principles 3 midterm from old quizzes
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Which of the following would best describe "Quality Assurance" (QA)?
the process of activities to maintain and/or increase the quality of products and services
The source-to-skin distance for fixed fluoroscopic exams is
15”
The source-to-skin distance for mobile fluoroscopic exams is
12”
Which is the problem that SHOULD NOT occur in a properly run "repeat analysis" program?
Use data analysis to determine raises and/or punitive actions for R.T.s
"Boost" mode
not to exceed 176 mGy/min
Automatic mode (most common)
not to exceed 10 R/min
Normal mode
not to exceed 5 R/min or 44 mGy/min
Calculate the acceptance limits for the light beam/exposure field alignment when doing chest radiography at and SID 108 inches
2.16 inches
(108x.02)
What is the most common exposure artifact in radiographic imaging?
Foriegn objects due to improper patient preparation.
Flatfielding
Corrects irregularities of beam due to anode heel effect.
Lossy
Image compression that results in loss of information.
Lossless
Image compression that compresses file but maintains all information.
Interpolation
Process of software filling in and assigning signal values to "dead" pixels.
What variation is allowed in kVp accuracy of the external radiographic beam when checked by electronic detectors or a Wisconsin/Adran-Crookes test cassette?
5% or 4 kVp for a 80 kVp exposure
When checking AEC systems which of the following would be acceptable when blocking the AEC detector and/or diverting the x-ray beam away from the detector area?
1. Exposure ends at set back-up time.
2. Exposure ends at the earlier of 6 seconds or 600 mAs
3. Visual & audible indications of an AEC error.
1,2,3
What quality control standard is checked by radiographing a "nine penny" test or a specialized template?
X-ray beam/collimator alignment
The commonly used test pattern for daily visual checking of digital display monitors in medical imaging is the:
TG18-QC
Which of the following can be used to check acceptance of effective focal spot size?
1. Pinhole camera
2. Star test pattern
3. Synchronous top
4. Slit camera
5. Adran-Crookes test cassette
6. Resolution test tools
1, 2, 4, 6
What is the typical range of mA used during fluoroscopy?
0.5 – 5.0
What "needle-like" crystals make up the input phosphor layer of the image intensifier tube?
Cesium iodide
What is the name of the solid-state/semiconducting equipment that is rapidly replacing the video camera tube?
Charge-Coupled Device
In fluoroscopy, a multifield image intensifier can produce a magnified image. While magnification mode can improve spatial resolution, it can also introduce issues around image quality. What are these potential issues? (Select all that apply)
Pincushion Appearance
Vignetting
Quantum noise
The number of electrons emitted from the photocathode is indirectly proportional to the intensity of light that reaches it.
False
List the order in which the x-ray beam passes through the image intensifier tube.
Input Phosphor, Photocathode, Electrostatic Focusing Lens, Anode, Output Phosphor
What is the magnification factor for a 43 cm image intensifier when only the center 24 cm of the input is used to form the output image?
1.79
(43/24)
The image intensifier improved fluoroscopy by increasing image ________________
Brightness
What is the brightness gain for a 17cm image-intensifier tube with a flux gain of 120 and a 2.5 cm output phosphor? What is the minification gain? (Round all calculations to the nearest whole number)
5,520 & 46
Which of the following methods would be considered an effective dose reduction technique? (Select any that apply)
Last image hold
Pulsed fluoroscopy
Light produced at the output phosphor of the image intensifier has been increased _____________ times in intensity.
50 to 75
The human eye uses these structures for vision during dim viewing conditions. These structures are most numerous around the periphery of the retina and have low visual acuity.
Rods
The operator is using a 25/17/12 multifield image intensifier. If the operator switches from a 25cm to 12cm mode, then the voltage of the electrostatic focusing lenses decreases.
False
What part of the camera tube target assembly lies just past the window/face plate and conducts electricity?
Signal plate
Visual acuity in the eye is greatest at the _____________________, where ________ are concentrated.
Fovea centralis; comes
In the image intensifier tube, what compounds are found within the thin metal layer of the photocathode?
Cesium, antimony
The camera tube or CCD may be coupled to the output phosphor by one of these 2 methods.
Fiber optic bundle, optical lens system
What is the component of the television monitor where the video signal is transformed into an image?
Fluorescent screen
What is SNR? For digital fluoroscopy what SNR is necessary to ensure optimal contrast resolution?
Signal to Noise Ratio, 1000:1
In interventional radiography, a focal spot not greater than ______ mm is necessary for spatial resolution requirements of small vessel magnification.
0.3
What are the source-to-skin (SSD) distances for (1) stationary fluoroscopic units and (2) mobile C-arm units?
15” & 12”
What computerized-controlled technology can be utilized in interventional radiography to follow the flow of contrast from the abdomen to the feet?
Stepping table
Early versions of digital fluoroscopy used a conventional fluoroscopic chain with an added component. What is the added component?
Analog to Digital Converter (ADC)
An electron gun can be found in the ______? (Select all that apply)
Television monitor
This 18-gauge hollow _________ needle with a stylet, developed in 1953, is used to puncture the femoral artery.
Seldinger
What replaces the image intensifier in advanced digital fluoroscopy systems?
Flat-panel detector
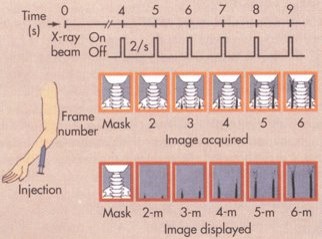
This image represents what type of digital subtraction technique and method? (Select all that apply)
Mask mode & TID mode
What fluoroscopic feature allows the position of the collimator plates to be viewed on the monitor without exposing the patient to radiation?
Last image hold
Which of the following is required of an indirect-capture detector? (Select all that apply)
Scintilla’s, TFT array, Amorphous silicon photodetector
What is the recording device that "photographs" the image off of the output phosphor?
Film cameras for spot filming
A technique available in digital fluoroscopy that enhances the visualization of the vasculature as a result of a venous injection of contrast medium.
DSA
Which of the following are advantages of using a CCD in digital fluoroscopy?
Linear response feature, requires less radiation, high SNR, better contrast resolution
The most common risk for a patient undergoing an angiography exam is what?
Bleeding at puncture site
For units that have a ABC/AERC, the intensity of the beam at tabletop should not exceed _____ mGy/min.
88
Due to the resolution produced, what is considered the weakest link in conventional fluoroscopy?
Television monitor
Coronal plane
Divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
Oblique plane
Transverse plane that is at an angle. Not parallel to the sagittal, coronal or axial planes.
Sagittal plane
Divides the body into right and left parts.
Axial plane
Divides the body into superior and inferior portions.
A radiographic image will show distortion if the object plane and image plane are not parallel of one another.
True
In digital imaging, the image's contrast can be adjusted during post processing by "windowing" or altering the window width. A narrow window width results in the image having ______ contrast or you could say that there are _______ shades of gray.
Higher, fewer
In a variable kVp system, ______ is kept constant and ________ is adjusted based on part thickness. To adequately penetrate the anatomy of interest, the variable is adjusted by _____ for every centimeter of patient thickness.
mAs, kVp, 2
What radiographic term applies to an image that shows unequal magnification and/or misrepresentation of the anatomy of interest?
Distortion
To minimize magnification on a radiographic image a ______ SID and ______ OID should be used if possible.
Large, small
Trendelenburg places the patient's body in a recumbent position on the table with their head lower than their feet.
True
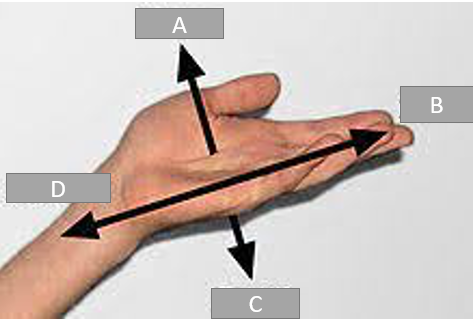
A
Palmer
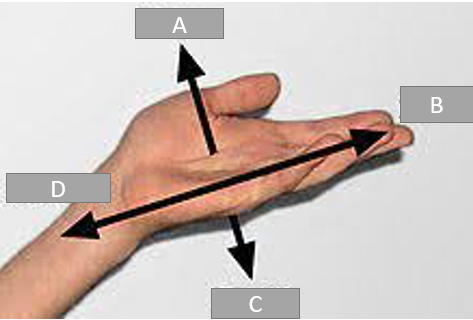
B
Distal
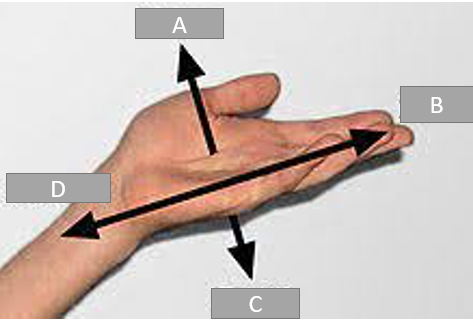
C
Dorsal
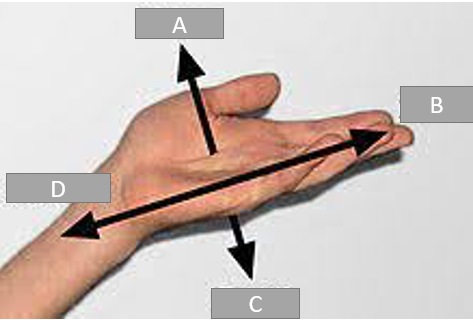
D
Proximal
Increasing _____ and decreasing _____ improves the spatial resolution of an image.
Pixel density, pixel pitch
Abduction
Lateral movement away from the body
Extension
Increases the angle of the joint
Elevation
Lift, raise or move part superiority
Inversion
Inward stress movement of foot without rotation
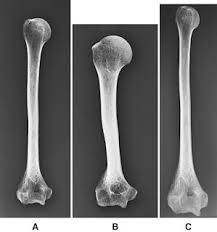
Using the image below, how would you describe the distortion present in images B and C (in order).
Foreshortened and elongated
The principle contributor to image noise is
Quantum noise
What are the two results of properly utilized technique charts? (Select all that apply)
Decrease in patient dose, decrease in exposures
Spatial resolution
Ability to image two separate objects and visually be able to distinguish one from the another. Also referred to as sharpness and definition.
Artifact
Unwanted brightness levels on a radiographic image. Examples may include foreign bodies, jewelry, scatter, motion.
Noise
A result of insufficient x-ray exposure to the image receptor.
Contrast resolution
Tissue thickness, tissue density, effective atomic number, and object shape all contribute to the difference in brightness levels.
Which exposure system uses the patient's body part of interest as the variable in determining when to terminate the exposure?
Automatic exposure control (AEC)
In a fixed kVp system, _____ is constant and _____ is adjusted based on part thickness. In general our variable's value that is adjusted, is _____ for every additional 4-5cm.
kVp, mAs, doubled