BIOMED 2.2
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
patholigist
person who studies diseases
Cytopathologist
examines cells under a microscope to look for signs of cancer
cytogeneticist
a scientist who studies chromosomes under the microscope
Music Therapist
a person who helps heal patients through the use of music
geneticist
a specialist in the field of genetics
genetic counselor
person trained to collect, analyze, and explain data about human inheritance patterns
differential diagnosis
a list of potential diagnoses compiled early in the assessment of the patient
solid mass tumors
Solid mass of tissue that forms when abnormal cells group together
Somatic Cells
Any cells that arent sex cells (Eggs and sperm)
Contain 46 chromosomes
Interphase G1
Cell grows and works. Cell is "diploid"
In chromatin form
Interphase Synthesis
Chromosomes in chromatin form replicate there DNA but still together
Interphase G2
Cell grows and works but organelles replicate
Prophase (mitosis)
chromatin condenses into chromosomes
centriole pairs separate, move toward opposite sides of the cell
Metaphase (mitosis)
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase (Mitosis)
sister chromatids separate
Telephase (Mitosis)
Cell begins to pinch off,new membrane from around cell
Cytokinesis
the cell itself divides, resulting in two genetically identical cells.
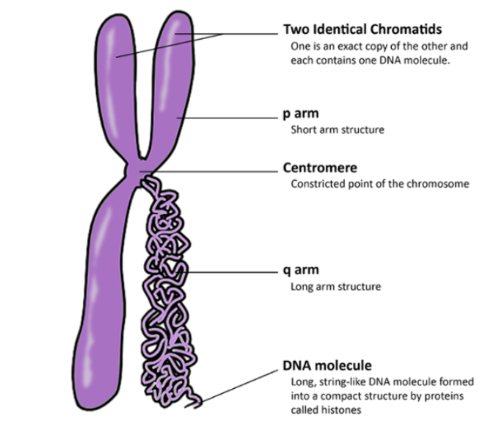
Chromatids
two identical chromosomes that split and contain the same genetic material
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
46 total and 23 pairs in human body
metastasis
The spread of cancer cells beyond their original site
basal cell carcinoma
type of skin cancer that originates in the basal cell layer of the epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin.
malignant tumor
cancerous tumors. These tumors are harmful and can invade other tissues or spread to other parts of the body if not treated.
benign tumor
considered harmless. They will not spread to other parts of the body or invade other tissues and are not cancerous.
Cancer Cells
Irregularly shaped, varrying size and shape, no specialized features and disorganized arrangement and boundaries
Neurofibromatosis type 1
Caused by mutation on Chromosome 17
Genetic Disorder
Health condition caused by changes to the sequence of DNA bases
Mutation
change to a DNA sequence
Protein Synthesis Transcription
happens in the nucleus
mRNA comes into Nucleus and to latch onto DNA which then mRNA gets edited and is sent to out to the ribosomes pr rough ER for translation
Protein Synthesis: Translation
occurs in nucleus and rough ER
If ribosome is free floating the cell will use energy but if ribsome is on rough ER cell will export energy out
During translation ribosome reads mRNA sequence and sends corresponsing tRNA connected to amino acid matches up mRNA to create a polypeptide
Where is the anti codon?
tRNA
Where is the codon?
mRNA
point mutation
a mutation affecting only one or very few nucleotides in a gene sequence.
Substitution, inversion
frameshift mutation
mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
Deletion and Insertion
Genotypes
Gene pair. A pair of letters
Phenotype
physical characteristics being expressed
Homozygous
Same alleles
Heterozygous
having two different alleles for a trait
dominant allele
Alleles that are expressed'
Usually UPPERCASE
Recessive allele
Alleles that are not expressed
Usually lowercase
Pedigrees
graphic organizer to track the frequency of a trait
autosomal dominant
One mutated allele is sufficient to cause symptoms in the individual
Autosomal Reccesive
Two mutated alleles are required for the individual to experience disease symptoms
homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes.
Familiar Cholesteral
autosomal dominant genetic condition. Causes LDL to be very high and makes atherosclerosis more likely
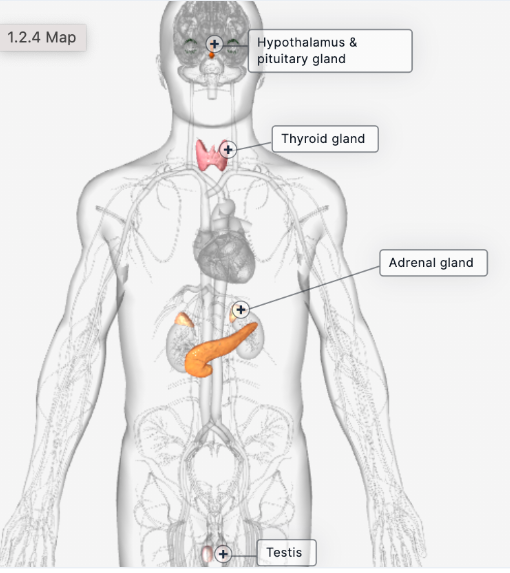
Endocrine System
network of glands that produce hormones regulating functions like growth, metabolism, and reproduction
Contains
Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
Pineal gland
Thyroid gland
Pancreas
Adrenal gland
Testis
Karyotype
organized profile of a person’s chromosomes
Karyotypes
help scientists quickly identify chromosomal alterations
Meiosis
Type of cell division that makes gametes
At the end of meiosis sperm and egg should contain 23 chromosomes
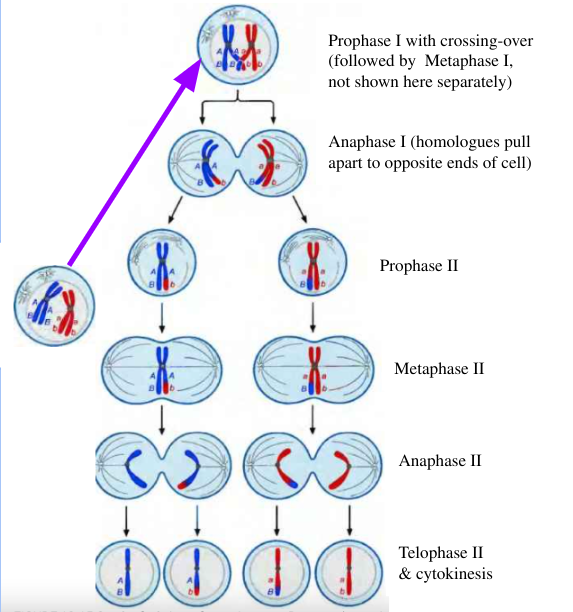
Diploid Cell
Haploid Cell
Glands
Organs that secrete chemicals
Independent Assortment
states that alleles of different genes segregate independently of each other during gamete formation
Hormones
Chemical signaling molecules
Help regulate growth and development, metabolism, reproduction, and sleep-wake cycles
Crossing Over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, leading to genetic variation in offspring.
Nondisjunction
When a member of a pair of chromosomes fail to separate in Meiosis I, or the sister chromatids don’t separate in Meiosis II
Monosomy
When there is only 1 chromosome instead of 2
Trisomy
When there are 3 chromosomes instead of 2
Chromosome Structure
Human Growth Hormone HGH
protein hormone made in the pituitary gland that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration. It is also responsible for increasing height during childhood and adolescence.
Insulin Like growth factor
protein hormone mainly secreted by the liver that stimulates HGH, helping children grow in height.
Direct to Consumer genetic test
Genetic tests that are marketed directly to consumers without the involvement of a healthcare provider.
Predisposition
individual's tendency or likelihood to develop a particular condition or behavior based on genetic, environmental, or other factors.
Genealogy
study of family history and lineage, tracing ancestors and descendants through generations to understand relationships and heritage.
Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
technique to amplify DNA
repeatedly heat and cool the sample amplification
Restriction Fragment Length polymorphism
A technique that analyzes DNA by cutting it with restriction enzymes, separating fragments by size
What shows no FH
ff (Codes for normal protein receptors on the liver cells grabs extra LDL changes into bile and put into intestine to excrete (Process that removes cholesterol)
FH homo
Severe FH
(FF)
All receptors mutated or missing
NO LDL into cells so stays in blood and tissue
NEED several meds to stop liver from making LDL, exercise and eat well (No fat)
FH heterozygous
Moderate form of FH
(Ff)
Some normal receptors some mutant receptors
Can only grab half the amount of LDL that a normal person can grab
Moderately high LDL and most likely need meds and good exercise and food habits
Is high cholesterol (High LDL) with (ff) caused by genes?
NO caused by what you eat and excercise habits
Usually med is not needed
What is added to the genes to make a pattern?
Restriction Enzyme
ff in gel
Goes along gel and no place to cut (Long strand)
FF in gel
Enzyme cuts ONCE (Cuts top off and seperates bottom)
2 small fragments 2 medium fragments
Ff in gel
1 long fragment, 1 medium fragment and 1 small fragment
Contains most bands
What is no sickle cell?
SS (Normal betaglobin in hemaglobin)
Hetero sickle
Ss half normal betaglobin, half mutant betaglobin
Sickle cell trait/carrier
Homo Sickle
ss ALL mutated beta-globin
Sickle cell disease
recessive
What does a colored shape on a pedigree mean?
recessive expressed trait
Can a pedigree determine if a trait is dom or recessive
YES
What do you do when you need to transcribe a DNA strand
Use mRNA and use AUGC
What do you need to do to translate a DNA strand
use amino acid chart
What are the symptoms of sickle cell?
When your a doc do you explain test reuslts w anyone that isn’t the patient?
NO unless you get permission
Diff between meiois and mitosis and end result?
Meiosis: Cell division resulting in 4 genetically unique haploid cells. Mitosis: Cell division resulting in 2 genetically identical diploid cells