EM E2: Trauma
1/86
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What is the initial assessment of any trauma pt focused on?
rapid identification and stabilization of life-threatening injuries
What wounds have high mortality rates?
head, chest, abd
What causes death in the 1st peak (sec-mins post-injury)?
severe brain injury, high spinal cord injury, rupture of heat, aorta, or other large blood vessels
*death often unavoidable d/t severity
What causes death in the 2nd peak (mins-hrs post-injury)?
subdural/epidural hematomas, hemopneumothorax, ruptured spleen, liver lacerations, pelvic fx, multiple other injuries w/ significant blood loss
What is golden hour?
critical period for rapid assessment and resuscitation (1st 60 min after injury), ATLS, crucial for receiving definitive care to improve survival and outcomes
What are causes of death during the 3rd peak (days-weeks post-injury)?
sepsis, multiple organ system dysfunction
*significantly affected by prior care
What is the leading global cause of mortality?
Road traffic
Pts meeting what criteria MUST be transferred to a trauma center?
GCS < 13
SBP < 90
RR < 10 or > 29
Pts w/ what injuries must be transferred to a trauma center?
penetrating injuries, flail chest, > 2 long bone fx, crushed mangled pulseless extremity, amputation proximal to wrist or ankle, pelvic fx, open fx, open/depressed skull fx
What mech of injury factors MUST go to a trauma center?
fall > 20 ft (adult) > 10 ft (child), high risk MVC, auto vs ped, motorcycle, assault w/ deadly weapon, head trauma from altercation
What pt populations usually get sent to a trauma center?
elderly, children, anticoagulant use, burn victims, pregnancy, intoxicated, under the influence
How early should the trauma team be assembled prior to a trauma pt arriving?
5 min, have everything set up and roles assigned
What are the ABCDE of primary survey?
Airway w/ C-spine stabilization, Breathing and vent, Circulation w/ bleeding control, Disability (neuro), Exposure and environmental control
If the pt is able to talk, is there airway compromise?
unlikely
What should you consider when assessing airway?
ability to speak, upper airway obstruction, ability to protect airway
→ reposition, remove FB, intubation
What should you do when assessing breathing?
evaluate bilateral breath sounds, oxygenation, ability to ventilate → needle decompression, intubation
What are the 6 quick killers in trauma medicine?
airway obstruction, tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, open pneumothorax, massive hemothorax, flail chest
What is the leading cause of preventable death in trauma?
hypovolemic shock d/t profuse bleeding
How should pulses be assessed?
central → carotid, femoral: weak, thready → identify source of bleeding and control
What are clues of bleeding when the source is hidden?
depressed LOC, dec skin perfusion (cold, clammy), weak pulse
What are the 6 potential spaces for blood to go?
environment, abdomen, retroperitoneum, chest, extremity, pelvis
What must be done for bleeding?
obtain definitive control, in unable must volume resuscitate, establish IV access (2 large bore IV), IVF, blood transfusion
What is assessed when checking for disability?
assess GCS, signs of brain or spinal cord injury
*verbal = 5pts, motor = 6pts, eye opening =4 pts (3 lowest, 15 highest)
What GCS score indicates severe brain injury?
< 8
What should be assumed w/ a reduced GCS score?
brain injury until proven otherwise
*try to prevent secondary injury
What should be done during the exposure step?
remove all clothing, ensure warm environment, log roll, evaluate back and crevices
What is check on a fast exam (US)?
CXR, gastric catheter, pulse ox, pelvic XR, ventilatory rate, ECG, urinary catheter, capnography, ABG
What is the secondary survey?
thorough and systemic evaluation after pt has been assessed and life-threatening injuries tx
What are the key components of a secondary survey?
detailed history, head→toes exam, targeted dx studies
*crucial for ensuring all injuries are identified and appropriately managed
What are considered traumatic injury sites?
head, spinal, chest, pelvis, femur
What imaging can be done to help assess blunt trauma?
*review indications: slide 47
“Pan-scan” or trauma scan
What factors inc risk of intra-abd injury?
seat belt sign, rebound tenderness, hypotension, abd distention, abd guarding, concomitant femur fx
What are indications for a thoracotomy in the ED?
*low survival rate, buys time to get to OR
penetrating trauma + loss of vitals in ED or loss of vitals < 15 min PTA
Which wounds have the highest rate of survival?
knife stab wounds
Where is the incision made for a thoracotomy?
5th intercostal space
-cross clamp aorta, open pericardium, control active bleeding
What is the massive transfusion protocol?
transfusion of 100% blood volume w/in 24 hr period OR > 50% blood volume w/in 4 hrs
*initiate if heavy uncontrollable bleeding
What is the ratio in a massive transfusion protocol?
1:1:1 = PRBC:FFP:Plts
What is permissive hypotension?
allowing lowest perfusing BP bc raising it may increase bleeding
*MAP btwn 55-65
What are causes of hypotension after trauma?
bleeding (hypovolemic shock), obstructive shock (cardiac tamponade, tension pneumo), spinal shock
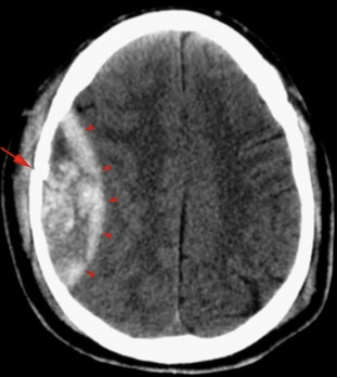
What does the CT show?
Epidural hematoma: Convex lesion
*emergent OR
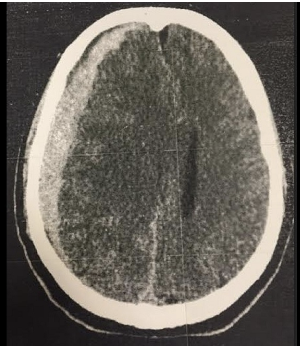
What does the CT show?
Subdural hematoma: Crescent shaped
*MC in elderly and infants
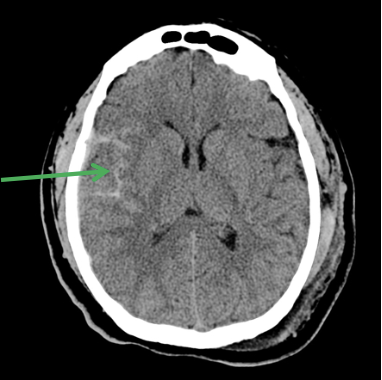
What does the CT show?
SAH
What is Cushing’s TRIAD?
*indicates inc ICP
inc systolic BP, dec pulse, dec respiration
What is sx of shock?
dec BP, inc pulse, inc respiration
What are the concussion return to play guidelines?
must be sx free x 24 hrs to advance to next step, restarts w/ each step
1- no activity
2- light aerobic exercise
3- sport specific exercise
4- non-contact training drills
5- full contact practice
Do post-concussive sx correlated w/ severity of initial injury?
nope -duration difficult to predict, sx vary
What is second impact syndrome?
severe neurological sequalea if pt suffers second head injury while still recovering from initial concussion
What is zone 1 of the neck?
thoracic inlet to cricoid
What is zone 2 of the neck?
cricoid to angle of mandible
What is zone 3 of the neck?
above mandible
What is the most dangerous neck zone to be injured?
Zone 2 -contains carotids, esophagus, nerves, and many other important structures
What are hard neck sings?
airway compromise, air bubbling wound, expanding/pulsatile hematoma, active bleeding, shock, compromised radial pulse, hematemesis, neurological deficit, paralysis, cerebral ishcemia
What are soft neck signs?
subcutaneous emphysema, dysphagia, dyspnea, non-pulsatile, non-expanding hematoma, venous oozing, chest tube air leak, minor hematemsis, paresthesias
Failure to penetrate which neck muscle suggests superficial injury?
Platysma muscle
What testing should be ordered for blunt or penetrating trauma of the neck?
CT angiogram
What should you suspect when a pt presents w/ delayed neuro sx after blunt trauma to the neck?
carotid artery injury
What accounts for ½ of spinal column injuries?
MVC
*C-spine MC injured
What should you do if you suspect the C-spine is injured?
immobilize → c-collar
What is the NEXUS criterial?
*if -, C-spine imaging probably unnecessary
no posterior midline C-spine tenderness
no evidence of intoxication
normal level of alertness
no focal neuro deficits
no painful distracting injuries
What is considered a distracting injury?
long bone fx, visceral injury (spleen lac), large laceration, crush injury, large burn
What criteria is used for cervical collar clearance?
negative imaging + absence of pain, normal neurological exam
What is a SCIWORA?
spinal cord injury w/o radiographic abnormality
*MRI needed, children more common
What causes central cord syndrome?
hyperextension injury usually in elderly pts w/ cervical stenosis
How does central cord syndrome present?
“CAPE” distribution, UE>LE, bladder control may be lost
*MC in elderly
What is the MC fx in the elderly?
Odontoid fx -C2
What are the classes of Odontoid fx?
Type 1: tip of dens
Type 2: base of dens
Type 3: extends into body of C2 -best prognosis
How does Brown-Sequard syndrome present?
I/L loss of motor, fine touch, vibration, proprioception
C/L loss of temp and pain sensation
What is the MC life-threatening thoracic injury?
Pulmonary contusion
*sx often delay
What is the tx for pulmonary contusion?
supportive care & trauma surg consult
What is considered a STABLE pneumothorax?
all present:
RR < 24, HR 60-120, BP norm, SO2 > 90% RA, can speak in whole sentences between breathes
What is the tx for a tension pneumothorax?
needle decompression
*done a 2nd ICS @ MCL
Which needle decompression location has the lowest predicted failure rate?
4/5th ICS @ AAL
*gets a chest tube after decompression
What is the blood loss in a hemothorax?
initial outpt > 1500ml
>200 ml/hr x 4 hrs
What is the MC location of an aortic rupture?
*d/t high impact injury
ligamentum arteriosum
What is the dx test of choice for an aortic rupture?
CTA
*CXR: widened mediastinum
What is the test of choice for stable abdominal visceral injury?
CT abd w/ IV contrast
*unstable dx w/ fast exam
What are abd visceral injuries?
Splenic or Liver injury
How does a splenic injury present?
s/p blunt trauma, suspect w/ left lower rib fx
*2nd mc injured
How does a liver injury present?
s/p blunt trauma, suspect w/ lower right rib fx
*MC injured abd organ
What is the MC injured organ d/t penetrating trauma?
Liver
*small bowel = 2nd
How are most renal injuries managed?
observation alone
What are pts w/ seat belt ecchymosis at inc risk of?
delayed injury (bowel wall hematoma)
*conservative management
What is most commonly injured in a handlebar injury?
*usually in peds
pancreas and duodenum (liver and spleen possible)
What is used for to stabilize open book pelvic fx?
Pelvic binder
What is the management for pubic rami fx?
early mobilization, rehab
elderly admit for pain control, young can potentially go home
How should chest tubes be placed in pregnant pts?
one rib space high
What should Rh- pregnant pts receive after blunt trauma?
RhoGAM