UCF Microbiology Exam 1 (MCB3020)
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Infuenza (Spanish Flu)
More Americans died than were killed during World War I, WWII, Korean and Vietnam wars combined (about 2 million)
Pandemic (world wide epidemic) that killed 50 million
Due to an antigenic drift
Small Pox
Over 300 million people killed, making it one of the biggest killers in history
Since the development of the vaccine no deaths reported since 1977 (said to be eradicated)
Categorized as a Biological Warfare Agent (30% mortality)
Black Plague
1/3 of the population of Europe (about 25 million) perished during one epidemic from 1346-1350
Antibiotics are available and control this disease
Categorized as a Biological Warfare Agent
New Emerging Diseases
Legionnaire's Disease (1976)
Lyme Disease
AIDS (1980s)
Hantavirus (1993)
Mad Cow Disease (1986)
Ebola (2015)
Asian Flu/H2N2 (1957), Swine Flu/H1N1 (2009)
Due to antigenic shift
Bird Flu/H5N1 (1997)
Due to antigenic drift
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) (2002)
Antigenic Drift
Vaccine efficacy wanes with time as new surface antigens appear from mutations in genes encoding them. Changes to the flu virus that happen slowly over time. This causes the changes to the seasonal flu that require us to get vaccinated against the flu each year
Antigenic Shift
Results when two different flu strains combine and infect the same cell.
Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
Subgroup of dangerous and feared viral pathogens
Most lethal infectious agents known
Handled by the CDC under biosafety level 4.
Ex's:
- Hantavirus (endemic to the US)
- Marburg Virus (Germany)
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Parasites
4 Kinds of Microorganisms that can lead to disease
Industrial Microbiology
Conversion of raw material to desirable end products by selected microorganisms. Utilization of microbes in manufacturing process. The old belief was the study of the fermentation process ==> production of beer and wine
Primary Metabolites
products are necessary for microbial growth (amino acids, alcohol, organic acids)
Secondary Metabolites
products are not necessary for microbial growth (antibiotics, steroids, etc.)
Agricultural Microbiology
Benefits from the cycling of nutrients. Bacteria forms nodules on legume's roots. Nodules convert N2 --> NH3 (called Nitrogen Fixation). Ammonia is then used for plant growth.
N2 -> NH3 -> NO3 --> (repeat)
Ruminant animals have MO's in their "rumen" vessels which allow them to digest nutrient poor cellulose such as grass.
Agricultural Microbiology can cause Disease
Microbial disease of plants can cause major economic loss.
Ex: contaminated food such as E.Coli or Salmonella from infected meat.
Jack in the Box - outbreak of E. coli 0157:H7 in hamburgers / 4 children died / 600 sick. Undercooked patties contained fecal material w/ bacteria
Blue Bell Ice Cream - listeriosis cases caused by Listeria monocytogenes - 10 people sick / 3 dead
Food Microbiology
spoilage, safety, production. Some food requires microorganisms
Ex: some dairy depends on key acids from microbial fermentation
Ex: fermentation of yeast alcoholic beverages and baked goods.
Glucose => 2 lactic acid => Proprionic acid + acetic acid = cheese / yogurt
Glucose => 2 Ethanol + 2CO2 => 2 Acetic acid = pickles / acohol
Energy Microbiology
Focuses on converting waste material into methane natural gas and ethanol. (biofuels)
Ex's: cellulose & cornstarch -> glucose fermented into alcohol
Biotechnology
Uses genetically modified microorganisms to synthesize products of high commercial value. Focuses on applying gene technology or recombinant DNA technology to develop products. Synthesis of an in vivo system of thousands of products useful to humanity. It makes a lot of gene products such as Interferon and Somatostatin.
Genentech
Uses human genetic information to discover, develop, manufacture and commercialize medicines to treat patients w/ serious of life-threatening medical conditions. First to produce somatostatin and insulin
Bioremediation
Uses living organisms to degrade pollutants in the environment . Bacteria can be used to degrade oil spills, PCBS (polychlorinated biphenyls), & trichloroethylene
Metabolism: nutrients become new cell material/waste & energy
Growth: increase in cell number
Evolution: Next generation has traces of parental cells
All cells include these properties
Motility: Self propulsion
Communication/Genetic Interchange: Sharing information among themselves
Differentiation: Modified cells that become specialized
Some cells include these properties
All cells have them. Cannot be changed.
- Cell membrane
- Ribosomes
- DNA
- RNA
Invariant Structures
Some cells have them.
- Cell wall
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
Variant Structures
Metabolism
Cells take up nutrients, transform them, an expel waste.
1) Genetic (replication, transcription, translation)
2) Catalytic (energy, biosynthesis)
Final result = 2 new cells
Growth
Nutrients from the environment are converted into new cell materials to form new cells. Catalysts are used
Antibiotic Selective Pressure
Refers to the impact of antimicrobial use on a population of organisms, in which organisms that are resistant to the antibiotic gain a survival advantage over those susceptible to the antibiotic.
Differentiation
Some cells can form a new cell structure such as a spore. Responds to specific triggers
Motility
Self-propulsion through the use of flagella, fimbriae, and pili.
Genetic Exchange
Cells can exchange genes w/ each other by several mechanisms. Independent of evolution, accelerates adaptation to the environment.
Chemical Machines that carry out chemical transformations in the confines of the cell or coding devices which store and processes genetic information (DNA) and passes it off to offspring. They work together to support cell growth.
Cells can be viewed as
Population
Group of cells derived from a single parental cell
Habitat
Where the population lives, interactions can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful
Ecosystem
All living organisms living together w/ the physical and chemical components of the environment. Greatly influence by microbial activity. Can expand and contract, population size and makeup can change
4.6 bya
3.8-3.9 bya
2 billion years
Within 1st billion years
within 2nd billion years (2.6 bya)
2 bya
0.5 bya
Earth is how old?
Microbial cells appeared how long ago?
How long was earth anoxic? (had N2 and CO2)
When did photosynthetic organisms appear?
When did cyanobacteria appear?
Multicellular life appeared?
Plants and animals appeared?
1) Microscope
2) Sterilization and aseptic techniques (pasteur)
3) Pure Culture Methods (koch)
3 things imperative in development of MicroBio
Robert Hooke
First to coin the term "cell"
Described fungi and mold with his primitive microscope. Discovered microorganisms.
Antonie Leeuwenhoek
First to see microorganisms . Discovery of bacteria
Semmelweis and Lister
Had evidence of the importance of aseptic techniques. Their handwashing technique was ignored.
Robert Koch
Developed the germ theory, proving that microorganisms are the causative agents of a disease. Developed postulates. Worked with anthrax, mice, tuberculosis. Developed Agar to culture microorganisms in the lab. Developed Pure culture technique.
1) Pathogen should be present in all cases of disease, absent in health animals
2) suspected organism should be grown in pure culture
3) When culture is inoculated into animals, it should initiate disease
4) Organisms should be re-isolated & shown to be same as original
Koch's Postulates
sufficient but not necessary to establish causation
Solidifying agent allowing for isolation of pure culture
Solidifies at 40 degrees C
Melts / Liquifies at 100 degrees C
At 60 degrees Celsius it can be solid or liquid
Agar
Evolution
Process of descent w/ modificiation which generates new variety and species. Variation is due to mutation and natural selection.
Linnaeus System
Haeckel System - 3 Kingdoms
Stainer System
Whitaker System - 5 kingdoms, 3 levels of organization
Woese System - 3 kingdoms, now 3 domains
Classification Systems for Naming Bacteria
Phylogeny
permits grouping of organisms based on the evolutionary lines of descent by DNA comparison
Taxonomy
grouping of organisms for convenience of laboratory study and hence focuses on phenotypic differences
Animalia (motile)
Plantae (non-motile)
Linnaean System
("based on observations")
3 Kingdoms
Animalia
Plantae
Protista (cannot easily be placed into other kingdoms)
Haeckel System
Haeckel's Protista
Unicellular or multicellular organisms that do not develop into differentiated tissue. Includes algae, fungi, protozoa, bacteria including cyanobacteria
Animalia
Plantae
Higher Protista (eukaryotic: algae, protozoa, fungi)
Lower Protista (prokaryotic: cyanobacteria, bacteria)
Stainer System
Animalia ( ingestion, consumer)
Plantae (photosynthesis, producer)
Fungi (absorption, decomposer)
Protista (eukaryotic, unicellular) / Algae, Protozoa
Monera (prokarytic, unicellular) / Bacteria, Cyanobacteria
Whittaker's Kingdom's
Based on genetics and evolution
Eukarya (eukaryotes)
Bacteria (prokaryotes)
Archaea (prokaryotes)
Woese's Domains
Woese rRNA sequencing
Cell DNA is extracted -> PCR makes many copies of the rRNA gene -> Gene is sequenced -> Sequence is aligned to other organisms -> Similarity is assigned -> Phylogenetic Tree
Archaea Phylum: Euryarchaeota
4 Groups of Organisms
1) Methanogens (anaerobes)
2) Extreme Halophiles (NaCl)
3) Thermoacidophiles / Thermoplasmatales (High Temp, Low pH
4) Hyperthermophiles (> 80 C)
Archaea Phylum: Crenarchaeota
Mostly hyperthermophiles & anaerobes
- Uses H2 as energy
chemolithotrophs or chemoorganotrophs
5 Kingdoms:
Monera, Protista, Fungi,Plantae,Animalia
3 Domains:
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
3 Domains and 5 Kingdoms
Morphology & Size: simple or negative stain
Differential Stain: Gram stain, due to different cell wall structure
Structural Stain: spores, capsule, flagellum
Staining Properties
1) Crystal Violet
2) Iodine
3) Decolorize w/ alcohol
4) Counterstain with safranin
Gram Stain Steps
Nomenclature
ex: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Genus and Species are the major taxonomic groups
- 1st letter of genus CAPITALIZED
- Species not capitalized
- Both names ALWAYS italicized or ALWAYS underlined, not both.
Prokaryotic Cells
They do not contain organelles. NO nucleus, coupled transcription/translation. DNA is found in the cytoplasm and it is circular.
Louis Pasteur
Recognized optical isomers, disproved spontaneous generation , used swan neck flask. He developed anthrax, cholera, and rabies vaccines. Confirmed the germ theory of disease
Prokaryote
Cell wall
Cytoplasmic Membrane
Nucleoid
Cytoplasm
Plasmid
Ribosomes
Organic Molecules/Inorganic ions
Mainly Circular DNA
1 Chromosome w/ 1 copy of each gene (haploid)
Plasmids
Eukaryote
Cell wall (plants, fungi)
Cytoplasmic membrane
Mitochondrion
Nuclear membrane
Nucleus
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cytoplasm
Golgi Complex
Chloroplast
DNA linear / packaged by proteins / diploid
Algae, Protozoa, fungi, slime mold, plant and animal cells.
Eukaryotic Types
Bacteria and Archaea domains. DNA in cytoplasm, couples transcription and translation
Prokaryotic Types
Viruses:
- DNA or RNA
- Protein Coat
Viroids:
- Only RNA
- NO protein Coat
Prions:
- Only Protein
- No protein coat or RNA/DNA
Acellular Microorganisms
Viruses
-Acellular
-Smaller than cell, lacks attributes
-Only alive when they affect host
- Lack metabolic activity
- Contain genome
- NO RIBOSOME
- Disease causing
- Sometimes helps cell by changing genome
Proteins (informational)
Nucleic Acids (informational)
Lipids (noninformational)
Carbohydrates (noninformational) / Polysaccharies
4 Main Macromolecules
Covalent Bond
forms when 2 atoms come bvery close together and share one or more of their electrons.
Ex's: C=C, C=O, N=N, P=O,
C=O-N-H, cytosine, phenylalanine
Hydrocarbon
Nonpolar, do not form H bonds, and are insoluble in water
Higher the Number of bonds = Shorter & Stronger
Bond Strength and Size
Purine: Adenine, Guanine
Pyrimidine: Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
Purines vs Pyrimidines
Amine: formed in water combined w/ H+ ion to make it POSITIVELY CHARGED
Amide: combining an acid & amine. UNCHARGED
Amine Vs Amide
Van der Waals Forces
- atoms approach each other and create non-specific bond
- Transient unequal distribution of electrons
H Bonds
- donor is electronegative
- H is acceptor
- polar
- intra or intermolecular
Hydrophobic Forces
Ionic Bonds
Weak Non-Covalent Bonds
Weak Non-covalent bonds:
Hydrophobic Forces
Ionic Bonds
1) Nonpolar molecules do not contain ions, possess dipole moment, or become hydrated
- Covalent bonds CC, CH, most common nonpolar bonds
- Decreases hydrophobes from interacting w/ water
- Important in protein Folding
2) Bonding electrons not shared, electron goes w/ more electronegative element. Do not have fixed orientations
- Polar
- stronger in the absence of water
- weak in aqueous solutions & salt
1) Lipids
2) Polysaccharides
1) Storage for excess carbon, prevents unrestricted movement of polar molecules
2) Important in cell wall, some are storage for carbon and energy
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds of C1H2O1. Monosaccharides. Pentoses are structural backbone of nucleic acid. Hexose are monomers of well wall polymers and energy storage. Derivatives have OH group replaced. D form predominates. Bound together by glycosidic bonds.
Glyceraldehyde
Ribose
Glucose
Dihydroxyacetone
Ribulose
Fructose
Aldoses (3,5,6)
Ketoses(3,5,6)
Enantiomers
Optical isomers that have the same molecular and structural formula. Cannot be superimposed. D or L depending on rotation to right or left.
L- Amino Acids (D in peptidoglycan)
D - Sugars (L cell wall of bacteria & archaea)
Most predominate isomers in Biological systems are
Polysaccharides
Held together by covalent glycosidic bonds (a or b). Diff. bonds give diff properties.
Complex forms
Glycolipid
Glycoprotein
Glycogen, starch:
important in carbon and energy storage in plants, animals, and bacteria
Alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond Glucose
Cellulose: found in plant and algae cell walls
Beta-1,4-glycosidic bond Glucose
When C that carries aldehyde/ketone group reacts w/ any OH group on a second sugar molecule.
1) glucose + glucose
2) glucose + galactose
3) glucose + fructose
Disaccharides:
Maltose
Lactose
Sucrose
Fatty Acids
Monomers that make up lipids found in Bacteria and Eukarya. Hydrophobic (methyl) and Hydrophilic (ionized)regions
Phytane
What are lipids in Archaea made of?
Simple Lipids
3 fatty acids esterified to glycerol (c3 alcohol)
- known as a triglyceride , formed by removal of water btw acidic carboxyl group and OH group of glycerol.
Complex Lipids
simple lipids with 2 fatty acids and additional elements such as phosphate group.
- known as Phospholipid
Oleic Acid (C18/ Unsat)
Stearic Acid (C18 / Sat)
Palmitic Acid (C16/ Sat)
Common Fatty Acids
dolichol phosphate
used to carry activated sugars in the membrane-associated synthesis of glycoproteins and some polysacccharides.
1) cholestrol
2) testosterone
2 main steroids
1) found in many membranes
2) male steroid hormone
Glycolipid
composed of hydrophobic region w/ 2 long hydrocarbon tails, a polar region containing 1 or more sugar residues, and no phosphate.
Pentose:
- RNA: Ribose
- DNA: Deoxyribose
N Base:
- Purine: A, G
- Pyrimidine: C, T, U
Phosphate
*Base attaches to sugar at C1 & on base N1 pyrimidine, N9 purine
phosphoester bond btw sugar and phosphate
Nucleotides
DNA
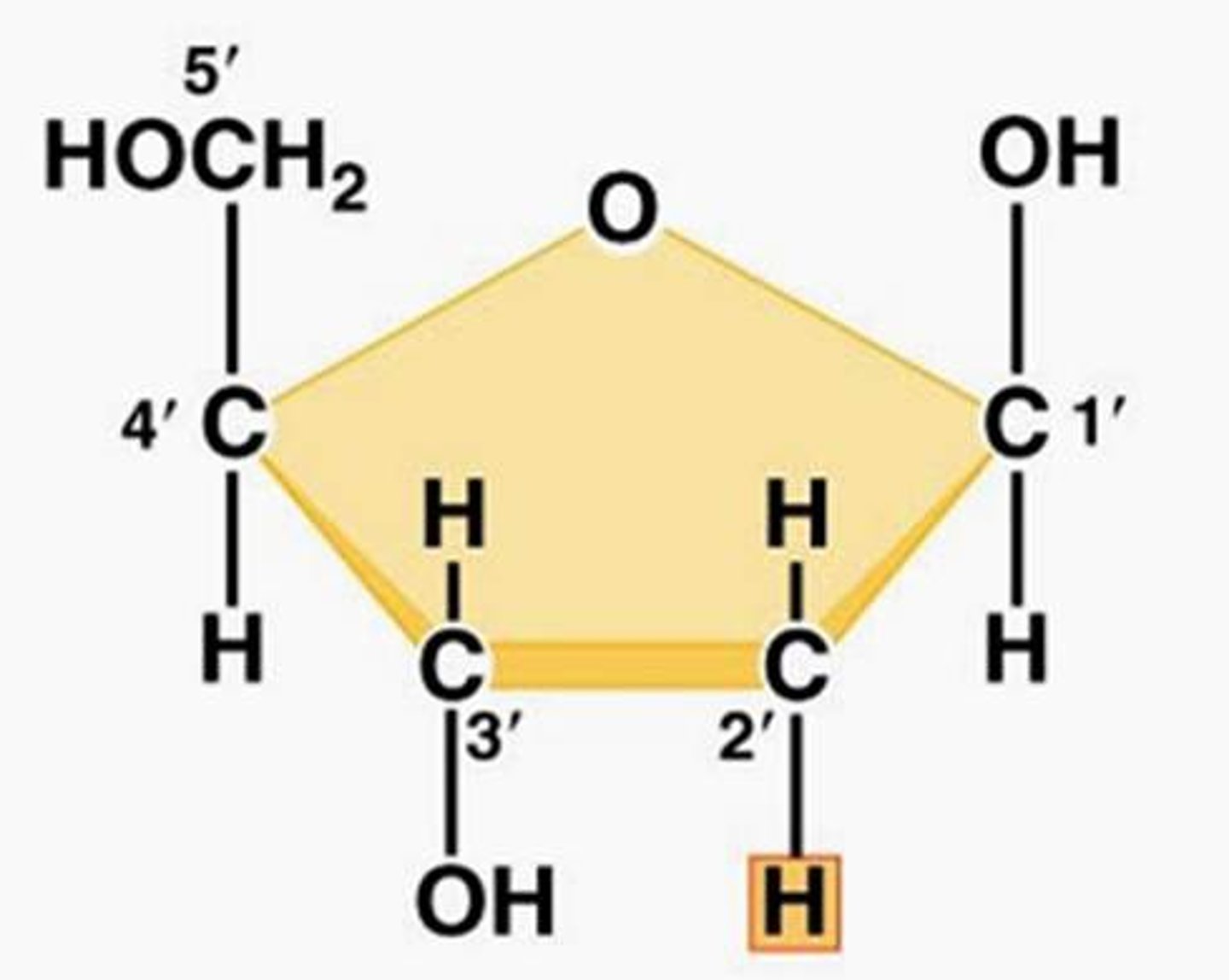
RNA
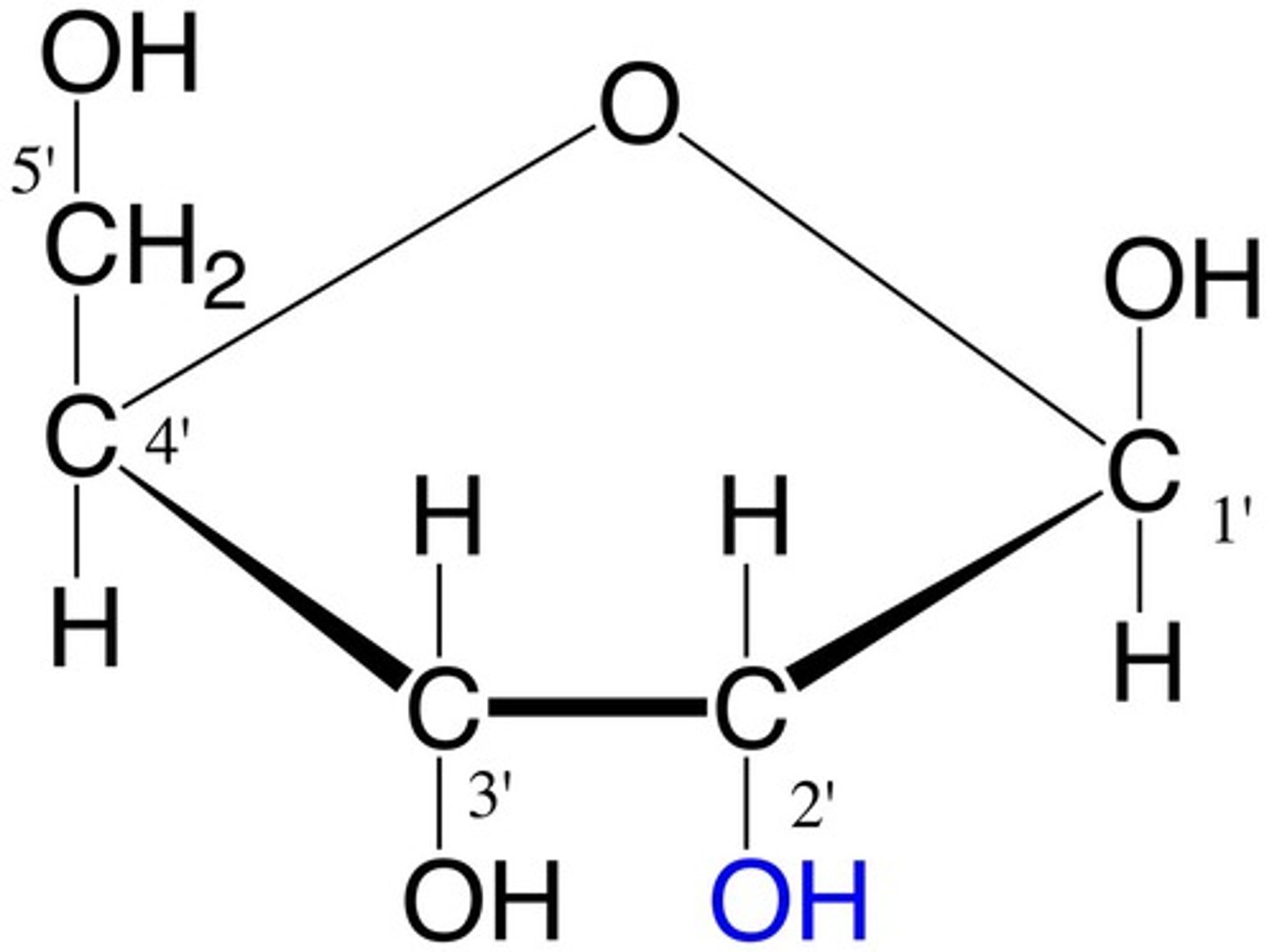
Nuceloside Triphosphate
or Nucleotide
ATP is what?
Pure As Gold
Adenine
Guanine
Glycosidic Bond: N9
Purines
Cytosine
Thymine (methyl group)
Uracil
Glycosidic Bond: N1
Pyrimidine
Thymine
Normally found in the keto form. Can be found in enol form where it will triple bond w/ guanine. Leads to spontaneous mutation.
Enol = OH--=
Keto = O=C
Nucleic Acid
Polymer made up of nucleotides. Backbone has sugar and phosphate molecules alternating & joined by covalent 3'5' phosphodiester bond. Synthesized by polymerase
5' to 3' direction
DNA/RNA synthesis occurs in which direction?
DNA
carries the genetic blueprint for the cell