Atomic Structure and Atomic Spectra
1/42
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Electronic structure of an atom
The arrangement of electrons around a nucleus
Hydrogenic atom
A one-electron atom or ion of general atomic number Z
Many-electron atom (Polyelectronic atom)
An atom or ion with more than one electron
Rydberg constant for the hydrogen atom
RH = 109677 cm^-1
Ritz combination principle
States that the wavenumber of any spectral line is the difference between two terms
Coulomb potential energy of an electron in a hydrogenic atom
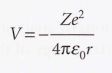
Radial wave equation
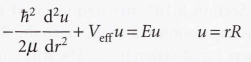
Bohr radius
It is called like this because the same quantity appeared in Bohr's early model of the hydrogen atom as the radius of the electron orbit of lowest energy
Atomic orbital
A one-electron wavefunction for an electron in an atom
Principal quantum number (n)
It can take the values n = 1, 2, 3, , and determines the energy of the electron
Bound states of the atom
Where the energy of the atom is lower than that of the infinitely separated, stationary electron and nucleus
Unbound states of the electron
The states to which an electron is raised when it is ejected from the atom by a high-energy collision or photon
Ionization energy (I)
The minimum energy required to remove an electron from the ground state, the state of lowest energy, of one of its atoms
Shell
All the orbitals of a given value of n
Subshell
The orbitals with the same value of n but different values of l
Angular momentum quantum number (l)
Depends on the principal quantum number
Radial distribution function P(r)
A probability density in the sense that, when it is multiplied by dr, it gives the probability of finding the electron anywhere between the two walls of a spherical shell of thickness dr at the radius r
Transition
When an electron moves from a higher energy orbital to a lower energy orbital
Selection rule
A statement about which transitions are allowed
Grotrian diagram
It summarizes the energies of the states and the transitions between the selection rules and atomic energy levels
Orbital approximation
Its when we suppose that a reasonable first approximation to this exact wavefunction is obtained by thinking of each electron as occupying its "own" orbital
Pauli exclusion principle
No more than two electrons may occupy any given orbital, and if two do occupy one orbital, then their spins must be paired
Pauli principle
When the labels of any two identical fermions are exchanged, the total wavefunction changes sign; when the labels of any two identical bosons are exchanged, the total wavefunction retains the same sign
Slater determinant
Any acceptable wavefunction for a closed-shell species
Valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom in its ground state
Building-up principle
It says that the order of occupation is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s
Hund's maximum multiplicity rule
An atom in its ground state adopts a configuration with the greatest number of unpaired electrons
First ionization energy
The minimum energy necessary to remove an electron from a many-electron atom in the gas phase
Second ionization energy
The minimum energy needed to remove a second electron from the cation
Electron affinity
The energy released when an electron attaches to a gas-phase atom
Potential energy of the electrons
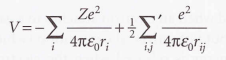
Quantum defect
An empirical quantity
Rydberg states
Singlet
The paired-spin arrangement
Triplet
The resulting state when the angular momenta of two parallel spins add together to give a nonzero total spin
Spin-orbit coupling
The interaction of the spin magnetic moment with the magnetic field arising from the orbital angular momentum
Spin-orbit coupling constant
The dependence of the spin-orbit interaction on the value of j
Fine structure of a spectrum
The structure in a spectrum due to spin-orbit coupling
A term symbol gives three pieces of information
The letter (P or D in the examples) indicates the total orbital angular momentum quantum number, L.
The left superscript in the term symbol (the 2 in P^2) gives the multiplicity of the term.
The right subscript on the term symbol (the 3/2 in P_3/2) is the value of the total angular momentum quantum number, J.
Total orbital angular momentum quantum number (L)
It tells us the magnitude of the angular momentum
Multiplicity of a term
The value of 2S + 1, where S is the total spin quantum number
Clebsch-Gordan series
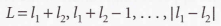
Russell-Saunders coupling
This scheme is based on the view that, if the spin-orbit coupling is weak, then it is effective only when all the orbital momenta are operating cooperatively