chapter 6 energy and metabolism
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
metabolism
-totality of an organism’s chemical reactions
an organism’s metabolism
-transforms matter and energy
-is subjected to the laws of physics
-amino acids take up space and have mass (they are matter)
-energy is required to link AA to form proteins (they also have matter)
metabolic pathways
-consists of 1000s of biochemical reactions that all require energy transformations
-many and many steps required
-end result is a product
-there are two types of pathways required to maintain the cell’s energy balance
in each step:
Is a separate chemical reaction
catalyzed by a specific enyzme
how does the end result of a metabolic pathway look like
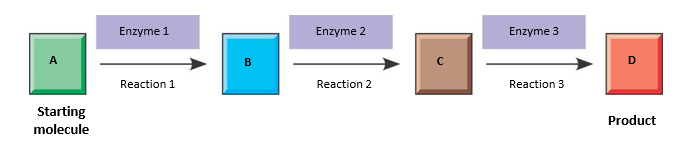
what are the two types of pathways required to maintains the cell’s energy balance
catabolic
anabolic
catabolic pathways- catabolism
break down complex molecules (food) into simpler ones
release energy
ex: cellular respiration→ the breakdown of glucose molecules
catabolic
large molecules are broken down into small ones and energy is released
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O2 → CO2 + H2O
anabolic pathways
build more complex molecules
require more energy
ex: photosynthesis
anabolic
small molecules are assembled into larger ones and enrgy is required
photosynthesis equation
CO2 + H2O → C6H12O6 + O2
energy
-the capacity to cause change
-exists in various forms
-sustains most of earth’s life
-bioenergetics
what are the various forms of energy
-some can perform work
-fundamental to all metabolic processes
-rearrange matter from one form to another
sustains most of earth’s life
comes from the sun
bioenergetics
study of energy flow through a living system
what are the types of energy
-potential energy
-kinetic energy
-thermal energy
potential energy
-stored energy, the energy matter has because of its structure
-membrane potential (Na+) moving in/out of cell
-chemical energy store in molecular structures
→like glucose molecules
-in a compressed spring
kinetic energy
energy in motion, movement of objects
thermal energy
-associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules
-heat: when thermal energy is transferred from one molecule to another
energy
can be converted from one form to another
free energy (aka Gibb’s Free Energy “G”)
-describes the energy available to do work
-similar to potential energy
usable energy
-available energy that can do work under cellular conditions
-often interested in the change in free energy, referred to as change in G
change in G
-determines whether a reaction is spontaneous or nonspontaneous
-affected by all chemical reactions/biological processes
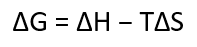
-change in H→change in total energy of the system (enthalpy change)
-T is temperature in Kelvins
-change in S→ change in entropy (energy lost due to disorder)
entropy increase
solid to gas
enthalpy increases
gas to solid
free energy and spontaneous change
-addition of external energy is NOT required
-free energy decreases and the stability of a sytem increases
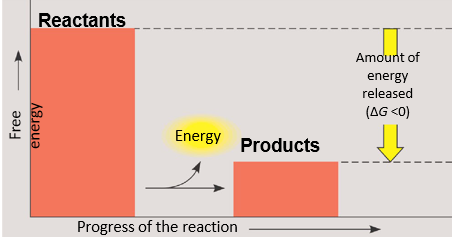
exergonic reactions
-energy is exiting the system
-spontaneous
-proceeds with a net release of free energy
-change in G is negative (change in G<0)→ this happends when energy is released in a chemical reaction
-change in G=Gfinal state-Gstarting state
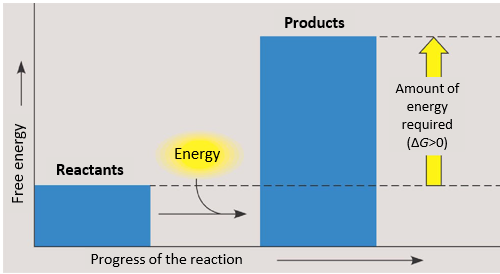
free energy and nonspontaneous change
-addition of external energy IS required
-free energy increase and the stability of a system decreases
endergonic reactions
-energy in entering the system
-nonspontaneous
-a reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings
-change in G is positive (change in G>0)→ this happens when energy is absorbed into a chemical reaction
--change in G=Gfinal state-Gstarting state
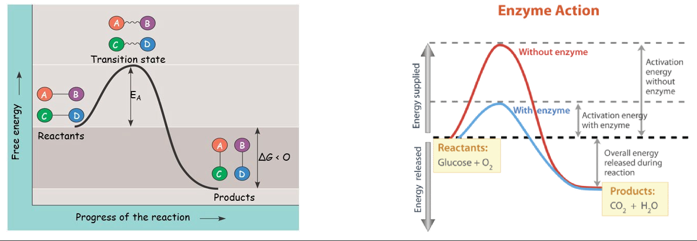
activation energy(EA)
-the initial energy required for a reaction to proceed/start
-heat energy is the main source in the cell
→usually obtained from the surroundings of the system
→helps reactants reach their transition state
-causes reactant(s) to becomes contorted and unstable
-allows bond(s) to be broken or made
-once in this state, the reaction occurs very quickly
→enyzmes function by lowering the EA barrier; the change in G is unaffected
thermodynamics
-the study of energy transformations
→how heat, work, temp, and energy react
→describes how energy in a system changes
→determines whether a system can perform useful work on its surroundings
closed system
-isolated from its aurroundings
-reactions in a closed system eventually reach equilibrium (change in G = 0)
open system
-energy and matter can be transferred between the system and surroundings
-organisms are open systems
→constant flow of food in and waste out
→prevents equilibrium (change in G does not equal 0)
a multistep open hydroelectric system
-cellular respiration is analogous to this system
-glucose is broken down in a sereis of exergonic reactions that power the work of the cell
- The product of each reaction becomes the reactant for the next, so no reaction reaches equilibrium
the laws of thermodynamics
-1st
-2nd