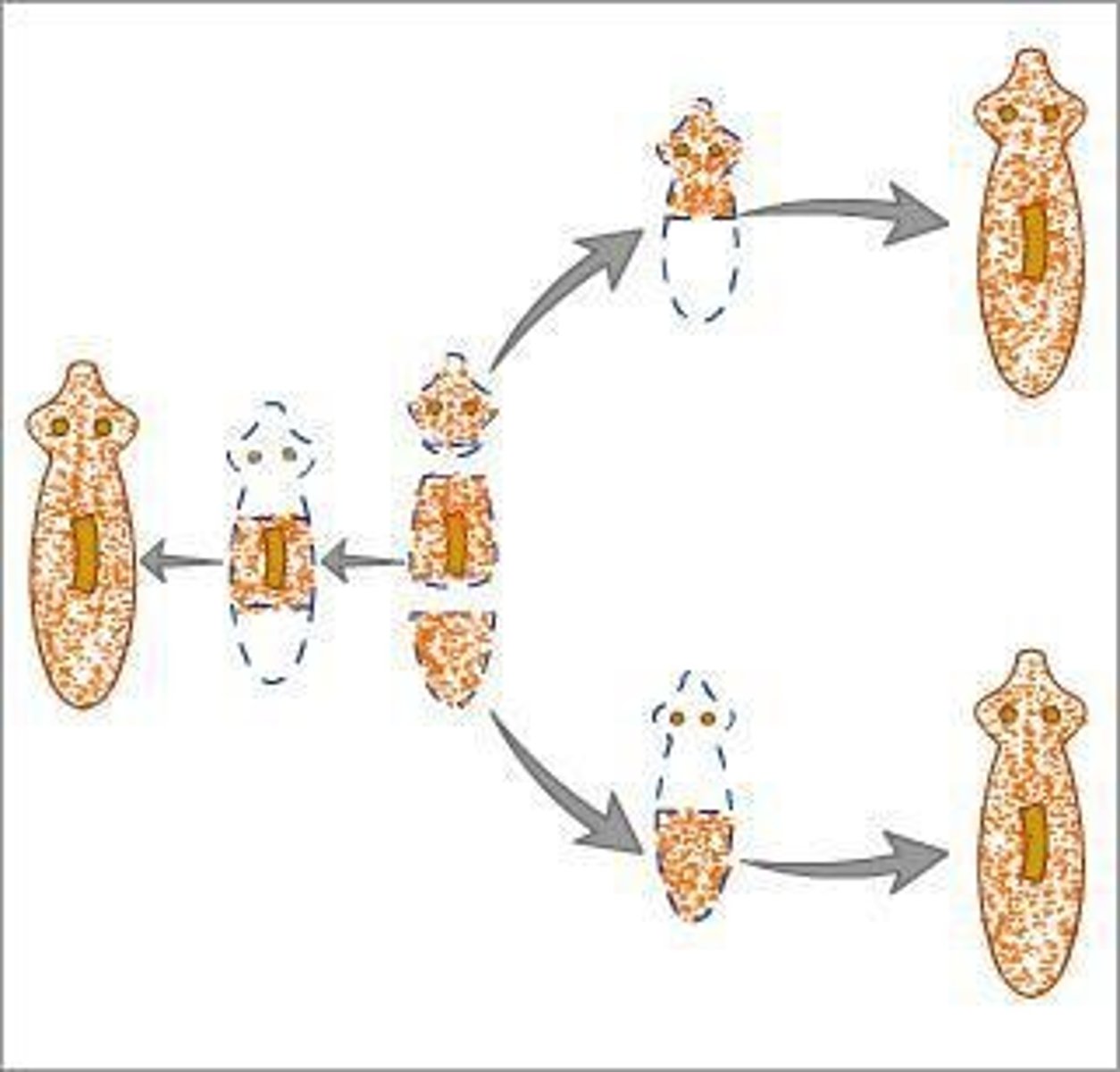
Regeneration
Offspring form from a part that breaks off a parent; examples include starfish and planaria.
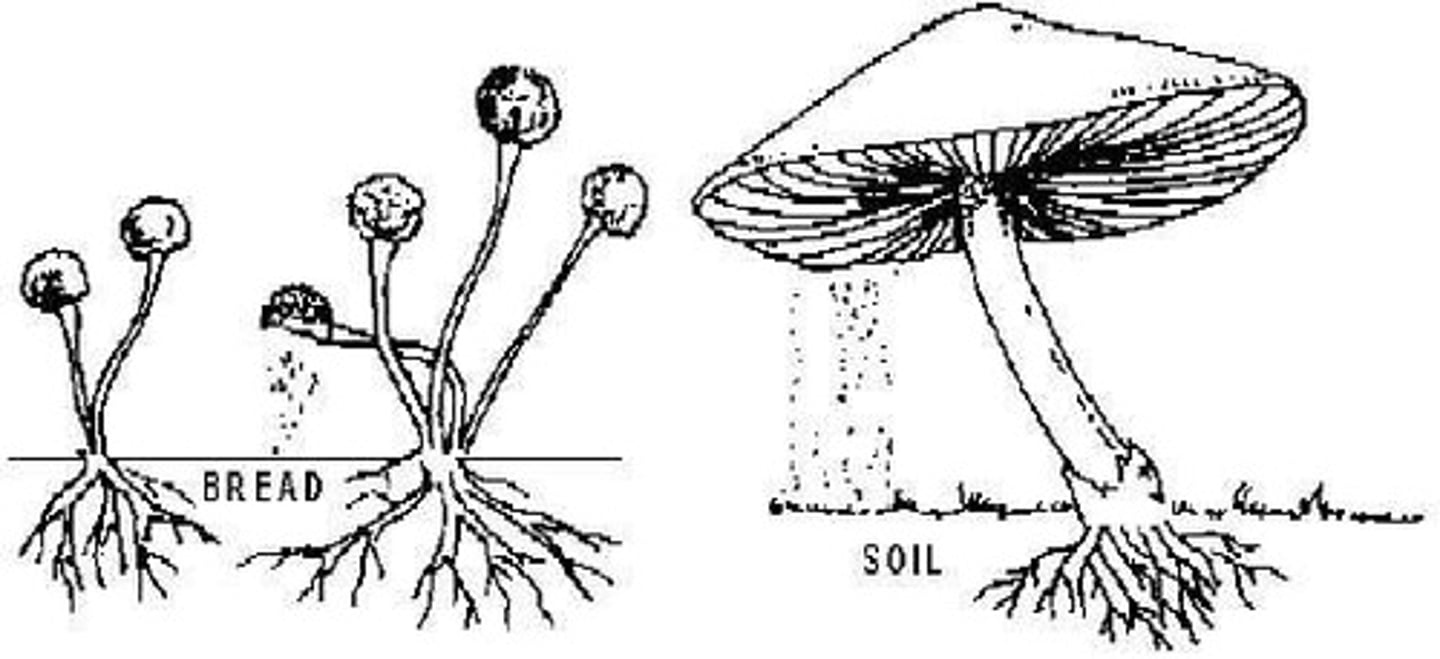
Sporulation
Release of many spores that produce individual offspring; examples include mould and fungi.
Vegetative Reproduction
New plants produced without seeds; examples include runners, cuttings, bulbs, grafting.
Parthenogenesis
Egg development without fertilization; examples include daphnia, aphids, reptiles.
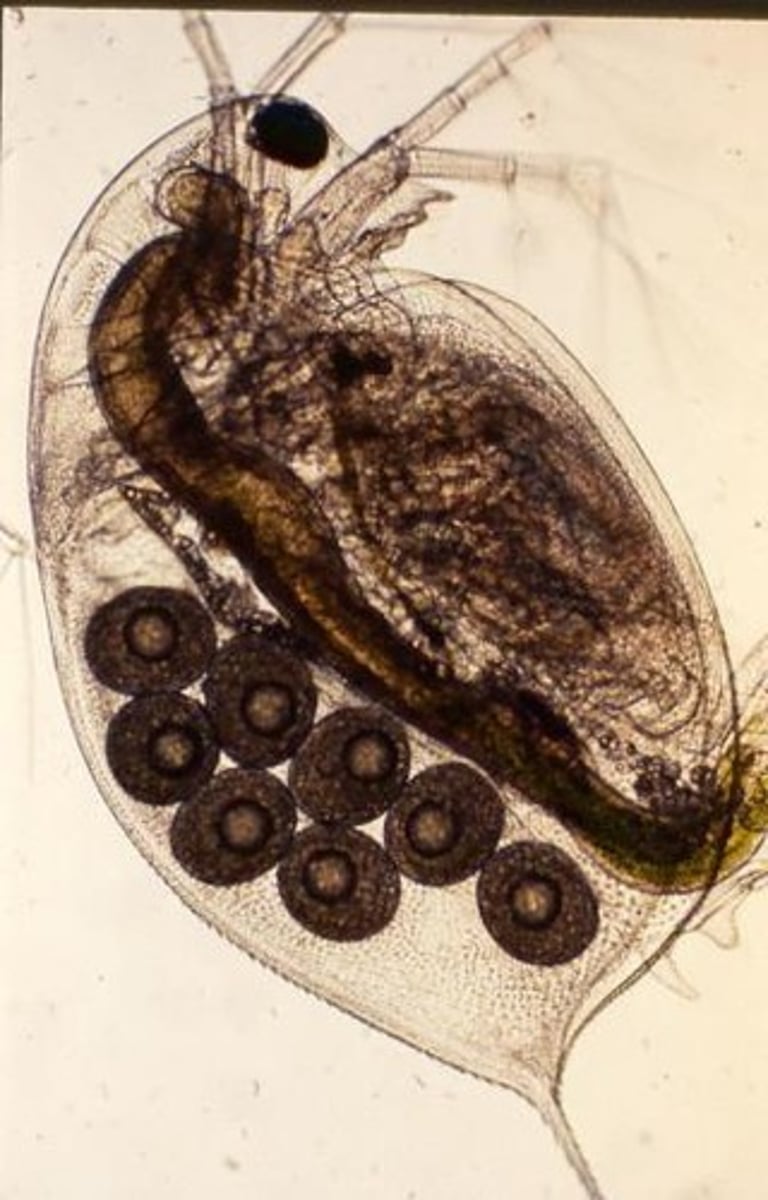
Genetic Continuity
Passing on genetic material to offspring.
Chromosomes
Structures made of DNA that carry genetic information.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, the molecule that carries genetic information.
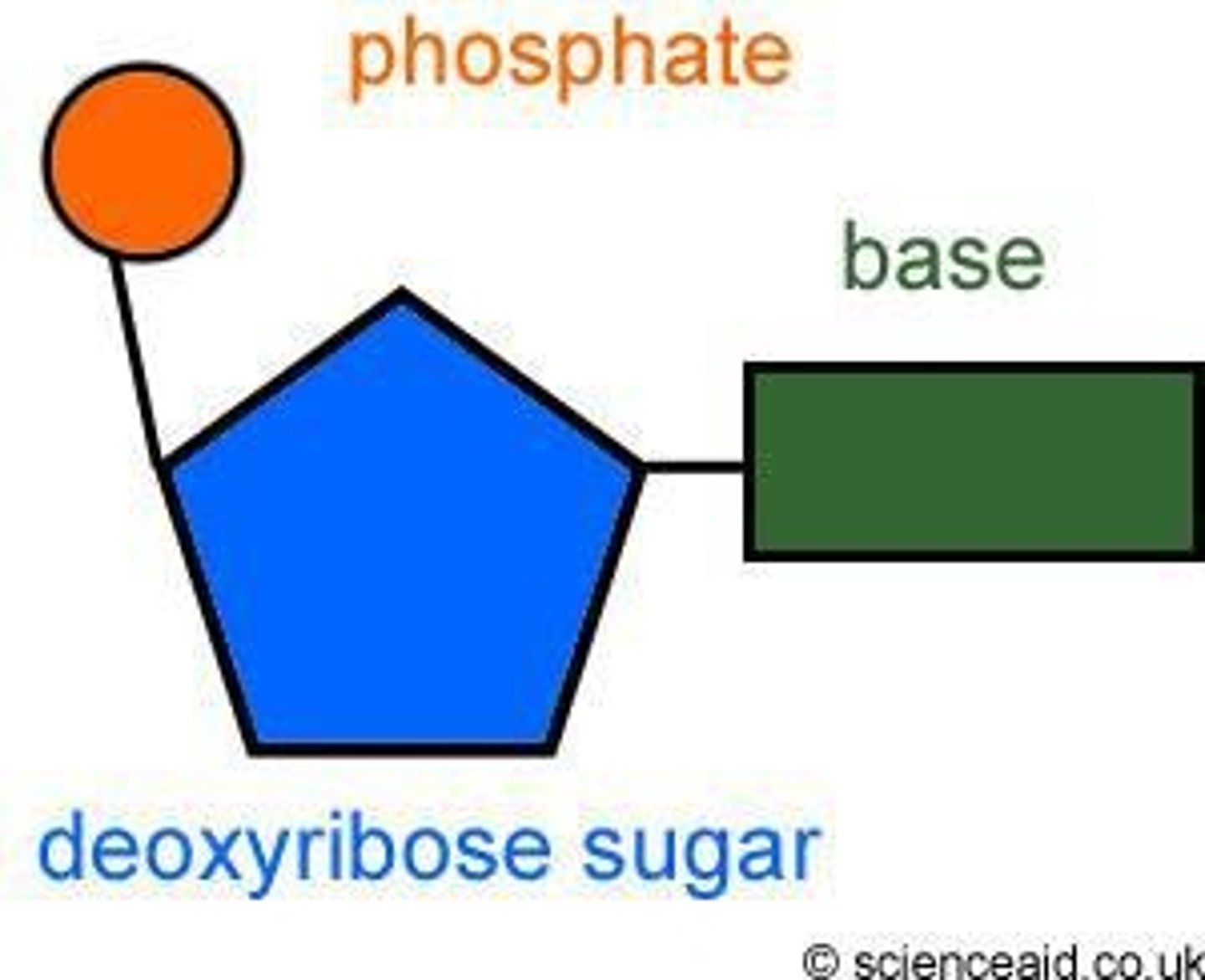
DNA Nucleotide
Monomer of DNA composed of a phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and nitrogenous base (A, T, C, G).
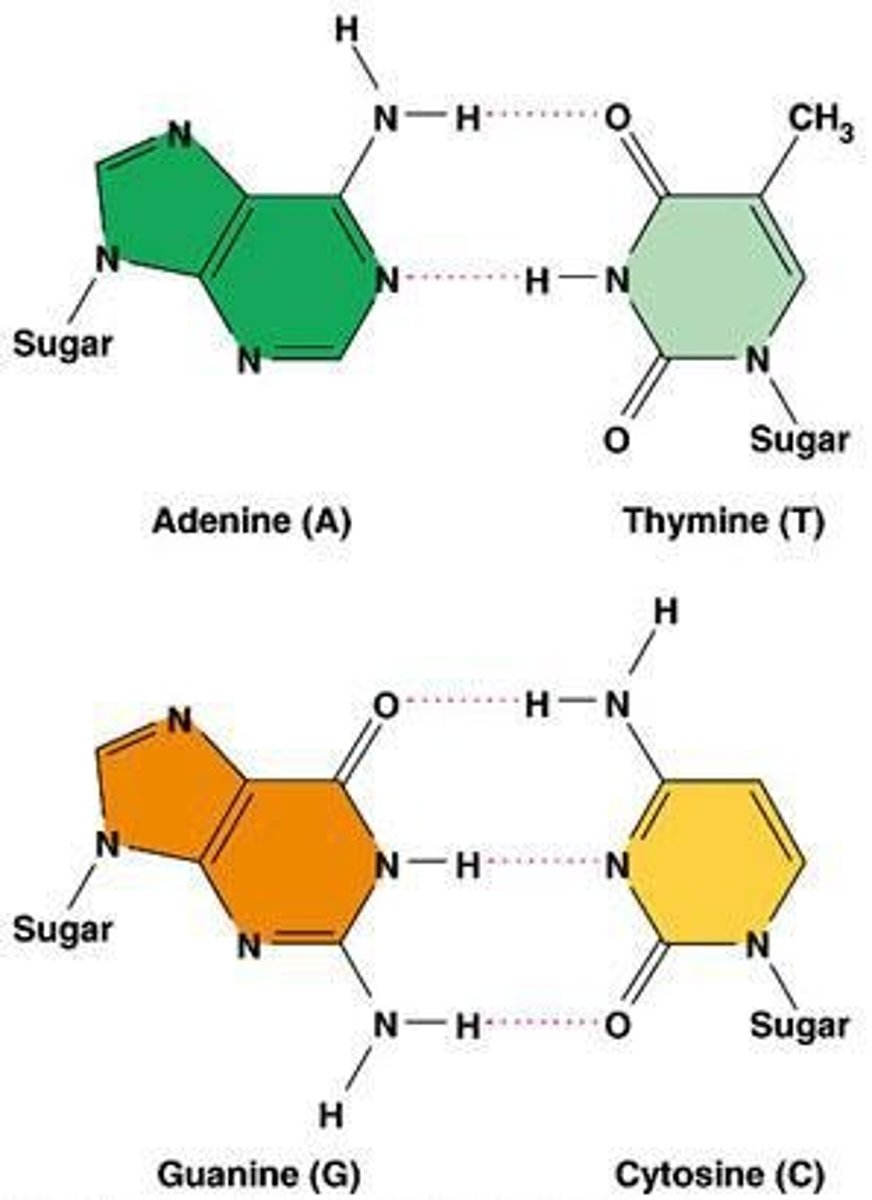
Complementary Base Pairs
Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Cytosine pairs with Guanine.
Gene
A specific sequence of nucleotides that codes for a specific amino acid sequence.
Codon
A sequence of 3 bases that codes for one amino acid.
Double Helix
The structure of DNA, which is double stranded.
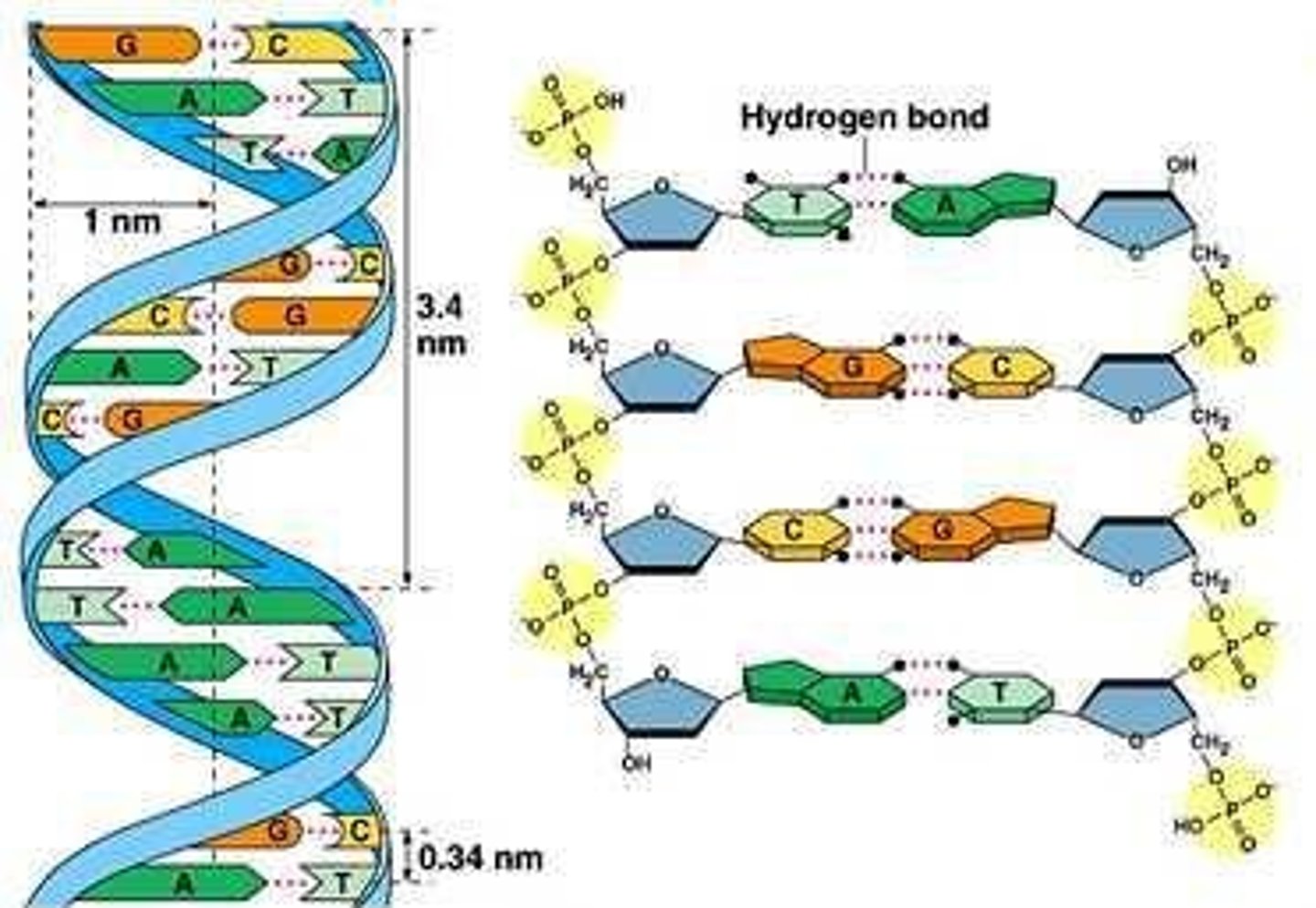
Nuclear Replication
Process by which copies of DNA are made, occurring in the nucleus before cell division.
Chromosome Number
Each species has a particular number of chromosomes; e.g., human - 46, fruit fly - 8.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that occur in pairs, similar in form and arrangement of genetic material.
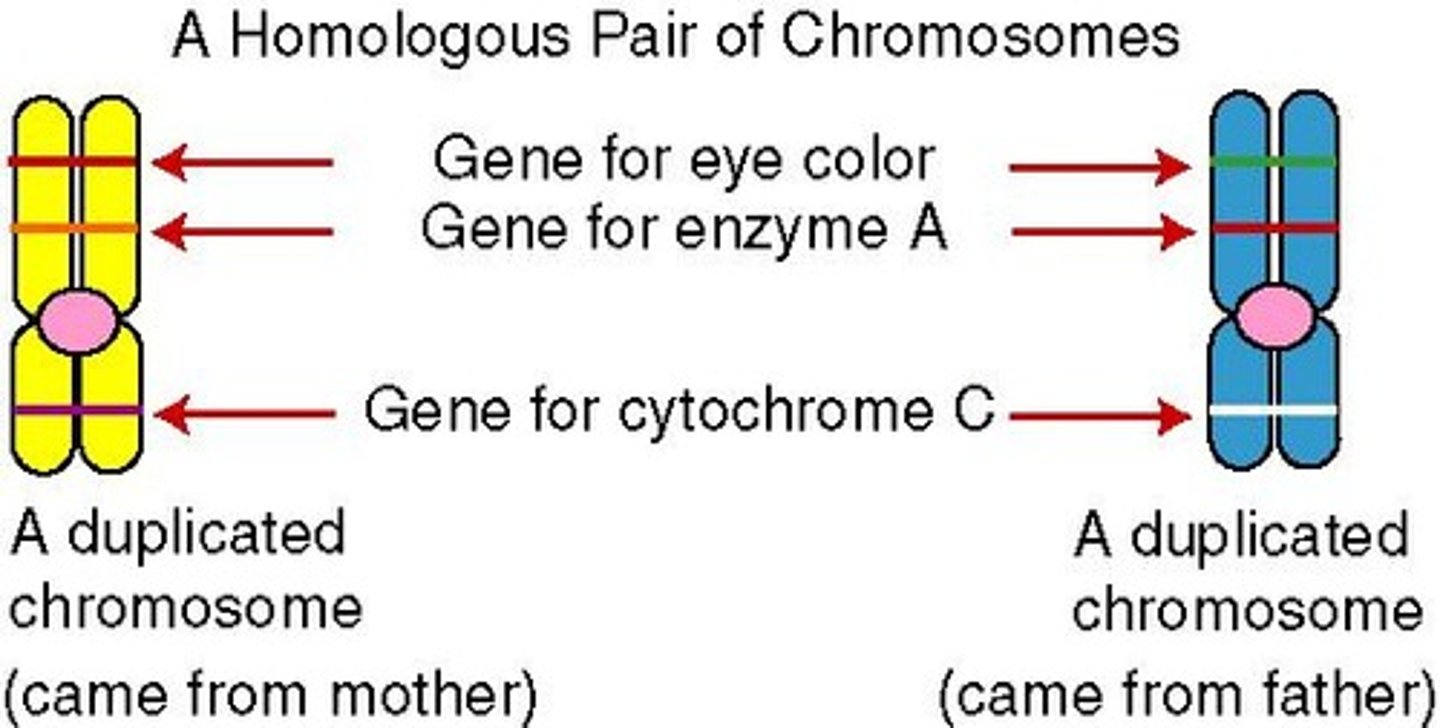
Allele
Alternate form of a gene located at a particular place on a chromosome.
Mitosis
Nuclear division characterized by chromosome replication and formation of two identical daughter nuclei.
Cell Cycle
The process through which a cell prepares to divide and actually performs steps of cell division.