Motion Graphics | Prelims
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Film Titles
Since the 1950s, these have evolved as a form of experimental filmmaking in commercial motion pictures; the first images that viewers experience once the lights are dimmed
Network Branding
Television companies have become increasingly image conscious, investing large amounts of time assessing their audiences and spending huge sums of money on developing their on-screen look
Station IDs/Station identifications/strings/network IDs
These identify the station or network being aired
Show Openers
Like a magazine cover or the introductory credits to a movie, these set the stage for the upcoming program; they help promote the network’s identity and tone and can make the difference between captivating viewers or making them reach for the remote
Show Packages
A “video information system” containing an assortment of design elements that are used to promote a program
Interstitials
These are 30- to 60-second mini-programs that appear between movies or other events, each having a specific objective
Bumpers/bump
A brief presentation that transitions between a program and a commercial break; these are typically between 2-5 seconds in duration, and in most cases, the name or logo of the show is displayed and is accompanied by an announcement that states the title of the presentation
Lower thirds
These are combinations of graphics and text that appear on the bottom portion of the screen to identify the station, the presenter(s), and the content being aired; most commonly found in news production and sometimes documentaries
Mortises
These are full screen graphics that are used to frame live footage; sometimes used in combination with lower thirds
Lineup
A full screen graphic that informs viewers about a network’s upcoming program schedule by displaying the names of the shows, dates, and times
Upfront
A marketing piece that is designed to promote a network’s shows to advertisers
Tag
A succinct, 3-4 second presentation that occurs at the beginning or end of a spot, news opening, or commercial
Promotional campaigns
These are designed to make the public more aware of a product, brand, or service
Commercials
These are one of the most desired campaign vehicles and one of the most effective methods of generating brand recognition to facilitate product sales
Public Service Announcement (PSA)
A noncommercial spot that aims to raise public awareness about specific issues such as energy conservation, global warming, homelessness, and drunk driving
Music Videos
Cinematic traditions that have been carried over from film into music videos have been enhanced with the incorporation of special effects and animation
Digital technologies
These are playing a much greater role in shaping our visual, public landscape
Light Emitting Diodes
Meaning of LED
LED technology
Unlike traditional “flat” LCD or plasma displays, these can be customized to any size and aspect ratio, allowing many possible geometric configurations
Immersive Environments
These shape a sense of place by providing order, ambience, comfort, and insight to a physical or virtual space; they are a unique confluence of architecture, interior design, images, motion graphics, and sound
Color
Typography
Composition
Movement
These must also be considered in Immersive Environments to communicate information clearly, concisely, and consistently
Exhibit Design
Today, this field combines graphic design, interactive media, motion graphics, and product design
Art Installations
Similar to the manner in which title sequence sets the tone of a film, these serve to establish the theme of a much larger exhibit; motion graphics are becoming an increasing component of these events
Educational Installations
In recent years, motion graphics have played a significant role in these, creating inspirational learning environment, disseminating news, and allowing visitors to select topics, upload information, and view streaming content
Retail Environments
In retail spaces, these can create genuine, emotional branding experiences by putting guests into new intuitive and exotic worlds
Animated Exteriors
Today, motion graphics are playing a much greater role in shaping our architectural, urban landscape, due to the rapid advancement of LED technology that can accommodate large-scale architectural installations
Low-resolution
These video grid systems are becoming more popular and affordable solutions to large-scale installations and architectural projects
Digital Signage
These are one of the fastest growing marketing opportunities in the world today—ranging from sports scoreboards to giant video screens in large public spaces such as shopping malls; it is used to present many forms of content over high-speed networks to video displays in public venues
Dynamic digital signage
These are emerging as a new generation of sign technology in the advertising industry, typically composed of a server, a monitor, and software; it is capable of delivering dynamic visual content to multiple locations, meaning that advertisers can communicate a brand or message locally or around the world to employees and customers from a central location
Performance
Musical concerts, ceremonies, and awards shows have increasingly integrated motion graphics substantially over the past decade
Alternate Spaces
Motion graphics have become an increasing entity in virtual spaces that were made possible by computer technologies during the 1990s
Virtual Reality (VR)
This allowed viewers to enter into a dimension that was set apart from their immediate physical space—dissolving the boundary of the frame, allowing designers to break away from familiar compositional devices
Augmented Space/Augmented Reality
This is a physical space that is amplified with electronic and visual information (e.g. static images, typography, animation, and live-action content), holding the potential of motion graphics
Video wall systems
These can display very large images without compromising screen resolutions, thriving throughout the world in almost every arena, including trade shows, showrooms, nightclubs, retail stores, restaurants, and sports arenas
Interactive Environment
This is any technology-based interface that reacts and responds to user input; a broad term used to categorize forms of computer-based media that instructs, communicates, and entertains as a result of user action
Connection Speed
Bandwidth
Challenges that designers were forced to overcome over the Web (2)
Java
Animation Formats - This was introduced in the early 1990s by Sun Microsystems. This network-oriented programming language enabled Web developers to create applications called applets that users could download and apply to their Web pages
Animated GIF
Animation Formats - Among rapidly developing Web technologies, these continue to be one of the more popular low-tech options for adding motion to Web pages; built into a single file, sequential images are displayed in succession like a traditional frame-by-frame animation
Flash
Animation Formats - This was considered by the majority of graphic designers to be the most effective interactive animation tool for delivering vector-based content to Web pages
dHTML
Animation Formats - During the release of 4.0 browsers; this was another programming development that occurred; it allowed Netscape to display hierarchical layers and provided a sophisticated way of handling text
Hypertext Markup Language
Meaning of HTML
Video over the web
Animation Formats - These formats allow data to be delivered over the Web through downloading or streaming
QuickTime
Windows Media Player
RealPlayer
Predominant Web video formats
Basic download
A Web video format that involves copying the content from a server to a local computer and playing it from the local machine’s hard drive
Progressive download
A Web video format that places the most critical information at the beginning of the file structure
Animated Navigation Systems
Type of Motion Graphics in Interactive Media - This provides an infrastructure that supports and directs users in a meaningful, logical way through the complexities of a Web site. It considers the interface—the intermediary between users and content—as well as the message, client, users, and medium
Animated Transitions
Type of Motion Graphics in Interactive Media - The Internet is a virtual space that consists of complex levels of information; in a Web interface, these can be effective in moving users between various levels of detail while maintaining the original context of a site
Splash Page Animations
Type of Motion Graphics in Interactive Media - Similar to traditional book covers, their purpose is to set a mood, reinforce a brand, intrigue visitors, and entice them into entering the site to learn more
Banners
Type of Motion Graphics in Interactive Media - These are often a key element of Internet advertising campaigns. As marketing devices, their strategy is to establish a strong, professional Web presence and create a favorable and lasting impression on those who view its content.
Advertisements
Type of Motion Graphics in Interactive Media - These, like television commercials, are designed to make viewers captive to information that might be missed in a banner ad. They appear for approximately 5-10 seconds before the expected content page loads or may appear between a main page and its secondary pages
Splash Pages
These are introductory pages to a Web site that appear before the main content of the site loads
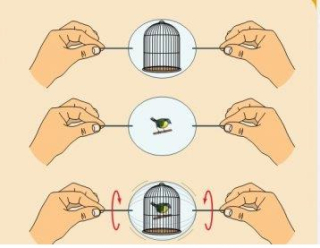
Thaumatrope
Pre-cinema - This is an optical toy that was popular in the 19th century; a disk with a picture on each side, attached to two pieces of string. When the strings are twirled quickly between the fingers the two pictures appear to blend into one
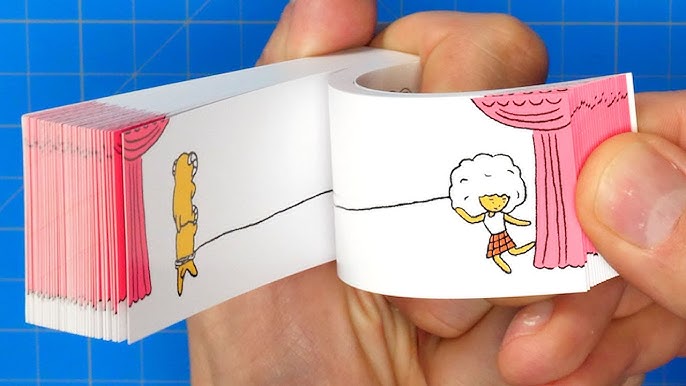
Flipbooks
Pre-cinema - These are simple yet effective devices that creates illusion of motion. They consist of a series of images that vary slightly from one page to the next. When the pages are flipped rapidly, the image appears to animate. This concept is based on the persistence of vision where the human eye retains an image for a fraction of a second after it has disappeared, allowing the brain to perceive a continuous motion
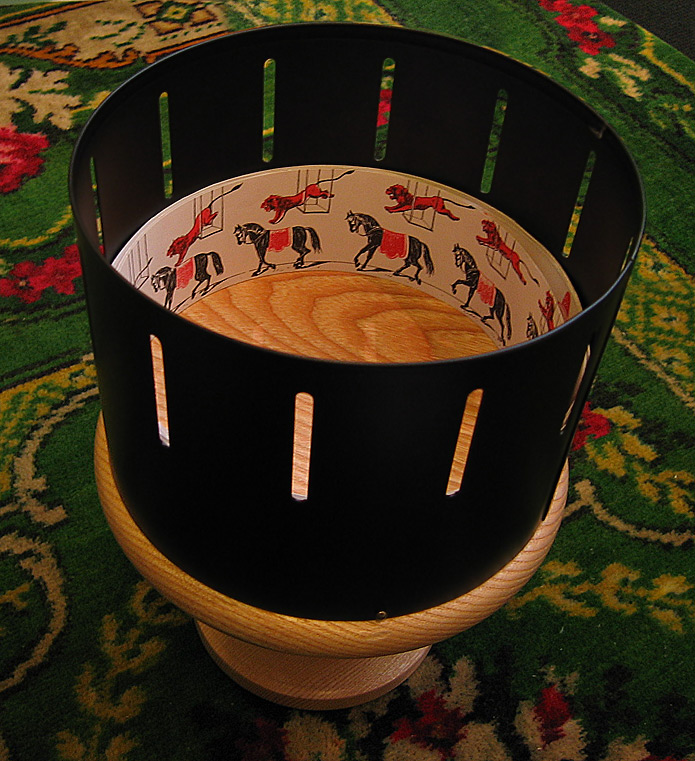

Zoetropes
Pre-cinema - Another early animation device. It consists of a cylindrical drum with vertical slits cut into the sides. Inside the drum, a strip of sequential images is placed. When the drum is spun, viewers look through the slits and see the images in rapid succession, creating the illusion of motion. It was invented in the 1830s and became a popular form of entertainment
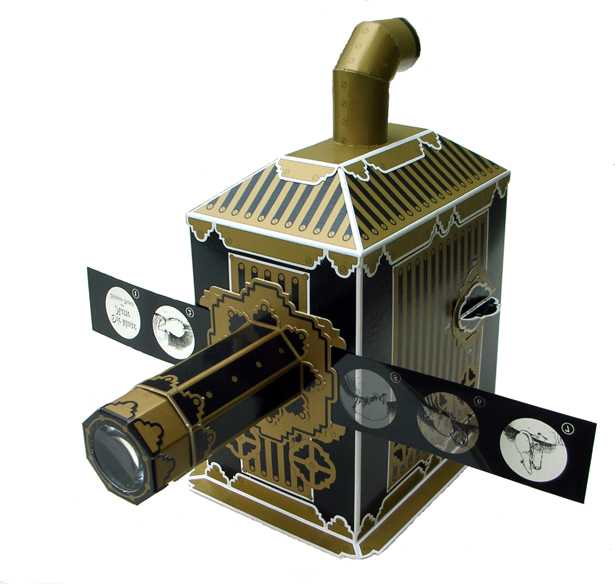

Magic Lanterns
Pre-cinema - These were early projectors that used light to project images from glass slides onto a wall or screen. These devices were used for entertainment and educational purposes, often featuring hand-painted slides that could tell a story or illustrate a concept
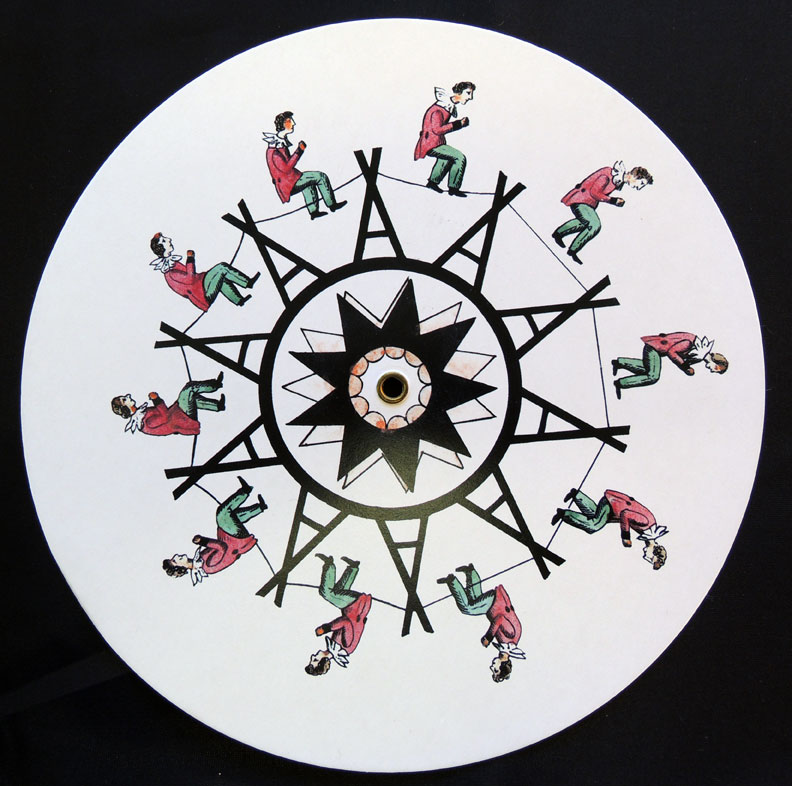

Phenakistoscopes
Pre-cinema - Similar to the zoetrope, this uses a spinning disc attached to a handle. The disc has a series of images arranged in a circle and slits around the edge. When the disc is spun and viewed in a mirror through the slits, the images appear to move.
Title Cards
Silent Film Era - These were also known as intertitles; essential in silent films to convey dialogue, narrative text, and other information. Since there was no synchronized sound, these cards provided context and helped the audience follow the plot
Stop Motion
Hand-drawn animation
Cutout Animation
Early Animation Techniques (3)
Stop Motion
Early Animation Techniques - This involved photographing objects or drawings frame by frame, slightly altering them between shots to create the illusion of movement.
Hand-drawn Animation
Early Animation Techniques - Pioneers like Winsor McCay created detailed animations by drawing each frame on paper
Cutout Animation
Early Animation Techniques - This technique used flat characters and backgrounds cut from paper or other materials. These cutouts were moved incrementally and photographed to produce animation

Oskar Fischinger
One of the famous pioneers of motion graphics—a German-American abstract animator, filmmaker, and painter, notable for creating abstract musical animation.
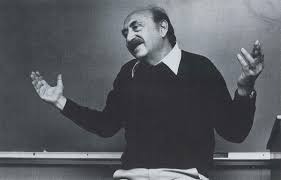
Saul Bass
One of the famous pioneers of motion graphics—an American graphic designer and Oscar-winning filmmaker, best known for his design of motion-picture title sequences.