HumanBio ATAR11 - DIgestive and Elimination System
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Fill out this diagram
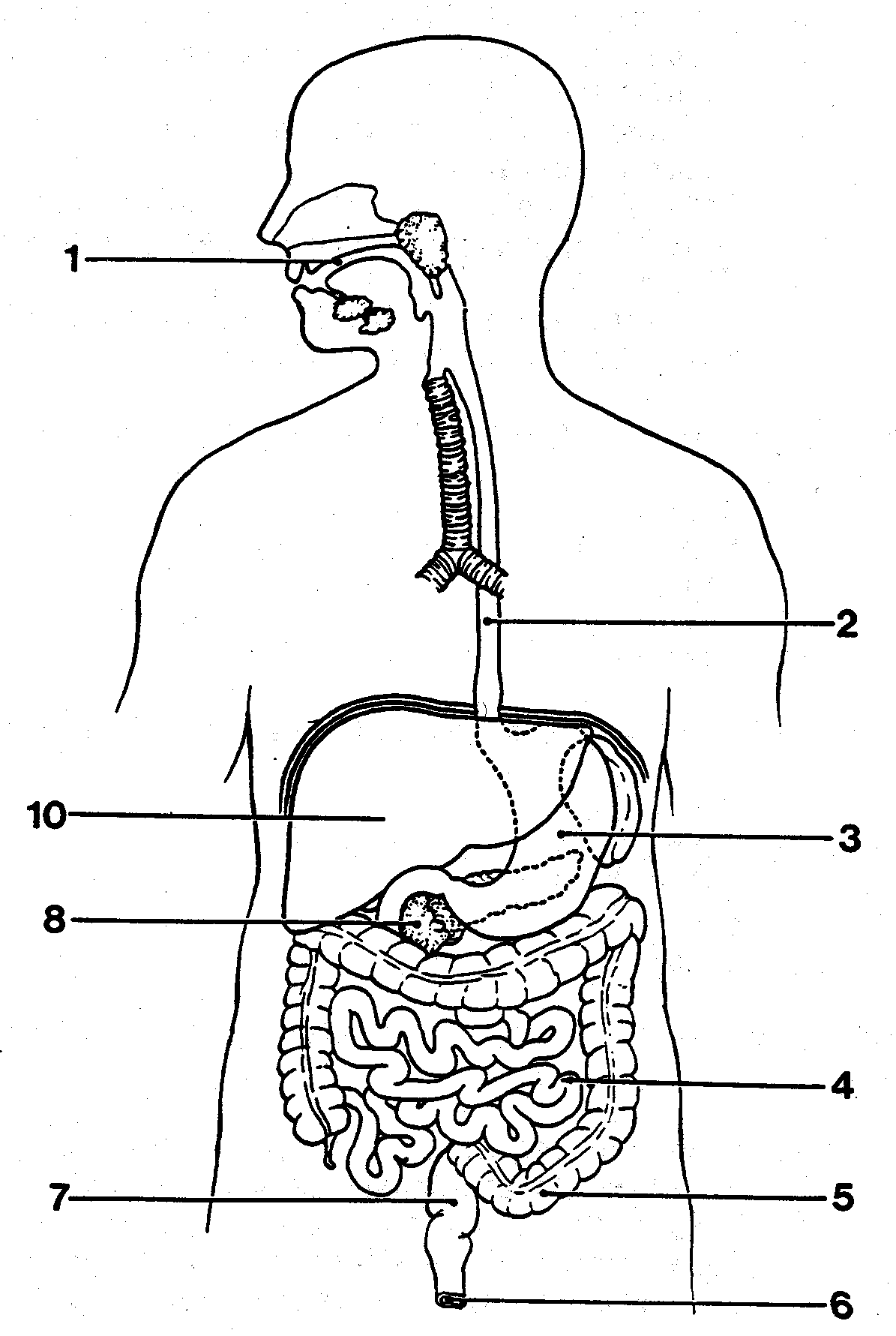
Name all types of human teeth and their purpose
Canines - ripping
Incisors - biting
Premolars and Molars - chewing
Mechanical Digestion in the mouth
Cutting, Biting, and Chewing for the teeth, the tongue shapes the food into a ball (bolus) and swallows
Chemical Digestion in the Mouth
Saliva from Salivary Glands use saliva amylase to break down starch and complex carbohydrates into maltose
Mechanical Digestion of the Stomach
Digests food in waves by churning using a third opaque layer of muscle
Mixed with stomach juice to churn into a thick soupy liquid called chyme
Chemical Digestion of the Stomach
Secretes gastric juices from gastric glands
pH = 2-3 to give enzymes the best environment to break down the bolus, and turn pepsinogen into pepsin into polypepsin. This protects the lining of the stomachs cells.
Mechanical Digestion of the Small Intestine
Pushes the bolus through the tubes using circular muscles
Uses segmentation to break the bolus up into pieces, increasing surface area for faster digestion.
Chemical Digestion of the Small intestine
Pancreatic juices are secreted into the small intestine which digests food by breaking it down using enzymes. E.g. pancreatic lipases turns fats into fatty acid and glycerol
Intestinal juice also digests food containing enzymes such as carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
Mechanical Digestion of the Large Intestine
Pushes through and forms faeces - made of water, undigested food, bile pigmentation, bacteria, and cell remains
Chemical Digestion of the Large Intestine
Absorbs water and other liquids + nutrients
Bacteria breaks down the remaining compounds
What are the parts of Villus
Blood capillaries, Epithelial cells, Lacteal, Micro-Villi, Amino acids and carbohydrates
Why is the Small Intestine suited for its job
The length is confined and villi gives the small intestine as much surface area as possible to digest.
Describe the role of the liver in excretion
The liver processes substances to be excreted. In order to use protein as an energy source, the amino acid NH2 must be removed from the body, so it is broken down in the liver into ammonia. Ammonia is toxic to the body, so it must be further broken down into urea, which then in excreted via urine.
Amino acid + oxygen —> carbohydrates + ammonia
ammonia + energy + carbon dioxide —> urea + water
Outline the organs involved in the excretion system and their use
Lungs: excretes carbon dioxide via respiratory system
Liver: processes substances to be excreted
Sweat glands: Sweats out by-products of metabolism (water, urea, etc)
Alimentary Glands: Excretes bile pigments
Kidney: Principle excretory system, makes urine
Describe how the kidneys and nephrons are suited for their job
Nephrons are made of unique cells to preform specific transport functions. Kidneys have these ig.
Label all parts of the excretory system
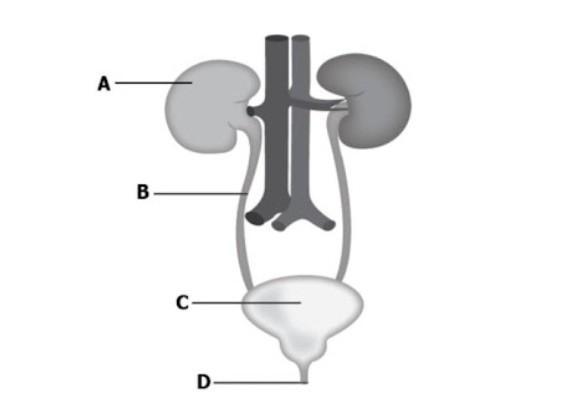
Label all parts of this diagram
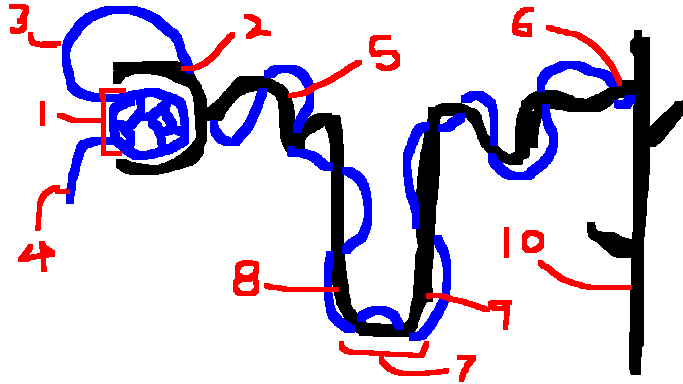
What does the glomerulus filter
Water, glucose, amino acids, salt
What does the descending limb and ascending limb reabsorb
descending: reabsorbs water
ascending: diffuses Na+ and Cl-
What is reabsorbed in the distal convoluted tubule
Sodium