Petroleum Geology (Introduction to Reservoir Properties) Final Examination
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:42 PM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
reservoir rock
a place that oil migrates to and is held underground.
2
New cards
* Sandstones
* Limestone and /or Carbonate rocks
* Limestone and /or Carbonate rocks
Examples of reservoir rocks includes:
3
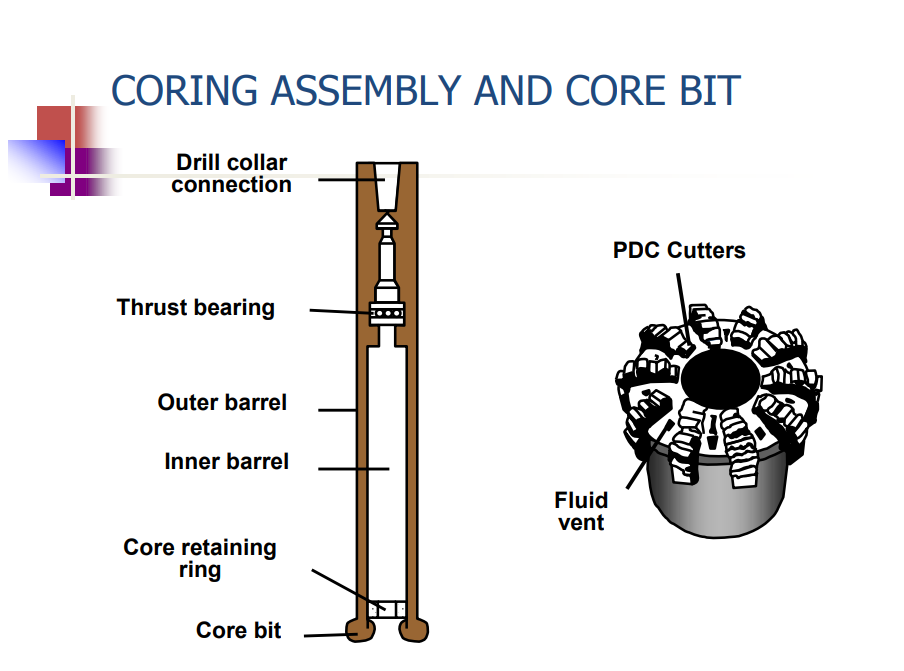
New cards
Coring
processes used to recover formation samples from petroleum reservoirs.
4
New cards
the capacity and ability of the reservoir rock to store and conduct petroleum fluids through the matrix
Physical sample of reservoir rock core is essential to evaluate the two most significant characteristics:
5
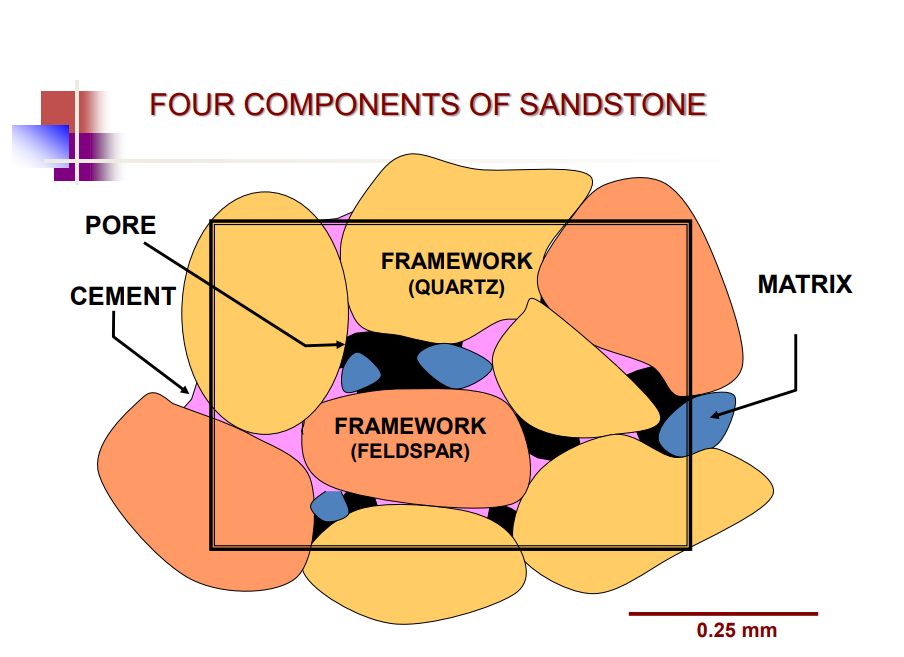
New cards
1. Framework
2. Matrix
3. Cement
4. Pores
Four major components of sandstone
6
New cards
7
New cards
8
New cards
3 to 7
90
90
Core diameters are typically from _ to *_* inches and are usually about ___ feet long
9
New cards
Sidewall Sampling Gun/Tool
can be used to obtain small plugs from the formation.
10
New cards
Sidewall Sampling Gun/Tool
The tool is run on a wireline after the hole has been drilled.
11
New cards
Sidewall cores
useful for identifying hydrocarbons zones, when viewed under UV light.
12
New cards
Whole Core
Provides larger samples
13
New cards
Whole Core
Better and more consistent representation of formation
14
New cards
Whole Core
Better for heterogeneous rocks or for more complex lithologies
15
New cards
Plugs or Sidewall Cores
Smaller samples
16
New cards
Plugs or Sidewall Cores
Less representative of heterogeneous formations
17
New cards
Plugs or Sidewall Cores
Within 1 to 2% of whole cores for medium-to highporosity formation
18
New cards
Plugs or Sidewall Cores
In low-porosity formations, Φ from core plugs tends to be much greater than Φ from whole cores
19
New cards
Plugs or Sidewall Cores
Scalar effects in fractured reservoirs
20
New cards
* Porosity
* Horizontal permeability to air
* Grain density
* Horizontal permeability to air
* Grain density
INFORMATION FROM CORES
Standard Analysis
Standard Analysis
21
New cards
* Vertical permeability to air
* Relative permeability
* Capillary pressure
* Cementation exponent (m) and saturation exponent (n)
* Relative permeability
* Capillary pressure
* Cementation exponent (m) and saturation exponent (n)
INFORMATION FROM CORES
Special Core Analysis
Special Core Analysis