Waves + Reflection / Refraction
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What are waves?
A way energy can be transferred between stores, they are oscillations or vibrations around a fixed rest position.
What are transverse waves?
Waves which vibrate perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
What do waves transfer?
Energy, not matter.
What mediums can transverse waves move in?
Solids and on the surfaces of liquids and gases.
What can transverse waves exist as?
Electromagnetic waves which move through all mediums including a vacuum.
What is the highest point of a wave called?
Amplitude.
What is the lowest point of a wave called?
Trough
What are 4 examples of transverse waves?
Ripples on water, vibrations on guitar strings, S-waves and electromagnetic waves.
What is the time period of a wave?
The time taken for a the cycle of a wave, peak to peak or trough to trough.
What is the speed of sound in air?
330m/s
What are longitudinal waves?
Waves which vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
What mediums can longitudinal waves move through?
Solids, liquids and gases but no vacuums.
In a longitudinal wave what is the area where the wave is close together called?
Compressions.
In a longitudinal wave what is the area where the wave is spread out called?
Rarefactions.
What are 3 examples of longitudinal waves?
Sound waves, ultrasound waves, P-waves and pressure waves
Are density and pressure constant in a longitudinal wave?
No.
When does a longitudinal wave travel the fastest?
In a solid
When does a transverse wave travel the fastest?
In a vacuum
What is amplitude?
The distance from the undisturbed position to the peak or trough of a wave.
How can wavelength be measured in a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave?
In a transverse wave it’s peak to peak whereas in a longitudinal wave it’s one compression to the next.
What is frequency?
The number of waves passing a point in a second.
What is the method of measuring the speed of sound between two points?
Two people stand around 100m apart
The distance between them is measured using a trundle wheel..
One person has two wooden blocks which they bang above their hand
The second person starts a stopwatch when they see the person bang, and stop it when they hear the sound.
What is the method for measuring speed of sound using echoes?
A person stands 50m away from a wall or cliff.
The distance is measured with a trundle wheel.
The person claps the block together repeatedly, the rhythm echoes.
A second person has a stopwatch and starts the timing when they hear one clap and stops the timer 20 claps later.
Calculate an average time after repeating the process.
What is the method for measuring speed of sound using an oscilloscope?
Two microphones are connected to an oscilloscope about 5m apart, using a tape measure to measure the distance.
The oscilloscope is set up so it triggers when the first microscope detects a sound, the time base is adjusted so sound arriving to microphones can be seen on the screen.
Two wooden blocks are used to make a large clap next to the first microphone.
The oscilloscope is then used to determine the time at which the clap reaches each microphone and the time distance between them.
What is the method for measuring wave speed in water?
Use a calm and flat water surface.
Two people stand a few metres apart using a tape measure to measure distance.
One person counts down from three and disturbs the water surface to create a ripple.
The second person starts a stopwatch to time how long it takes for the first ripple to reach them.
How do sound waves travel?
They transfer energy by the molecules vibrating and knocking into neighbouring molecules, the more molecules the faster the wavve.
What medium do sound waves travel the fastest in?
Solids as they have the most particles.
What happens when sound moves from a denser medium to a less dense medium?
The wavelength of the sound decreases and the velocity decreases, the frequency stays the same.
What happens when sound moves from a less dense medium to a denser medium?
The wavelength of the sound increases and the velocity increases, the frequency stays the same.
How does speed of sound change on warmer days?
Air molecules move faster so carry sound waves faster, increasing the speed of sound.
What is the method for measuring wave properties RQP? (using a ripple tank)
Fill the ripple tank with water to a depth of up to 1cm
Turn on the power supply and light source to produce a wave pattern on the screen.
Measure the wavelength of the waves using a ruler to measure the length of the screen and dividing the distance by the number of wavefronts.
Determine frequency by timing how long it takes for a given number of waves to pass a particular point and divide by the number of wavefronts by the time taken.
What is the method for measuring wave properties RQP? (using string)
Adjust the frequency of the signal generator until a solid wave is produced, then record the frequency shown.
Use a ruler to measure the wavelength (divide by number of wavelengths seen)
Repeat and adjust frequency until another solid wave is produced.
What type of wave is sound?
Pressure wave.
How are sound waves heard by the ear?
The sound wave travels down the ear canal towards the eardrum, pressure variations created exert a varying force on the eardrum causing it to vibrate. The eardrum vibration is transferred to the three small bones which move to the cochlea. The cochlea produces electrical signals that go to the auditory nerve where they are interpreted.
What is the range of frequency humans can hear?
20 Hz to 20000 Hz
What are 4 uses of sound waves?
Echo sounding, ultrasound, reflection seismology to detect oil and gas, seismic activity.
What is ultrasound?
Sound waves with a frequency above the human hearing range.
What are uses of ultrasound?
Cleaning jewellery, checking cracks in metal, breaking kidney stones and creating pictures of things like foetuses and organs.
What do high frequency waves sound like?
High pitched.
What do high amplitude wave lengths sound like?
Very loud.
How does echo sounding work?
A sound wave is emitted which is reflected of the bottom of the ocean, the time it takes for the sound to return is used to calculate the depth, the distance the wave travelled is twice the depth of the ocean.
What are the two types of waves earthquakes produce?
P-waves and S-waves
What are P-waves
Longitudinal waves that are fast and pass through solids and liquids with a very low frequency sound.
What are S-waves?
Transverse waves which are slow and only travel through solids.
What do P-waves and S-waves reveal about the structure of the Earth?
On the opposite side of the Earth to an earthquake only P-waves are detected suggesting the mantle is solid as both waves can pass, the outer core is liquid as S-waves can’t penetrate it. Refractions between layers cause shadow zones where no P-waves are detected suggesting the inner core is solid.
When does reflection occur?
A wave hits the boundary between two media and doesn’t pass through so stays in the original medium.
What is the law of reflection?
The angle of incidence = the angle of reflection.
What is specular reflection?
Reflection from a smooth and flat surface like a plane mirror, produces an upright and virtual image.
What does a virtual image mean?
Image rays appear to diverge to appear from behind the mirror.
Can virtual images be projected?
No but real image can be.
What are real images?
Images that are produced by light convergence that are inverted and can be projected onto a screen.
What is diffuse reflection?
Occurs on a rough surface so light is scattered in all directions so a distorted image is formed or no image at all.
What is transmission?
When a wave passes through a substance.
When does absorption occur?
When energy is transferred from the wave into the particles of a substance, for example sound waves being absorbed by concrete walls.
When is light absorbed?
If the frequency of the light matches the energy levels of the electrons, it will be absorbed and then reemitted over time as heat.
What does it mean if an object appears red?
Only red light has been reflected so all other frequencies of visible light have been absorbed/
What is refraction?
The change in direction of a wave at a boundary.
What happens to a light ray as it enters a glass block?
Glass is denser so the light ray slows down, if it meets a boundary at an angle to the normal it will bend towards it. It speeds up as it leaves and bends away from the normal at the same angle/
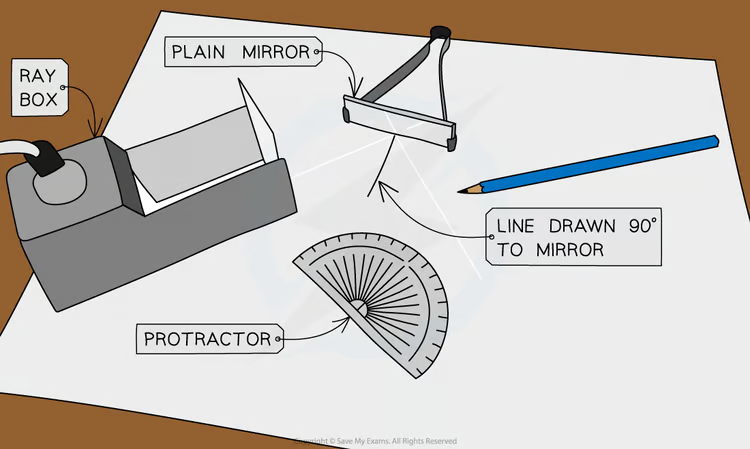
What is the method for the investigating reflection RQP? (using a mirror)
In the middle of a piece of paper use a ruler to make a 10cm straight line.
Use a protractor to draw a 90 degree line that bisects the 10cm line.
Place the mirror on the first line, switch on the ray box and aim a beam of light at the point where the two lines cross at an angle.
Use a pencil to mark the light beam after it leaves the ray box and the point of the reflected beam around 10cm away from the mirror.
Turn off the light box and remove the mirror.
Use a ruler to join the two marked positions to the point where the line originally crossed.
Use a protractor to measure the two angles from the 90 degree line, the angle for the ray towards the mirror is the angle of incidence.
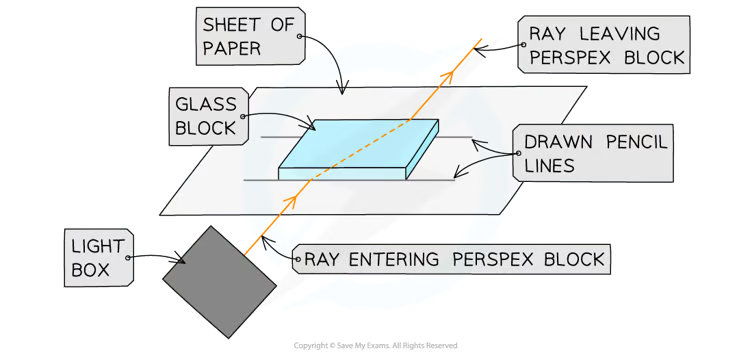
What is the method for the investigating reflection RQP? (using a Perspex block)
Place the glass block on the piece of paper and draw around it using a pencil.
Switch on the ray box and direct a beam of light at the side face of the block.
Mark on the paper a point on the ray close to the box, the point where it enters and leaves the block and a point on the exit light ray which is about 5cm away.
Draw a dashed line normal to the outline of the block where the points are.
Remove the block and join the marked points with three straight lines.