Complete Denture Procedures, Anatomy, and Impression Material
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture given on 8/20/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what are the key landmarks to capture in preliminary impressions on the maxilla?
hamular notches, posterior palatal seal area, vestibular depth
what are the key landmarks to capture in preliminary impressions on the mandible?
retromolar pad, retromylohyoid fossa (lingual pouch), vestibular depth
the most critical goal of a preliminary impression is to…
capture the posterior extension of the denture bearing area because this determines the stability, retention, and support of the final denture
what is the mucous membrane composed of?
mucosa and submucosa
what is the mucosa formed by?
stratified squamous epithelium (often keratinized) and a layer of connective tissue (lamina propria)
what does the submucosa contain?
glandular cells, fat cells, muscle cells, and transmits the blood and nerve supply
what are the 2 areas of a surface impression?
stress-bearing (supporting) area
peripheral (limiting) area
what are the goals of an impression?
create good support for the denture, create retention, create stability, achieve optimal esthetic result
support (denture definition)
the resistance to vertical (occlusal) forces that try to push the denture toward the tissue
aka how well the denture base and underlying tissues stop the denture from sinking into the mucosa
what are the key features of support on a denture?
coverage of broad denture-bearing areas (maxillary palate, mandibular buccal shelf, retromolar pad)
firm, keratinized attached mucosa
proper adaptation of the denture base to the tissues
*what are the primary support / stress bearing areas on a maxillary denture?
posterior ridge crest, palatal surface
*what are the secondary support areas on a maxillary denture?
palatal rugae, anterior ridge crest
*what are the primary support / stress bearing areas on a mandibular denture?
buccal shelf, posterior crest, retromolar pad
*what is the secondary support area on a mandibular denture?
anterior crest
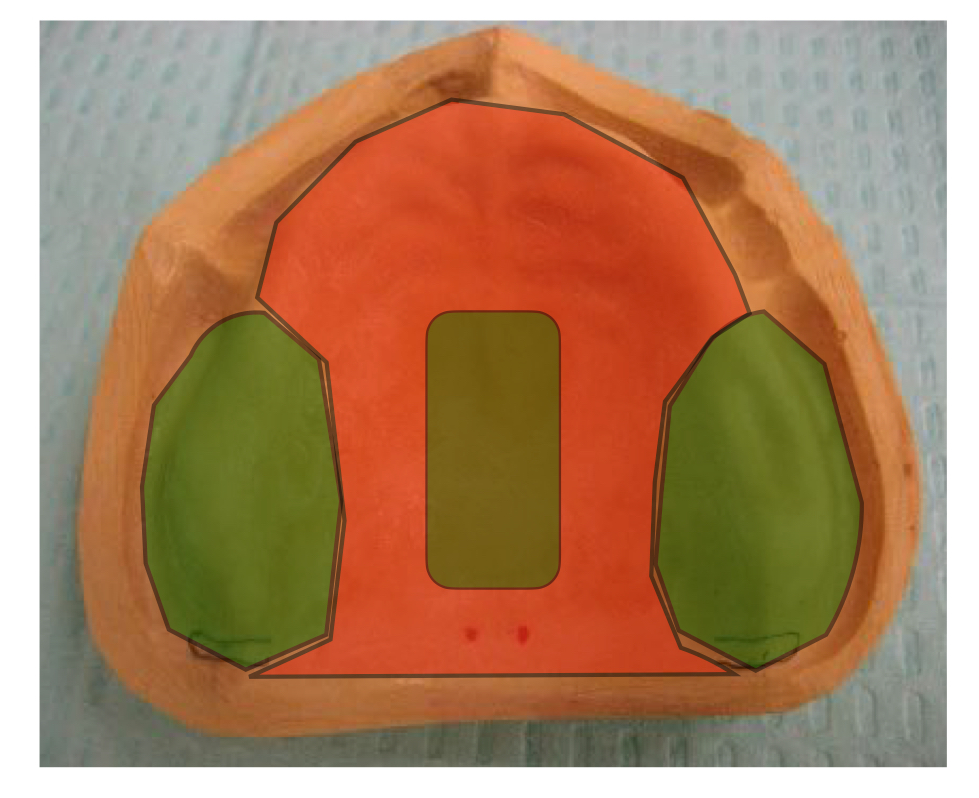

what areas are shaded in green?
primary support areas
posterior ridge crest, palatal surface
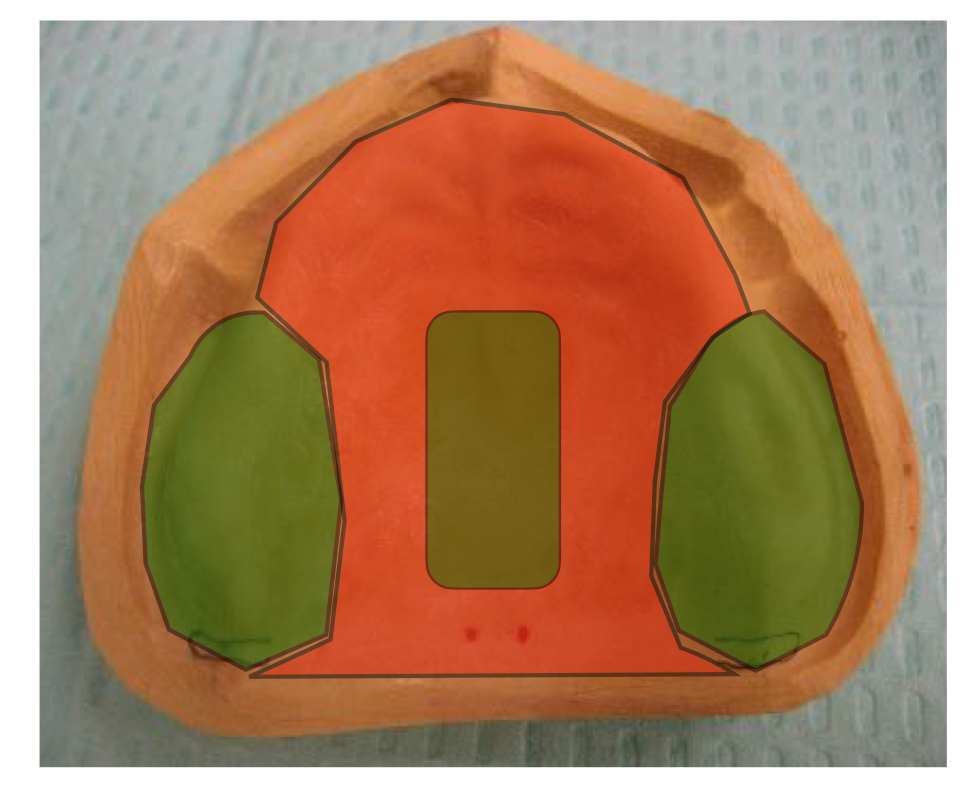

what areas are shaded in orange?
secondary support areas
palatal rugae and anterior ridge crest
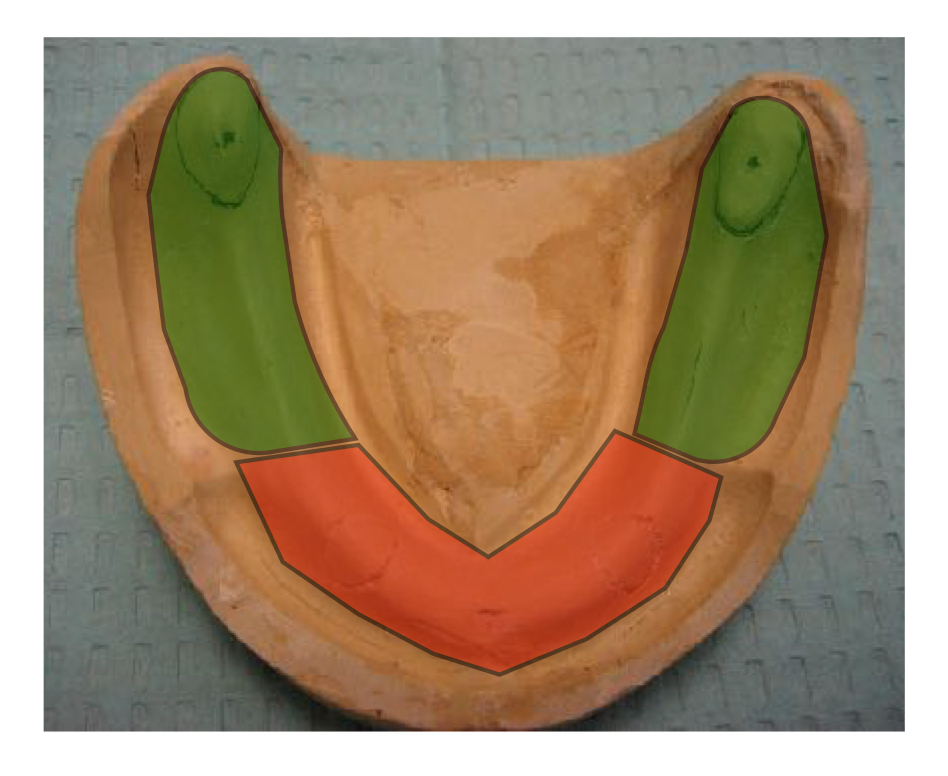
what area is shaded in orange?
secondary support area
anterior crest
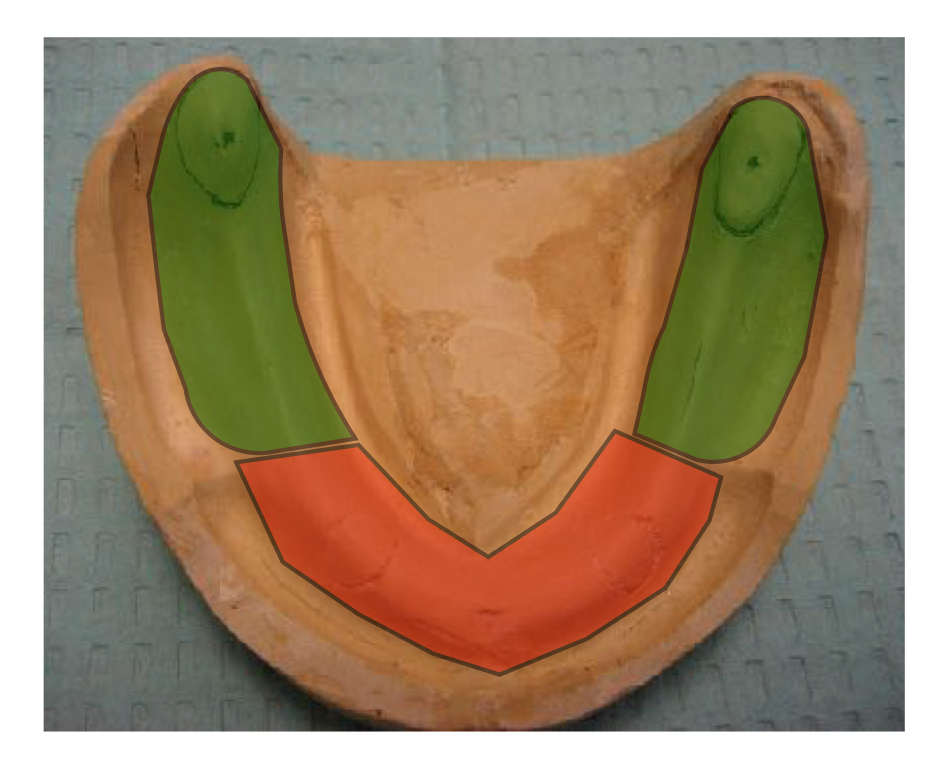
what areas are shaded in green?
primary support areas
buccal shelf, posterior crest, retromolar pad
retention (denture definition)
the resistance to vertical forces that try to dislodge the denture away from the tissue
aka how well the denture stays seated when you try to pull it out
what are the key features of retention on a denture?
proper border seal, adhesion/cohesion and surface tension of saliva between the denture base and mucosa, palatal seal (maxillary) and accurate impression technique
stability (denture definition)
the resistance to horizontal (lateral or rotational) forces
aka how well the denture resists tipping or rocking side to side or back to front
what are the key features of stability in a denture?
balanced occlusion (even contact across arch), proper ridge height and form, correct extension into the vestibular area for bracing, proper tooth arrangement, and polished surfaces that guide functional movements
what are the 2 broad categories of impression materials?
rigid and flexible
what are the 3 types of impression material that fall into the rigid category?
dental compound, impression plaster, zinc oxide eugenol
what are the 2 categories that fall within the flexible impression material category?
aqueous elastomers and non-aqueous elastomers
what are the impression materials that fall within the aqueous elastomers category?
alginate (irreversible hydrocolloid) and agar (reversible hydrocolloid)
what are the impression materials that fall within the non-aqueous elastomers category?
polysulfide rubber, polyether rubber, condensation silicone, addition silicone
dental compound impression material
thermoplastic impression material that softens when heated and hardens when cooled, has a type I and type II
what is type I dental compound used for?
making preliminary impressions on edentulous patients
what are the properties of type I dental compound?
softer (suitable for recording mucostatic impressions without much pressure), good for taking impressions in stock trays, rigid after cooling (not ideal for undercuts), comes in sheets
what is type II dental compound used for?
border molding of custom trays
what is type II dental compound known as?
greenstick
what are the properties of type II dental compound?
stiffer at mouth temperature (records functional movements at borders), ideal for shaping the periphery of trays to achieve good border seal
what is irreversible hydrocolloid used for?
preliminary impressions (it is alginate)
what are the pros of irreversible hydrocolloid (alginate)?
hydrophilic (can capture detail even in the presence of saliva), easy to mix and manipulate, inexpensive
what is a con of irreversible hydrocolloid (alginate)?
low dimensional stability (must be poured immediately to avoid distortion from syneresis or imbibition)
syneresis
losing water
imbibition
absorbing water
what is the main use of elastomeric impression material (addition vinyl silicone)?
final impression material
what are the properties of addition silicone (VPS/PVS)?
excellent dimensional stability (minimal shrinkage, can be poured multiple times, impressions can be stored before pouring), high accuracy (records fine details, suitable for crowns/bridges/implants/RPD framworks), elastic and strong (resists tearing when removed from undercuts), hydrophobic, dimensionally stable for up to 1 week