Chapter 17 Inflation, Unemployment, and Federal Reserve Policy
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Macro Economic
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
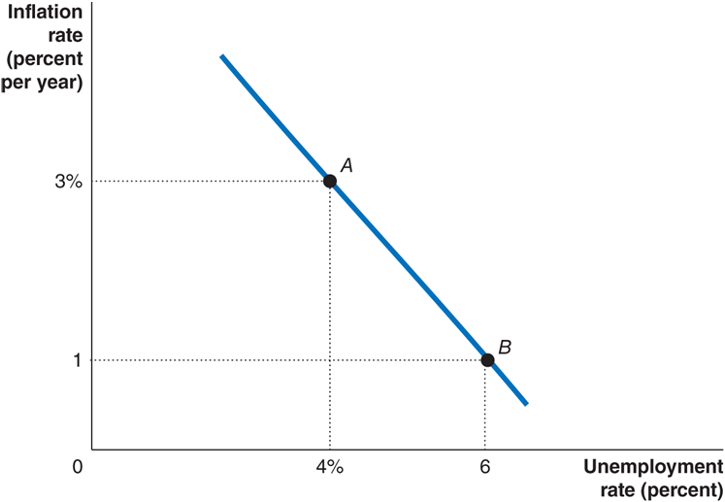
Philips Curve
A graph showing the short-run relationship between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate
structural relationship
a relationship that depends on the basic behavior of consumers and firms and that remains unchanged over long periods
Long-run aggregate supply curve
was vertical in the late 1960s and so the long-run philips curve was also vertical
real wage
= nominal wage/ price level
non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment
the level of unemployment at which inflation does not accelerate, often referred to as the "natural rate of unemployment."
Demographic changes
Younger and less skilled workers have higher unemployment rates
Changes in labor market institutions
a change in the availability of unemployment insurance, the prevalence of unions, or legal barriers to firing workers
Past high rates of unemployment
During long periods of unemployment, workers’s skills may deteriorate or they may become dependent on the government for support
Low inflation
slow adjustment since workers and firms seem to ignore inflation
Moderate but stable inflation
Quick adjustment stable but noticeable inflation is easily incorporated into expectations
High and unstable inflation:
quick adjustment again, but for a different reason: forming rational expectations about inflation becomes very important, so workers and firms pay a lot of attention to forecasting inflation.
rational expectations
expectations formed by usin all available information about an economic variable
deemphasizing the money supply
During Greenspan’s term, the Fed continued to move away from using the money supply as a target. the relationship between the money supply and inflation appeared to have broken down
Emphasizing Fred Credibility
The Fed learned to follow through on policy actions that it had announced. Markets and market participants must believe the Fed for monetary policy to be effective
too-big-to fial policy
a policy under which the fed gov doesn’t allow large financial firms to fail for fear of damaging the financial system. This policy aims to prevent systemic risk by providing support to major financial institutions during crises to stabilize the economy.