Lesson 1 - Foundations of the Web
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Internet
the physical network - the hardware, wires, and “pipes”.
World Wide Web (WWW)
Invented by Tim Berners Lee. It is the system of web pages and media we see on the internet.
Packets
Your data is broken down into tiny “envelopes” called packets.
Routing
These packets travel through different paths (cables under LA streets) to reach their destination.
Reassembly
Once they arrive at your computer, they are put back together to show you the website.
Fiber-Optic Cables
Under major streets like Vermont Ave and Heliotrope drive, glass cables carry data using pulses of light.
Data Center
Large, high-security buildings in Downtown LA (like One Wilshire) act as the “intersections” where different internet companies connect.
Community Hubs & LAPL
act as your local entry points to this global system.
Hardware
The physical parts (computers, cables, routers)
Software
The programs that run on the hardware (web browsers like Chrome or Edge).
Infrastructure
The underlying systems of cables and centers that make communication possible.
Authentication
Verifying the identity of the person or device attempting to access the system

Blog
A Web log, which is a journal or newsletter that is updated frequently and published online.
Browser
A program that allows the user to find and view pages on the world wide web.

Cloud Computing
The practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.

Download
To transfer a file from the Internet or other computer to your own computer

E-Commerce
Electronic business or exchange conducted over the internet

Messages distributed by electronic means from one computer user to one or more recipients via a network.

Email Filter
A tool that automatically sorts your incoming email messages based on specific criteria

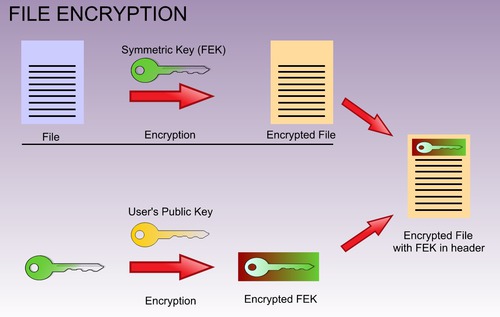
Encryption
A process of encoding messages to keep them secret, so only "authorized" parties can read it.
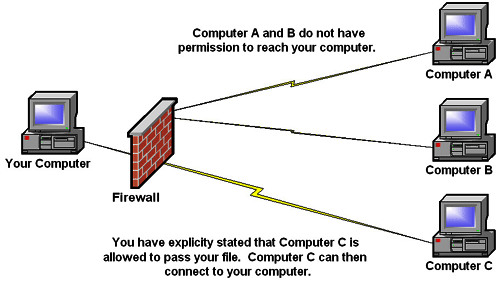
Firewall
A part of a computer system or network that is designed to block unauthorized access while permitting outward communication.
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language, a standardized system for tagging text files to achieve font, color, graphic, and hyperlink effects on World Wide Web pages.

HTTP
HyperText Transfer Protocol - the protocol used for transmitting web pages over the Internet

HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Encrypts HTTP traffic with SSL or TLS using port 443.

IP Address
A number that uniquely identifies each computer or device connected to the Internet.
ISP
(Internet Service Provider) A company that provides access to the Internet.

Malware
Software that is intended to damage or disable computers and computer systems.
Phishing
An attack that sends an email or displays a Web announcement that falsely claims to be from a legitimate enterprise in an attempt to trick the user into surrendering private information.
Router
A device that transfers data from one network to another in an intelligent way.

Social Media
Websites and applications that enable users to create and share content or to participate in social networking.

Spam
Unwanted e-mail (usually of a commercial nature sent out in bulk).

Trojan
A program disguised as a harmless application that actually produces harmful results.
URL
A location or address identifying where documents can be found on the Internet; a Web address.
Web Page
A document which can display text, graphics, audio, video and other elements through a web browser.

XML
Extensible Markup Language, a way of writing data in a tree-structured form by enclosing it in tags.
