astronomy
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
galaxies
a gravitationally bound systems of gas, dust and millions or billions of stars and solar systems
shapes
elliptical
spiral
barred (spiral)
irregular (anything that dones’t fit above

milky way (our galazy)
our systems is on the Orion Arm
closest galazy: Andromedo
200-400b stars
100,000 lights years in diameter
solar systems
gravitationally bound systems of the Sun + the objects orbit it
constellations
group of stars as seen from earth that appear to form a familiar shape
contellations examples
many different cultures have own stories/ diff meanings to it
e.g emu in the sky. the emu indicate various seasonal activities like egg-laying season
stars
a luminious body of gas that shines due to nuclear fusion
absolute magnitude
how bright a star actually is
if it was 10 parsecs from Earth
apparent magnitude
how bright a star appears from Earth
affected by distance from earth
more negative=
brighter
more positive=
dimmer/ less brighter
small stars
e.g neutron stars 20-40k diameter
large stars
e.g supergiants 1500 x larger than our Sun
colour of stars
determined by temperature

hottest stars
blue/violet
coller stars
red
nuclearfusion
nuclei fuse (atoms joins together) → create energy
light atoms (e.g H) joins + become heavier atoms (e.g He) ‘H+’H=2He
hertz- russel diagram
shows relationship between stars tempoerate + brightness (luminosity. shows how they change during lifestyle
x-axis=temperature
->left is hot
->right is cooler
y-axis=luminosity(absolute magnitude)
->bright stars at the top
->dimmer stars at bottom
On the diagram stars are ranked from bottom to top in order of decreasing magnitude (increasing brightness) and from right to left by increasing temperature
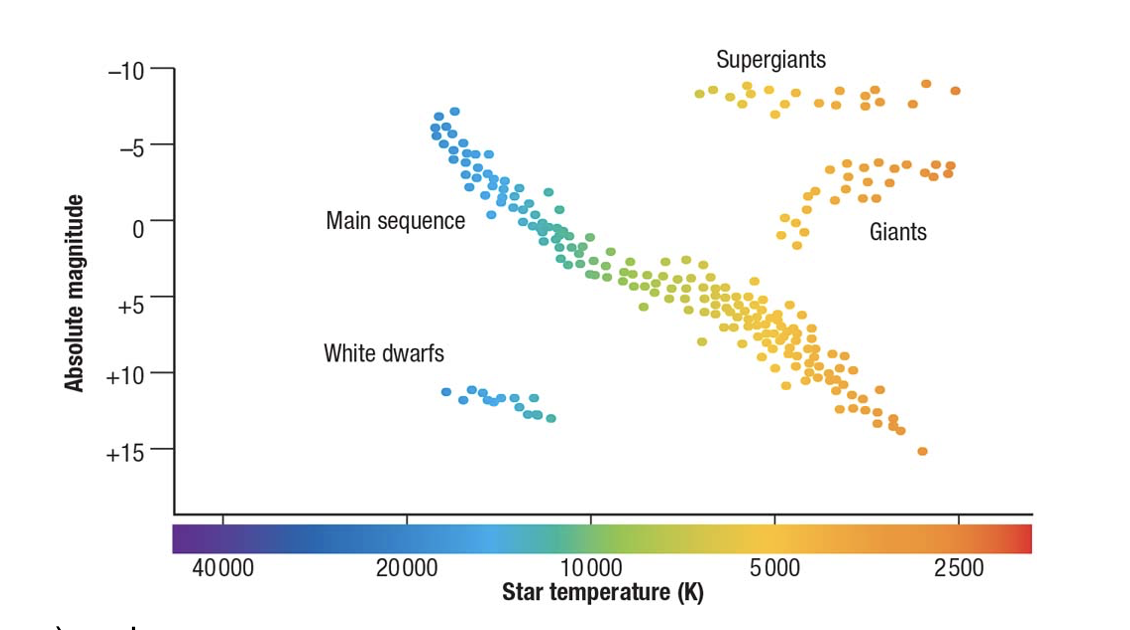
bigger stars →
hotter + brighter
more gravity
more nuclear fusion → releases energy
Doppler effect
when objects are moving, the waves (sound/light) are produced by that object will be either lengthened or shortened due to their motion
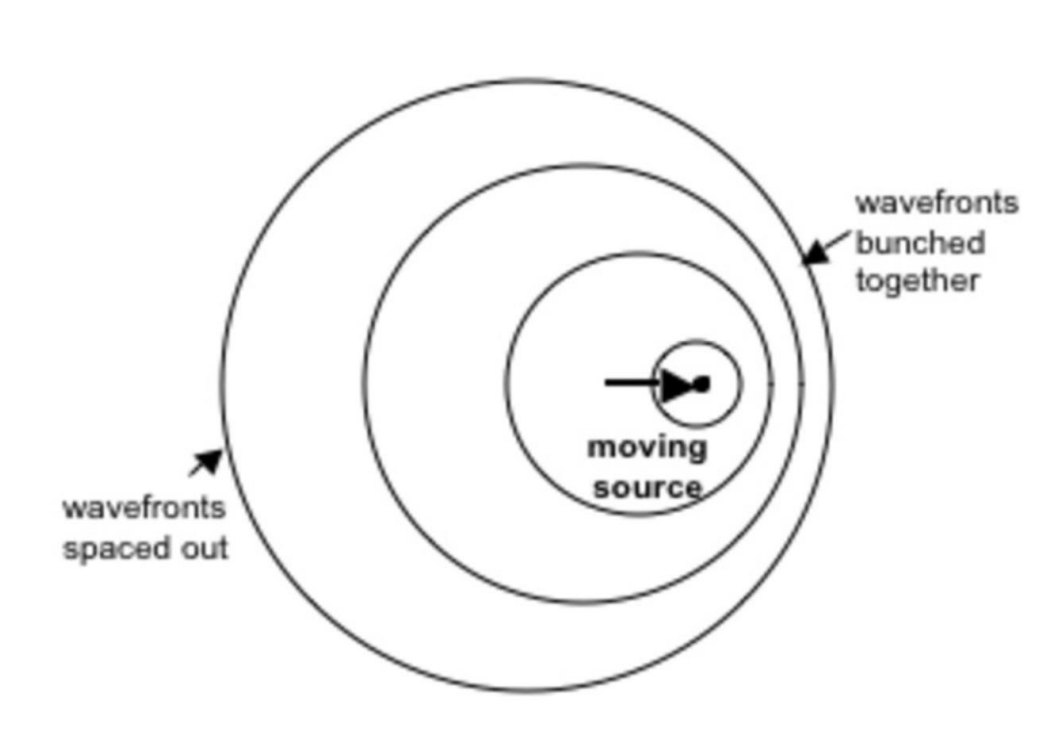
blue shift + red shift
light from stars occurs when light waves from stars
blue: object approaching
red: object receding
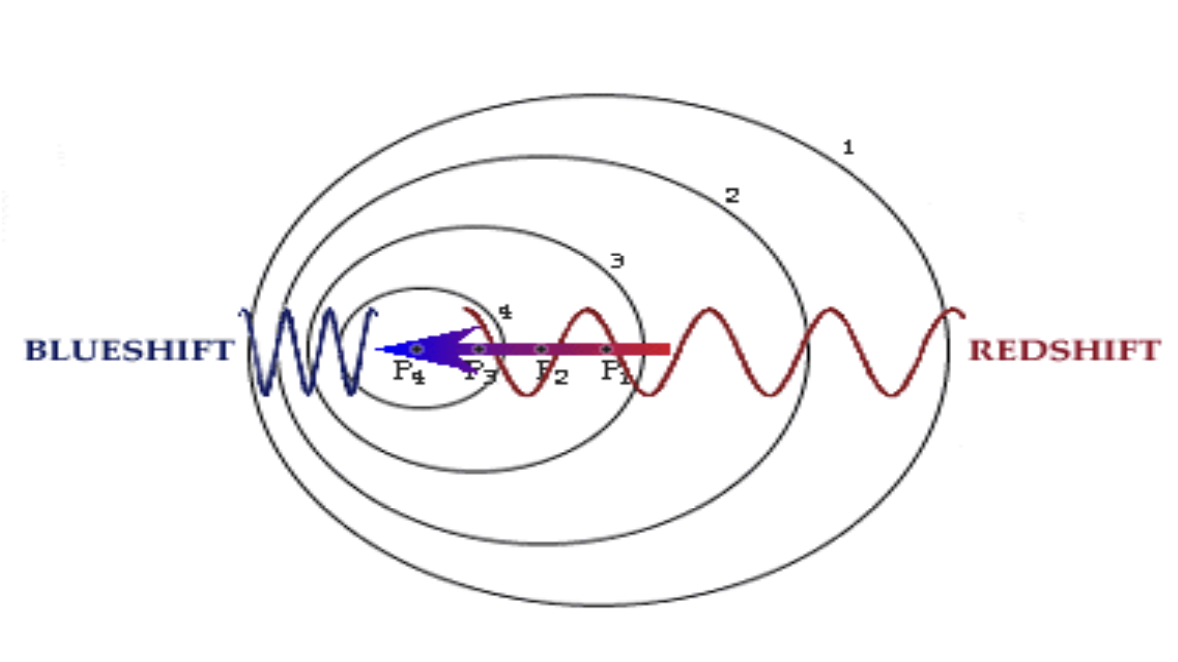
blue shift
light from stars moving towards us will be compressed (blue shifted) + more blue than actual, wavelengths get shorter
red shift
light from, stars moving away from us will be stretched (red shifted) and more red than actually is, wavelengths get longer
moving sound source
long wave-length: low frequency
small wavelength: high frequency

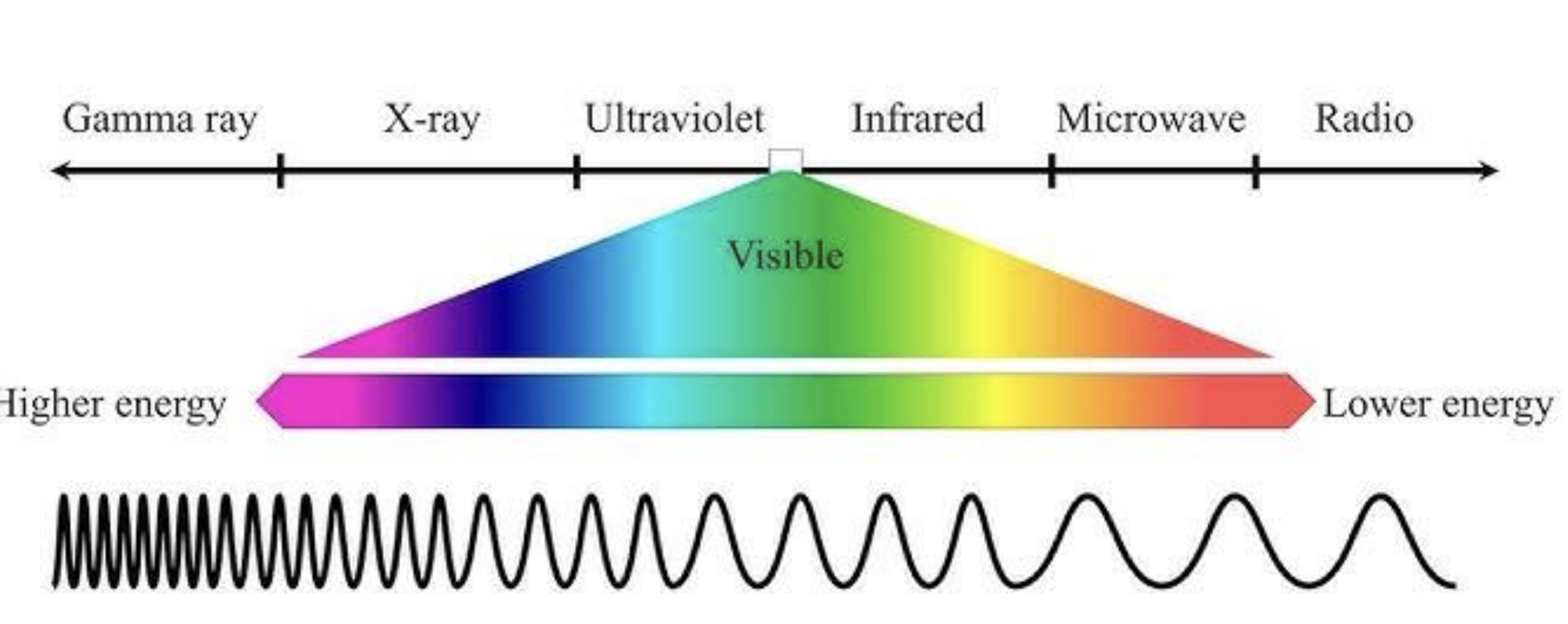
electromagnetic spectrum description
small wavelegnths= high energy, higher frequency
long wavelegnths= lower energy, lower frequency
why are most galaxies red shifted
move away from us, universe is expanding → refers to big bang theory
sequence of their life
stars start bottom right of main sequence and move upwards and left during their life
big bang theory
an explanation of how the universe was created
what does the theory say?
-13.7b years ago universe started as a singularity (single point)
what does the theory mean now
explosion → universe started to expand and cool
universe is explanding
cosmic mircowave backgroun radiaiton
left over radiation for big bang
radiation appears red shifted
→ moving away
→ universe is expanding
what is the universe made of
hydrogen (74%) + helium (25%)
formation of elements
hydrogen formed first
other elements form via nuclearfusion
the age of stars
some are 13b years old
universe has to be older
→ big bang happen 13.7b+ years ago
life cycle of stars
nebula → protostar → main sequence star → red giant → white dwarf→ black dwarf. → red super giant → supernova → neutron star → black hole
birth of a star stage 1- nebula
a star is born in a huge, cold cloud of gas and dust called a nebula
birth of a star stage 2- nebula contracts
nebula slowly contracts under own gravity and clump of matter forms inside cloud
birth of a star stage 3- clump heats up
gravity continues pulling in more matter + clump collapse inward, becomes dense and compressed begins to heat up
birth of a star stage 4- star shines
core of collapsing clump so hot + compressed nuclear reactions start, hydrogen fuses form helium releasing energy = sun to shine
death of a star stage 1- red giant forms
hydrogen used up → helium core collapse and outer layer expands and cools. star shines less brightly = red giant. death of a star after the red giant shape depends on size of star
death of a star stage 2- beyond a red giant
small starr → massive star → really massive star
death of small star
becomes red giant, outer layer drifts. core reamins = white dwarf, cooles and eventually stops shining and becomes black dwarf
death of a massive star
becomes red giant, nuclear reactions in helium core continue and form other elements around iron core. collapse core= explosion → super nova. remains form tiny, very dense neutron star.
death of a really massive star
red giant stage, nuclear reaction create iron core which explodes as supernova and forms neutron star. difference= core of neutron star collapses further and results in black hole
black hole
place and space where gravity pulls so much that lught can not get out
range in size: 1 atom- 1 millions suns in diameter
every large galazy contains a supermassive black hole at its centre