APES 1.1-2
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
temperate desert
A biome characterized by grassed prairies with cold, harsh winters, and hot, dry summers with plants such as cacti and sagebrush
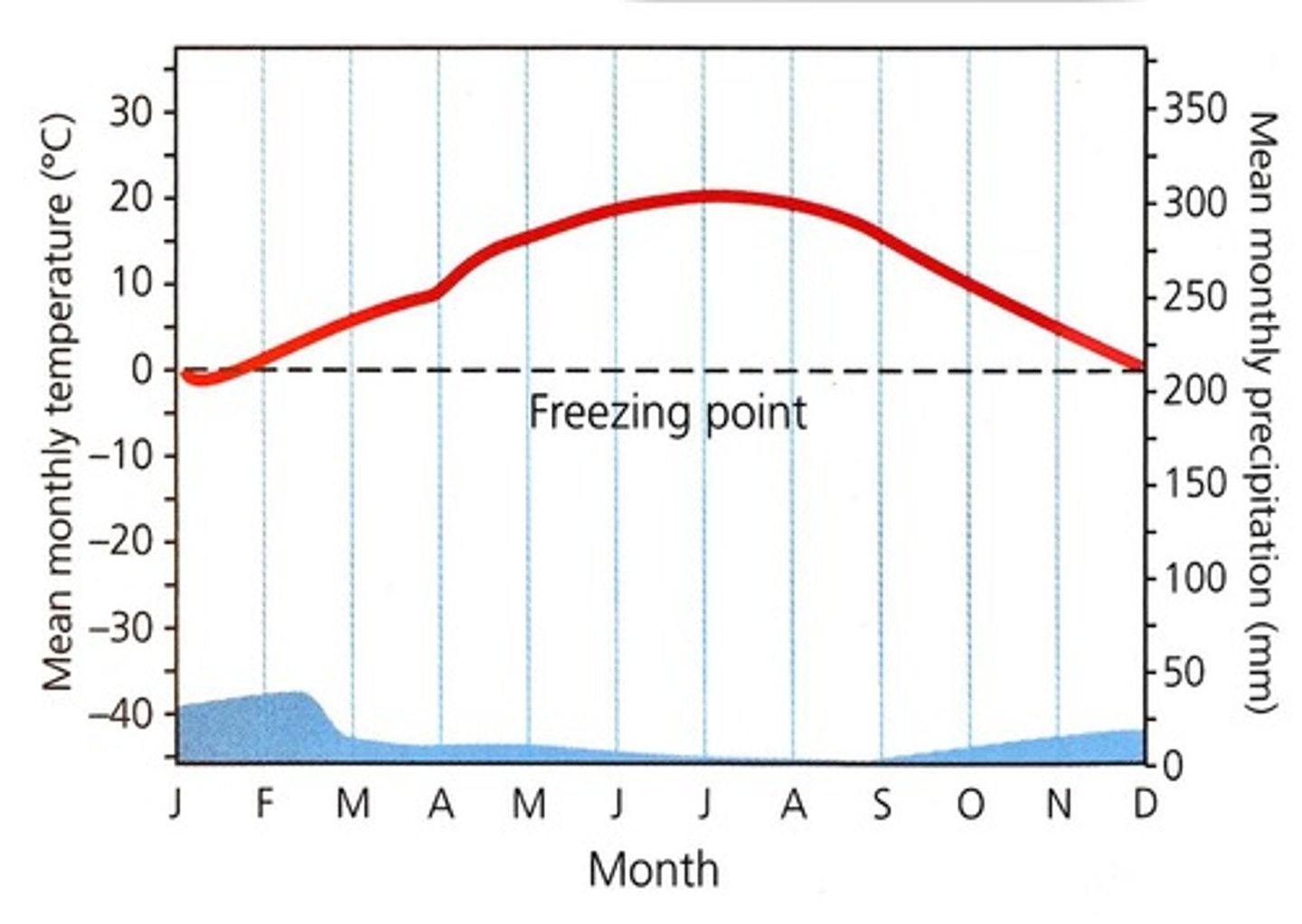
temperate rainforest
biome south of the boreal forest characterized by broad-leaved, deciduous trees, pine trees, etc. well-defined seasons, and average yearly precipitation of 75-150 cm. ex= pacific northwest
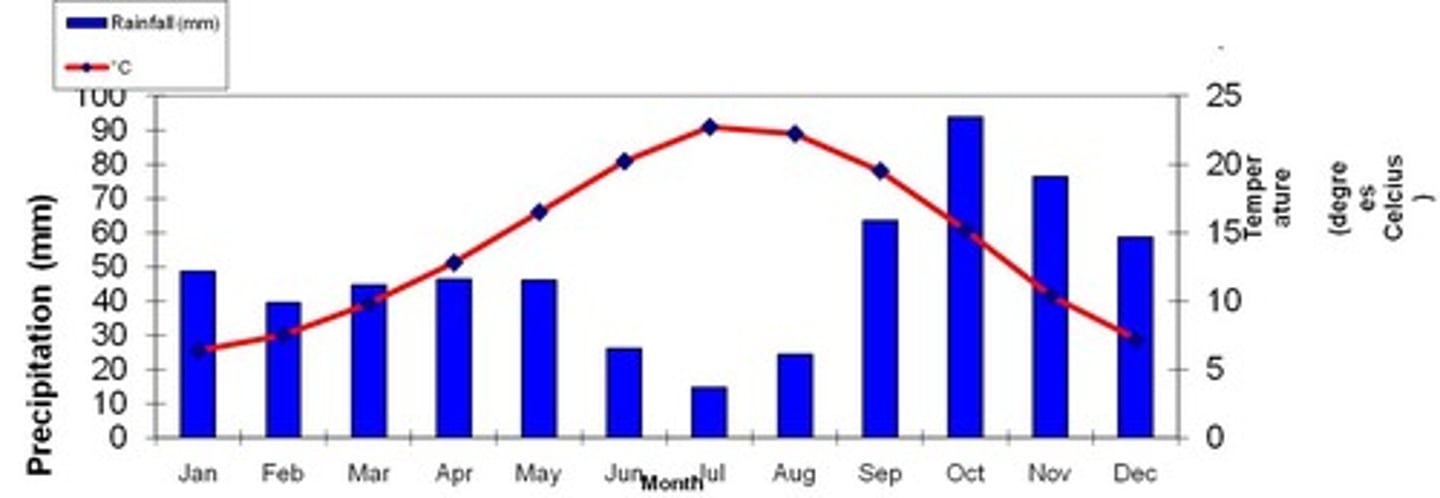
temperate grassland
biome characterized by deep, nutrient-rich soil that supports many grass species found in 30-60 latitudes such as the midwest of the US
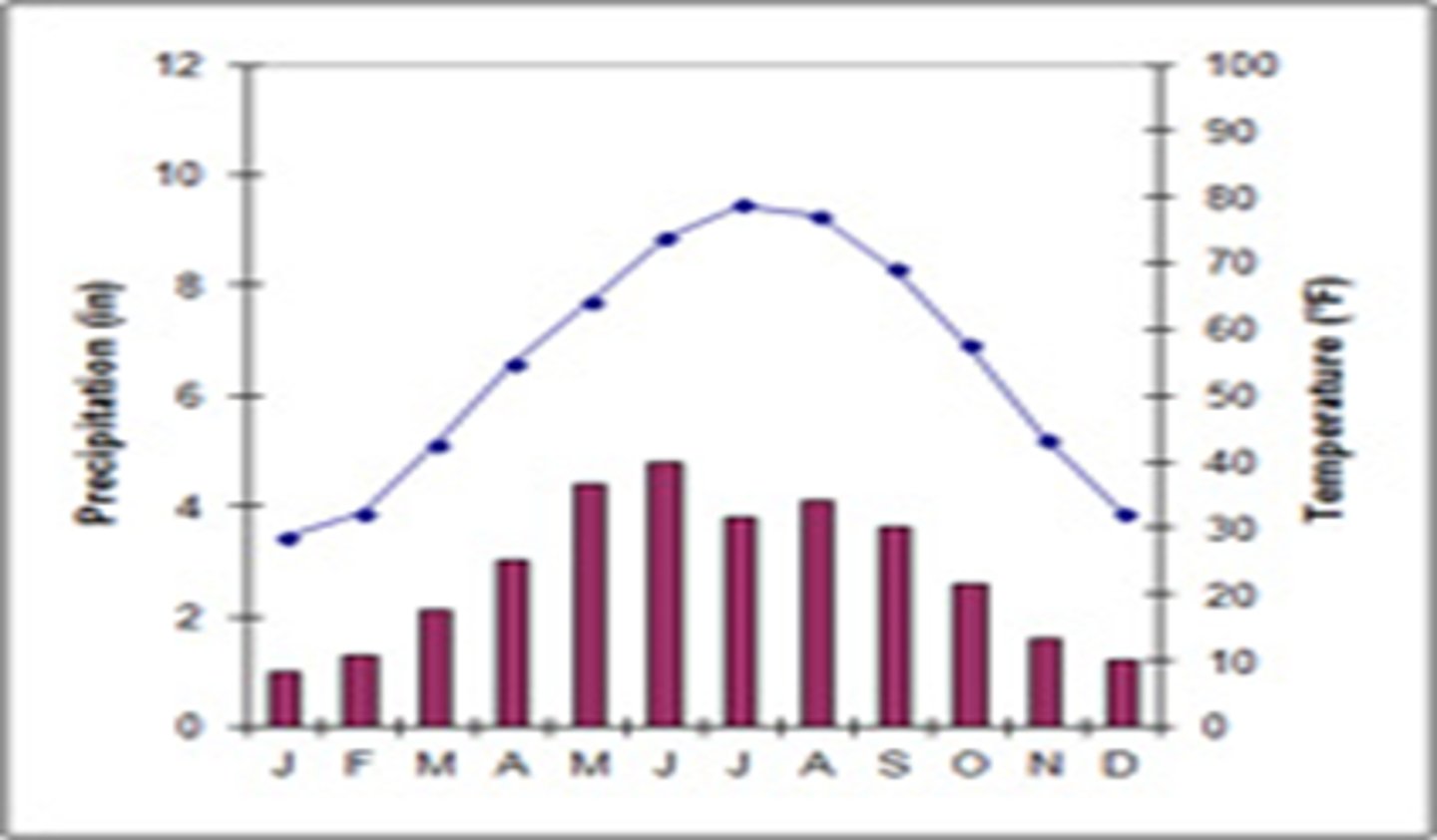
tropical desert
a biome characterized by hot temperatures, low precipitation and nutrient-poor soil ex= the Sahara
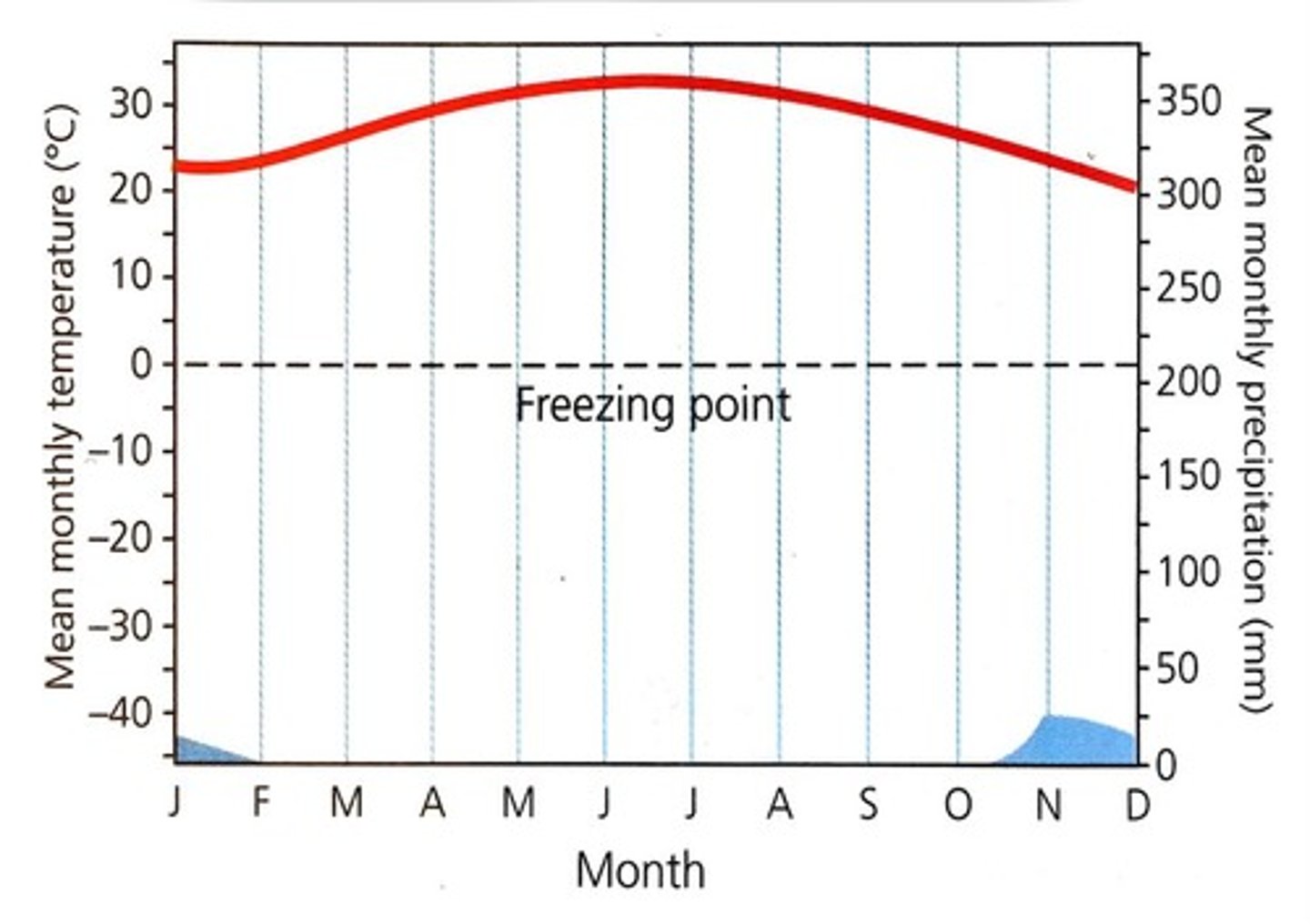
tropical rainforest
biome near the equator with warm climate wet weather and lush plant growth; no seasons; high biodiversity
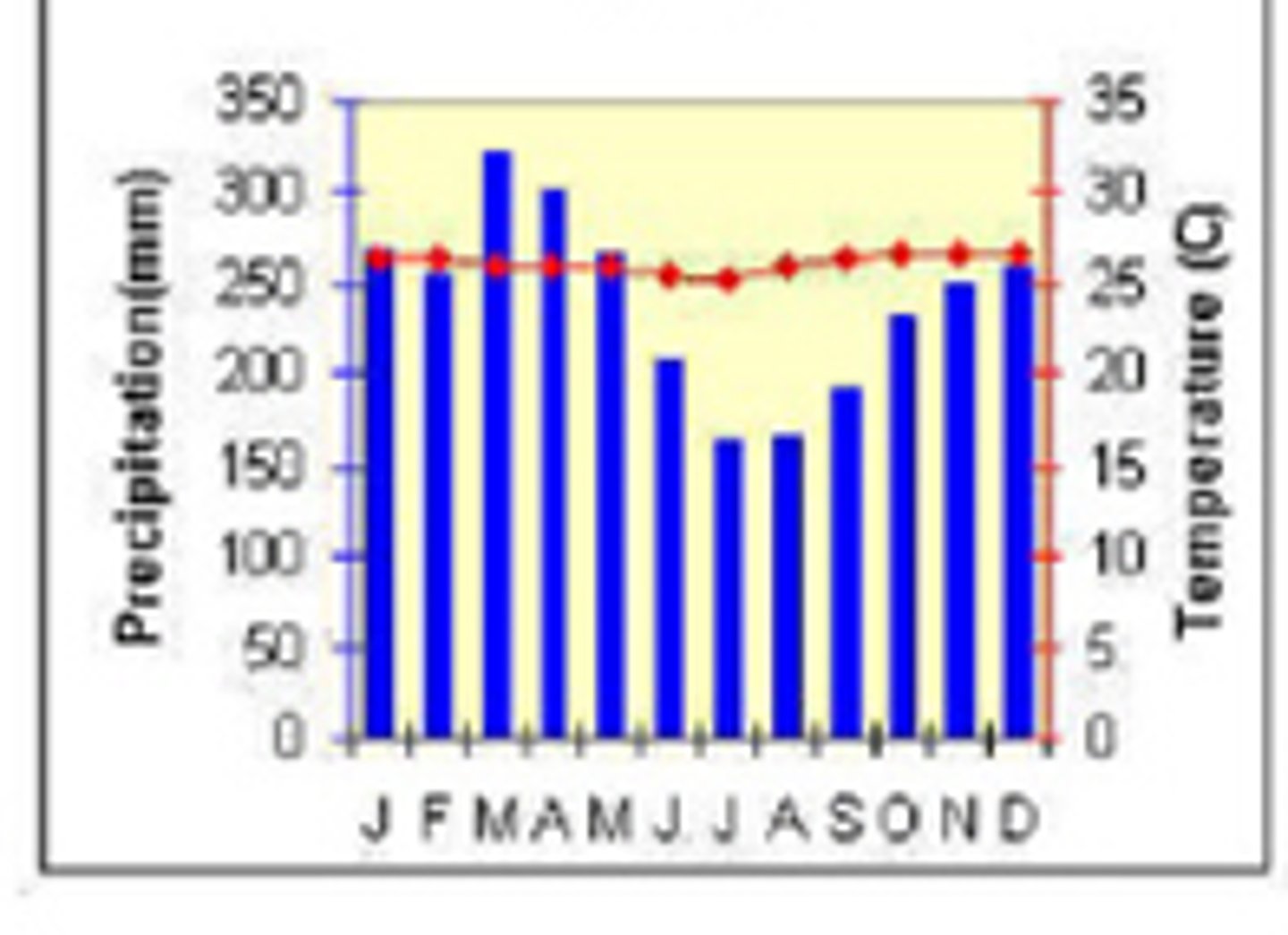
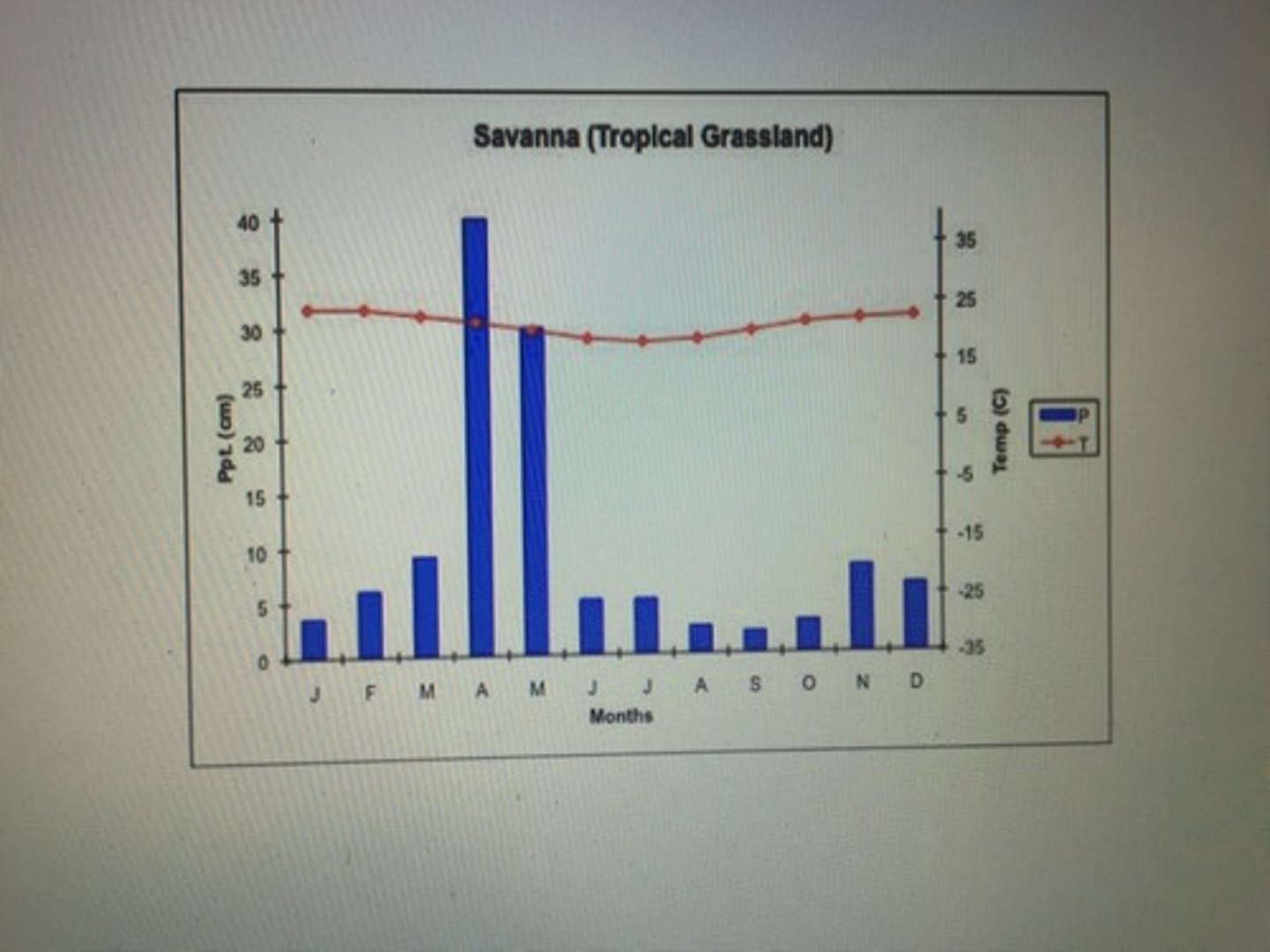
tropical grassland
located north and south of the equator, often called savannas
winters are warm and dry
summers are hot and rainy
rainfall 18-50 inches each year; distinct rainy and dry seasons
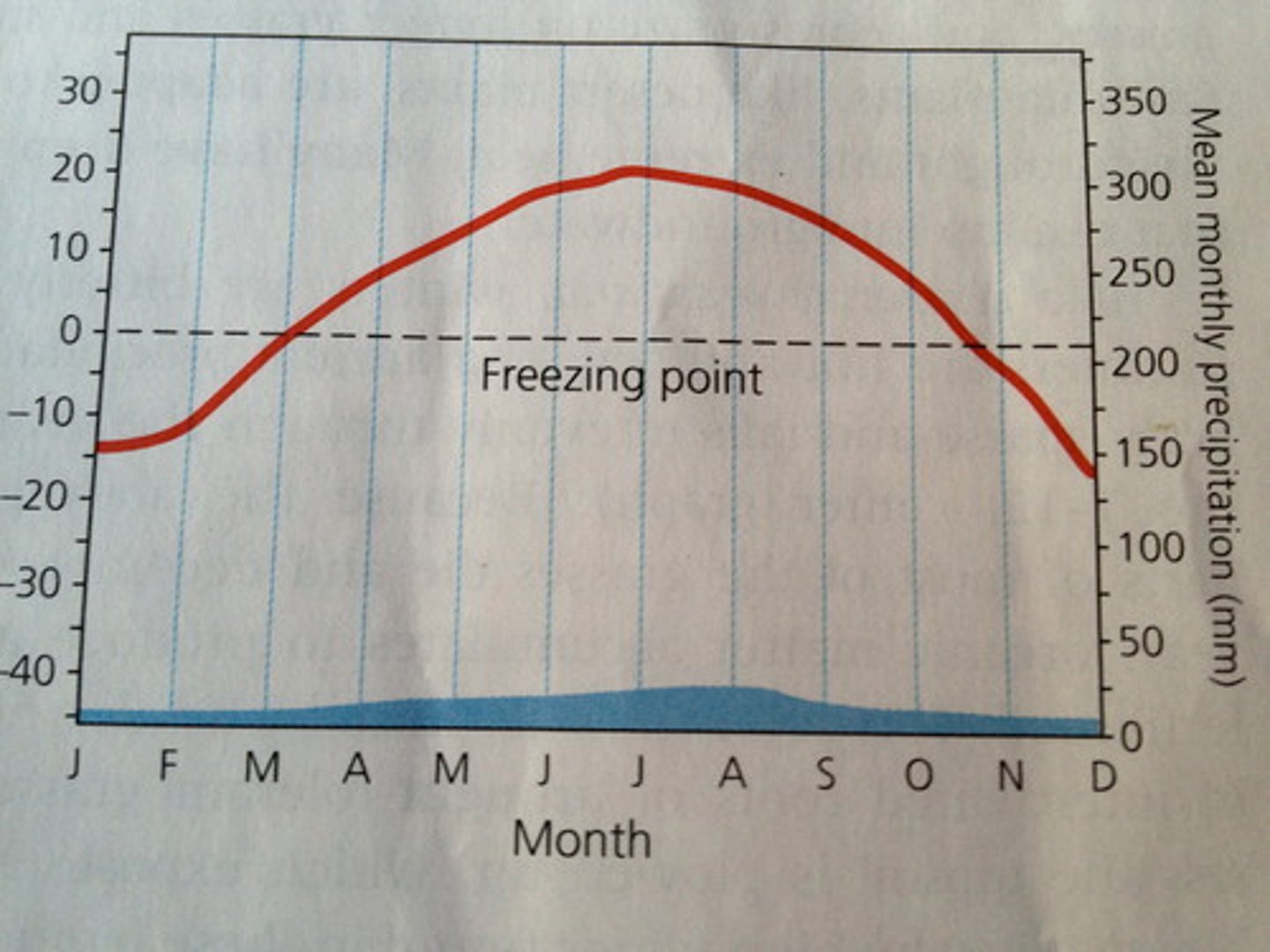
cold desert
A type of desert where vegetation is sparse, winters are cold. summers are warm or hot, and precipitation is low. ex= Gobi desert
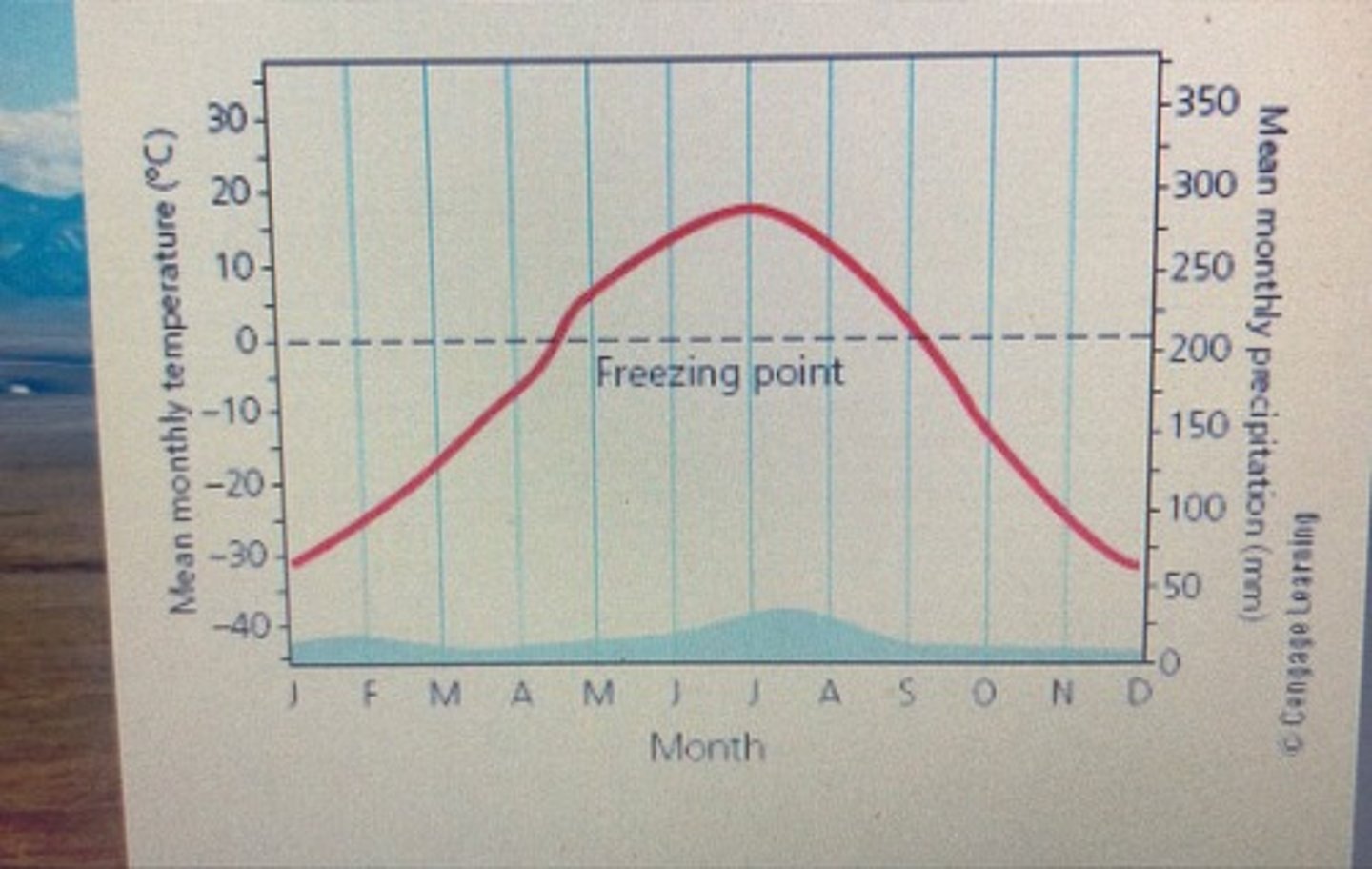
cold grassland/ tundra
bitter cold, windy, covered in snow and ice, little precipitation most as snow, winters have little light treeless, thick spongy mat of plants under the snow, has permafrost (permanently frozen soil below the surface)
taiga biome/ boreal forest
coniferous forests that have long, cold winters. the trees have needles instead of broad leaves. located in Canada and Russia
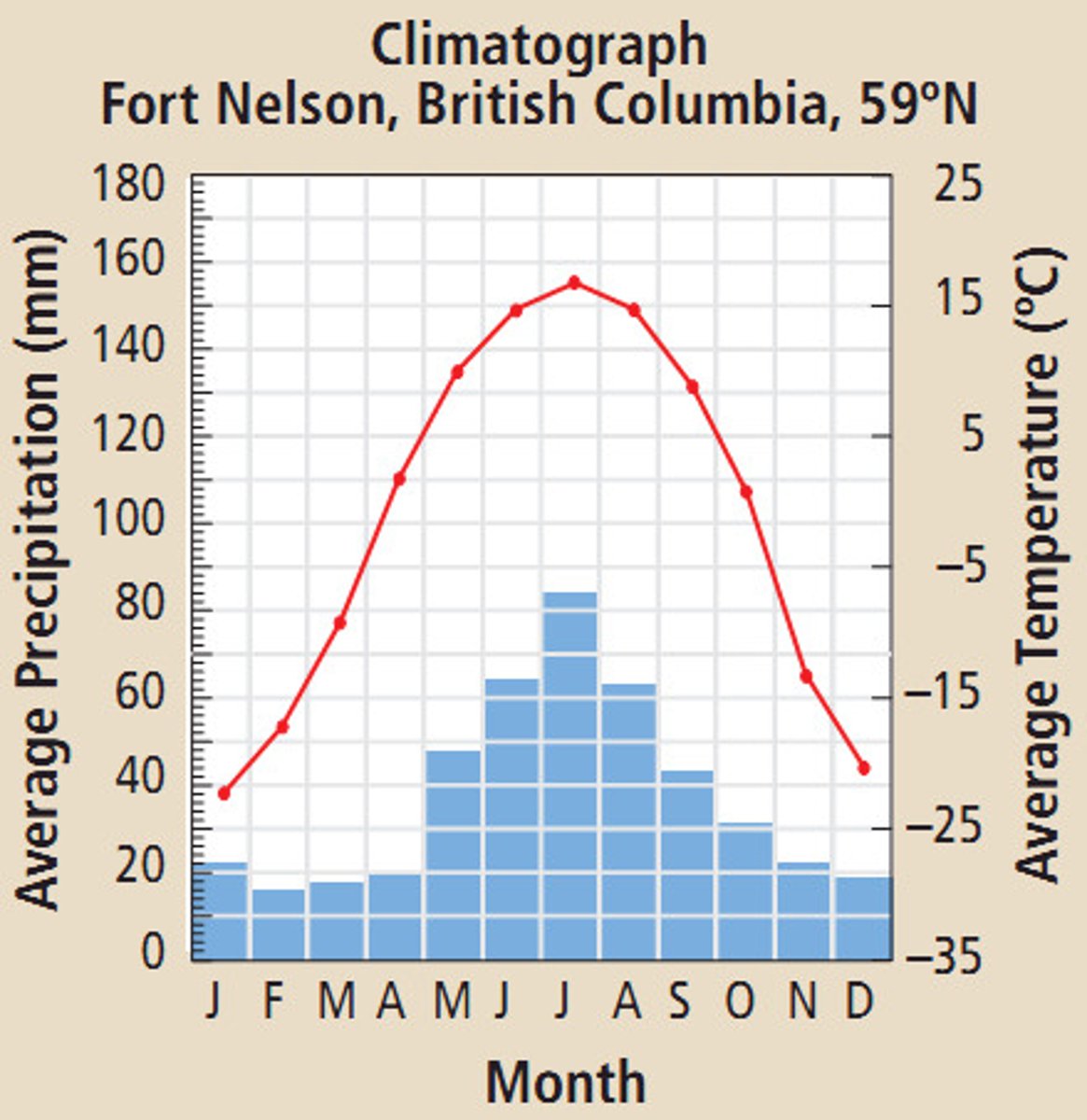
chaparral biome
areas that have hot and dry summers, mild winters. located on most continents with flat plains, rocky hills and mountain slopes includes California
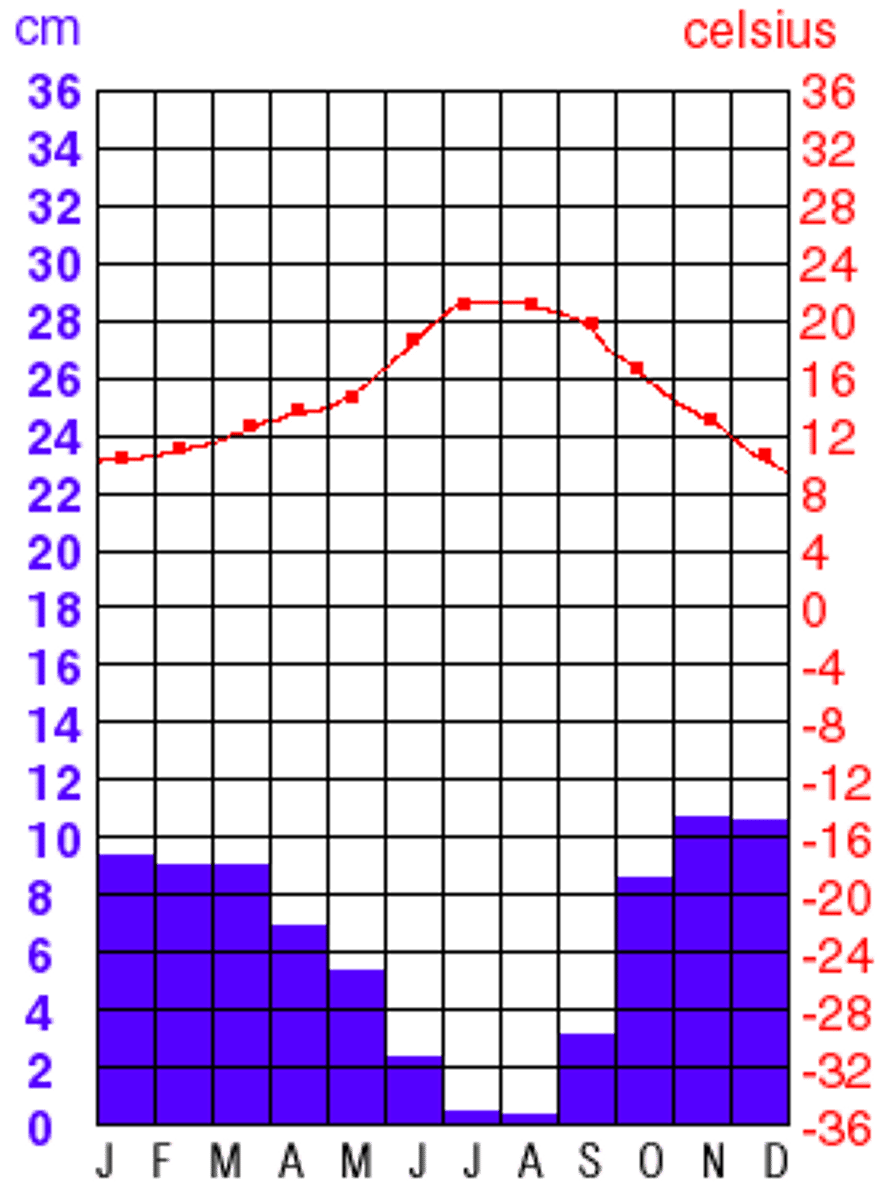
alpine biome
biome at high mountain altitudes, which has vegetation & climate similar to those of the Arctic tundra
(though no permafrost)
mutualism
a +/+ relationship where both species benefit
commensalism
a +/0 relationship where one species benefits while the other is unaffected
parasitism
a +/- relationship where one species benefits while the other is harmed.
resource partitioning
The division of environmental resources by coexisting species such that the niche of each species differs by one or more significant factors from the niches of all coexisting species
temporal partitioning
Two species reduce competition by utilizing a resource a different times
morphological partitioning
using different resources based on different evolved body features such as different beak shapes
spatial partitioning
using different areas of a shared habitat
predator prey
When one organism feeds on another organism; offset increasing and decreasing populations in response to one another