N16- Renal transplantation and CKD
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the treatment choices in CKD stage 5
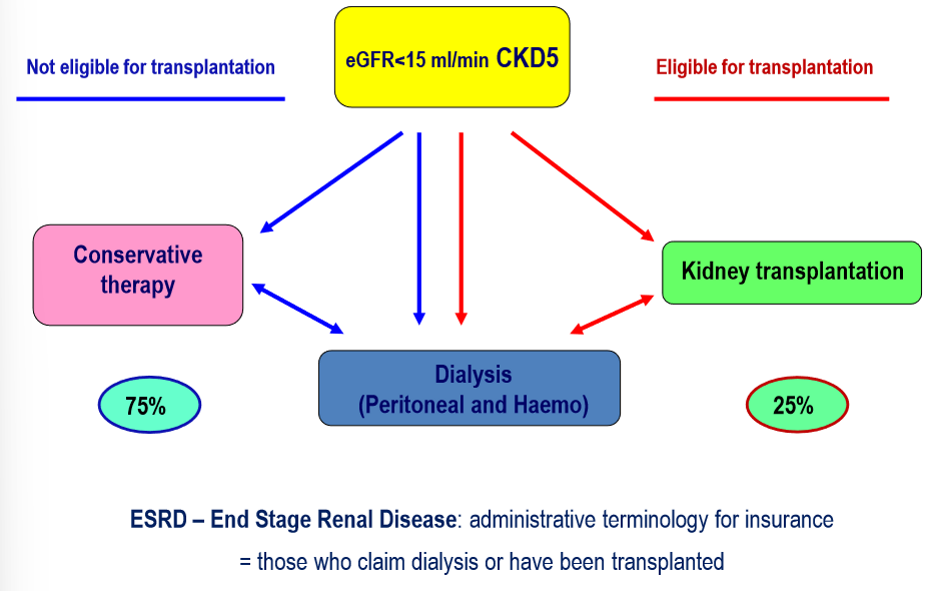
What are renal replacement therapies
kidney transplant
haemodialysis
peritoneal dialysis
What is the indication of kidney transplantation
CKD if eGFR <20ml
best results with transplantation without starting dialysis
limit of eGFR for getting on waiting list
What are the absolute contraindications of transplantation
active malignant disease
if sustained disease free state cannot be reached
instable, irreversible CV disease
severe, irreversible- peripheral atherosclerosis
“ “ coronary vascular disease
“ “ progresive vitium
“ “ instable cardiac failure, high pulmonary artery BP
decompenssated hepatic cirrhosis
simultaneous transplant should be considered
severe irreversible respiratory failure
psychosocial instability
if temporary contraindication becomes sustained
if expected survival <2years
What are relativve contraindications of transplant
ABO incompatibility- in Hungary
severe obesity BMI>40- relative if BMI >35
optimal age:<75
HIV seropositivity is not a contraindication if HAART successful
Temporary contraindications of transplantation
surgical/ technical cause
arterial occlusion, stenosis, urological malformation or disorder
increased peri and early postoperative risk
MI, stroke
increased risk of immunosupression
infections, malignancies
if an active disease is directly harmful for kidney graft
immunologiclaly active recurring GN
What are the types of donors
living
dead
What are the types of living donors
Living unrelated
emotional relative- spouse, mate, friend
Living related
What are the types of deceased donors
heart beating donor
donation after brain death
non heart beating donot
donation after circulatory death
What do you need to check before transplantation
screen for malignancy
(chest Xray, abdomen US, gyne/uro evaluation, mammography, repeated faecal occult blood negativity)
infections
(viral HEP, HIV, EBV, CMV, VZV, toxoplasma, treponema)
otolaryngology and dental check-up
artery check-ups, atherosclerosis, ECG
surgical and anaesthetic consultation,
HLA status
What are the donor organ allocations- conditions
negative crossmatch
no antibody in recipient’s serum against donor HLA antigens
blood group compatibility
other factors
HLA match
urgency, level of immunisation, waiting time
What are the advantages of living kidney donation for the recipient
better graft survival vs deceased after 1 year
“half life” of kidney is better 20 vs 13 years
no need for dialysis in the postop period due to immediate kidney function
shorter waiting time, preemptive transplantation
What are the advantages of living kidney donation for the donor
surgically safer, quick healing
donor discharge after 4 days
after 4 weeks they live their normal life
Who can be a living donor?
competent adult with disposing capacity (no children)
near genetic relatives
emotional relatives (after approval by ethics committee)
adequate function of both kidneys
donor can revoke consent at any time
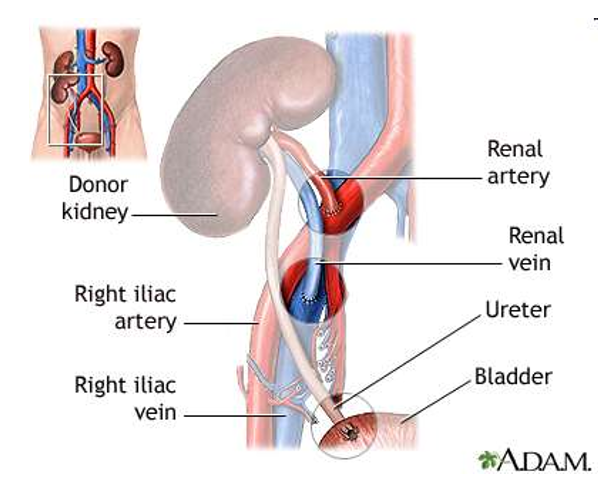
What is the location of transplantation
Heterotopic- iliacal fossa, extraperitoneal
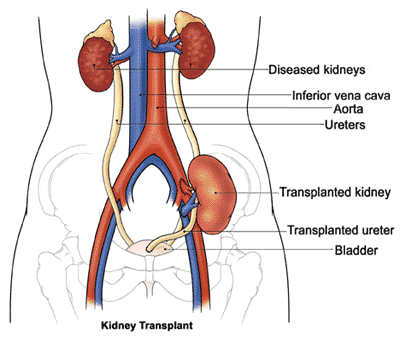
What are the possible anastomoses of grafts
common iliac artery + vein
external iliac artery + vein
internal iliac artery + vein
ureter: neoimplantation or end-to-end anastomoses
What are the complciations in early postoperative period- 2 weeks
delayed graft function
surgical
arterial, venal- technical failure
ureter- leakage,- reanastomosis
wound healing
peri graft fluid, lymphocele
immunonlogical
acute infection, T cell or/ and antibody mediated
infections
respiratory, urinary tract
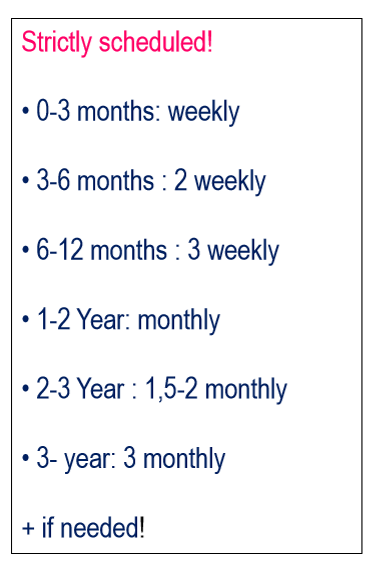
When is the follow up after Tx
What is the alloreactive immune response
innate immunity
ischemic reperfusion injury at the time of resuming circulation
adaptive immunity
cell mediated- T cell mediated rejection
antibody mediated rejection
What is the induction therapy
IL2R antibody monoclonal
Basiliximab
Anti CD52 monoclonal antibody
Alemtuzumab
anti thymocyte polyclonal antibody immunoglobulines
thymoglobulin
ATG fresenius- grafalon
What is the maintenance immunosuppression
steroids
prednisolone, methylprednisolone
calcineurin inhibitors- CNI
cyclosporin, tacrolimus
proliferation inhibitors mTOR
everolimus, sirolimus
lymphocyte proliferation inhibitors
selective- mycophenolate- mofetil, Na
non selectiev- Azothioprine
What is the combination maintenance immunosuppression
be careful for CAVE rug interactions
without steroids only 15-20%
CNI + mycophenolate
CNI + mTOR
mycophenolate + mTOR
CAVE- myelosuppression, anaemia, GI SE
azothioprine
CAVE- allopurinol
What are the side effects of immunosuppressants
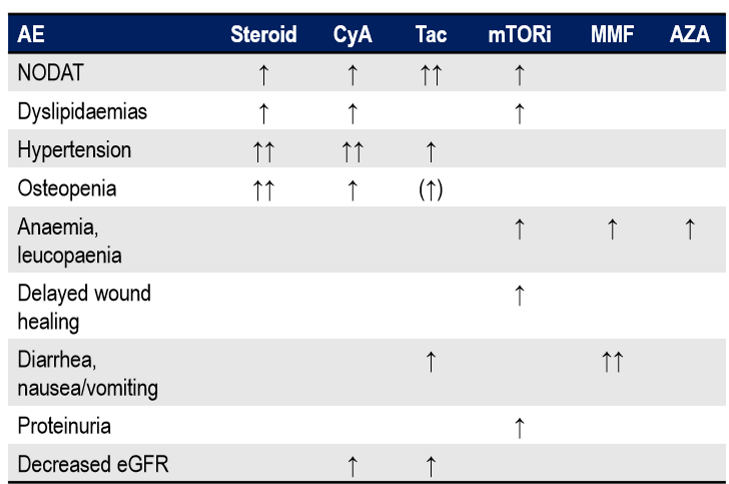
What are the renal consequences of transplantation
rejection
surgical complications
DGF
baseline disease relapse
de novo kidney disease
nephrolithiasis
graft failure
What are the extrarenal consequences of transplantation
HT
glucose metabolic disturbances
lipid abnormalities
CV disease
haematological complications
post transplant lymphoproliferative disorder
bone disorders
infections
tumours
psychological, psychiatric disorders
What are the types of non transplant related predictors of long term outcome
traditional
non tranditiona
What are the traditional non transplant related predictors of long term outcome
age, gender, ethnicity
BMI
ESRD cause
ESRD tratment, duration
comorbidities
diabetes
HT
dyslipidemia
smoking habits
CV
What are the non traditional non transplant related predictors of long term outcome
graft function- GFR
proteinuria
anaemia
Ca-P metbaolic disturbances
FGF23, PTH, Vit D
malnutrition inflammation complex syndrome
ADMA
homocystein
angiopoietin 2
depression, mood disorders
OSAS
What are the transplant related predictors of long term outcome
donor, allocation and surgical consequences
native and adaptive immunity
delayed graft function
rejection
methods for preserving graft function and their consequences
immunosuppression- efficiency vs toxicity, infections, malignancies
immunological tolerance
What are the avantages of transplantation
QoL is better
life expectancy is double
shorter dialysis the better outcome
living kidney is best
cost benefit