SDL 18: plasma cell neoplasms
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
plasma cell neoplasms (plasma cell dyscrasias)
clonal proliferations of immunoglobulin (Ig)- producing plasma cells or lymphocytes that make and secrete a single class of Ig or a polypeptide subunit that is detectable as a monoclonal protein (M-protein) on serum or urine protein electrophoresis
a destructive plasma cell tumor involving the axial skeleton
multiple myeloma presents as
presence of ≥10% plasma cells on bone marrow biopsies (normal: 0 - 3.5%)
most important diagnostic criterion off multiple myeloma
-mature: indistinguishable from normal cells, clock face
-immature
-pleomorphic
what are the 3 classes of myeloma cells?
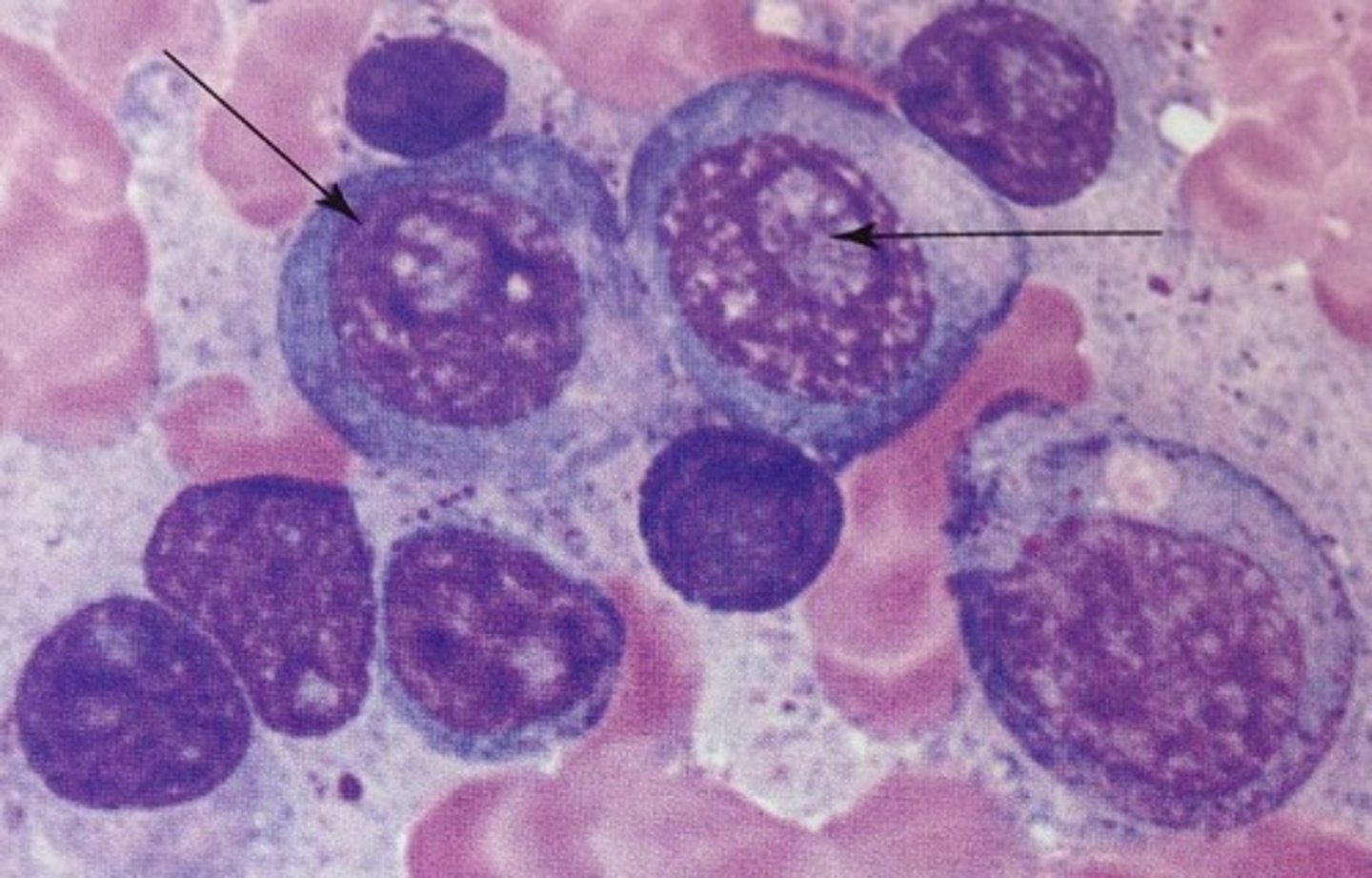
Dutcher body
an intranuclear globular inclusion that is highly specific to neoplastic myeloma cells, and there is little doubt regarding the neoplastic characteristics if observed.
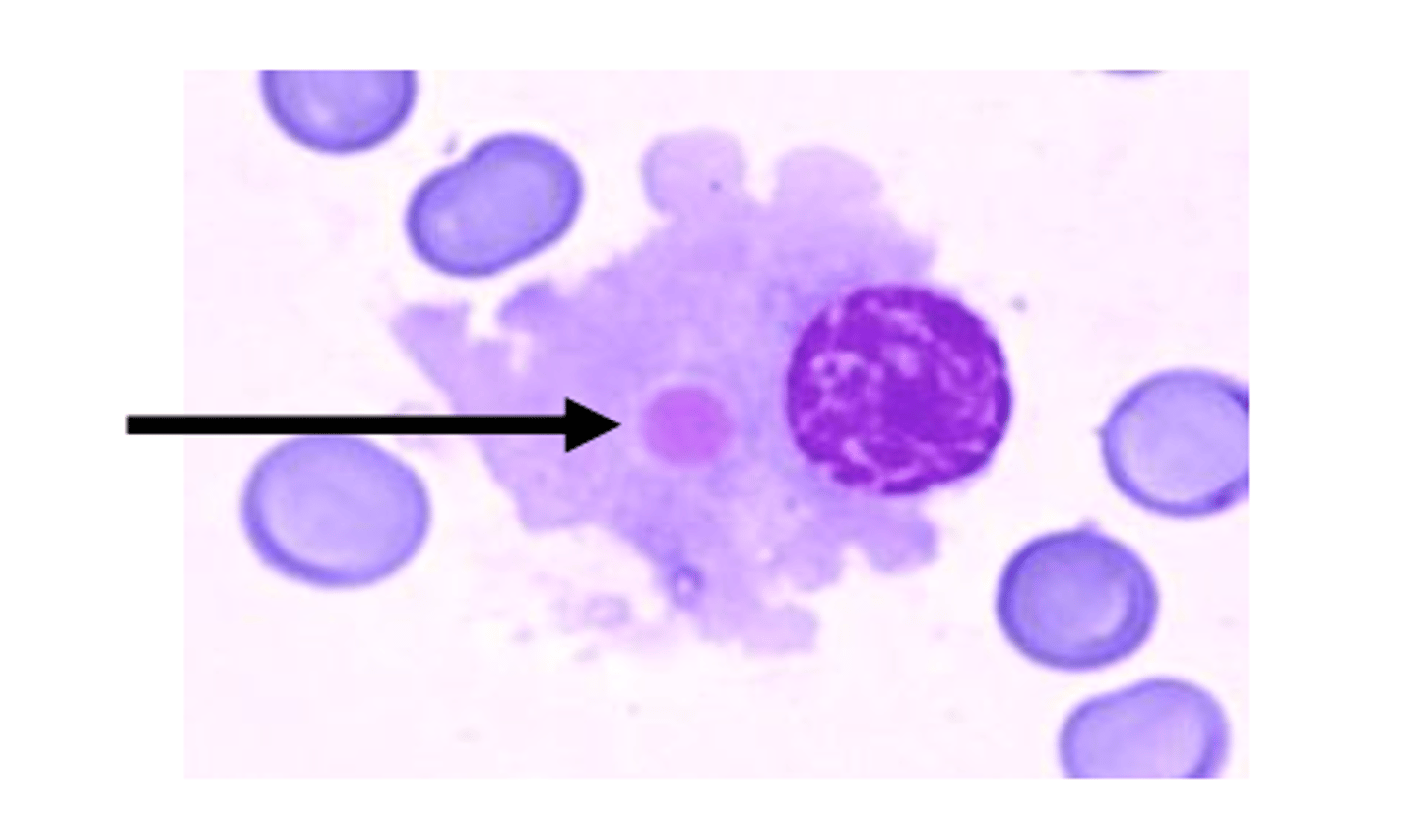
russel body
grapelike globular inclusion associated in a Mott cell
-associated with multiple myeloma
CD38 and CD138
-CD138 more specific for plasma cells
CD marker for both normal and myeloma plasma cells
CD56
70% of myeloma cells express this CD marker, which is negatively on normal plasma cells
(i) infiltration of plasma cells into the bone or other organs, (ii) kidney damage from the production of excessive immunoglobulins, which often have abnormal physicochemical properties, and (iii) suppression of normal humoral immunity
main clinical features of multiple myeloma
C (calcium elevated in plasma), R (renal failure), A (anemia), and B (bone pain).
CRAB acronym for multiple myeloma menas
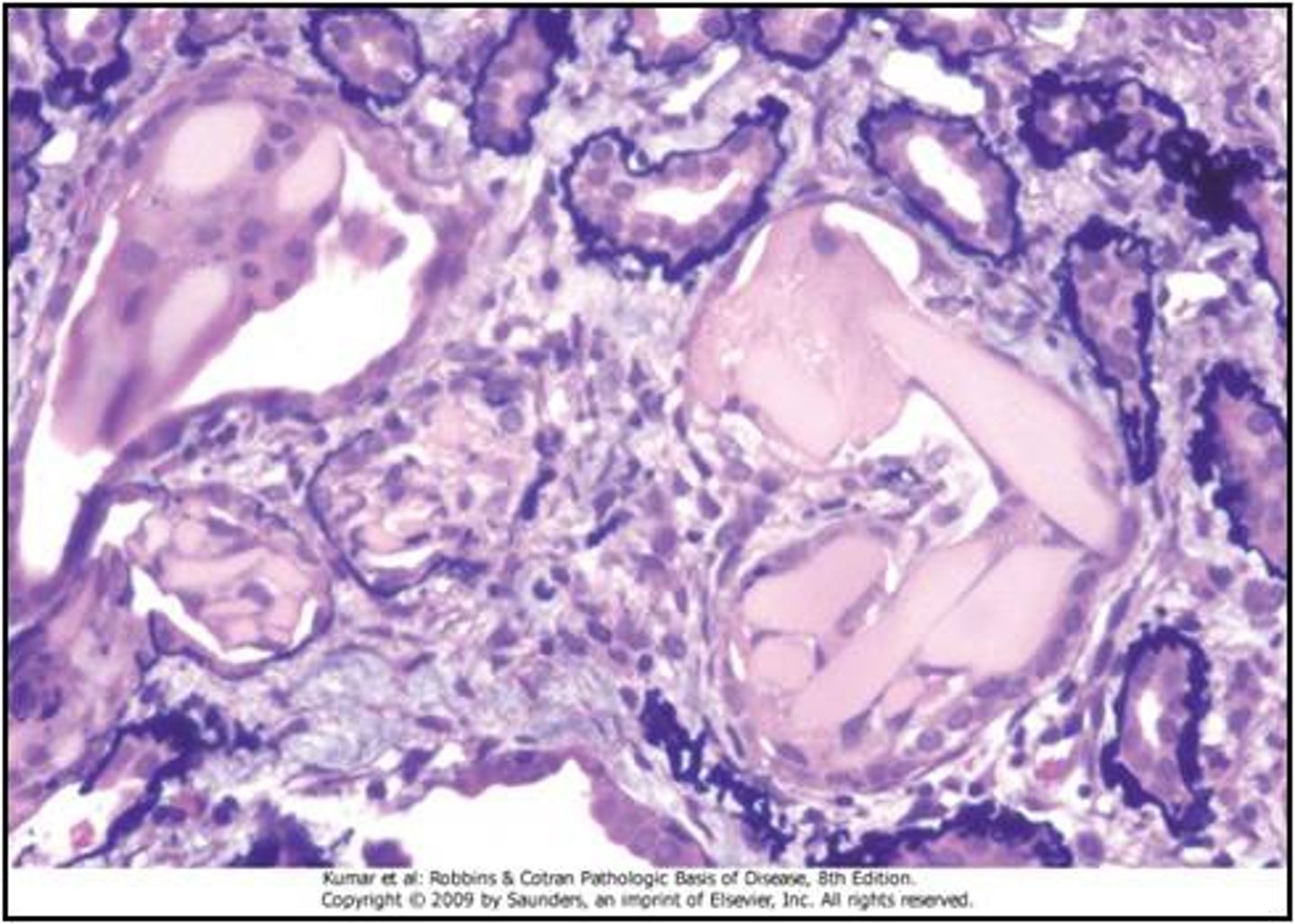
light chain cast nephropathy
most frequent form of renal damage inn multiple myeloma
normocytic and normochromic
type of anemia associated with multiple myeloma
spine
-results in neuro symptoms
______ is the bone site that is most frequently affected by myeloma induced bone osteolysis
Symptoms of hyperviscosity are much less frequent in myeloma than in Waldenström macroglobulinemia
is hyperviscosity common in multiple myeloma
3.2 centipoise
the reference range of whole blood viscosity at a physiologic hematocrit
Streptococcus pneumoniae and Gram-negative organisms
bacteria most frequently impacting pts with MM
-bleeding problems AND VTE
bleeding problems associated with multiple myeloma
10-15%
up to ____% of MM develop overt clinical AL amyloidosis
the myeloma cell mass
the amount of M protein reflects
-B2 microglobulin
-LDH
-elevated ESR
general lab findings associated with multiple myeloma
proteinuria
urine findings of MM
skeletal surveys
-reveal lytic lesions
-not as sensitive as PET
first image in assessment of MM
trisomies and translocations
the two main types of of cytogenic abnormalities in MM
mutations in KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, and TP53.
-effect the MAPK pathway
mutations associated with MM
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
Virtually all MM cases are preceded by a premalignant plasma cell proliferative disorder known as
cytogenetic abnormalities, which are the product of an abnormal plasma cell response to antigenic stimulation----> plasma cell producing monoclonal immunoglobulin
-classic two-hit genetic model of malignancy
MGUS develops as the result of
-additional genetic abnormalities
-some pts go to more advanced pre-malignant stage of smoldering multiple myeloma
how does MGUS progress to MM
IL-6 and IGF-1
cytokines associated with the progression of MGUS to MM
smoldering multiple myeloma
a more advanced premalignant stage of plasma cell proliferation, in the spectrum between MGUS and symptomatic MM and is characterized by a much higher risk of progression to MM
IgH translocations involving the MYC oncogene, activating mutations of RAS gene, and deletions at 17p13
second 'hits' causing transformation of MGUS to SMM or MM
extramedullary myeloma
a clonal plasmacytic infiltrate at anatomic sites distant from the bone marrow in a patient with underlying MM
focal adhesion kinase (FAK)
enzyme that is critical in progression of MM to extramedullary myeloma
MGUS (monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance)
-the most common plasma cell dyscrasia
-characterized by excess serum M protein
MGUS (monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance)
patients are asymptomatic, the serum M protein level is <3 g/dL, and bone marrow biopsies reveal <10% monoclonal plasma cells
-absent CRAB
-imaging norrmal
The risk of progression to active myeloma is 1% per year
prognosis associated with MGUS
-one type arises from lymphoid cells
-one type arises from plasma cells
what are the two types of MGUS
smoldering multiple myeloma
presence of a serum monoclonal protein (IgG or IgA) of ≥3 g/dL and bone marrow plasma cells of >10% of all nucleated cells
bone, can be foundd in soft tissues
solitary plasmacytoma most frequently occurs in
-SP lacks CRAB features, bone lytic changes, and serum or urinary monoclonal protein
how is solitarry plasmacytoma distinct from MM?
plasma cell leukemia
a clinically aggressive variant of MM
-may present with CRAB features , or manifestations of other leukemias
total leukocyte count is elevated with >20% plasma cells on the differential count.
lab criteria to diagnose plasma cell leukemia
light chain deposition disease
caused by the deposition of monoclonal light chains in multiple organs
-DIFFERENT from AL amylodosis
hypertension, micro-hematuria and proteinuria (often in the nephrotic range)
typical presentation of light chain deposition disease
nodular glomerulosclerosis
granular deposits are present on glomerular basement membrane, mesangium and tubular basement membranes
kidney biopsy finding associated with LCDD
restrictive cardiomyopathy. Liver involvement is asymptomatic. Involvement of peripheral nerves is associated with pain, loss of sensation and muscle weakness.
non-kidney manifestations of light chain deposition disease
peripheral neuropathy (P), a monoclonal protein in plasma (M), and other paraneoplastic features, the most common of which include organomegaly (O), endocrinopathy (E), and skin changes (S).
define the features of POEMS syndrome
symmetric peripheral polyneuropathy ----> pt in wheelchair
this sign dominates the clinical picture of POEMS syndrome
lambda
type of light chain almost always seen with POEMS syndrome
hyperpigmentation, hemangiomas, and hypertrichosis.
major dermatologic findings associated with POEMS
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
a low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma composed of cells exhibiting a spectrum of B-cell differentiation ranging from small lymphocytes to plasmacytoid lymphocytes and plasma cells.
syndrome of Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM)
-LPL cells have capacity to synthesize and secrete high amounts of immunoglobulins
-associated with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
pancytopenia
most lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma pts present with
epistaxis, gingival and gastrointestinal bleeding or menorrhagia, visual disturbances because of retinal hemorrhages, headaches, vertigo, and dizziness
hyperviscouos symptoms associated with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
The hyperviscosity-related retinopathy features central retinal hemorrhages and blood vessel dilation
fundoscopic findings associated with lymphooplasmacytic lymphoma
Myelin Associated Glycoprotein (MAG)
most frequently reported antigen recognized by monoclonal IgM in lymphoplasmacytic lymphhoma
normocytic and normochromic
type of anemia associated with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
MYD88 gene
-dimerizes to form myddosome
gene mutation assciated with LPL
indolent, incurable disease with a median survival of 5 to 10 years
prognosis associated with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma