AP Psych: unit 3 vocab
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
intensity
the amount of energy in a light/sound wave, determined by wave's amplitude (ex. brightness or loudness)
absolute threshold
minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time (ex. hearing tests w/ beeps)
accommodation
process when the eye's lens changes shape to focus on near/far objects on the retina, adapts to our schemas (understandings) to incorporate new information (ex. eye is accomidating to understand new information)
audition
sense or act of hearing (ex. audio)
binocular cues
depth cues (retinal disparity), that depend on the use of 2 eyes (ex. BI-nocular)
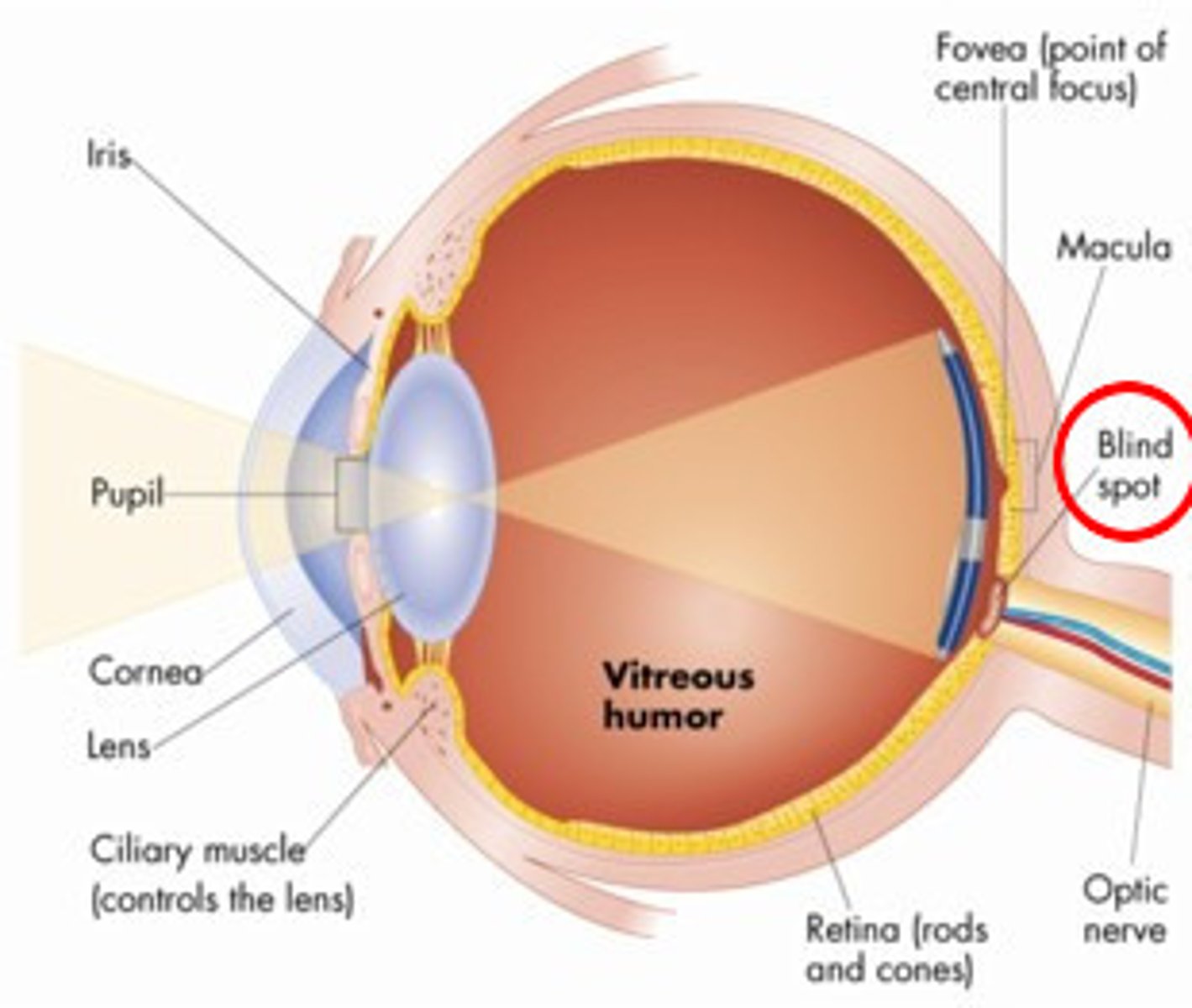
blind spot
point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, no receptor cells are there
bottom up processing
analysis that begins with the sensory receptors and works UP to the brains interrogation of sensory information (ex. if I flash a random picture on the screen, your eyes detect the features, your brain pieces it together, and you perceive a picture)
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment (ex. observers often fail to notice major differences introduced into an image while it flickers off and on again)
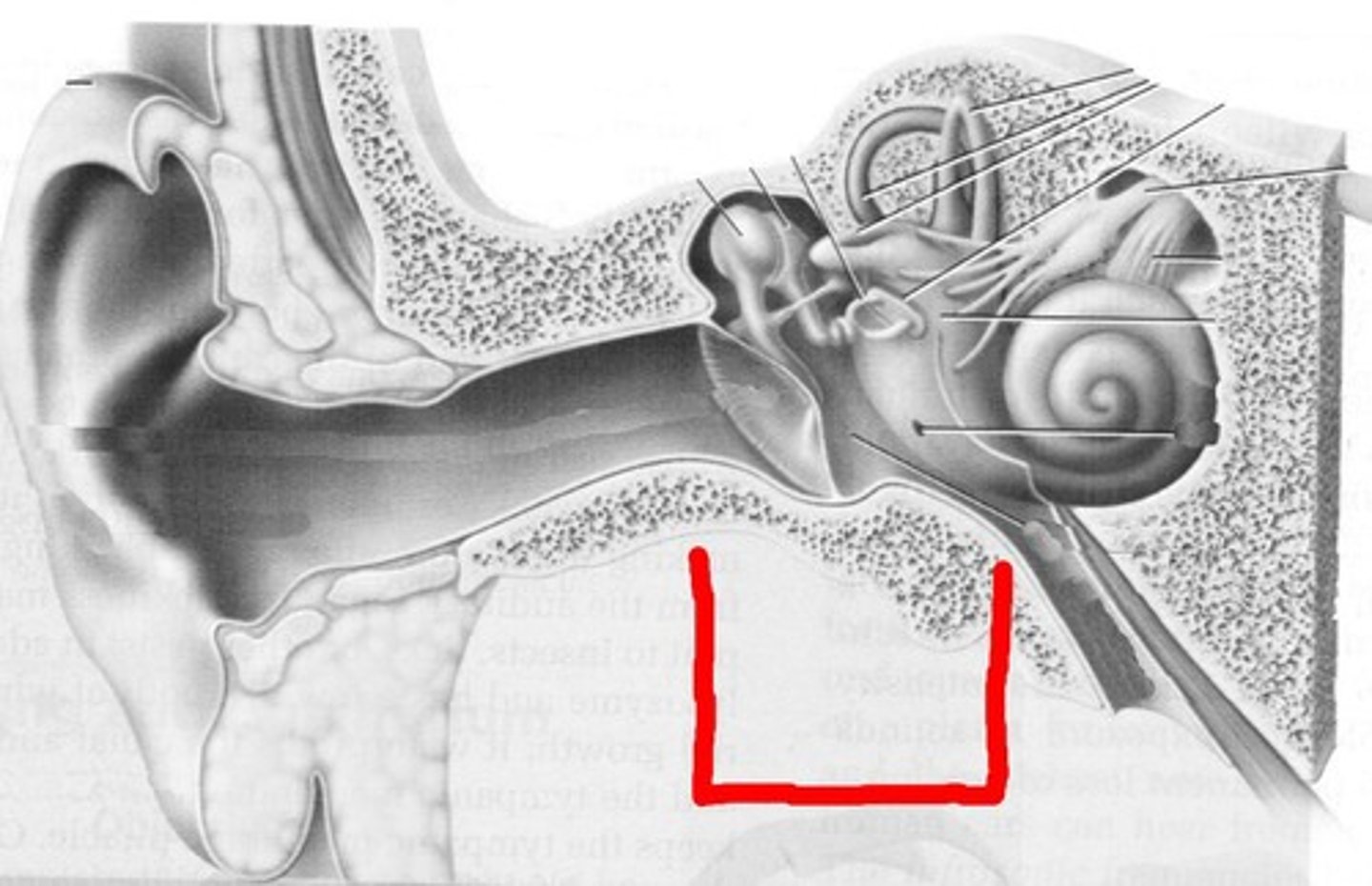
cochlea
coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
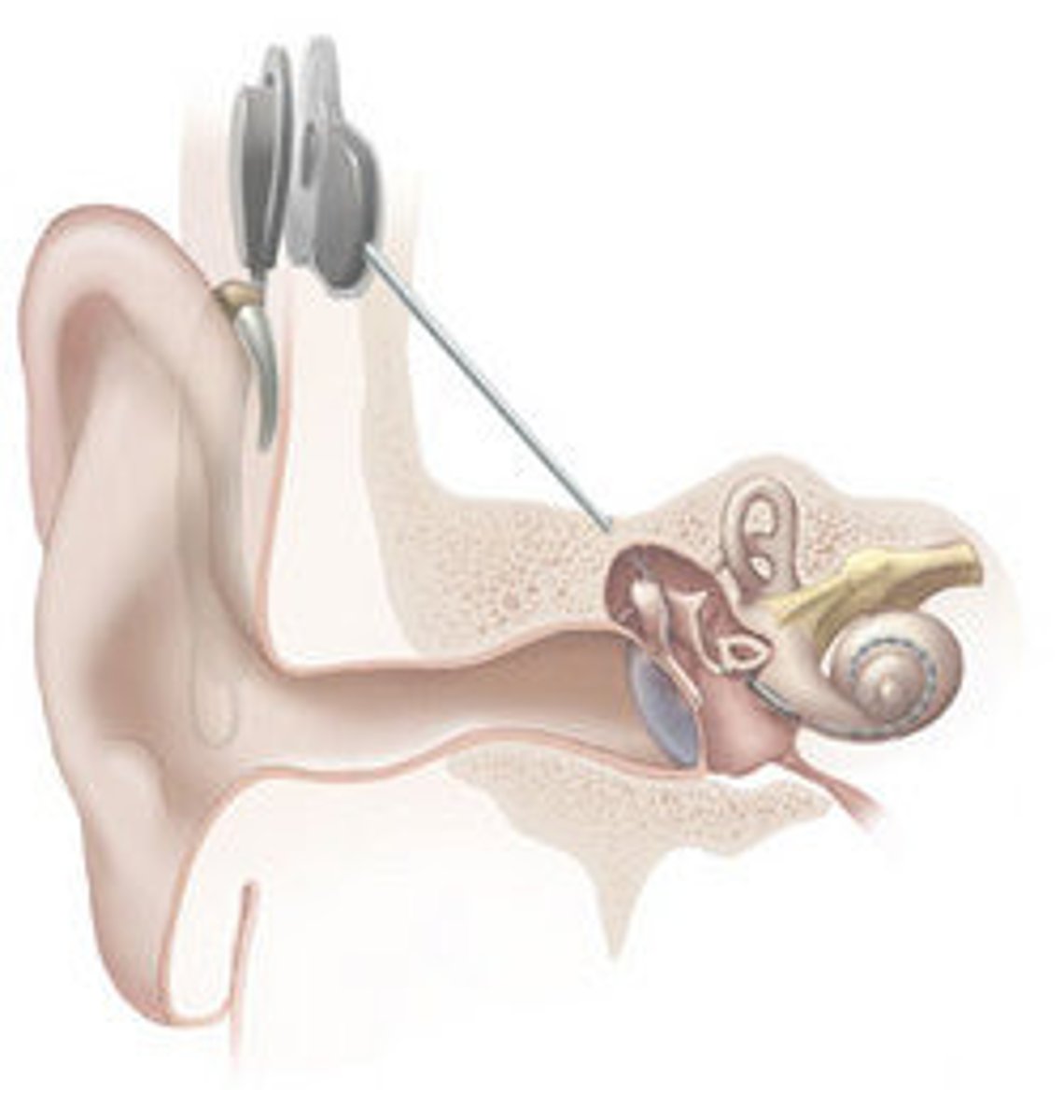
cochlear implant
device converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulating the auditory nerve through electrodes threaded into the cochlea
color constancy
perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color, even changing illumination alters the wavelengths reflected by an object
conduction hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea (ex. loss due to a middle-ear infection combined with a sensorineural loss caused by aging)
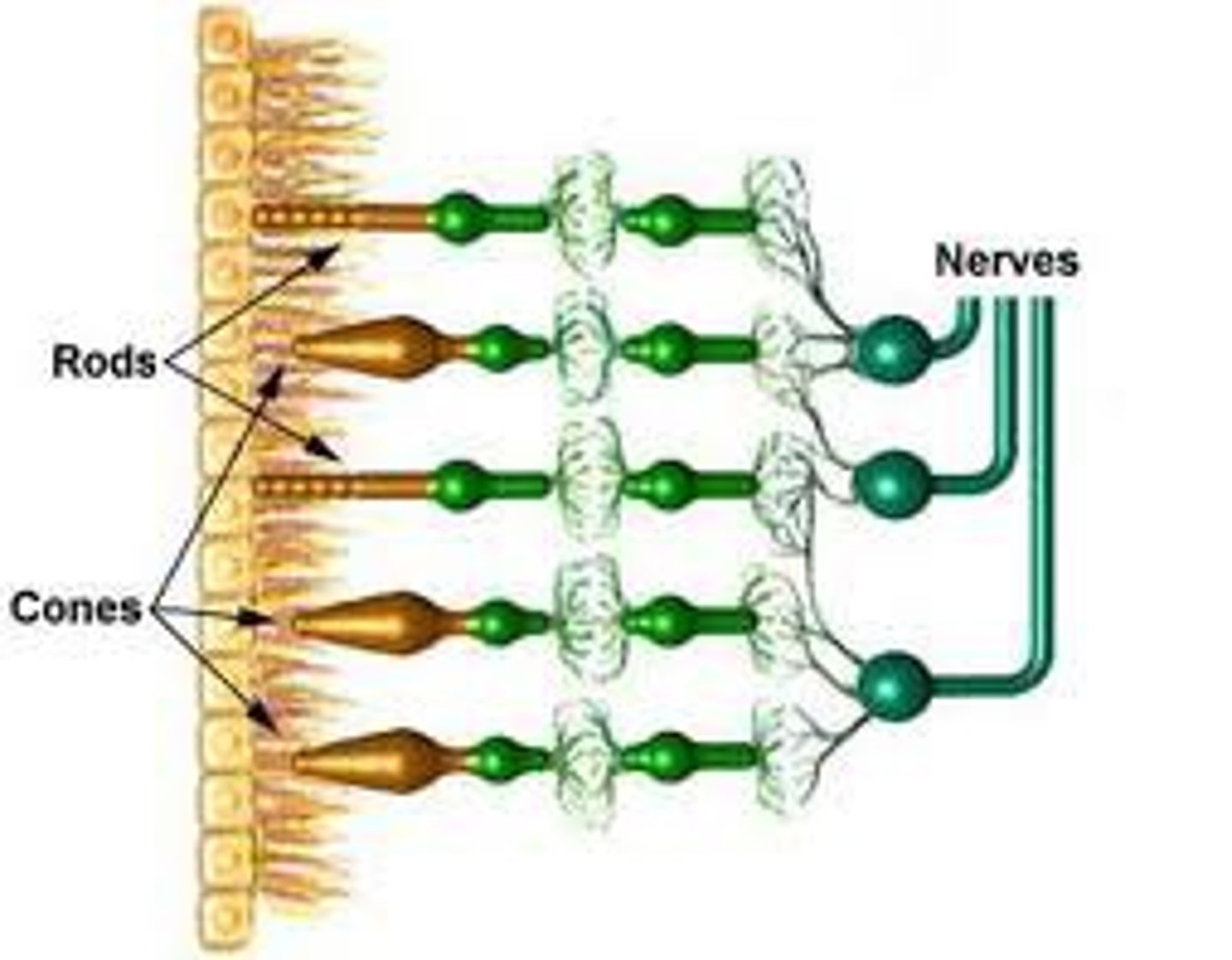
cones
retinal receptor cells that are concentrated near the center of the retina, they detect Color (ex. Color - Cones)
depth perception
ability to see objects in 3D images that strike the retina are 2D (ex. helps us judge distance)

difference threshold
amount of change needed to notice that a change has occurs (ex. turing up music in the car, starting off quiet & getting louder = noticeable difference)
extrasensory perception (ESP)
controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input (Ex. telepathy)
feature detectors
nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features of stimulus (ex. shape, angle, movement)
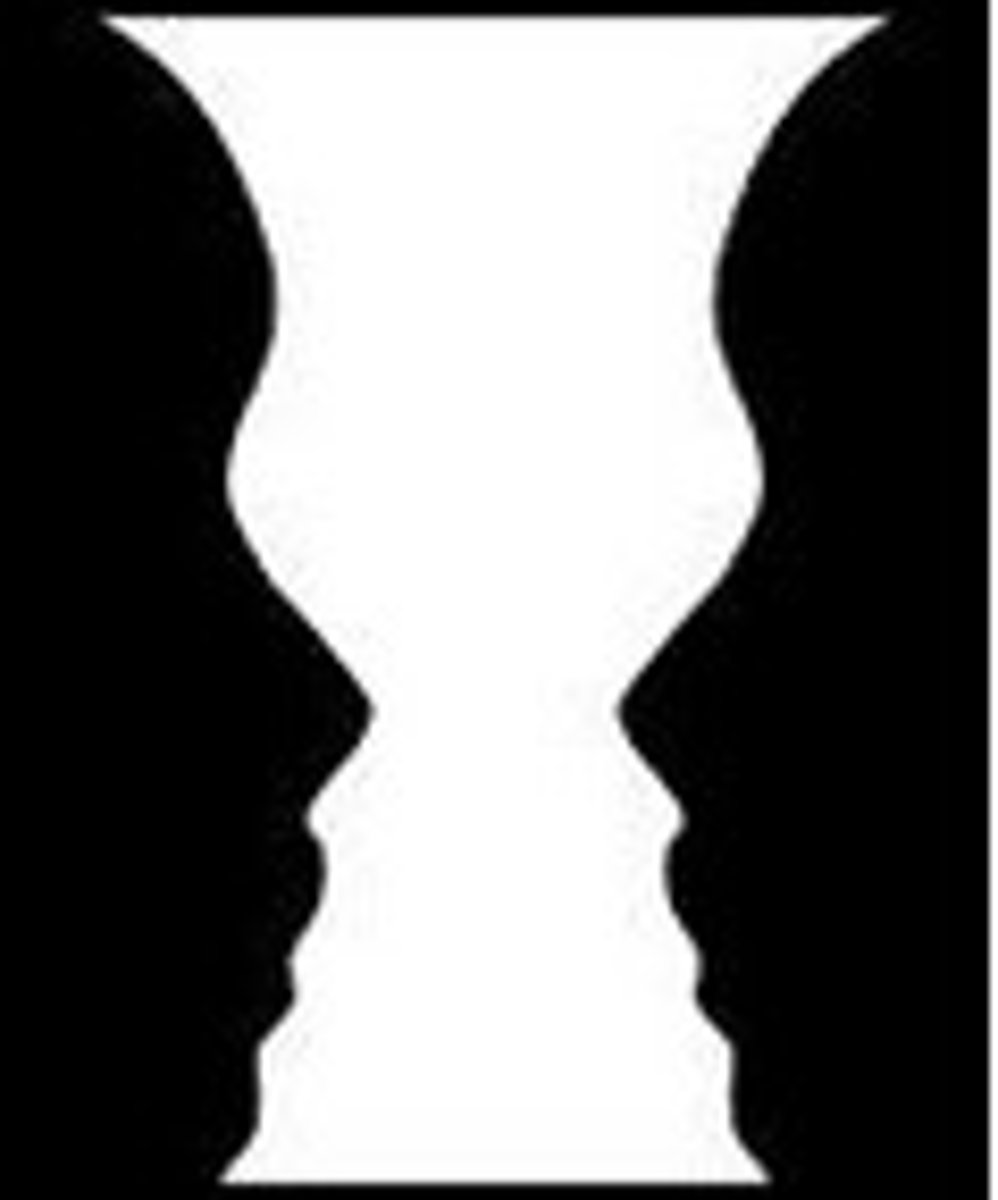
figure ground
the organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from surroundings (ex. In Gestalt psychology it is known as identifying a figure from the background)

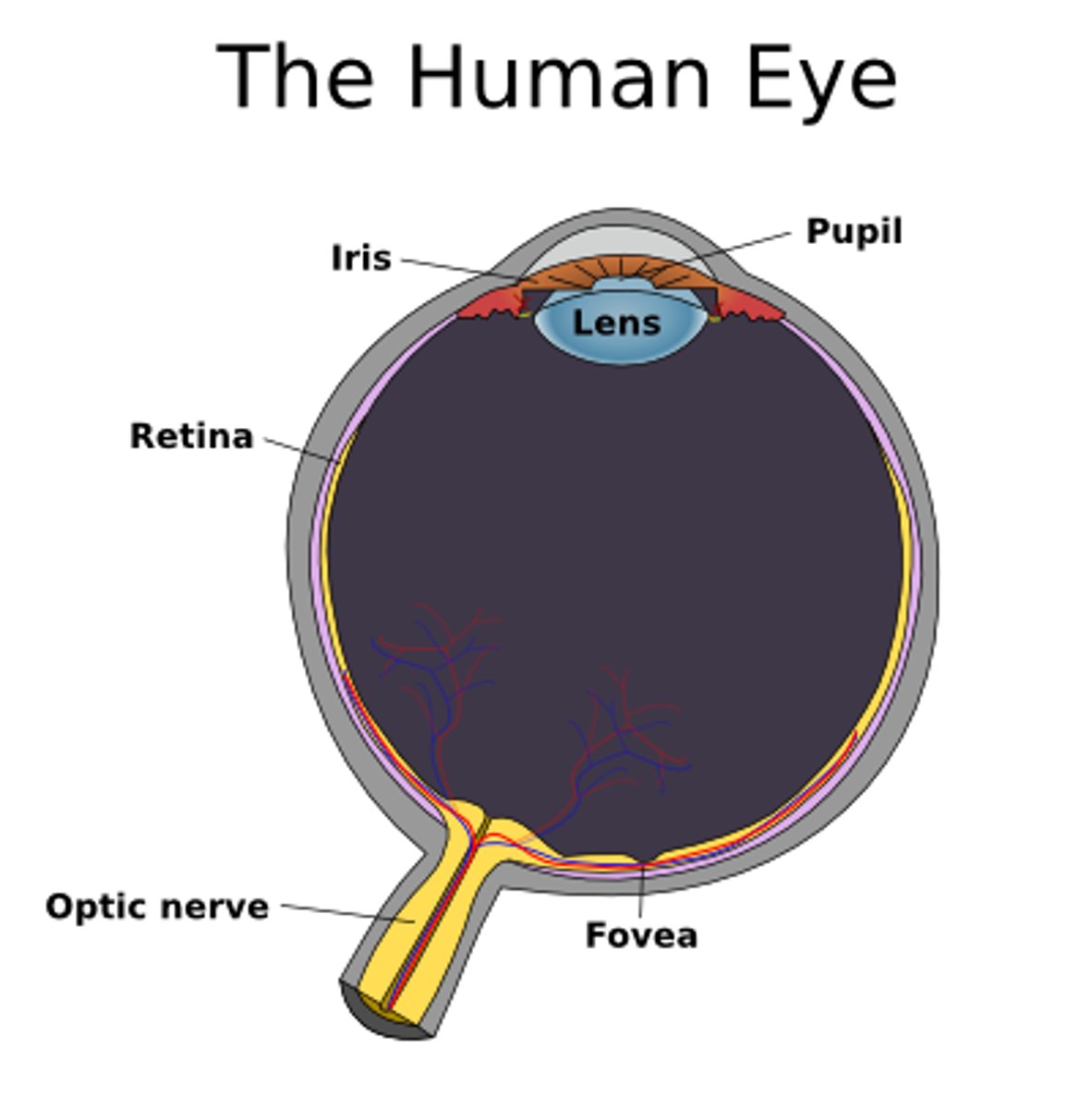
fovea
central focal point in the retina, eye's cones cluster around this
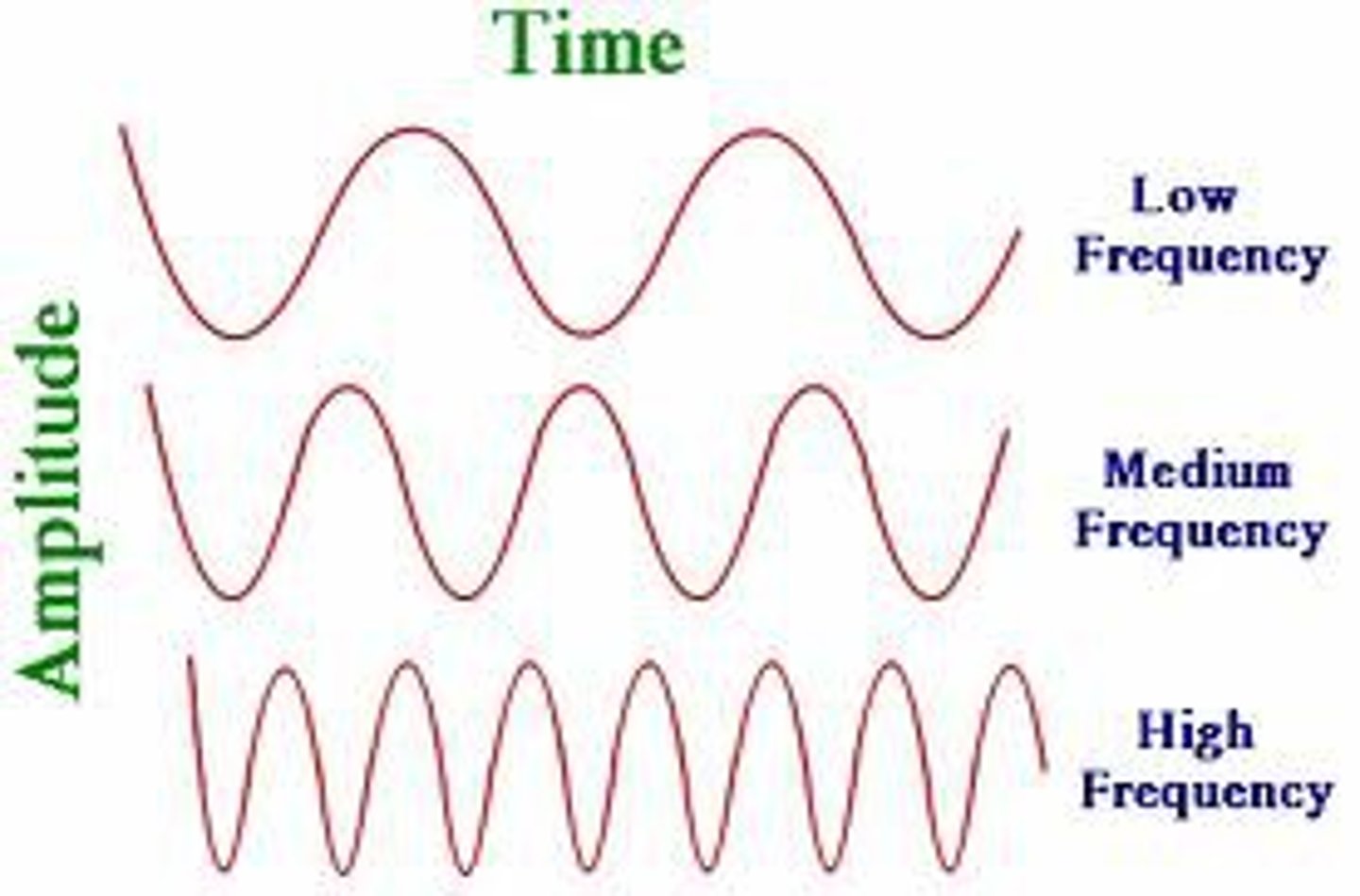
frequency
number of wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
frequency theory
hearing theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, enabling us to sense it's pitch
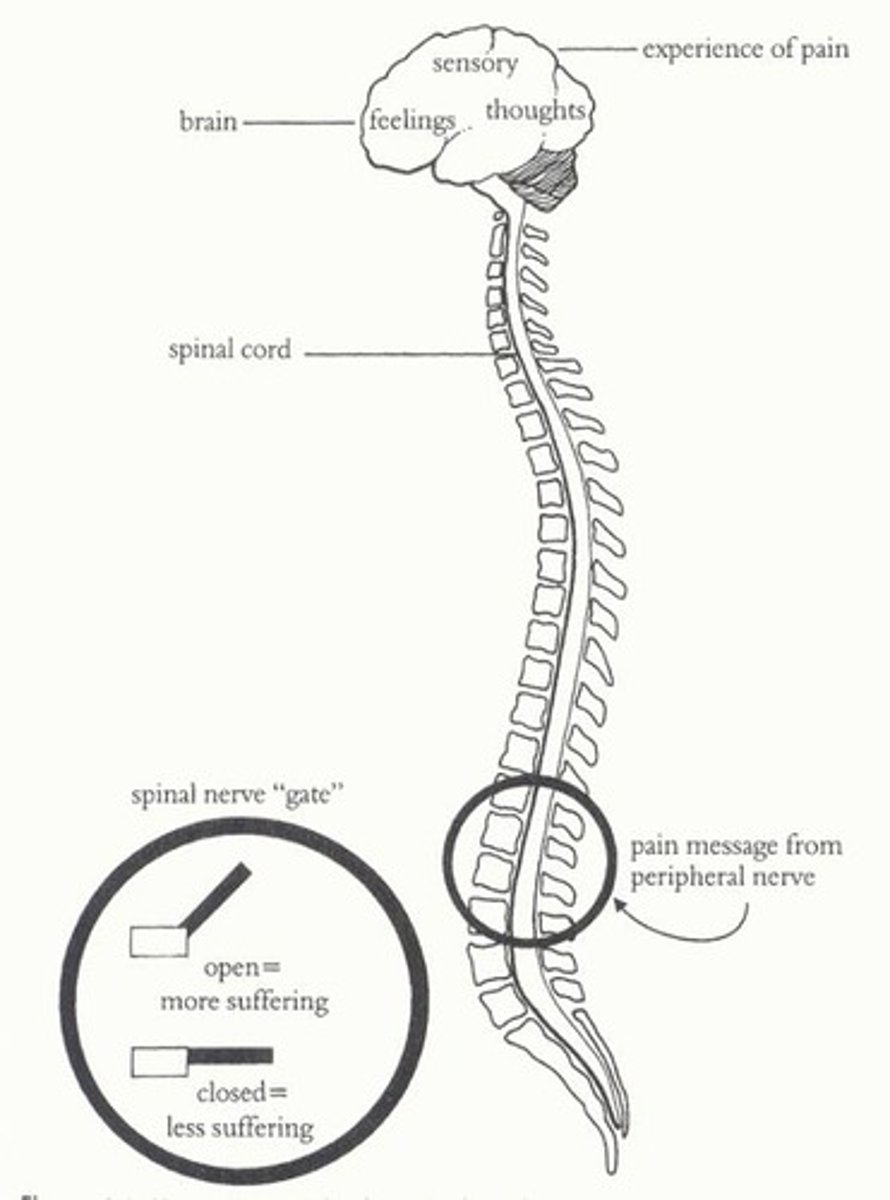
gate control theory
states that the spinal cord contains a neurological "gate" that blocks pain signals/allows them to pass into the brain
gestalt
organized whole, psychologists integrate pieces of info into a whole
grouping
tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups
hue
dimension of color that is determined by the wavelength of light (ex. blue, green,etc.)

inattention blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
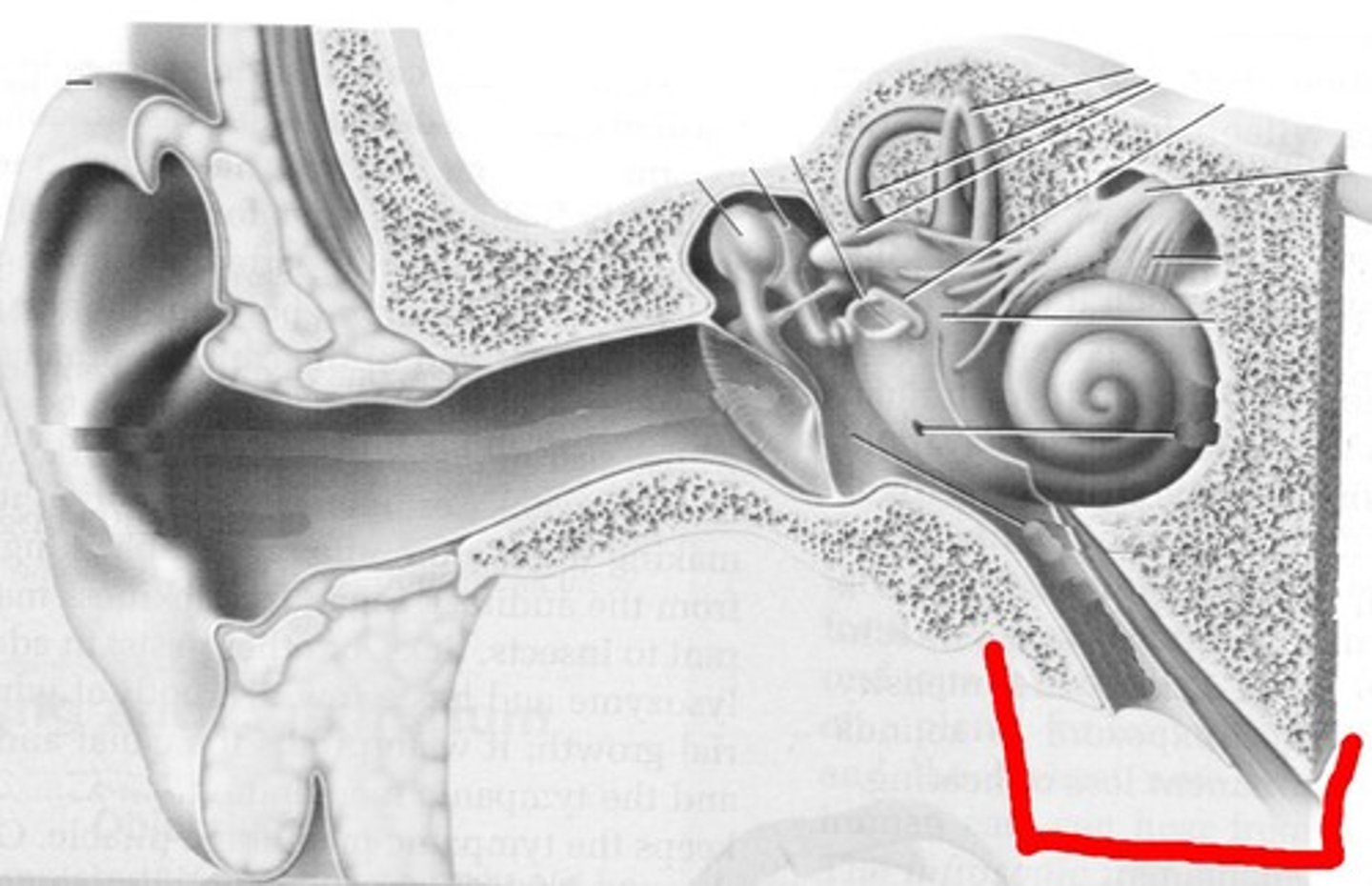
inner ear
innermost part of our ear (containing cochlea, semicircular, canals, vestibular sacs)
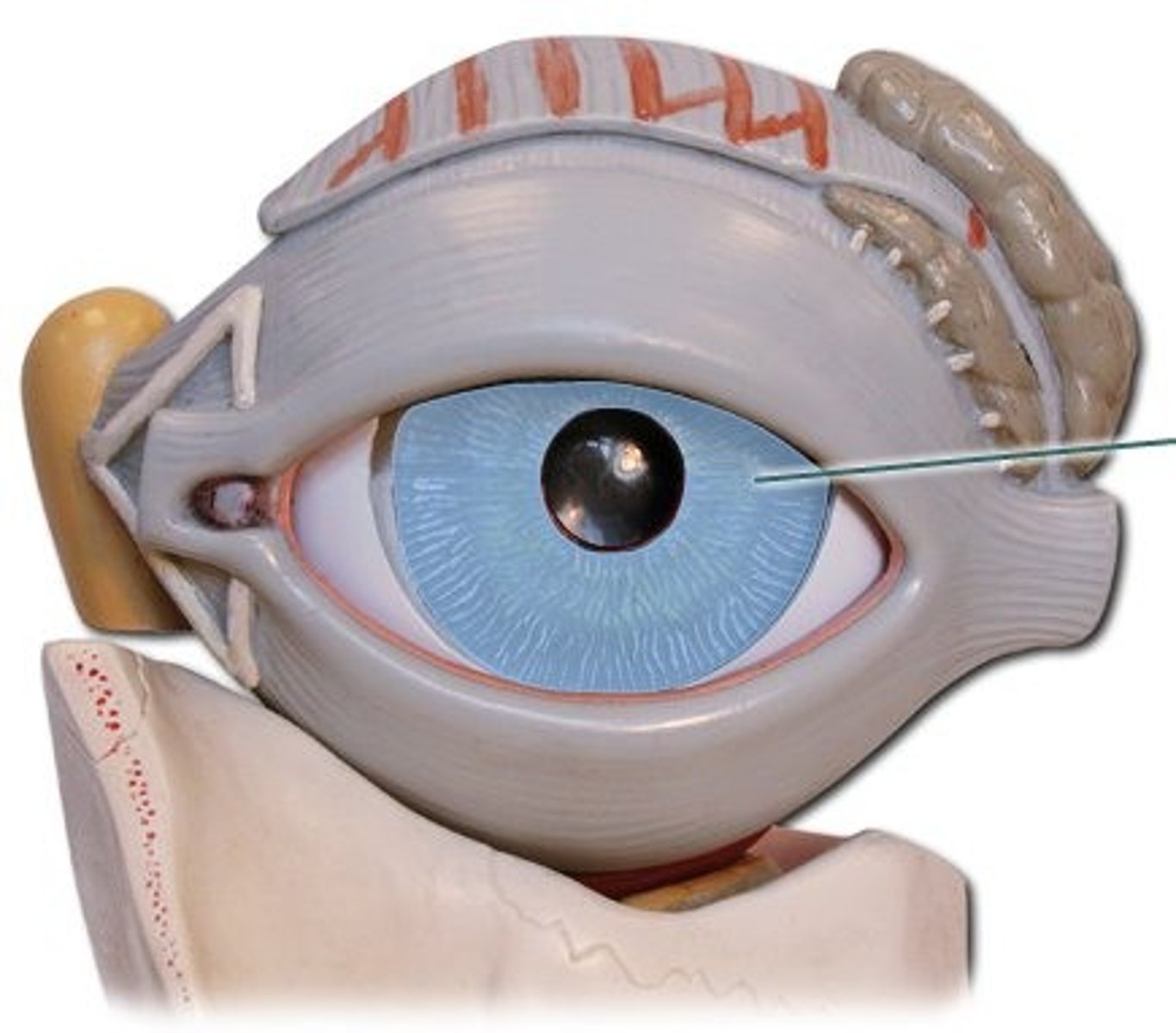
iris
ring of muscular tissues that form the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening
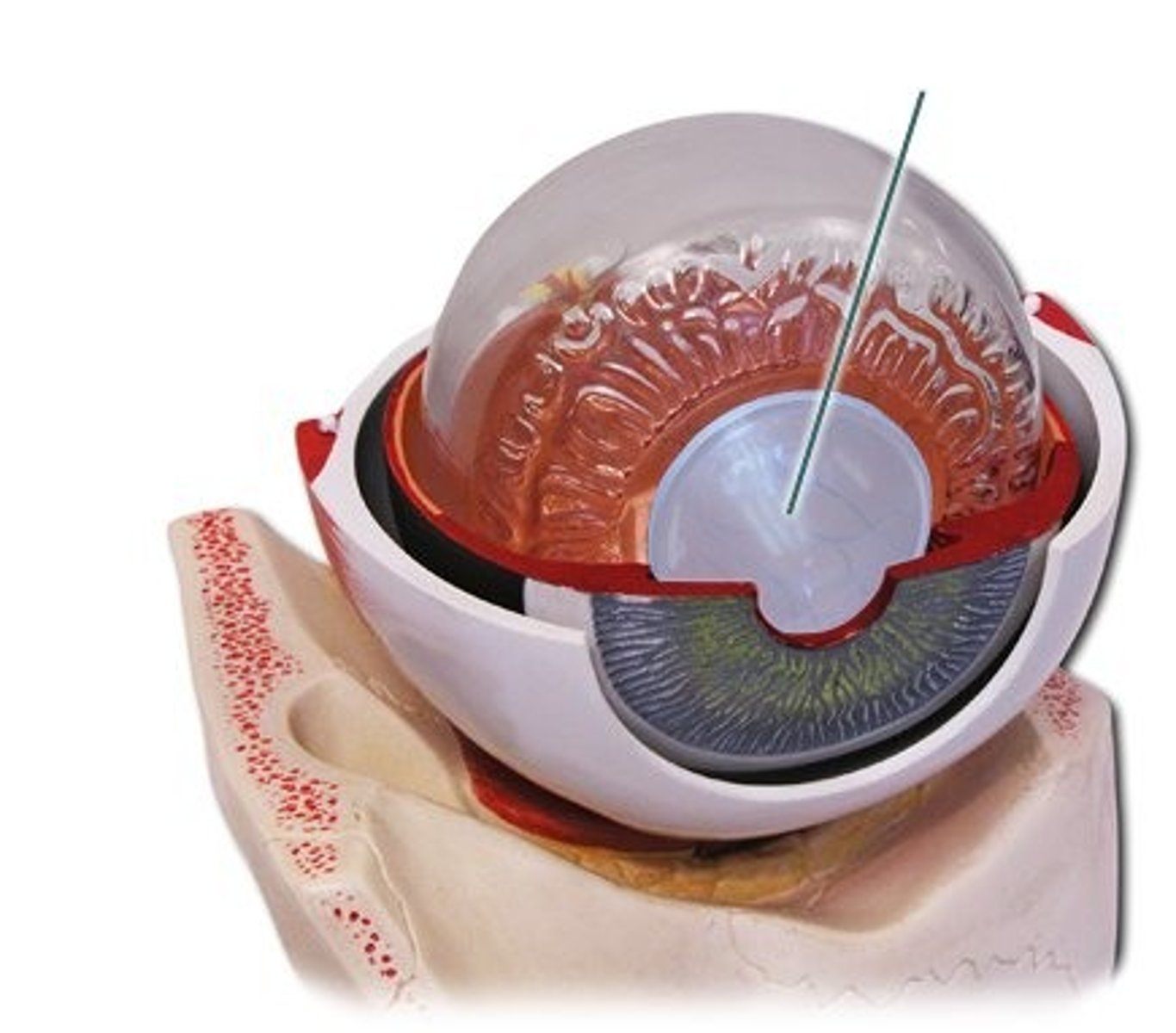
kinesthesis
the system for sensing the position and movement of body parts (ex. helps us detect weight, body position, or the relationship between movements in our body parts such as joints, muscles and tendons)
lens
transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
middle ear
the chamber between the eardrum and cochlea that concentrates the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea's oval window (contains 3 bones: hammer, anvil, stirrup)
monocular cues
depth cues available to the eye ALONE (ex. interposition, linear perspective, MONO = 1)
apponet process theory
states that opposing retinal processes enable colored vision (ex. red-green, yellow-blue, black-white)
optic nerve
nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
parallel processing
processing many aspects of a problem at the same time (ex. vision)
parapsychology
study of paranormal phenomena (ex. ESP, psychokinesis)
perception
organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize events (ex. the way we view things in a good/bad way)
perceptual adaptation
in vision, ability to adjust to an artificially displaced field of vision (ex. one rests one's hand on a table, one immediately feels the table's surface on one's skin)

perceptual consistency
perceiving objects as unchanging (Ex. consistency in shapes, size and lightness)
perceptual set
mental dispostion to perceive one thing and not another (ex. young woman and old lady in picture)

phi phenomenon
illusion of movement created when 2 or more lights blink on and off quickly (ex. christmas lights)
pitch
tone's experienced (highness/lowness) depends on frequency
place theory
audio, theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochleas membrane is stimulated
priming
activation of certain associations predisposing ones (Ex. memory and response)
psychophysics
study of relationships between physical characteristics of stimuli (ex. intensity) and our psychological experience of them
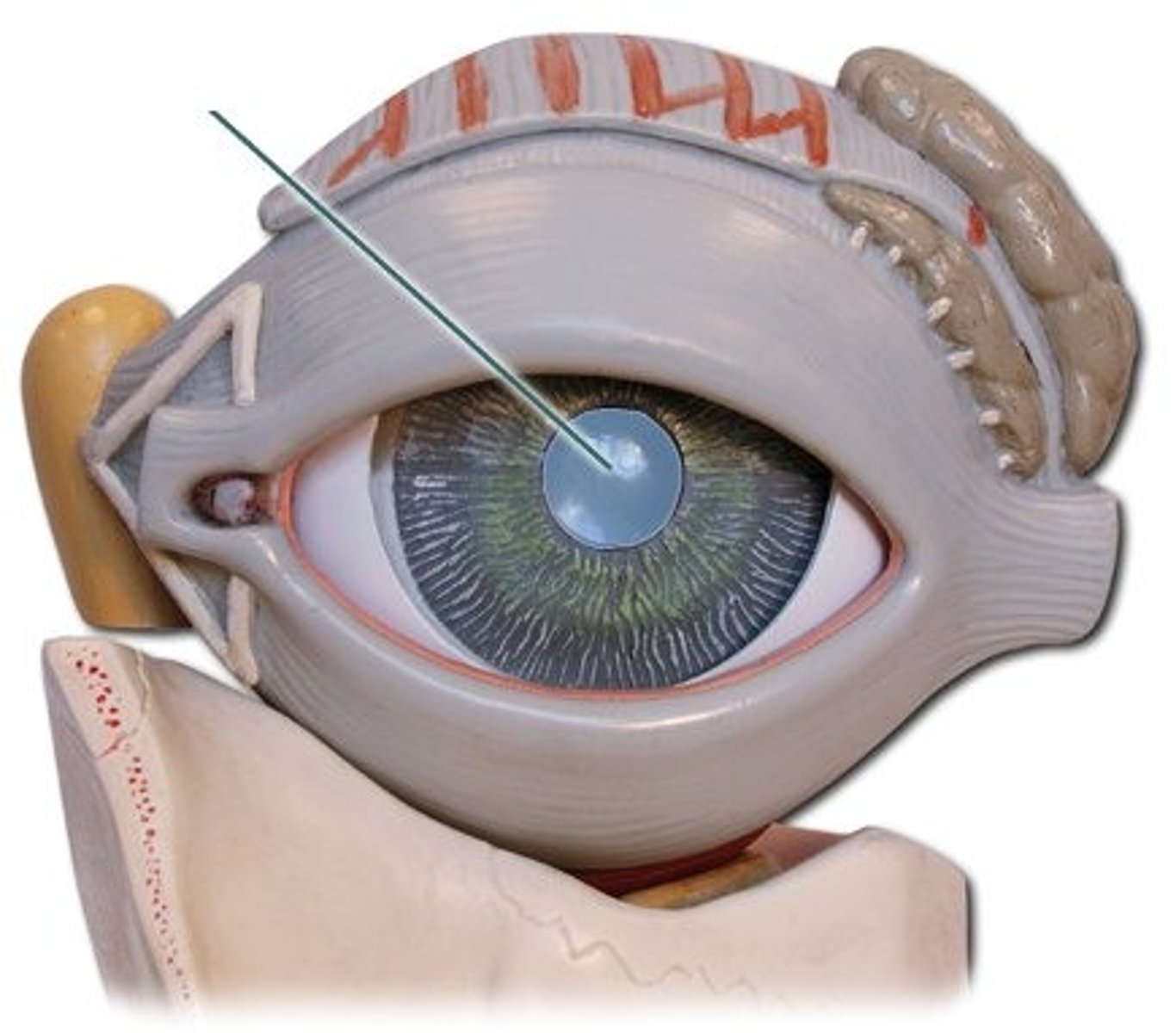
pupil
adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
retina
light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, contains: rods, cones and neurons
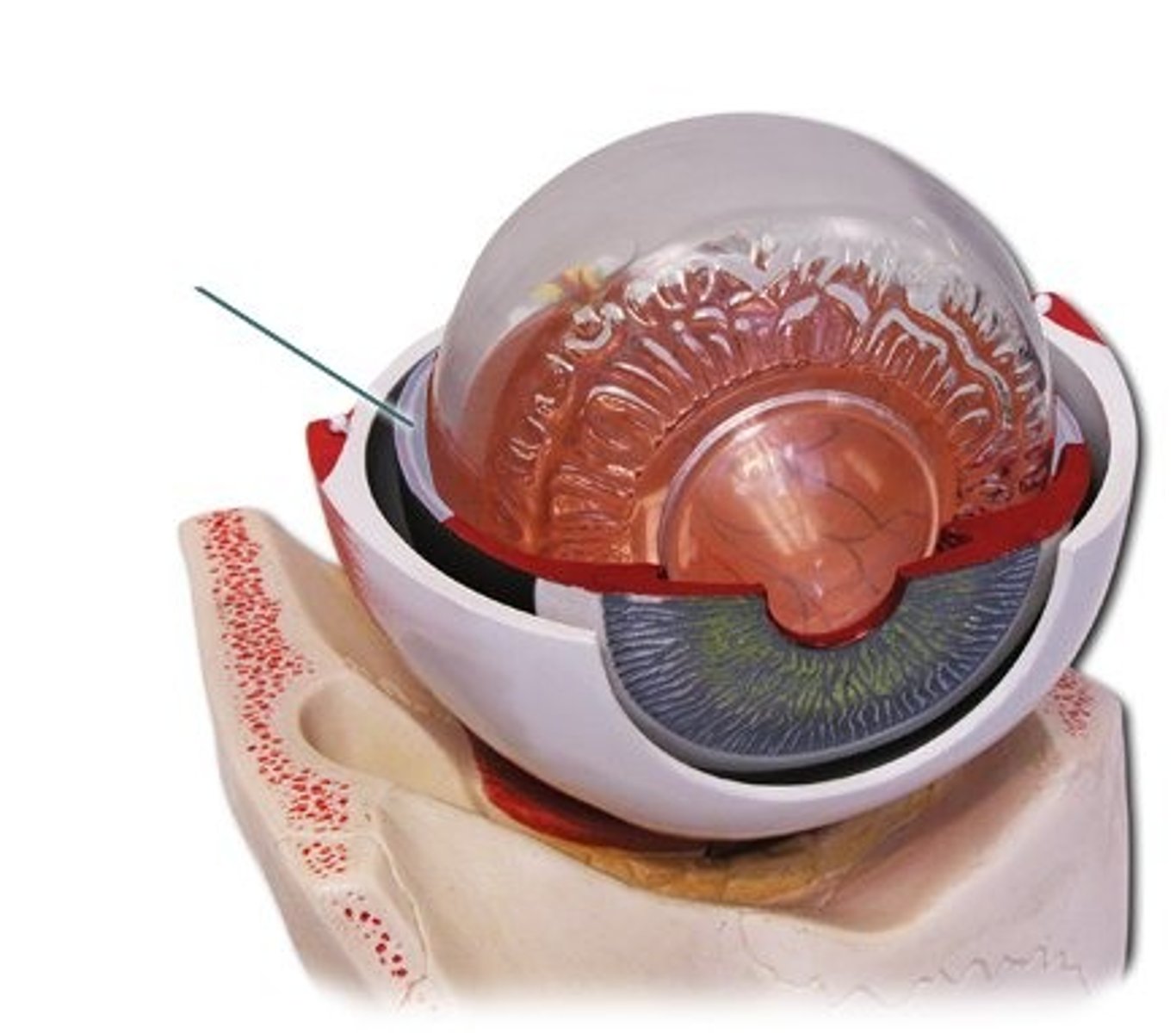
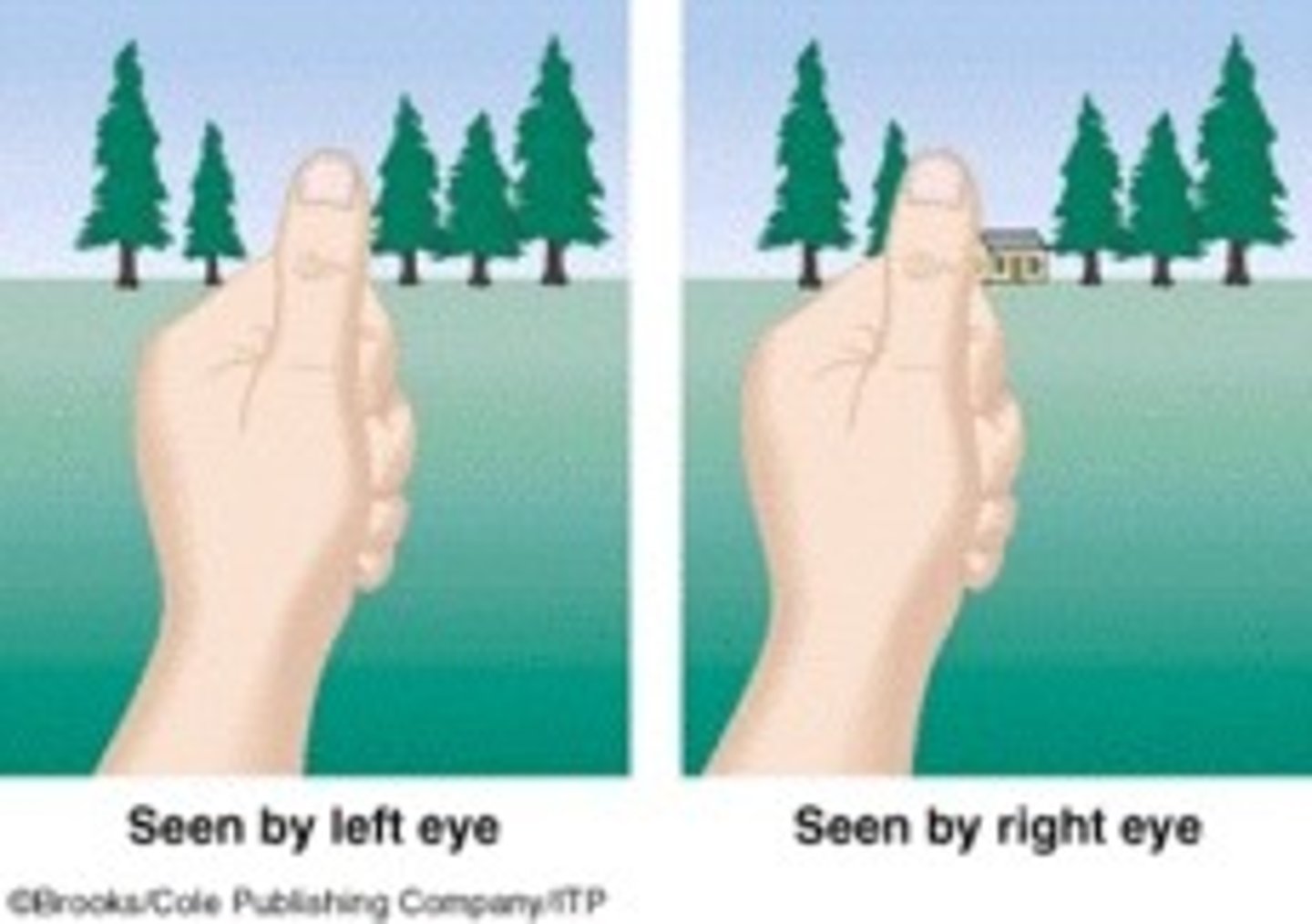
retinal disparity
binocular cue for perceiving depth by comparing images of the retinas in 2 eyes, the brain computes this distance (Ex. greater the difference between 2 images = closer the object)
rods
retinal preceptors that detect black, white and gray; needed for peripheral and twilight vision
selective attention
focusing on conscious awareness on a particular stimulus (ex. not paying attention to something on purpose)
sensation
process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment (ex. 5 senses)
sensorineural hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to the cochleas receptor cells or the auditory nerves (ex. nerve deafness)
sensory adaptions
diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation (Ex. light and dark adaption)
sensory interaction
states that one sense may influence another (Ex. smell of food influences taste)
signal detection theory
theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus with background noise (ex. mother hears the cry of her baby in a crowd)
subliminal
psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which people re-channel their unconscious mind
top down processing
info processing guided by higher level mental processes (ex. Your brain applies what it knows and what it expects to perceive and fills in the blanks)
transduction
conversion of one form of energy to another (ex. changing physical energy into electrical signals that can make their way to the brain.)
vestibular sense
the sense of body movement/position including sense and balance

visual cliff
lab device for testing depth perception in infants
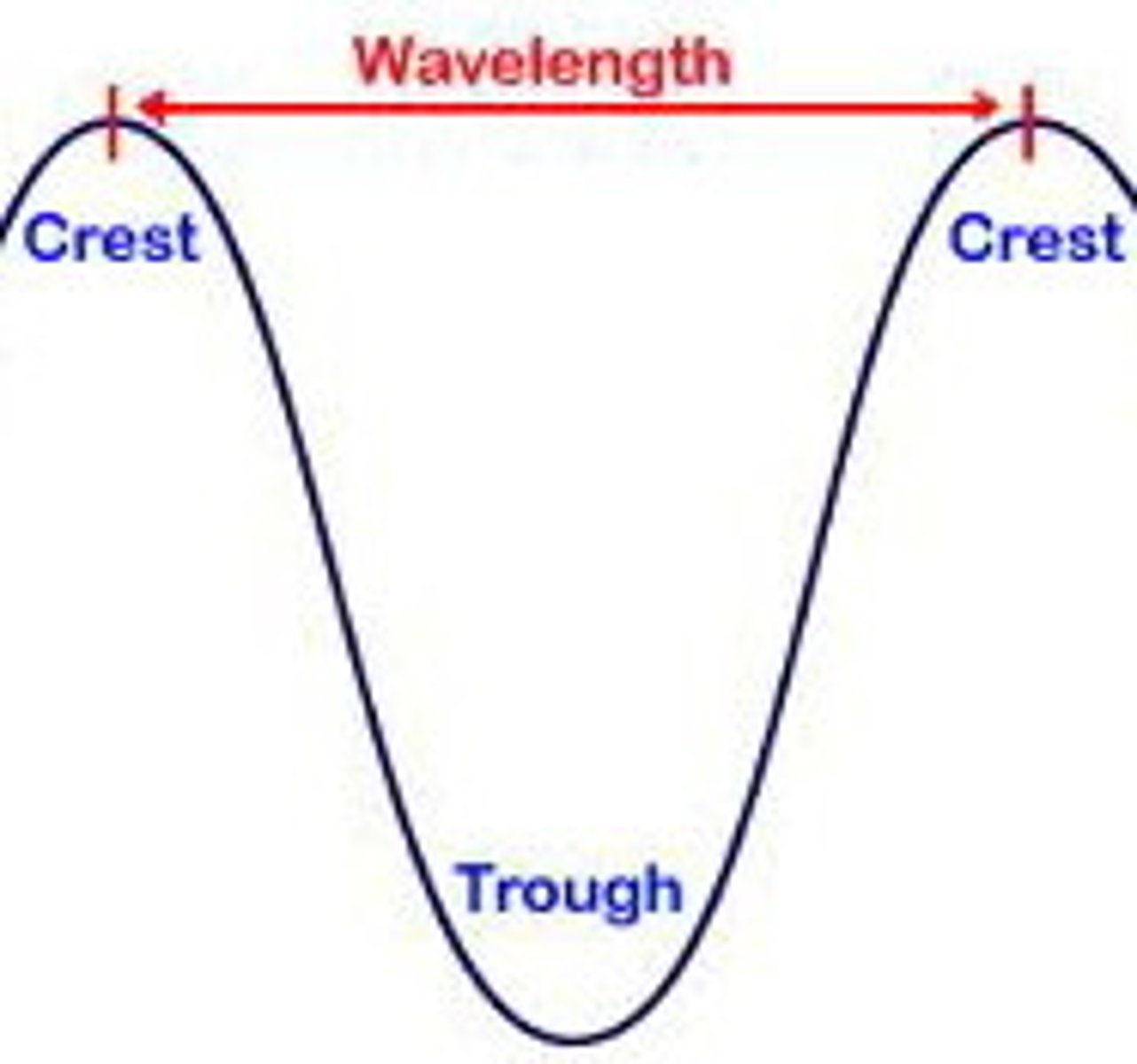
wave length
distance from the peak of one light or sound wave to the peak of the next
webers's law
to be seen as different, 2 stimuli must differ by a constant percentage
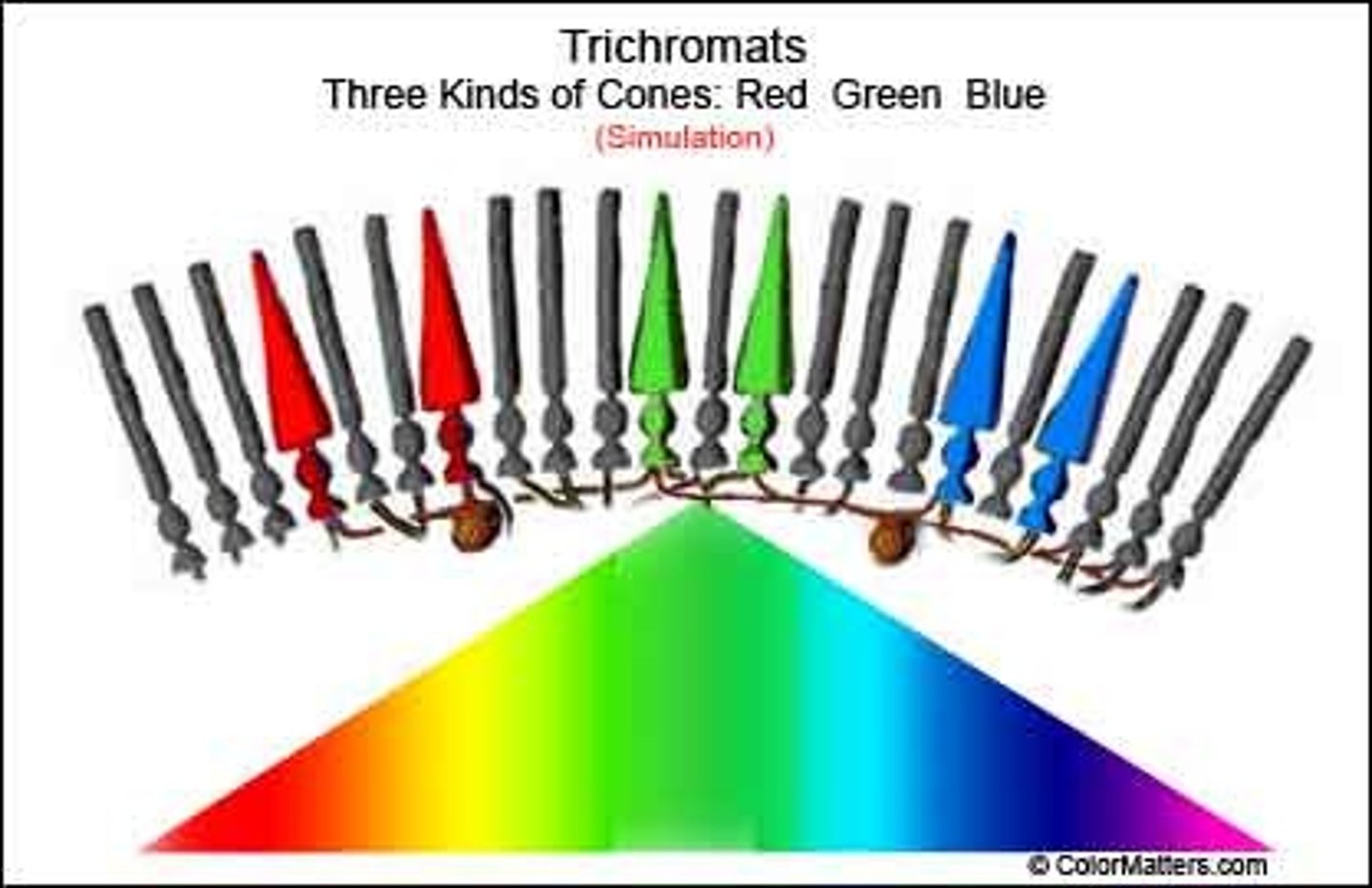
(young-helmotz) trichromatic theory
retina sees 3 different colors (red, green, blue) and when combined, they create any color