5-Kearns- Cell Cycle Specific
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the 2 classes of Topoisomerase Inhibitors and the names of the drugs in those classes?
Camptothecins
Irinotecan (Camptosar)
Topotecan (Hycamtin)
Epipodophyllotoxins
Etoposide
Teniposide
What phase of the cell cycle does each topoisomerase inhibitor class inhibit?
Camptothecins- S PHASE
Epipodophyllotoxins - S—>G2 TRANSITION
Which topoisomerases does each class of drugs inhibit? Top I or Top II?
Camptothecins- Top I
Epipodophyllotoxins- Top II
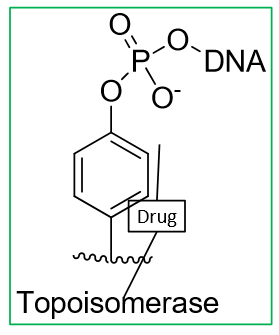
What is the MOA Camptothecins?
bind to DNA-top I complex
intermolecular interactions between drug and top lead to a stable Drug-DNA-Top I complex
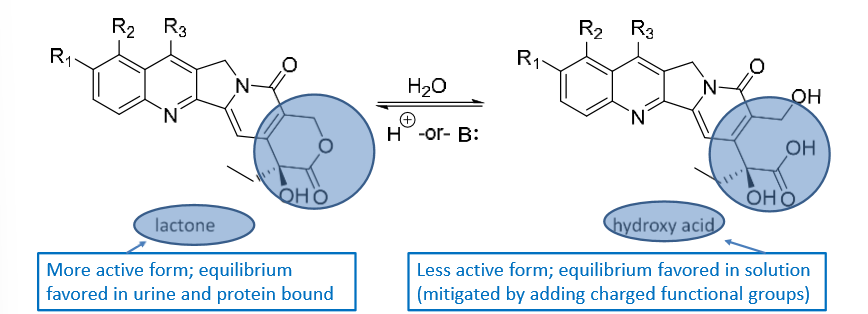
Camptothecins can have a lactone or hydroxy acid R group. Which is more active?
lactone—> more active
hydroxy acid—→ less active
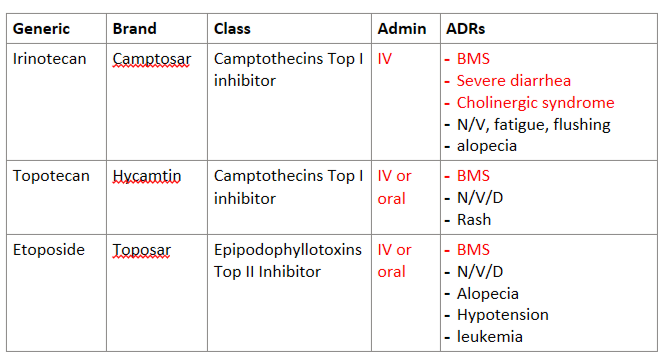
Answer the following table about Topoisomerase inhibitors:
Generic | Brand | Class | Admin | ADRs |
Irinotecan |
|
|
|
|
Topotecan |
|
|
|
|
Etoposide |
|
|
|
|
Which top inhibitor is a prodrug? What is the active metabolite?
Irinotecan—> active metabolite is SN-38
What is a normal creatine clearance?
90 ml/min
Topotecan and Etoposide are __________ eliminated and dosed based on CrCl or kidney failure.
renally
Epipodophyllotoxins like Etoposide and Teniposide have a resistance to what?
P-gp
Camptothecins are isolated from a tree called Camptotheca acuminata and Epipodophyllotoxins are isolated from mandrake root. Can natural products containing these substances be useful in cancer?
nah
Do topoisomerase inhibitors work through covalent or intermolecular bonds?
intermolecular
Antimetabolites inhibit _______________ and are specific to what phase?
inhibit DNA synthesis and are S PHASE SPECIFIC
Do antimetabolites have a cytotoxic or cytostatic effect? What is the difference?
cytostatic effect!!!
cytostatic- can reverse, keeps the DNA intact/locks it up and the cell cycle will not progress
cytotoxic- CANNOT reverse, induces apoptosis and there is not return
Name the classes and drugs within the them that are considered “antimetabolites”
antifolates
methotrexate
pyrimidine antagonists
pemetrexed
5-FU
capecitabine
purine antagonists
6-MP
6-Thioguanine
nucleoside analogues
cytrabine
gemcitabine
miscellaneous:
pentostatin
hydroxyurea
Methotrexate inhibits what enzyme? What conversion does this block?
dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)—> inhibits the conversion of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate
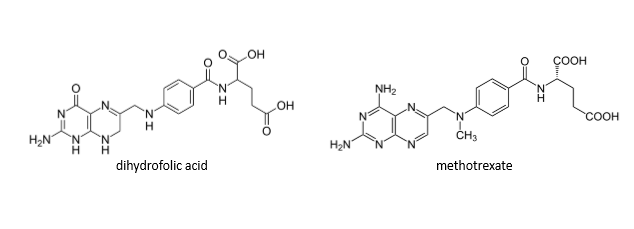
Inhibiting folic acid would inhibit which of the following:
a. purine synthesis
b. pyrimidine synthesis
c. both
c (one exception is the pyrminidine cytosine)
Answer the following about methotrexate:
To exert its action methotrexate needs what to get into the cell?
How can methotrexate be administered?
What are the ADRs of methotrexate?
What drugs should be avoided?
transporters
IV, IM, SQ, intrathecal, oral
BMS, N/V/D. alopecia, mucositis, rash, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity
drugs that decrease excretion (cisplatin, PCNs, sulfa, NSAIDs)
Once methotrexate enters a cell what happens to it?
becomes polyglutamated
What is the rescue drug for Methotrexate? When is it usually required?
rescue drug- LEUCOVORIN (wellcovorin)
required for high dose MTX
What drugs are pyrimidine antagonists? (brand/generic)
Pemetrexed (Alimta)
Fluorouracil (5-FU)
What is the MOA of Pemetrexed? What are these enzymes that this drug inhibits normally do?
weak inhibitor of DHFR
converts dihydrofolate to tetrahydrafolate
INHIBITS THYMIDYLATE SYNTHASE
thymidylate synthase normally converts dUMP to dTMP
INHIBITS glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (GARFT)
tetrahydrofolate to IMP
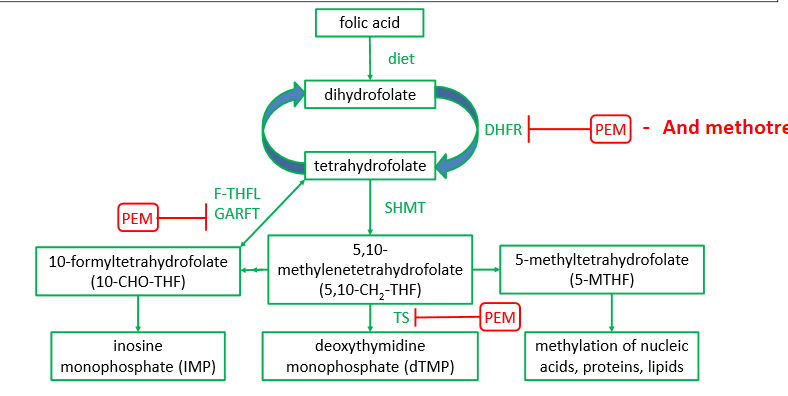
How does the MOA of methotrexate compare to pemetrexed?
methotrexate only inhibits 1 enzyme, while pemetrexed inhibits 3 enzymes
Answer the following about Pemetrexed (Alimta):
administration
what must be supplemented?
avoid use in what?
ADRs
IV administration
B12 and folic acid MUST be supplemented
avoid use in decrease kidney function (and NSAIDS)
ADRs:
myelosuppression
others: fatigue/drowsiness, renal toxicity, rash, N/V/D, stomatitis, pharyngitis
What is the MOA of 5-FU?
inhibitor of THYMIDYLATE SYNTHASE!!!!!
Which pyrimidine antagonist is a pro-drug? What is the active metabolite? Is the active metabolite hydrophilic or lipophilic?
5-FU IS A PRODRUG!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
active metabolite is Capecitabine
VERY LIPOPHILLIC!! (good for solid tumors)
How is capecitabine (prodrug of 5-FU) metabolized?
the enzyme CYTIDINE DEAMINASE converts Capecitabine to 5-FU
If the enzyme cytidine deaminase was overexpressed, what would happen to the concentration of 5-FU in cells?
increase
What enzyme is responsible for the catabolism of 5-FU?
DPD (dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase)
What drugs are purine antagonists?
mercaptopurine (6-MP) (Purinethol)
What is the main goal of purine antagonists?
inhibit the synthesis of purines (A and G) by messing with IMP
What is the MOA of Purine antagonists?
Overall: Block conversion of IMP to GMP and AMP
HGPRT (Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase) converts 6-MP into TIMP and TGMP
TIMP INHIBITS 3 pathways associated with IMP
the conversion of PRPP to IMP
conversion of IMP to AMP
conversion of IMP to XMP
TGMP is incorporated into DNA/RNA as false nucleotides
Purine antagonists are PRODRUGS that must be converted to what? using what enzyme?
must be converted to ribonucleotides (TIMP and TGMP) by hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT)
What is a prodrug for 6-MP?
Azathioprine
Answer the following Mercaptopurine (6-MP):
administration?
decrease dose if taken with…
ADRs
oral administration
decrease dose with allopurinol (gout medication)
ADRs- BMS, hepatotoxicity, hyperuricemia
others: rash, N/V/D, malaise
Which of the following are administered as an anti-cancer tx?
a. nucleoside analogues
b. nucleotide analogues
a
What are nucleoside analogues converted into? What is the result?
nucleoside analogues converted into nucleotide analogs for activity (phosphorylation). inhibits DNA elongation——results in apoptosis of the cell.
What drugs are nucleoside analogues? (brand/generic)
Cytarabine (ara-C) (Cytosar-U)
Vyxeos is a combination of cytarabine and _____________.
daunorubicin
Answer the following about Cytarabine:
administration
analogue of what?
inhibits what?
ADRs
IV, intrathecal
cytidine analogue (AraCTP competes with dCTP)
inhibits DNA polymerase
ADRs
BMS, N/V/D, cerebellar toxicity, malaise, conjunctivitis
Hydroxyurea inhibits what enzyme?
ribonucleotide reductase
How is hydroxyurea (Droxia) administered and what are the ADRs?
administered orally
ADRs- BMS, N/V/D, CNS disturbances, dysuria, stomatitis, alopecia, hepatotoxicity
PRACTICE:
Which of the following are NOT cell cycle specific:
a. nucleoside analogues
b. alkylating agents
c. pyrimidine antagonists
d. purine antagonists
e. methotrexate
b (ALL OF THE ANTIMETABOLITES ARE S PHASE SPECIFIC!!!)
What classes of drugs inhibit microtubules? What are the drugs within each class?
vinca alkaloids
Vinblastine
Vincristine
taxanes
paclitaxel
docetaxel
Microtubule inhibitors are specific to what phase?
M phase
How do Vinca alkaloids and Taxanes inhibit microtubules? (polymerization, and stabilization)
vinca alkaloids- INHIBIT POLYMERIZATION
microtubule DESTABILIZING (means we stop it from growing)
taxanes- INHIBIT DEPOLYMERIZATION
microtubule STABILIZING (means as we grow we just keep it wherever it is)
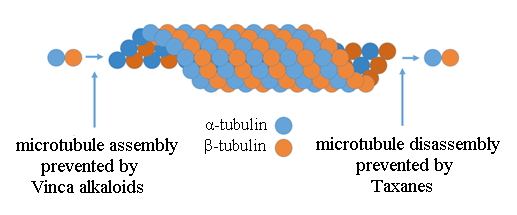
How do vinca alkaloids cause microtubule destabilization? Does it bind at the + end or - end
binding to GTP binding sites on the + end, and inhibits GTP from coming in and the microtubule will not grow any more
What’s the difference in SAR between Vincristine and Vinblastine?
Vincristine- more hydrophilic- has oxygen
cleared more slowly, cumulative toxicity
Vinblastine- more lipophilic- has methyl
more potent, better in solid tumors
All microtubule inhibitors have a resistance to what?
P-gp
Vinca alkaloids should NEVER be administered how?
intrathecal
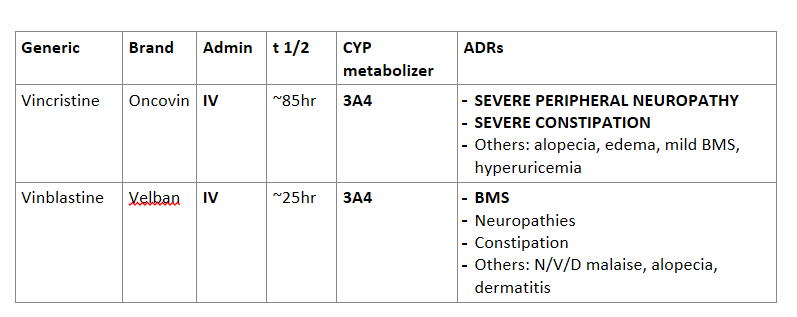
Answer the following about Vinca alkaloids:
Generic | Brand | Admin | t 1/2 | CYP metabolizer | ADRs |
Vincristine |
|
|
|
|
|
Vinblastine |
|
|
|
|
|
Can you administer a vinca alkaloid with a taxane?
yes—> give combo
Paclitaxel can be administered in what because of its low solubility?
castor oil (FYI: there’s also albumin formulations)
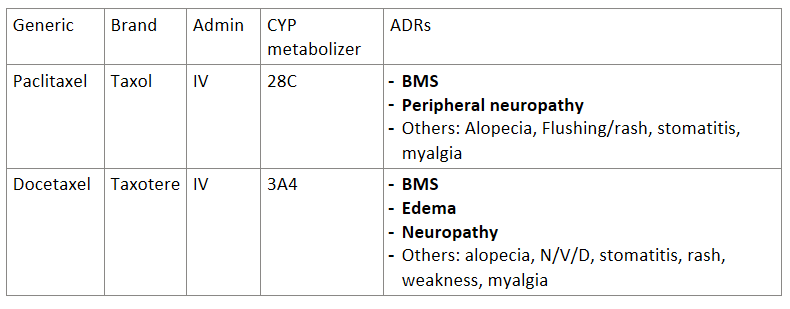
Answer the following about taxanes:
Generic | Brand | Admin | CYP metabolizer | ADRs |
Paclitaxel |
|
|
|
|
Docetaxel |
|
|
|
|
In general all microtubule inhibitors (taxanes and vinca alkaloids) have a risk of what ADR?
peripheral neuropathy