B4.2 Ecological Niche
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Factors affecting the niche of species
BIOTIC factors
include living things
food availability, predators
ABIOTIC factors
temperature, soil nutrients, light, and other non-living factors
Niche Construction
the process by which an organism alters its own or other species local environment
ex: earth worms chemically + physically modify the soil, thus other aquatic animals can live on the land
Types of Ecological Niches
Fundamental niche
niche of an org. when there are no limiting factors on the environment + resources the organism can use
theoretical, pre-competitive
potential of a spp based on adaptations + tolerance limits
Realized niche
niche that’s occupied by a viable population of a species in the presence of competitor spp
post-competitive, actual
actual extent of a spp when in competition with other spp
Competitive exclusion
two diff spp cannot occupy the same niche → if 2 spp share a niche, this leads to INTERSPECIFIC COMPETITION for resources
inevitably, 1 spp will hv an advantage over the other
the less well-adapted spp will struggle to survive and reproduce

Resource Partitioning
2 spp can avoid competing for the same resource by choosing different time for feeding or different foraging behavior
Types of Resource Partitioning
temporal
same resources but diff time
spatial
use of diff habitat of resources
morphological
use of body shape + size
Importance of ecological niches
niches reduce competition for resources
interspp competition → evolutionary change
niche includes spot in food chain (if missing → may cause whole chain to die)
segregation of organisms into niches avoids confusion of activities in the community + more order
allows for full exploitation of all available resources
Differences b/t obligate anaerobes, facultative anaerobes, obligate aerobes
Obligate Aerobes: require O2
Obligate Anaerobes: killed by O2
Facultative Anaerobes: grow better with O2 but can live without it
Mode of Nutrition in different organisms
an organism’s mode of nutrition depends a lot on its ecological niche + the adaptations to the biotic and abiotic factors
Autotroph
synthesize organic compounds (sugar, aa, fats) by using other sources of energy
photoautotroph
produce organic compounds from CO2, water, and light energy thru PS
chemoautotroph
producce org. compounds from other elements (iron, NH3) thru chemosynthesis
Heterotroph
obtain org. compounds by consuming other organisms internally or externally
saprotrophs
secrete enzymes onto dead + decaying matter and digesting externally (decomposer)
parasites
obtains food from other organism without killing it
holozoic
complex food particles are taken in and broken down
herbivore
carnivore
omnivore
detritivore (an animal that feeds on dead organic material, especially plant detritus)
Mixotroph
organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy
Photosynthesis as the mode of nutrition in plants, algae, and several groups of photosynthetic prokaryotes
algae, seaweed, kelp, many types of bacteria, plants
Holozoic (obtaining nourishment as animals do by ingesting complex organic matter) nutrition in animals
animals obtain their nutrients by consuming food
the large food molecules must be broken down into smaller ones before they can be absorbed into the bloodstream + transported to cells in the body where needed
ingestion: eat
digestion: breaking down food
absorption: moving food into cells
assimilation: making food part of cells
elimination/egestion: remove unused food
single celled organisms like amoeba can do holozoic nutrition even w/o multi-organ controlled digestive system by endocytosis/engulfment
Autotroph
synthesize organic compounds (sugar, aa, fats) by using other sources of energy
photoautotroph
produce organic compounds from CO2, water, and light energy thru PS
chemoautotroph
producce org. compounds from other elements (iron, NH3) thru chemosynthesis
Heterotroph
obtain org. compounds by consuming other organisms internally or externally
saprotrophs
secrete enzymes onto dead + decaying matter and digesting externally (decomposer)
parasites
obtains food from other organism without killing it
holozoic
complex food particles are taken in and broken down
herbivore
carnivore
omnivore
detritivore (an animal that feeds on dead organic material, especially plant detritus)
Mixotroph
organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy
can do PS
can consume other organisms
FACULTATIVE MIXOTROPH
CAN BE entirely autotrophic, entirely heterotrophic, or use both modes
OBLIGATE MIXOTROPHS
MUST USE both modes of nutrition. often the case if a type of nutrient cannot be synthesized by themselves
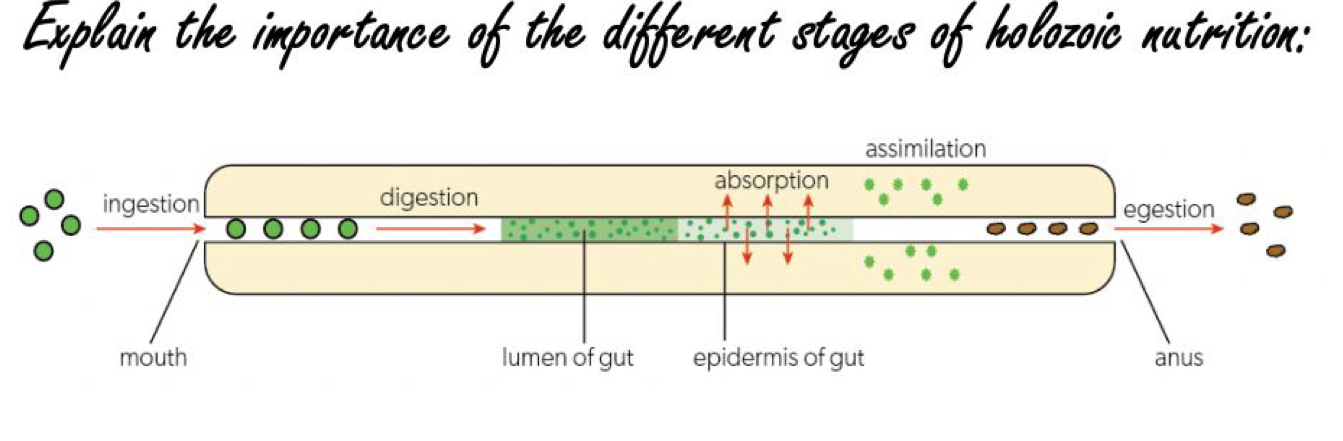
Different Stages of Holozoic Nutrition
Ingestion
take food into body
Digestion
breaking down food
Absorption
moving food into cells
Assimilation
making food part of cell
Elimination
removing unused food
many single celled organism such as amoeba are also capable of holozoic nutrition (even without a multi-organ controlled digestive system)
Saprotrophic nutrition in some fungi + bacteria (part of heterotrophs)
fungi are also called decomposers, bc they break down DOM and release important elements back into the ecosystem. extracellular enzymes are released into the substrate + break down polymers
bacteria are also saprotrophs by digesting food thru secretion of enzymes to break down OM externally. the products are then absorbed
Diversity of nutrition in archaea
phototrophic, chemotrophic, heterotrophic
Relationship between dentition and the diet of omnivorous and herbivorous representative members members of the family Hominidae
teeth give a lot of info about the feeding style of an individual
herbivores: large + flat to grind fibrous plant material
omnivores: hv mix of diff types of teeth to break down both meat + plants in their diet
molars: flat to crush seeds
incisors: for slicing (in the front)
canines: used for tearing
Adaptations of herbivores for feeding on plants
most insects are herbivores
those with jaw-like mouthparts for biting off, chewing, and ingesting pieces of leaf
those with tubular mouthparts for piercing leaves or stems to feed on the phloem sap
aphids hv modified piercing mouth parts called stylets.
these secrete enzyme pectinase to break down polysaccharide pectin which holds tgt the cell wall of plants. that way the style can easily pass thru to sap
herbivorous animals (cows + sheep)
have specialized back teeth
their digestive systems are adapted to digesting plant matter
bacteria + archaea living in the rumen help to break down cellulose
Adaptations of plants for resisting herbivory
castor beans produce seeds that contain ricin, which is highly toxic
toxins that cause nausea, cardiac problems, or hallucinators when ingested
plants have spikes/thorns
plants detract/move, scaring animals away
Adaptations of predators for finding, catching, and killing prey
Finding Prey
Enhanced senses: Acute vision (eagles), hearing (owls), smell (sharks), or electroreception (platypus)
Specialized detection: Infrared heat sensing (pit vipers), echolocation (bats)
Camouflage: Disruptive coloration allows predators to remain hidden while stalking prey
Catching Prey
Speed and agility: Cheetahs (70 mph sprints), peregrine falcons (240 mph dives)
Ambush tactics: Trapdoor spiders, anglerfish with luminescent lures
Specialized appendages: Sticky tongues (chameleons), modified limbs (praying mantis)
Pack hunting strategies: Wolves, lions, orcas use coordinated attacks
Killing Prey
Mechanical adaptations: Sharp teeth/claws (big cats), powerful jaws (crocodiles)
Venom delivery systems: Fangs (snakes), stingers (scorpions), spines (lionfish)
Digestive enzymes: Spider venom liquefies prey internally
Constriction: Pythons and anacondas restrict blood flow to prey's vital organs
Adaptations of prey for resisting predation
Defensive Structures
Shells (turtles), spines (porcupines), exoskeletons (beetles)
Avoiding Detection
Camouflage (stick insects), mimicry (viceroy butterfly)
Escape Mechanisms
Speed (gazelles), flight, autotomy (lizard tail shedding)
Chemical Defenses
Toxins (poison frogs), noxious secretions (skunks)
Behavioral Adaptations
Alarm signals, group living (herds), mobbing behavior
Reproductive Strategies
High reproductive rates, synchronized breeding events
Adaptations of plant form for harvesting light
Plants in very dense forests (like rainforests) hv to develop adaptations to harvest light for photosynthesis
epiphytes get up into the understory/canopy to access sunlight. their roots attach to the tree trunks and collect water trickling along the branch
vines can climb up the trunk of the tree
large surface area of leaves help plants in the shrub layer of the forest to catch light
lianas are vines that take root on the forest floor + use trees as a scaffold to grow up high into the canopy