Cytoskeleton and Microtubule Functions in Cells Module 8 Final
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Microtubules
Assembled from the protein tubulin
Actin filaments
One of the three filamentous structures that compose the cytoskeleton
Intermediate filaments
One of the three filamentous structures that compose the cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
Provides structural support to the cell
Functions of the cytoskeleton
Structural support, organelle positioning, material movement
Microtubule structure
Protofilament ↔️ Longitudinal rows of tubulin
αβ-tubulin heterodimer
One α-tubulin and one β-tubulin subunit
Plus end of microtubules
Row of β-tubulin subunits
Minus end of microtubules
Row of α-tubulin subunits
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
Proteins that stabilize microtubules
Tau
A MAP implicated in Alzheimer's disease due to abnormally high phosphorylation
Cell shape in animal cells
Radial array from the nucleus
Microtubule transport defects
Examples include ALS and Lou Gehrig's disease
Motor proteins
Use ATP hydrolysis to generate movement along microtubules
Motor protein superfamilies
Kinesin, dynein, myosin
Kinesin
The smallest and best understood microtubular motors
Kinesin structure
Tetramer of two heavy and two light chains
Kinesin movement direction
Moves toward the plus end of microtubules
Hand-over-hand mechanism
Processive movement along microtubules used by kinesins
Kinesin-mediated transport
Tends to move cargo outward toward the cell's membrane
Cytoplasmic dynein role
Moves cargo toward the minus end
Cytoplasmic dynein function in mitosis
Positions the spindle during mitosis
Microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs)
Specialized structures for microtubule nucleation
Centrosome
The major MTOC in animals
Microtubule growth
Grow at their plus ends and remain anchored at the MTOC
Basal body
MTOC at the base of cilia or flagella
γ-tubulin
A critical protein in microtubule nucleation
Cytoskeleton
Network providing structural support and shape to cells.
Microtubule Organizing Centers (MTOCs)
Structures that organize microtubule assembly in cells.
Dynamic instability
Microtubules can rapidly grow and shrink.
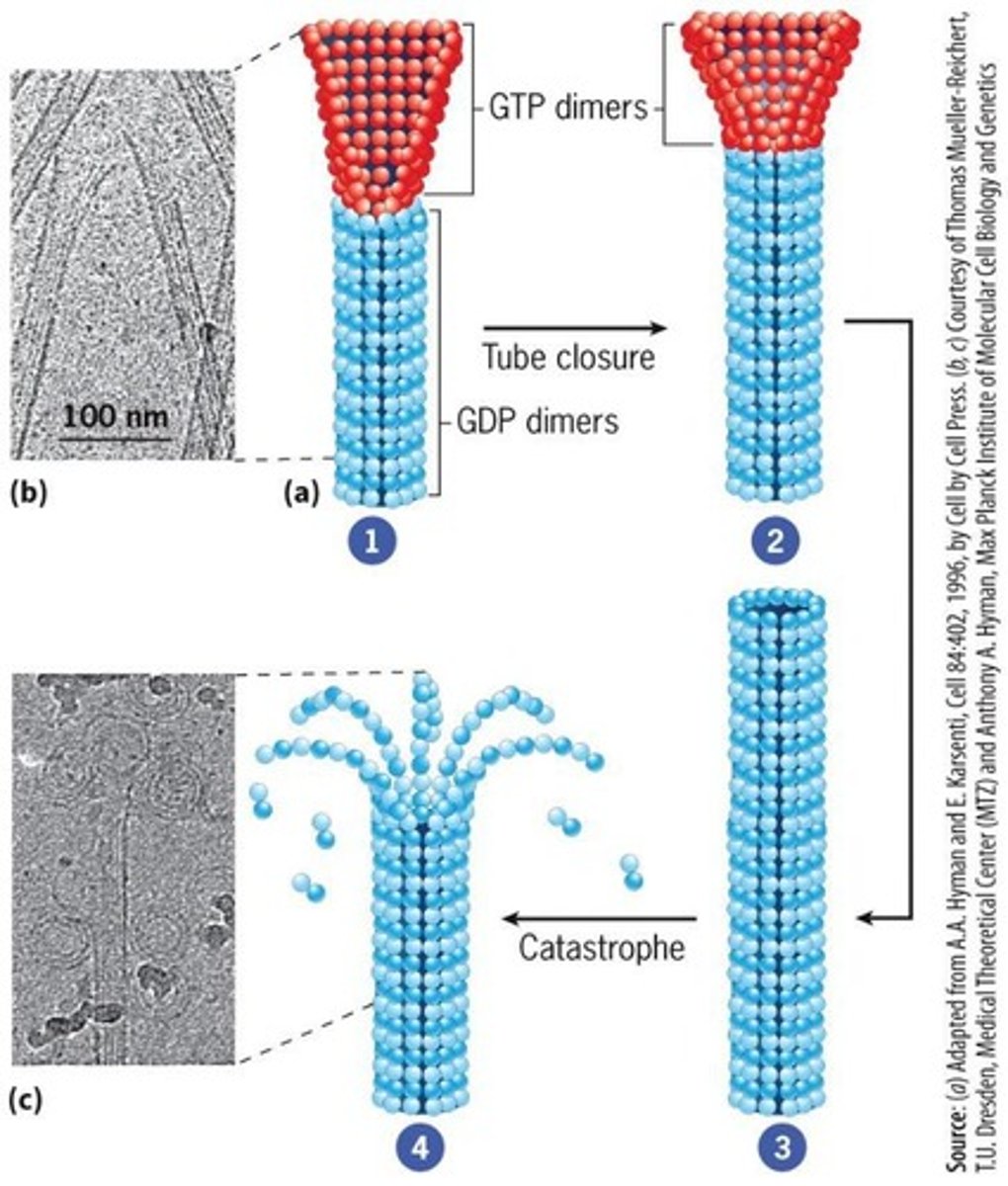
GTP-tubulin
Active form of tubulin promoting microtubule growth.
GDP-tubulin
Inactive form of tubulin leading to microtubule shrinkage.
Cilia
Hairlike organelles for movement and sensing in cells.
Flagella
Long, whip-like structures for cell motility.
Intermediate filaments
Cytoskeletal components providing mechanical strength.
Mitotic spindle
Microtubule structure separating chromosomes during cell division.
Microtubule stability
Determined by microtubule-interacting proteins like MAPs.
Posttranslational modifications
Chemical changes to proteins after synthesis affecting function.
Hydrostatic pressure
Pressure exerted by a fluid, affecting microtubule stability.
Cold temperature
Environmental factor inducing microtubule disassembly.
Calcium concentration (Ca2+)
Elevated levels can trigger microtubule disassembly.
Cilium
Short, hair-like structure for movement or sensing.
Flagellum
Long, whip-like structure for cell motility.
Basal body
Structure from which cilia and flagella emerge.
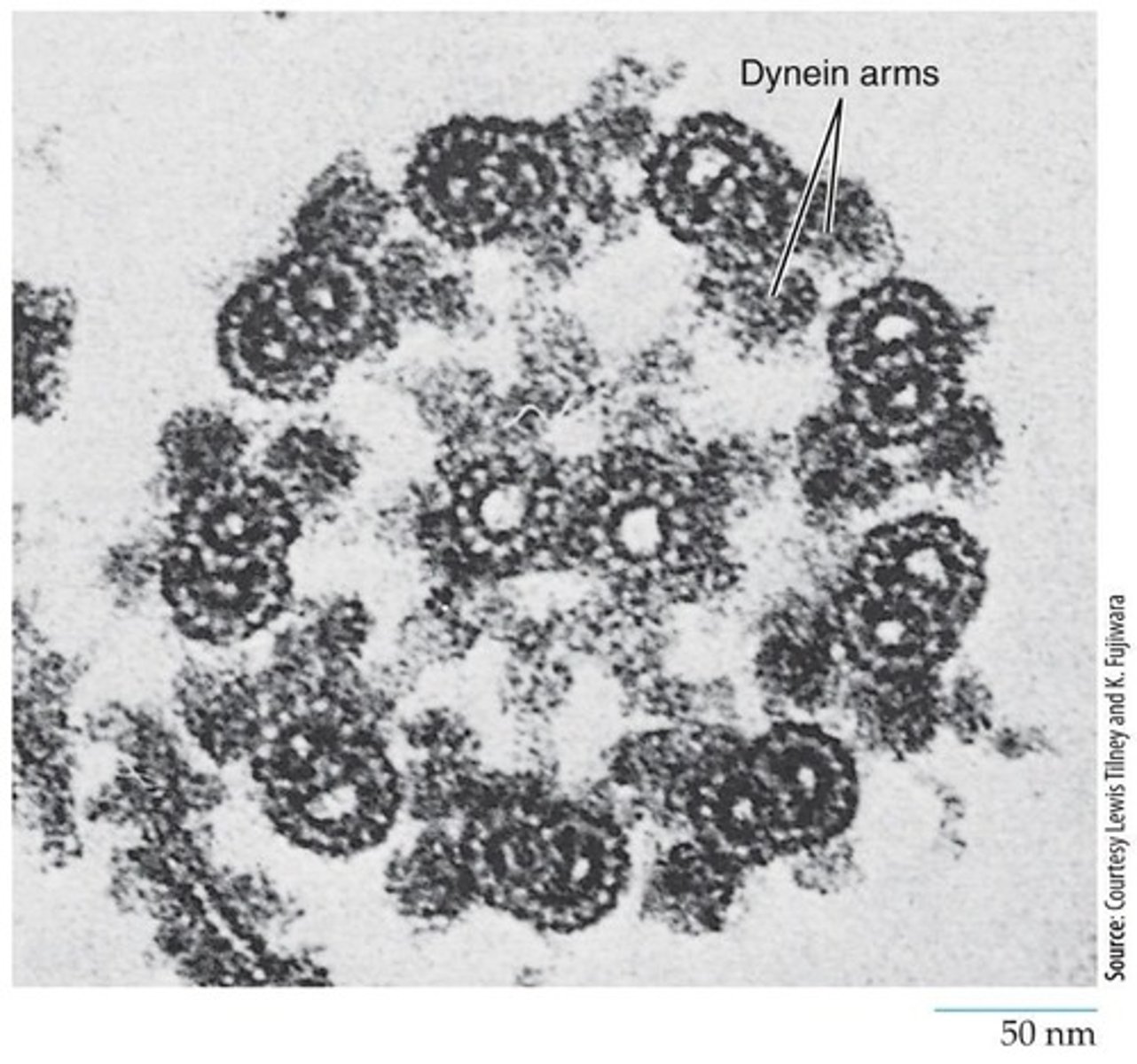
Axoneme
Core structure of cilia and flagella.
9 + 2 array
Nine doublet microtubules surrounding two central microtubules.
Intermediate filaments
Strong, flexible fibers providing mechanical strength.
Keratin
Intermediate filament protein in epithelial cells.
Vimentin
Intermediate filament found in mesenchymal cells.
Desmin
Intermediate filament protein in muscle cells.
GFAP
Intermediate filament protein in astrocytes.
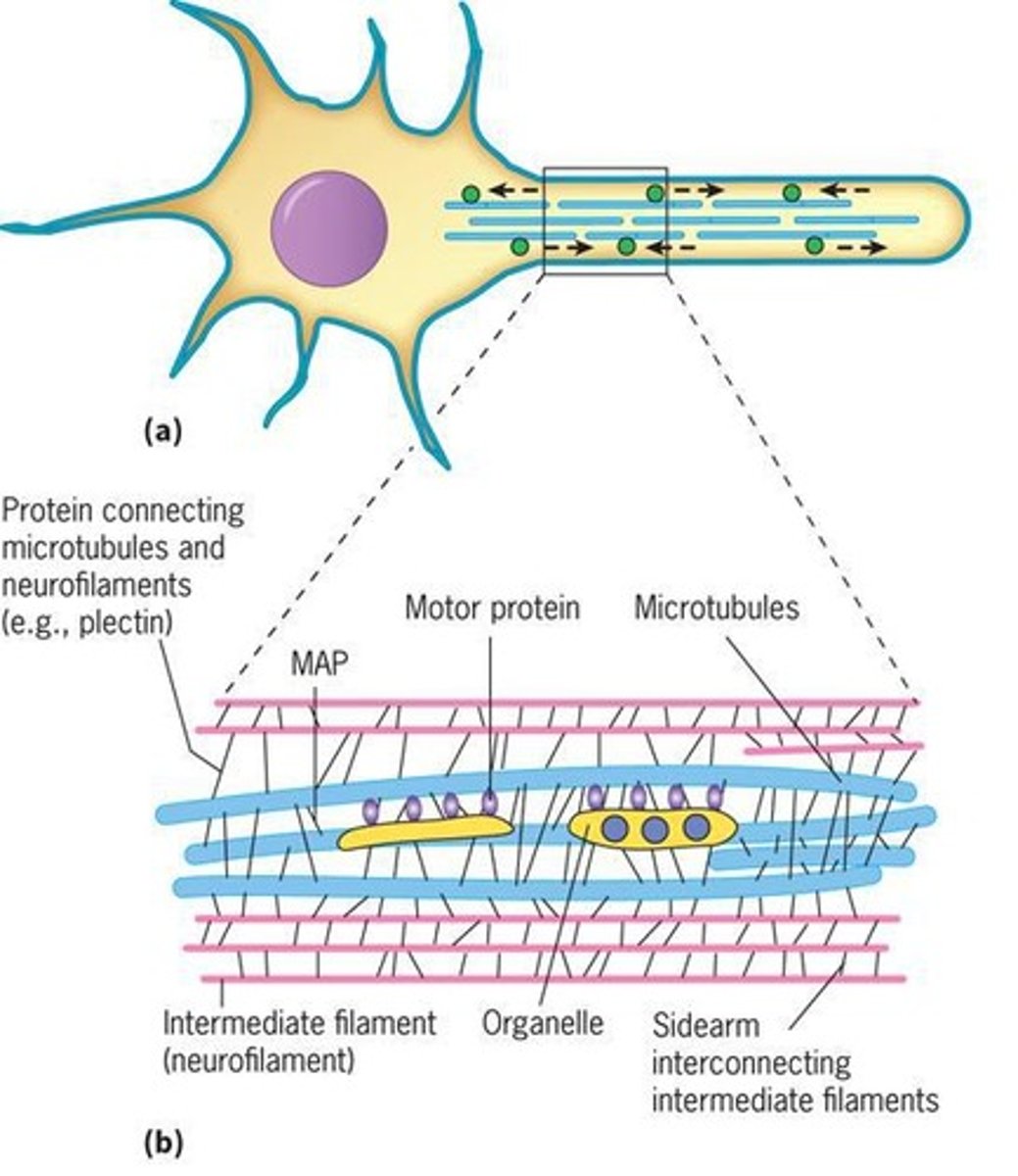
Neurofilament proteins
Intermediate filaments in neurons.
Plectin
Protein connecting intermediate filaments to other filaments.
Tetramer
Basic subunit formed by two dimers in IF assembly.
Dimers
Two monomers associated in parallel orientation.
Assembly of IFs
Does not require ATP or GTP involvement.
Phosphorylation
Regulates assembly and disassembly of intermediate filaments.
Desmosomes
Cell structures anchoring keratin IFs at cell edges.
Hemidesmosomes
Anchors keratin IFs to the extracellular matrix.
Neurofilaments function
Support and maintain structure in neuronal axons.
Unit length of IF
Formed by eight tetramers in intermediate filaments.
Chemical heterogeneity
Diverse protein composition of intermediate filaments.
Intermediate filament architecture
Monomers form dimers, then tetramers, then filaments.
Mechanical stress absorption
Function of keratin IFs in epithelial cells.
Cytoskeletal elements
Components that provide structure and support to cells.
Cytoskeleton
Skeletal system of eukaryotic cells.
Microtubules
Hollow, rigid structures made of tubulin.
Actin filaments
Thin filaments aiding in cell movement.
Intermediate filaments
Provide mechanical support to cells.
Motor proteins
Proteins that move along microtubules.
Kinesins
Motor proteins moving toward microtubule plus end.
Dyneins
Motor proteins moving toward microtubule minus end.
Microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs)
Sites where microtubules are nucleated and organized.
Protofilaments
Longitudinal rows of tubulin in microtubules.
α-tubulin
One subunit of the tubulin dimer.
β-tubulin
Other subunit of the tubulin dimer.
Plus end
End of microtubule with β-tubulin.
Minus end
End of microtubule with α-tubulin.
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
Proteins that stabilize and promote microtubule assembly.
Tau protein
MAP linked to Alzheimer's disease when hyperphosphorylated.
Cell shape
Determined by microtubule distribution and organization.
Cellular locomotion
Movement generated by cytoskeletal components.
Neurotransmitter transport
Movement of chemicals along nerve cell microtubules.
Lou Gehrig's disease
Neurological disease from microtubule transport defects.
Hydrolysis of ATP
Primary energy source for molecular motors.
Cell division machinery
Cytoskeletal components essential for cell division.
Mechanical support
Resisting forces that compress or bend fibers.
Radial array
Microtubule arrangement extending from the nucleus.
Kinesin
Microtubular motor moving toward plus end.
Dynein
Microtubular motor moving toward minus end.
Myosin
Motor protein that moves along actin filaments.
Cytoplasmic Dynein
Moves organelles and chromosomes during mitosis.
Kinesin Structure
Tetramer with two heavy and two light chains.
Kinesin Heads
Globular heads that bind microtubules and hydrolyze ATP.
Kinesin Tail
Fanlike structure that binds to cargo.
ATP Hydrolysis
Provides energy for motor protein activity.
Unidirectional Movement
Motor proteins move in one direction along tracks.
Conformational Changes
Alterations enabling mechanical cycles of motor proteins.
Processivity
Ability to move long distances without detaching.
Kinesin Cargo Transport
Transports vesicles outward to plasma membrane.