NURS 201: Unit 2 - Primary Healthcare
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Primary Healthcare (PHC)
- The approach of the whole-of-society to health
- Aims at highest possible level of health and well-being
- Works towards an equitable distribution of health by focusing on people
s needs and preferences
- Works along the continuum of heath from health promotion all the way to palliative care
- Should be as close to people's everyday environment
Main Differentiating Characteristics of Primary Health Care
- Whole-of society approach
- Principle-based
- Comprehensive
- Improves the health of populations along a continuum
- Works across the lifespan
- Focuses on population, community, and individual level health strategies
- Acknowledges the broader conditions that influence health
- Values/principles are included into policy and implemented into programs and practice
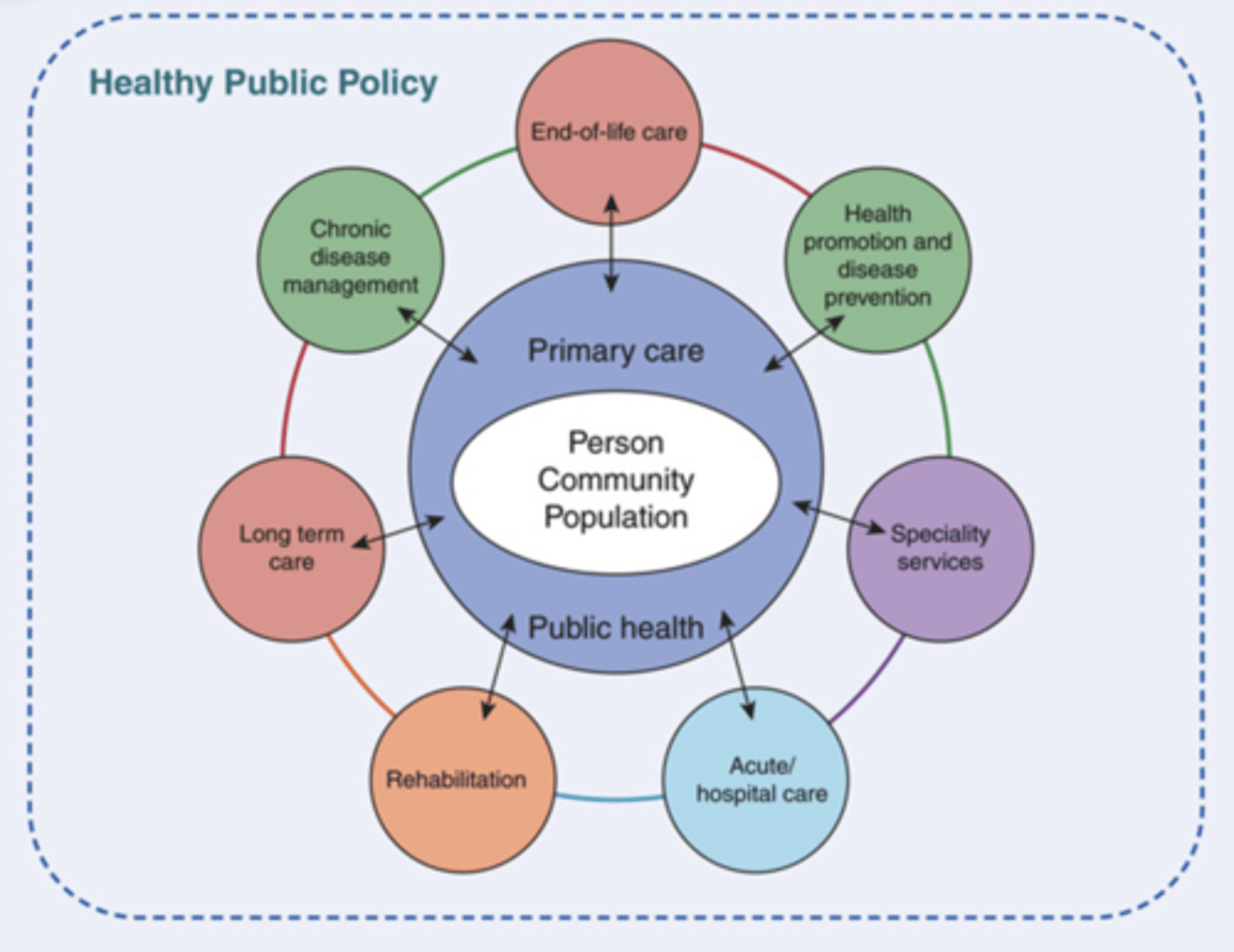
Main Differentiating Characteristics of Primary Care
- Focus is on personal health services
- Refers to the delivery of community-based clinical health services
- Provides coordinated care
- Enables equitable and timely access to other services and providers
- Focuses on preventing, diagnosing, treating, and managing conditions
- Also promotes health
1978-Alma Ata Declaration-I
A document that emphasized the importance of PHC of achieving health for all
PHC is both a . . .
Philosophy and an approach
3 multiple choice options
5 Principles of PHC
- Accessibility
- Active public participation
- Health promotion and chronic disease prevention and management
- Use of appropriate technology and innovation
- Intersectoral collaboration
2 Types of Accessibility
- Tangible
- Intangible
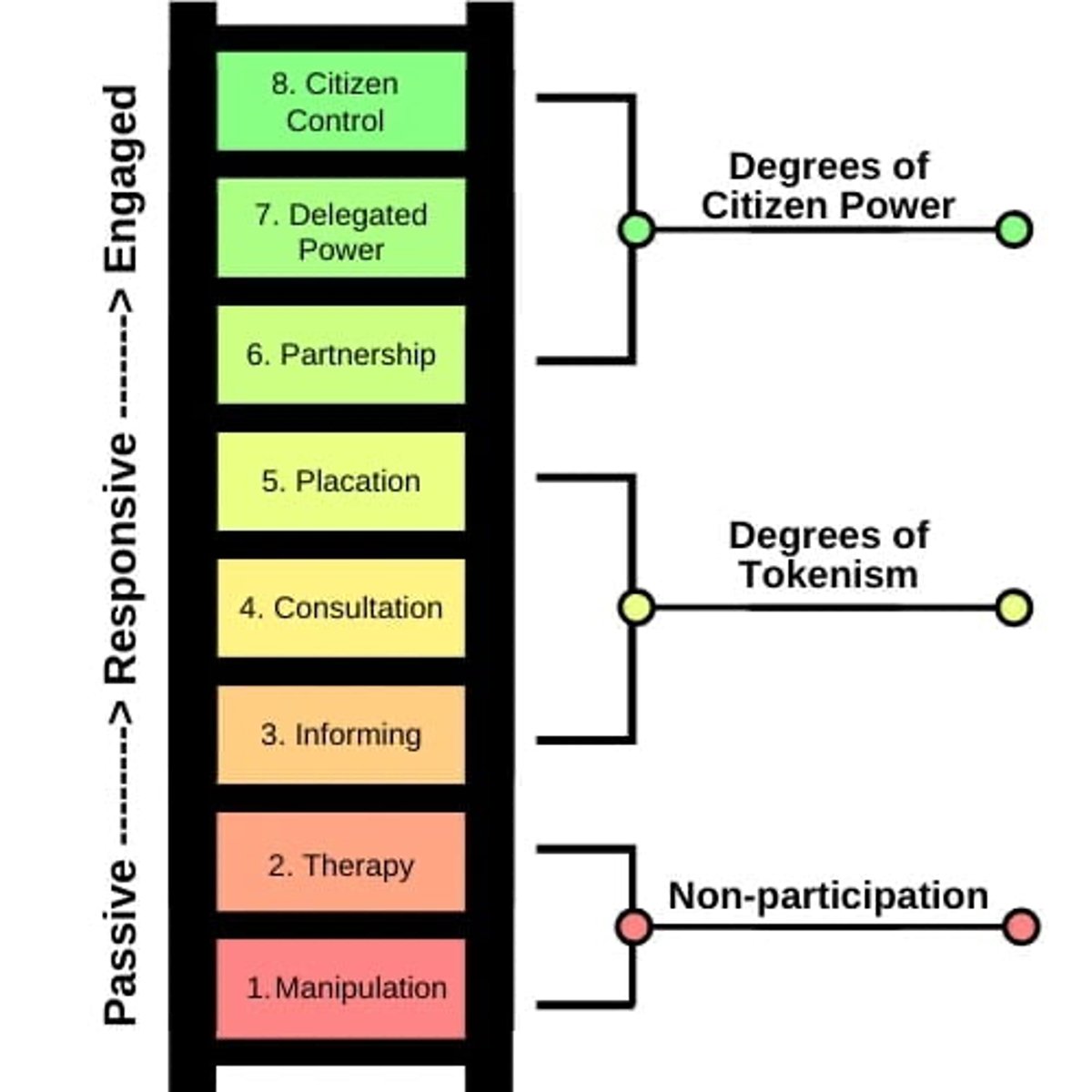
Arnstein's Ladder
Model illustrating levels of citizen participation
Main Goal of Health Promotion
To enable individuals, families, and communities to live healthier lives
3 multiple choice options
3 Approaches of PHC
- Primary care and essential public health
- Multi-sector policy and action
- Empowered people and communities
Characteristic of Quality Primary Care
- Evidence-informed
- Community-delivered
- Person-centered
- Provides first point of contact
- Continuous
- Comprehensive
- Coordinated
5 Main Population-Based Services
- Health protection
- Health promotion
- Disease prevention
- Surveillance and response
- Emergency preparedness
Health Protection
Risk assessment and supervision of enforcement and control of activities for minimizing exposure to health hazards in order to protect the population, by ensuring environmental, toxicological, road and food safety
Health Promotion
The process of enabling people to increase control over, and improve their health
Disease Prevention
Action that is taken to avoid or forestall illness/disease
Surveillance and Response
A combination of monitoring and prevention of diseases
Emergency Preparedness
An aim to address unforeseen and catastrophic circumstances that create a surge of demand for health services and strain resources and infrastructure (Ex. Covid)
4 Categories of Multisectoral Interventions for PHC
- Fiscal measures
- Laws and regulations
- Changes in the built environment
- Information, education, and communication campaigns
Health in All Policies (HiAP)
A whole-of-government approach to multisectoral policy and action at the national, subnational and regional levels
3 Expressions of Empowerment and Engagement for People through PHC
- Advocates
- Co-developers of health and social services
- Self-carers and givers
4 Pillars of PHC
- Teams
- Access
- Information
- Healthy living
Reasons for the Slow Progression of PHC in Canada
- Not the focus of the Canadian health system
- Many Canadians view the healthcare system as providing curative care
- Many Canadians value expensive technology and "quick fixes"
Reasons Why Canada Should Adopt a PHC Approach
- Continues calls for healthcare reforms
- Health indicators are below international comparisons
- An aging population
- Rising costs of hospital-based care
- Ensures health equity